When your dashboard breaks at 3 AM, you need to know which upstream source changed and what else will fail. Data lineage shows exactly where your data comes from, how it transforms through each system, and which reports depend on it. Modern lineage tools capture this automatically, reducing root cause analysis time from hours to minutes and helping teams avoid compliance penalties that can reach $15 million annually.
Data Lineage at a Glance
| Aspect | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual map of data’s journey from source to consumption | Understand dependencies before changes break downstream |
| Scope | Tracks origins, transformations, movements, and consumers | Covers entire data lifecycle for complete visibility |
| Granularity | Table-level or column-level tracking | Column-level catches field-specific errors |
| Automation | Captured automatically from query history and metadata | No manual documentation, always current |
| Primary Users | Data engineers, analysts, governance teams | Technical and business stakeholders both benefit |
Discover Atlan’s Data Lineage Capabilities – Start Tour
What is data lineage?
Permalink to “What is data lineage?”Data lineage maps your data’s complete journey, showing source systems, transformation logic, and downstream consumers. It automatically captures relationships between tables, columns, and processes so you know which dashboard will break when you modify a field. When analysts question metric accuracy, lineage traces the calculation back to its origin in seconds.
Data lineage is a feature that tracks how your data moves and changes inside your organization over time—its origins, how it’s been edited and transformed, and which reports and applications are utilizing it. This visibility helps you understand:
- Origins: Which source systems provide the data
- Transformations: How ETL/ELT processes modify it
- Dependencies: What reports and dashboards consume it
- History: When changes occurred and who made them
In this article, we’ll discuss the basic concepts behind data lineage, different types of lineage, and how data teams and business owners can leverage it to improve the quality of their data.
Data lineage and metadata
Permalink to “Data lineage and metadata”Lineage extracts relationships from the metadata your systems already generate. Every SQL query, dbt model, and BI report creates metadata about what data it reads and writes. Modern lineage tools parse this metadata automatically to build the complete map of dependencies, eliminating the manual spreadsheet tracking that becomes outdated the moment you publish it.
Data lineage is an all-encompassing term for the flow of data and associated metadata from your data pipelines, workflow engines, and ETL/ELT processes. It tracks how data travels from upstream producers to downstream consumers and every stop in between.
Data engineering processes contain a trove of useful operational metadata, from the capture of source data to the consumption layer. Your organization can leverage this metadata to enrich its understanding of data processes and improve data quality and reliability.
Metadata Sources for Lineage
| Source System | Metadata Type | What It Reveals |
|---|---|---|
| ETL/ELT Tools (dbt, Airflow) | Transformation logic | How data is cleaned, joined, aggregated |
| Data Warehouses (Snowflake, BigQuery) | Query history | Which tables read/write to each other |
| BI Tools (Tableau, Looker) | Report definitions | Which dashboards depend on which tables |
| Data Catalogs | Business context | Owners, definitions, certification status |
| Version Control (GitHub) | Code changes | When transformations were modified |
Where do you get data lineage metadata?
Permalink to “Where do you get data lineage metadata?”There are many places where you can get lineage metadata. The most valuable and reliable source is the scripts responsible for moving data from one layer to another—ETL scripts.
These ETL scripts can be pure SQL or written in a programming language like Python, Scala, Go, etc. You can also use workflow engines like Airflow, Luigi, or Argo to extract it.
Many teams enrich metadata by adding comments and business context to data assets. You can store these comments in various places, such as a data catalog. There are many other ways of storing and extracting data lineage, most of which are based on the type of information they hold. Modern metadata management platforms consolidate these sources into a unified view.
Types of data lineage
Permalink to “Types of data lineage”Lineage comes in four main types: table-level (how datasets connect), column-level (how individual fields transform), business lineage (context and ownership), and technical lineage (system-level dependencies). Most teams start with table-level for quick wins, then add column-level when debugging field-specific errors like precision loss or unexpected nulls.
There are two ways to divide data lineage: table-level vs. column-level lineage, and business vs. technical lineage.
