Why does governance matter before Databricks migration?
Permalink to “Why does governance matter before Databricks migration?”Without governance planning, you’ll discover security gaps after migration when they’re significantly more expensive to fix. Organizations face substantial financial losses from poor data quality during migrations. Most teams underestimate this risk. Moving from legacy data warehouses or on-premises Hadoop to Databricks requires rethinking governance for lakehouse architectures, not just migrating technical infrastructure.
Post-migration discovery costs devastate budgets. Teams find themselves fixing unauthorized data access incidents, compliance violations, and data quality issues reactively rather than proactively. The vast majority of migrations without governance frameworks fail to meet objectives. This compares unfavorably to teams implementing concurrent governance.
Regulatory pressure intensifies during cloud migrations. GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA enforcement agencies scrutinize data movement between systems. You need classification, access controls, and audit trails operational before production data lands in Databricks. Governance isn’t optional anymore—it’s the difference between migration success and expensive failure.
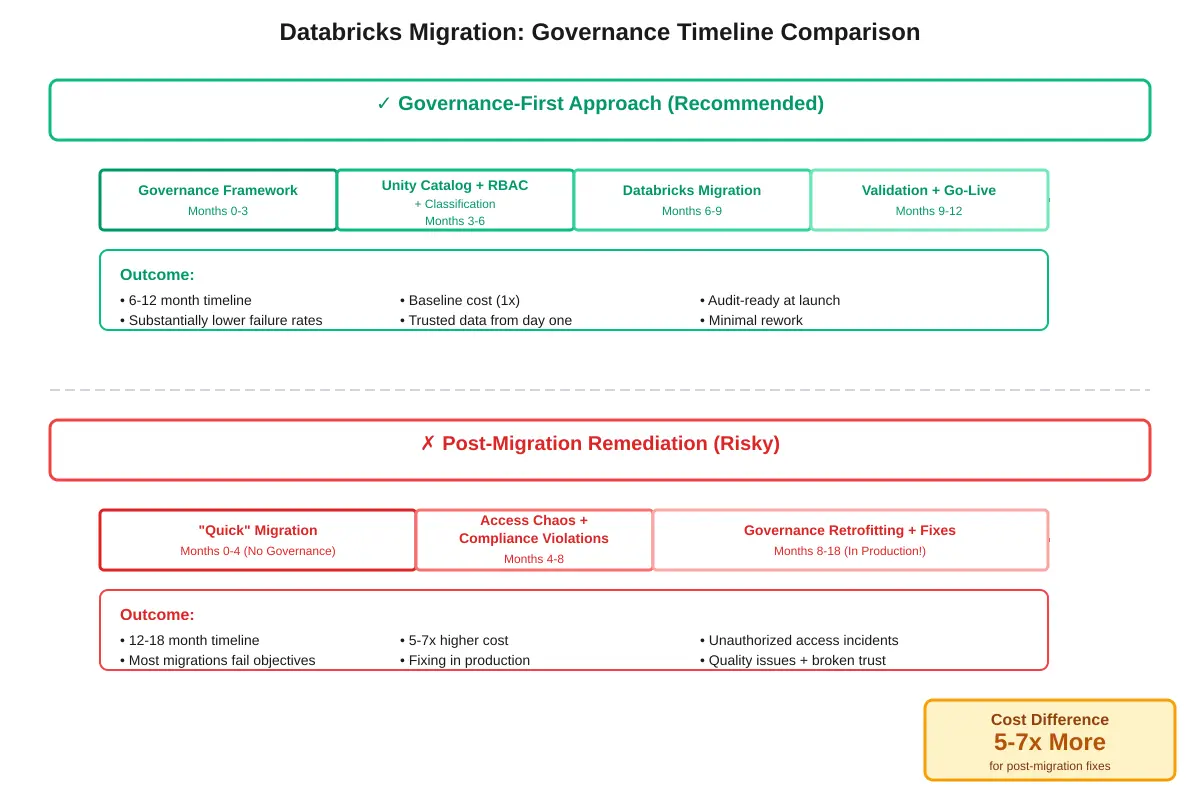
Concurrent governance implementation reduces migration timeline by 4-6 months and costs 5-7x less than post-migration remediation.
