Data and metadata are essential components of information management.
See How Atlan Streamlines Metadata Management – Start Tour
Data refers to raw facts and figures that can be processed to extract meaningful insights.
In contrast, metadata is data that describes other data, providing context and meaning.
Understanding the differences between these two concepts is crucial for effective data management and utilization.
What is the difference between data and metadata?
Permalink to “What is the difference between data and metadata?”The main difference between data and metadata lies in how we use the two pieces of information. Data is a set of raw facts that help identify useful information when they are cleaned, processed, and organized. Metadata, on the other hand, is data about data.
If data is the new oil, metadata is the refinery. Without metadata, there is no way to understand or use the data in hand.
Here’s a table that highlights the differences between data and metadata.
4 Key differences between data and metadata
Permalink to “4 Key differences between data and metadata”| Factors | Data | Metadata |
|---|---|---|
| Use | Data helps in gathering insights and discovering hidden patterns. | Metadata helps in understanding the data comprehensively. |
| Value | Data may or may not prove to be of value. | Metadata is always valuable. |
| Processing | Data doesn’t have to be processed before it is stored. | Metadata is always stored as processed information. |
| Management | Data’s storage and management are dependent on its type and use case. | Data admins can make metadata management generic across an enterprise, regardless of the data type or its use case. |
| Example | This blog is a piece of data, which explains the differences between data and metadata. | Metadata for this blog includes the author, publishing date, and total number of words. |
To understand the difference better, let’s start with defining data and metadata.
Data vs Metadata. Source: Atlan
Data is a set of raw facts that help identify useful information when they are cleaned, processed, and organized. For example, analyzing sales data can help a business identify trends or gaps and predict future possibilities. Without data, it’s not possible to get this information accurately or in a timely manner.
Metadata, on the other hand, is data about data. It helps people understand the essential attributes of data, like its origin, time period, geographic coverage, etc.
Metadata also includes the human tribal knowledge associated with data assets. It gives information about the data, without even opening it. Without this contextual information, you will not be able to extract the maximum value from your data assets.
The most common metadata examples are:
- Title
- Description
- Tags or categories
- Date of creation
- Who created it
- Source or origin
- Count and description of variables or attributes (e.g. rows and columns count for a data table)
Want to learn more about metadata? Read this article: What is Metadata?
Examples of data and metadata
Permalink to “Examples of data and metadata”Let’s look at a few examples of data and metadata to understand the difference better.
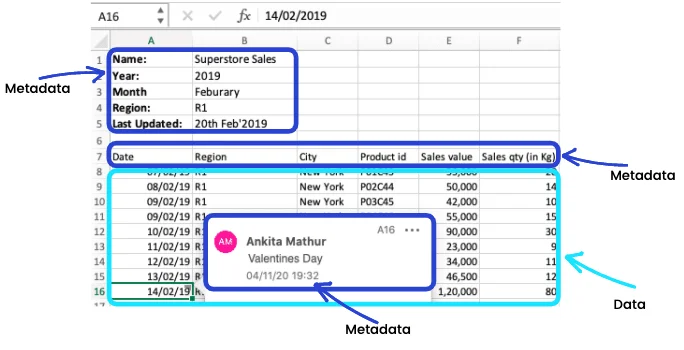
1. An Excel spreadsheet
Permalink to “1. An Excel spreadsheet”
Data vs Metadata in Spreadsheet. Source: Atlan
Here are some common metadata fields in a spreadsheet:
- File name
- Tab name
- Column names
- Number of rows
- Number of columns
- Comments
2. Files on our computer
Permalink to “2. Files on our computer”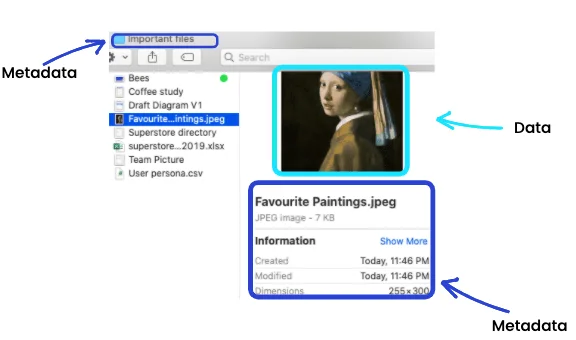
Data vs Metadata in a file on our computer. Source: Atlan
Here are some common metadata fields in a data system:
- Folder name
- Type of file
- Created date
- Last modified date
- Dimensions
- File size
Common challenges with metadata
Permalink to “Common challenges with metadata”Most of us are aware of the role metadata plays in adding value to data. Without metadata, drawing inferences from data will be like shooting in the dark. However, since metadata is difficult to manage, businesses get stuck at actually implementing it. Even in the businesses that invest in creating and managing metadata, metadata’s ROI often doesn’t live up to expectations.