Table-level lineage vs. column-level lineage
Permalink to “Table-level lineage vs. column-level lineage”Table-level lineage is the lineage metadata of a relational database or data warehouse table.
This data lineage tells you how one table maps to another. However, it can’t capture fine-grained details about the details and history of a table’s columns.
For example, table-level lineage can describe the intermediary tables used during a table’s cleansing and transformation. It can even show how data transformation processes further transformed it into a dimensional table.
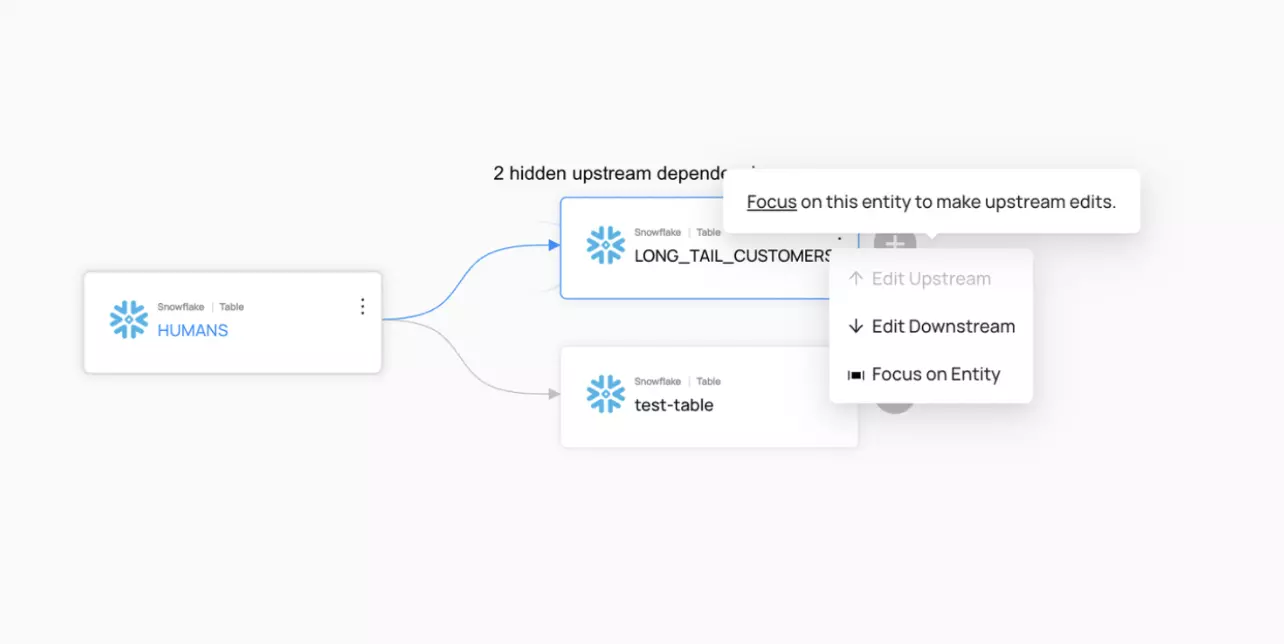
Table-level lineage shows how tables relate to one another but can't depict changes at the column level. Source: Atlan.
Column-level lineage, by contrast, traces the changes in a table’s columns. You can see the changes in attributes such as data type and precision, how new columns were created from combining other columns, and other alterations. Learn more about column-level lineage and its implementation.