Step 1: How do you establish a governance framework? (2-3 months)
Permalink to “Step 1: How do you establish a governance framework? (2-3 months)”Establish governance before technical migration through three components: an executive-sponsored governance council, distributed data stewards, and a clear decision-rights model. Begin by securing executive sponsorship. Organizations with C-level champions complete implementations significantly faster than teams without. You’ll spend 2-3 months forming this framework, but it accelerates every subsequent step.
Form your governance council first. Include executives (Chief Data Officer or VP Engineering), business domain leaders (Finance, Sales, Operations), technical leads (Data Platform team), and compliance representatives. Meet bi-weekly initially to make policy decisions. Active councils make regular decisions throughout the week. Without this decision-making body, governance stalls on access requests and policy questions.
From there, appoint data stewards across business domains using a federated model. Each domain (Finance, Sales, Engineering) needs an owner responsible for data quality, classification, and access approvals in their area. Centralized governance teams can’t scale. You need distributed ownership with clear escalation paths.
Document decision rights through a RACI matrix. This means defining who approves access requests (data stewards), who implements technical controls (platform admins), who monitors compliance (security team), and who escalates policy conflicts (governance council). This clarity prevents the access request backlog that plagues many governance programs.
| Role | Key Responsibilities | Time Commitment |
|---|---|---|
| Governance Council Chair | Policy decisions, executive alignment, conflict resolution | 5-8 hrs/week |
| Data Steward (Domain) | Access approvals, data quality, classification for domain | 10-15 hrs/week |
| Data Platform Admin | Technical implementation, Unity Catalog configuration | 20-30 hrs/week |
| Security/Compliance Lead | Audit monitoring, policy enforcement, compliance reporting | 10-15 hrs/week |
| Executive Sponsor | Strategic direction, resource allocation, organizational buy-in | 2-4 hrs/week |
Define your core governance policies before migration begins. Cover data access (who can see what), classification standards (how you label sensitivity), retention rules (how long you keep data), and quality expectations (what constitutes production-ready data). These policies guide every technical decision in subsequent steps.
Step 2: How do you design Unity Catalog architecture? (3-4 weeks)
Permalink to “Step 2: How do you design Unity Catalog architecture? (3-4 weeks)”Unity Catalog provides centralized governance for Databricks through a three-level namespace: metastore, catalog, schema, and table. Design this hierarchy aligned to your organizational structure over 3-4 weeks. Your architecture decisions here determine how you’ll isolate data, manage permissions, and organize assets for the next 3-5 years.
Establish one metastore per cloud region to avoid cross-region latency issues. The metastore is your top-level container storing governance metadata: catalogs, schemas, tables, permissions, and lineage. Multi-region organizations need separate metastores. Don’t try to span regions with a single metastore.
Choose your catalog strategy based on organizational structure. You have three options: environment-based (Dev/Staging/Prod catalogs), business unit-based (Finance, Sales, Engineering catalogs), or hybrid. Most enterprises use the hybrid approach. This means separating production from non-production, then organizing production catalogs by business domain.
| Strategy | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment-based | Small teams, simple workflows | Clear separation, easy SDLC | Doesn’t scale to large orgs |
| Business unit-based | Large enterprises, federated governance | Aligns to ownership, scales well | Complex for shared data |
| Domain-based (data mesh) | Mature data organizations | True decentralization, product thinking | Requires mature governance |
| Hybrid approach | Most enterprises | Balances isolation and collaboration | Requires planning upfront |
Catalogs are your primary data isolation boundary. Permissions granted at the catalog level cascade down automatically. Use catalogs to separate data that different teams own or that has different sensitivity levels. Within catalogs, organize schemas by project or data domain. Tables and views sit within schemas.
Decide on managed vs. external tables strategically. Managed tables store data in Unity Catalog-controlled storage (S3, ADLS, GCS) with full governance. External tables reference data in your existing storage with Unity Catalog providing governance at the Databricks boundary. Apply managed tables for new data. Register external tables for legacy data you’re migrating gradually.