It’s a vicious cycle — as businesses struggle with metadata, they invest less time in it, making it less valuable and more difficult. However, to improve the quality of data management and make data useful, businesses must address metadata challenges.
Here are some key challenges in managing metadata:
- Manual enrichment: Enriching metadata is a manual process, hence it takes time and dedicated energy from someone on staff.
- Missing metadata: The documents that store metadata can get misplaced, leading to missing metadata.
- Discovery: It can be very difficult to search through the existing metadata files. Sometimes, even good metadata management systems aren’t search-friendly.
- Regular updates: After the metadata is created, it requires dedicated efforts to keep it up to date. The management system needs to create enough incentives for the steward or data manager to keep adding new metadata.
- Separation of data and metadata: Metadata is usually stored away from the data. This reduces its value to provide context when it’s needed the most.
It is time that we start addressing data and metadata challenges separately, as their nature and use are different for businesses.
However, this does not mean that we have to keep data and metadata separate. In fact, it’s critical to bring them as close to each other as possible to avoid information silos.
Data Vs Metadata - Atlan Case study: Metadata Management at WeWork
How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
Permalink to “How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan”The recently published Forrester Wave report compared all the major enterprise data catalogs and positioned Atlan as the market leader ahead of all others. The comparison was based on 24 different aspects of cataloging, broadly across the following three criteria:
- Automatic cataloging of the entire technology, data, and AI ecosystem
- Enabling the data ecosystem AI and automation first
- Prioritizing data democratization and self-service
These criteria made Atlan the ideal choice for a major audio content platform, where the data ecosystem was centered around Snowflake. The platform sought a “one-stop shop for governance and discovery,” and Atlan played a crucial role in ensuring their data was “understandable, reliable, high-quality, and discoverable.”
For another organization, Aliaxis, which also uses Snowflake as their core data platform, Atlan served as “a bridge” between various tools and technologies across the data ecosystem. With its organization-wide business glossary, Atlan became the go-to platform for finding, accessing, and using data. It also significantly reduced the time spent by data engineers and analysts on pipeline debugging and troubleshooting.
A key goal of Atlan is to help organizations maximize the use of their data for AI use cases. As generative AI capabilities have advanced in recent years, organizations can now do more with both structured and unstructured data—provided it is discoverable and trustworthy, or in other words, AI-ready.
Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes
Permalink to “Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes”- Tide, a UK-based digital bank with nearly 500,000 small business customers, sought to improve their compliance with GDPR’s Right to Erasure, commonly known as the “Right to be forgotten”.
- After adopting Atlan as their metadata platform, Tide’s data and legal teams collaborated to define personally identifiable information in order to propagate those definitions and tags across their data estate.
- Tide used Atlan Playbooks (rule-based bulk automations) to automatically identify, tag, and secure personal data, turning a 50-day manual process into mere hours of work.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization in establishing and scaling data governance programs.
Summary of data vs metadata
Permalink to “Summary of data vs metadata”Data and metadata go hand in hand. The closer we bring metadata to the actual data workings, the easier and quicker it will be to derive context for data. This will also solve for demonstrating the ROI of maintaining metadata.
As HDI said, “If data is the new oil, metadata is the refinery”. Without metadata, there is no way to understand or use the data in hand.
Want to know more about Atlan’s metadata management solution? Book a call with Atlan Team
FAQs about data vs metadata
Permalink to “FAQs about data vs metadata”1. What is the difference between data and metadata?
Permalink to “1. What is the difference between data and metadata?”Data refers to raw facts and figures, while metadata is data that describes other data, providing context and meaning. Understanding this difference is essential for effective data management.
2. What is an example of data and metadata?
Permalink to “2. What is an example of data and metadata?”An example of data could be a sales report, while metadata for that report might include the author, creation date, and file format. This context helps users understand the data better.
3. Is metadata considered data?
Permalink to “3. Is metadata considered data?”Yes, metadata is considered a form of data. It provides descriptive information about other data, making it easier to manage and understand.
4. What is the difference between metadata and userdata?
Permalink to “4. What is the difference between metadata and userdata?”Metadata describes the characteristics of data, while userdata refers to the actual content created or used by individuals, such as documents or images.
5. How do data and metadata work together?
Permalink to “5. How do data and metadata work together?”Data and metadata work together to enhance data management. Data provides the raw information, while metadata offers context, making it easier to find, use, and understand the data.
6. Why is understanding data vs metadata important?
Permalink to “6. Why is understanding data vs metadata important?”Understanding the difference between data and metadata is crucial for effective data governance, management, and utilization. It helps organizations leverage their data assets more efficiently.
Share this article



