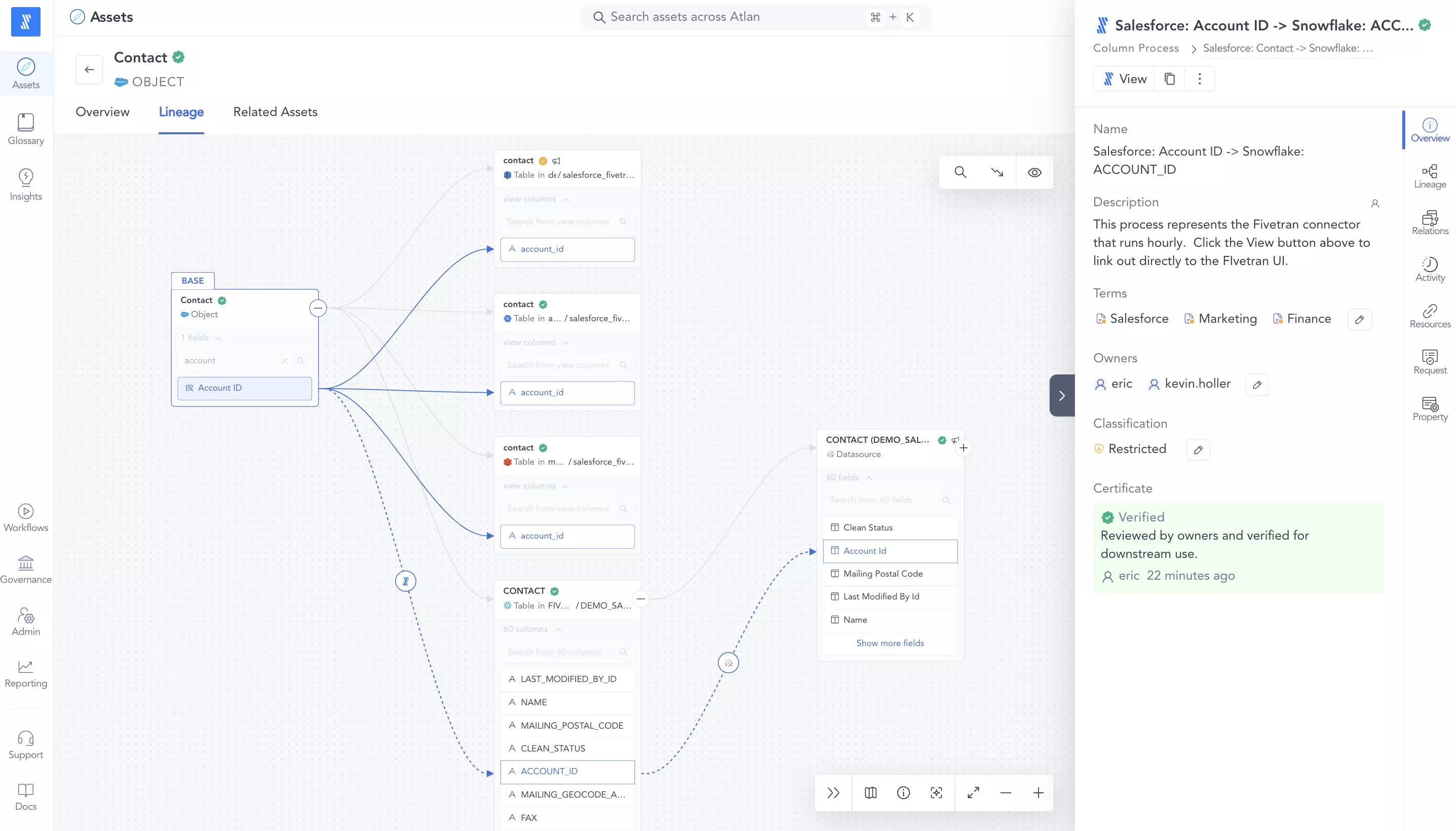
How column-level lineage shows the relationship between data over time at the most granular level. Source: Atlan Product Screenshot
Business vs. technical lineage
Permalink to “Business vs. technical lineage”Business data lineage provides context on the business purpose and everyday use of data. It could be comments, data classifications, justifications for data masking, notes for consumers, and more.
On the other hand, technical data lineage is primarily meant for engineers and technical analysts. It provides an end-to-end, detailed insight into how data reached its destination team. Users of data orchestration tools such as dbt and Airflow can extract technical lineage easily.
To bridge these two worlds, modern platforms often use a context graph to unify technical lineage with business context.