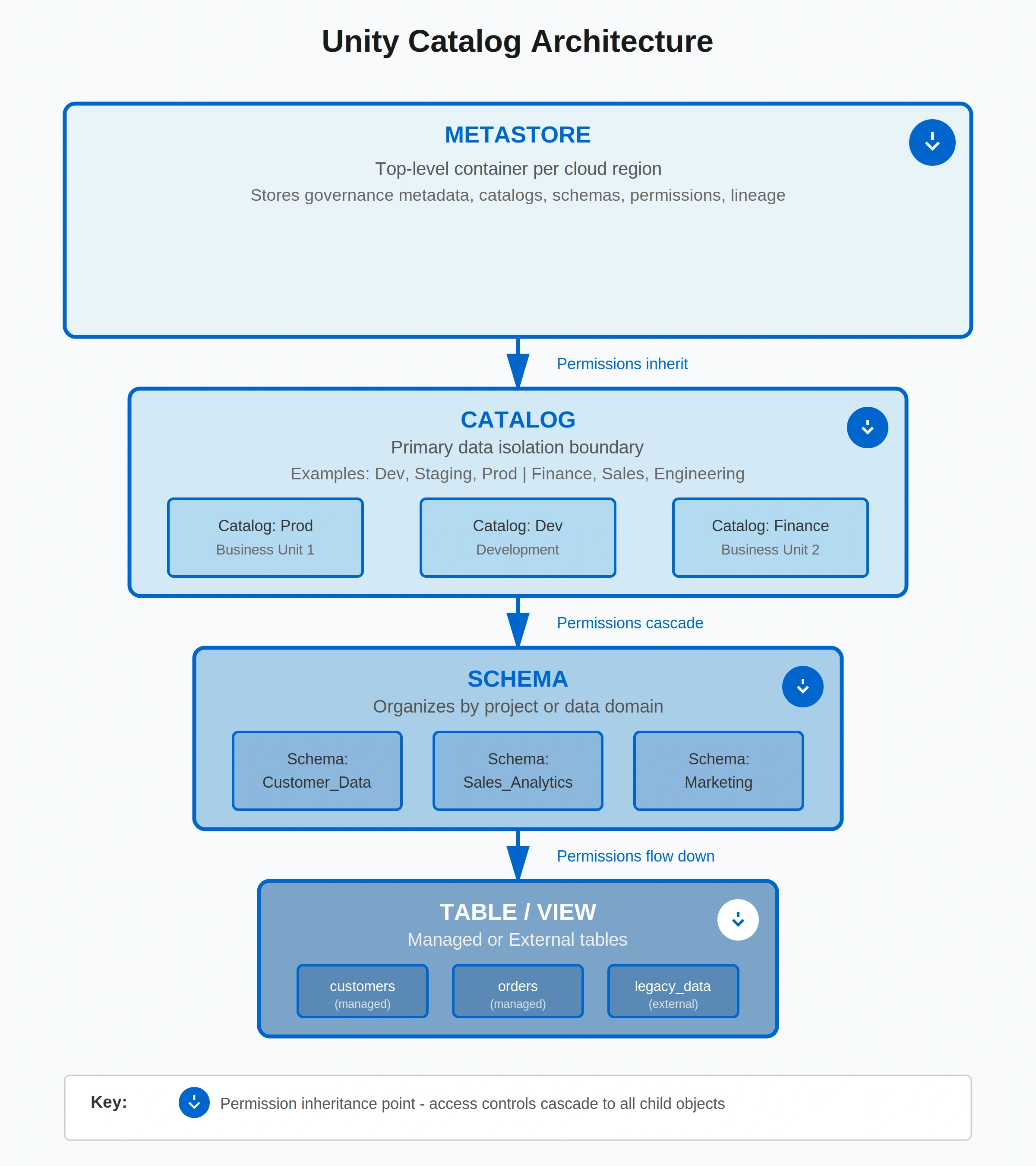
Unity Catalog's three-level namespace provides granular access control from account to column level with permission inheritance.
Step 3: How do you configure identity and access controls? (3-4 weeks)
Permalink to “Step 3: How do you configure identity and access controls? (3-4 weeks)”Configure RBAC through three layers: account-level identity provisioning via SCIM, catalog and schema permissions, and table and column-level access controls. All principals (users, groups, and service principals) must be defined at the account level for Unity Catalog. SCIM provisioning from your identity provider (Okta, Azure AD, Google Workspace) significantly reduces manual overhead.
Connect your identity provider first. Set up SCIM 2.0 to automatically sync users and groups from your IdP to the Databricks account. This avoids workspace-level provisioning, which creates governance gaps. Unity Catalog only sees account-level identities. Configure synchronization to run every 30-60 minutes so group membership changes propagate quickly.