Lineage Type Comparison
| Type | Granularity | Best For | Typical Users | Implementation Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table-Level | Dataset to dataset | Understanding high-level flows | Business analysts, managers | 1-2 weeks |
| Column-Level | Field to field | Debugging precision errors, null values | Data engineers, quality teams | 4-8 weeks |
| Business Lineage | Business context | Governance, ownership, policies | Stewards, compliance teams | 2-4 weeks |
| Technical Lineage | System dependencies | Performance optimization, migrations | Platform engineers, architects | 2-6 weeks |
Why do data teams need lineage?
Permalink to “Why do data teams need lineage?”Without lineage, teams waste hours tracing errors through tangled pipelines and risk breaking downstream reports with every change. Lineage solves this by automatically mapping dependencies, enabling impact analysis before deployments, and providing audit trails for compliance. Organizations using automated lineage reduce root cause analysis time substantially and catch breaking changes before they reach production.
Tracking data lineage brings multiple benefits:
- Trust and transparency in data practices
- Data quality and reliability
- Data and application debugging
- Data security and compliance
Trust and transparency in data practices
Permalink to “Trust and transparency in data practices”Teams in your organization consume data at different points in its journey. Data lineage enables trust and transparency by allowing teams to track data from the source to the consumption layer. It renders data movement, change, and transformation more visible.
Without consolidated and automatically generated lineage, teams must scour individual SQL scripts, data pipeline workflows, detailed documentation (which might be outdated), and test suites to vet data. Data lineage provides this information on demand for everyone in your company with comparatively little effort.
According to Dataversity, data lineage provides a complete audit trail for GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA compliance, making it essential for regulatory transparency.
Data quality and reliability
Permalink to “Data quality and reliability”Data quality is more than just the visibility of workflows. It ensures that data in your organization is reliable and meets certain standards. Data lineage helps certify that data meets your quality bar.
According to the 2023 Data Integrity Trends and Insights Report by Precisely, 70% of data professionals who struggle to trust their data cite data quality as the biggest issue impacting their confidence in data-driven decision-making.
Throughout its journey, data is moved, reshaped, transformed, enriched, backfilled, and so on. Many of these activities are lossy—some data or precision is shed.
Even if the loss is intentional (e.g., adjusting date precisions), it can create errors and bugs in downstream data consumers. With column-level data lineage, you can easily identify which transformation process introduced an error. Modern data quality tools integrate with lineage to automate issue detection.
Data and application debugging
Permalink to “Data and application debugging”Data lineage is one of data and analytics engineers’ most valuable debugging tools. It provides a new information layer that isn’t usually available in standalone data quality, data profiling, and testing suites.
Data lineage enables two types of enhanced data debugging support.
With root cause analysis, you can trace a data error—e.g., a precision error, unexpected null values, malformatted data—back to its ultimate source. Fixing an error at its source fixes it not just for one broken report or app, but for all downstream consumers. This improves the overall reliability of your data estate.
Using impact analysis, you can identify data problems before they happen. When your data engineers submit pipeline changes to GitHub, it can trigger an automated check that detects if the alteration would break any downstream consumers. This proactive approach to data quality can eliminate hundreds of hours spent debugging issues.
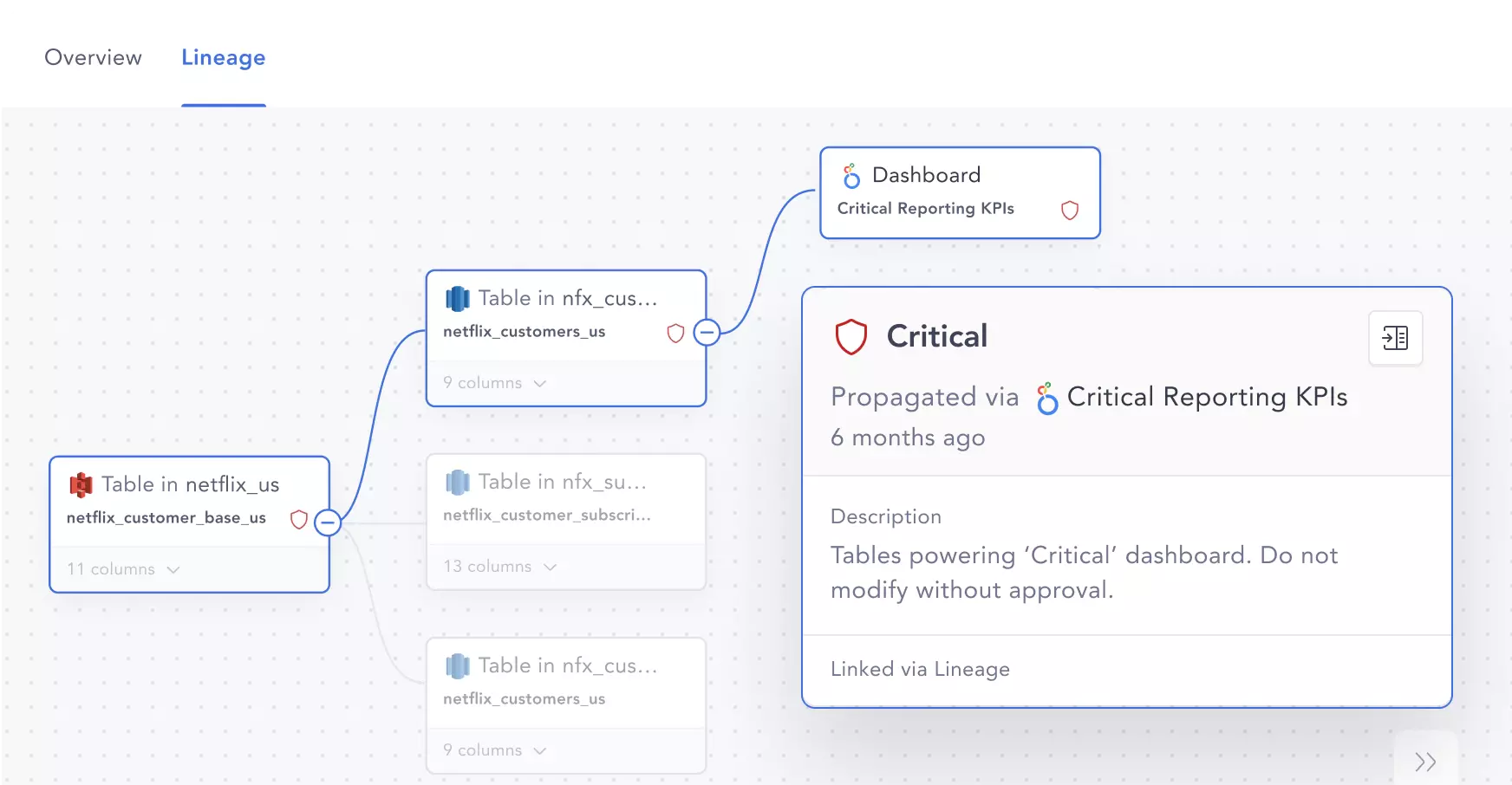
In this example, data lineage shows which tables are powering a key dashboard used for reporting progress to senior leadership. This allows teams to take extra care when considering modifications to these critical assets. Source: Atlan.
Data security and compliance
Permalink to “Data security and compliance”Data lineage can also show your organization how it handles data security and compliance with regulations at different stages of the data journey. This makes data lineage an essential tool for auditing and compliance.
According to ISACA, data lineage prominence started in the banking sector to meet compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR. This capability has since become essential across industries for demonstrating proper data handling.
Organizations must know where in the journey they’ve masked and virtualized data. They must also certify that they’ve addressed all privacy and security issues before moving data (e.g., importing it into a clean room).
Validating compliance across your organization is especially critical when handling Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Personal Health Information (PHI). Noncompliant handling of PII and PHI can incur hefty fines. Lack of compliance can cost organizations up to $15 million per year.
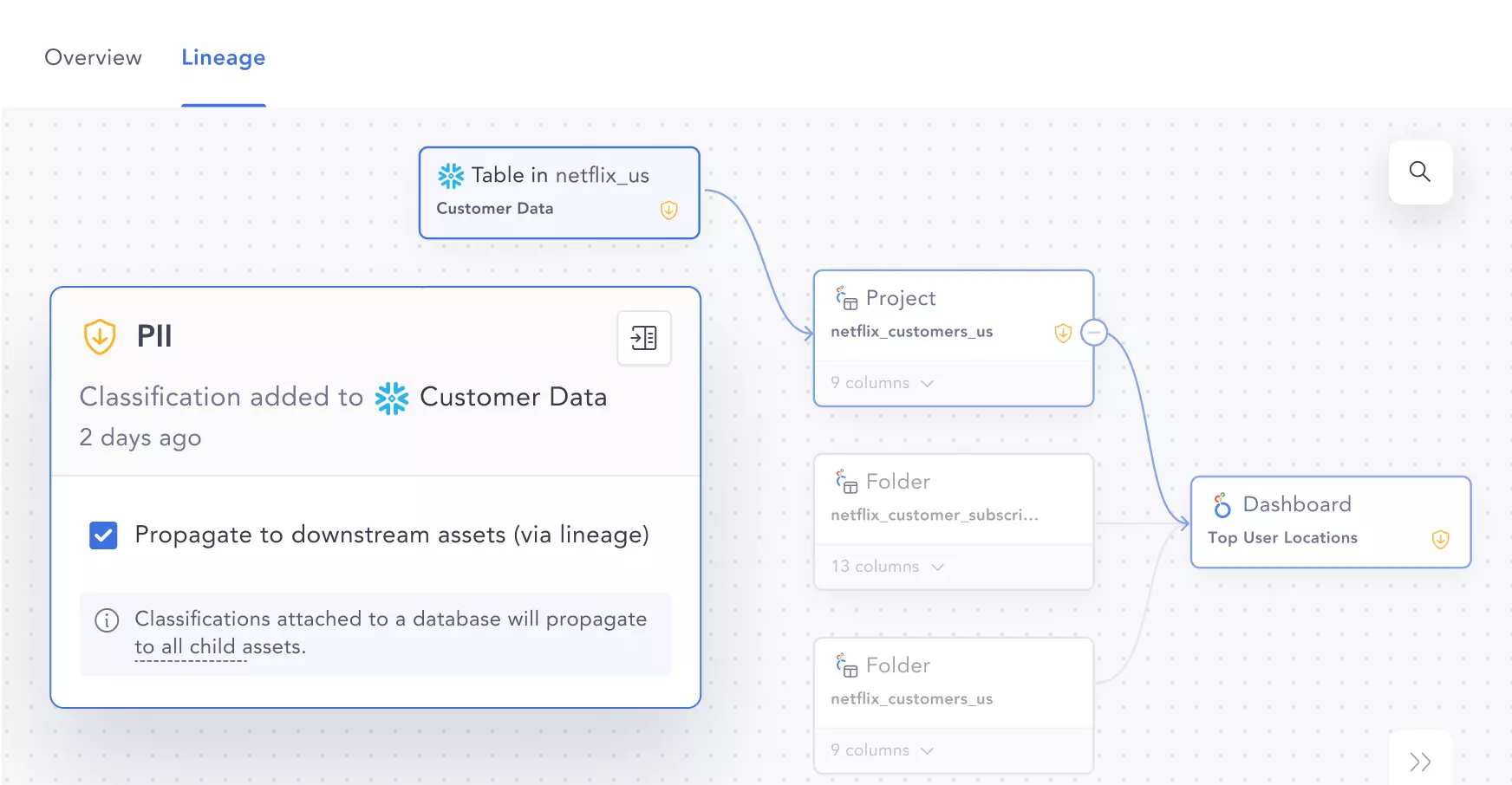
An example of propagating data classification tags using data lineage. Source: Atlan
Modern data governance platforms leverage lineage to automatically propagate classifications and access policies through data pipelines.
Also, read → Driving ROI with Data Lineage | Smarter artificial intelligence with data lineage
How do you implement data lineage?
Permalink to “How do you implement data lineage?”Modern lineage tools connect to your data stack and extract relationships automatically from query logs, transformation code, and BI definitions. You configure connectors once, and the tool continuously updates lineage as your pipelines run. This automation replaces the manual spreadsheet tracking that organizations previously spent weeks maintaining, only to have it become outdated immediately.
To fully leverage the benefits of data lineage, use a tool that connects across your modern data stack and automatically generates lineage metadata.
Implementation Steps:
- Connect to source systems (1-2 weeks)
- Link your data warehouse, transformation tools, BI platforms
- Modern tools support 100+ connectors for no-code setup
- Configure lineage extraction (1-3 weeks)
- Parse and map relationships (Automated)
- Tool analyzes SQL, code, and metadata
- Builds visual graph of dependencies
- Validate and enrich (Ongoing)
- Verify critical lineage paths
- Add business context and ownership
- Activate lineage (Immediate)
- Use for impact analysis before changes
- Enable alerts for pipeline breaks
When evaluating a data lineage tool, look for the following capabilities:
- Automated data lineage
- Manual enrichment and editing of data lineage
- Advanced SQL parsing for inferring data lineage
- Granular, column-level data lineage
- Support for a variety of data sources for extracting data lineage
According to Databricks, compliance regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, BCBS 239, and SOX require organizations to have clear understanding and visibility of data flow, making automated lineage essential for audit readiness.
Need more help? Check out our list of top data lineage tools in 2026.
How Atlan Benefits Customers with Data Lineage
Permalink to “How Atlan Benefits Customers with Data Lineage”Challenge: Data teams struggle with fragmented lineage tools that only cover part of their stack. Lineage from Snowflake might exist, but connections to dbt, Tableau, and Looker require separate tools. Manual stitching creates gaps where dependencies hide. When pipelines break, engineers waste hours jumping between systems trying to trace the issue, and impact analysis before changes becomes guesswork.
Approach: Atlan automatically captures end-to-end, column-level lineage across your entire modern data stack through pre-built connectors. The platform stitches together transformation logic from dbt and Airflow, query history from data warehouses, and consumption patterns from BI tools into a unified graph. Active metadata features then activate this lineage—automatically alerting owners when upstream changes affect their assets, propagating classifications through dependencies, and surfacing usage metrics on lineage edges. Lineage transformations appear in business-friendly language so analysts understand impacts without reading SQL.
Outcome: Takealot improved their time-to-resolution for root cause analysis by 50% using Atlan’s automated lineage feature. Aliaxis leverages Atlan’s pipeline observability and end-to-end lineage features to find pipeline breaks 95% faster, accelerating issue resolution time from 1 day to 1 hour. These results come from lineage that’s always current, covers the complete stack, and activates automatically in workflows rather than requiring separate portal visits.
Atlan makes lineage transformations easier to understand by translating them into business-user-friendly explanations.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization capture end-to-end, column-level lineage.
What’s the future of data lineage?
Permalink to “What’s the future of data lineage?”Data lineage is evolving from a compliance checkbox to an active system that prevents issues before they occur. The next generation of lineage tools will predict breaking changes using machine learning, automatically classify sensitive data as it propagates through pipelines, and provide natural language explanations of complex transformations for business users.
As organizations scale AI and machine learning initiatives, lineage becomes essential for model governance—tracking which training datasets influenced which predictions, ensuring models retrain when source data changes, and explaining model outputs to regulators. The teams that implement comprehensive lineage today will be the ones who can move fast tomorrow, making changes confidently while maintaining compliance and data quality.
Modern platforms like Atlan leverage active metadata to make lineage actionable in real-time, surfacing insights where teams work rather than requiring separate tool visits.
Ready to see how automated lineage accelerates debugging and impact analysis? Request a demo to explore Atlan’s column-level lineage capabilities.
FAQs about Data Lineage Explained
Permalink to “FAQs about Data Lineage Explained”1. What is data lineage, and why is it important?
Permalink to “1. What is data lineage, and why is it important?”Data lineage tracks data flow from origin to destination, capturing every transformation along the way. It’s important because it provides visibility into data dependencies, enables faster debugging, and supports regulatory compliance. Organizations use lineage to trace errors to their source, assess the impact of changes before deployment, and demonstrate proper data handling to auditors.
2. How do organizations explain data lineage effectively?
Permalink to “2. How do organizations explain data lineage effectively?”Organizations explain lineage using visual tools that map data flows as interactive graphs. These diagrams show source systems at the left, transformations in the middle, and consumption points at the right. Color coding indicates certification status, and click-through reveals transformation logic. This visual approach helps both technical and non-technical stakeholders understand dependencies without reading code.
3. What tools can I use to track and document data lineage?
Permalink to “3. What tools can I use to track and document data lineage?”Modern data lineage tools include platforms like Atlan that offer automated lineage extraction and active metadata features. Open-source options include Apache Atlas, DataHub, and Marquez for OpenLineage integration. When evaluating tools, prioritize automated discovery over manual documentation, column-level granularity over table-level only, and cross-system lineage that connects your entire stack. The best tools also provide impact analysis and data quality integration.
4. How does data lineage support regulatory compliance?
Permalink to “4. How does data lineage support regulatory compliance?”Data lineage provides a clear trail of how sensitive data (like PII) is used, transformed, and stored. This transparency is essential for meeting regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. According to ISACA, lineage enables organizations to demonstrate proper data handling during audits. It also allows you to quickly respond to compliance audits and inquiries by providing evidence of data governance practices.
5. Why is understanding data lineage critical for audits?
Permalink to “5. Why is understanding data lineage critical for audits?”Understanding data lineage is crucial for audits as it provides clear evidence of data handling practices. It helps auditors trace data transformations, assess data quality, and verify compliance with industry regulations, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
6. How can data lineage improve data governance?
Permalink to “6. How can data lineage improve data governance?”Data lineage improves data governance by offering insights into data usage and dependencies. It helps organizations enforce data policies, maintain high data quality, and ensure that data flows align with governance standards.
7. How long does it take to implement data lineage?
Permalink to “7. How long does it take to implement data lineage?”Implementation timeframes vary by scope. Table-level lineage for a single data warehouse typically takes 1-2 weeks with automated tools. Adding column-level lineage extends this to 4-8 weeks. Full stack lineage covering ETL, warehouses, and BI platforms usually requires 2-3 months including validation. Modern tools with pre-built connectors significantly accelerate deployment compared to custom-built solutions that can take 6-12 months. Most organizations see value within the first month even with partial coverage.
8. What’s the difference between data lineage and data provenance?
Permalink to “8. What’s the difference between data lineage and data provenance?”Data provenance focuses specifically on the origin and custody chain of data—where it came from and who handled it. Data lineage encompasses provenance plus all transformations, movements, and usage patterns throughout the data lifecycle. Think of provenance as the birth certificate, while lineage is the complete life story. Both support governance, but lineage provides the broader operational context needed for impact analysis and debugging. Organizations typically implement lineage first as it delivers more day-to-day value.
9. Why isn’t my lineage showing expected connections?
Permalink to “9. Why isn’t my lineage showing expected connections?”Missing lineage connections usually stem from three issues: query history isn’t captured (enable in your warehouse settings), transformation code isn’t accessible (grant read permissions to lineage crawler), or custom ETL logic requires manual mapping (configure custom connectors). Dynamic SQL and code that builds queries at runtime can also break automatic lineage extraction. Most modern tools provide gap reports showing where lineage is incomplete and offer manual override options for complex cases.
10. How does Atlan’s lineage differ from open-source options?
Permalink to “10. How does Atlan’s lineage differ from open-source options?”Atlan provides automated column-level lineage across 100+ connectors without custom code, whereas open-source tools often require engineering teams to build and maintain integrations. Atlan’s active metadata features automatically alert stakeholders about changes, propagate governance policies, and surface usage metrics on lineage edges. Open-source tools excel for customization and on-premises deployments, while Atlan optimizes for fast time-to-value with managed infrastructure and automatic updates. Organizations often use both—Atlan for production, open-source for experimentation.
Share this article



