Understand Unity Catalog’s permission hierarchy: Account, Metastore, Catalog, Schema, Table/View, then Column/Row. Permissions granted at higher levels cascade down automatically. Grant USE CATALOG and USE SCHEMA permissions carefully. These let users see metadata even if they can’t read data. For maximum security, grant these only to users who need data visibility.
Define role-based groups in your IdP, not in Databricks. Build groups like data-engineers-prod, analysts-finance, and ml-engineers-dev that map to access patterns. Grant permissions to groups, never to individual users. When someone changes roles, update their group membership in your IdP. This means permissions update automatically via SCIM.
| Permission Level | Granted To | Typical Use Case | Key Privileges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Account Admin | IT administrators | Account setup, billing, high-level config | Full account control, user management |
| Metastore Admin | Governance leads | Top-level governance setup | Create catalogs, manage metastore |
| Catalog Owner | Domain data stewards | Domain-level governance | Grant permissions, manage schemas |
| Schema Owner | Project leads | Project-level data management | Create tables, grant read access |
| Data Consumer | Analysts, engineers | Read data for analysis | SELECT on tables/views |
Implement least privilege access from day one. Start with no access. Grant permissions only as needed. For service principals (automation accounts), use separate principals per workflow with minimal permissions. Rotate service principal credentials every 90 days using secret management tools (Vault, Key Vault, Secrets Manager).
Configure row and column-level security for sensitive data. Unity Catalog supports dynamic views that filter rows based on user identity. Apply these for multi-tenant tables or region-restricted data. For column-level security, create views that exclude sensitive columns or use column masking (redacting SSNs, hashing emails).
Step 4: How do you implement data classification? (2-4 weeks)
Permalink to “Step 4: How do you implement data classification? (2-4 weeks)”Implement automated classification through three mechanisms: pattern-based rules for PII detection, ML-powered sensitive data discovery, and tag propagation via lineage. Automated classification achieves significantly higher accuracy than manual tagging. You’ll spend 2-4 weeks setting up classification rules and validating results before migration begins.
Define your classification taxonomy first. Most organizations use four tiers: Public (shareable externally), Internal (employee access), Confidential (restricted business use), and Restricted (highest sensitivity including PII, financial data, and trade secrets). Map these tiers to access controls and compliance requirements.
| Classification Level | Definition | Access Controls | Data Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public | Shareable externally | No restrictions | Press releases, public product info |
| Internal | Employee access only | Authenticated users | General business docs, metrics |
| Confidential | Restricted business use | Role-based access | Financial forecasts, strategy docs |
| Restricted | Highest sensitivity | Explicit approval required | PII, SSNs, payment cards, health records |
Begin with pattern-based rules for structured PII. Deploy regex patterns to detect Social Security Numbers (\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}), credit card numbers (Luhn algorithm validation), email addresses, and phone numbers. Unity Catalog’s classification APIs let you scan columns and apply tags automatically when patterns match.
Layer in ML-powered classification for unstructured and semi-structured data. Modern classification tools analyze column names, sample values, and statistical distributions to infer sensitivity. They catch PII that doesn’t match regex patterns, like free-text fields containing personal information.
Propagate classification tags downstream automatically using lineage. When you classify a source table as “Restricted,” all downstream tables and views inherit that classification through lineage relationships. This prevents sensitive data from spreading untagged across your environment. Configure bi-directional sync between your governance platform and Unity Catalog so tags stay consistent.
Validate classification accuracy before trusting automation. Review a sample of auto-classified assets (500-1,000 tables) to measure precision and recall. Adjust rules based on false positives (over-classification) and false negatives (missed sensitive data). Most teams achieve high accuracy after 2-3 tuning iterations.
Step 5: How do you set up data lineage tracking? (3-4 weeks)
Permalink to “Step 5: How do you set up data lineage tracking? (3-4 weeks)”Data lineage shows you exactly where your data comes from and where it goes. Enable lineage through Unity Catalog APIs for within-Databricks tracking, capturing most transformation lineage automatically. Then extend to cross-system lineage across source databases, ETL tools, and BI platforms. When a source system changes, you’ll know which downstream reports break in seconds instead of hours.
Configure Unity Catalog lineage extraction first. Unity Catalog automatically captures column-level lineage for SQL queries, Delta Live Tables pipelines, and Databricks notebooks accessing tables. This lineage tracks transformations within single workspaces, showing how raw data becomes transformed into analytics tables.
Understand Unity Catalog’s lineage limitations. It tracks lineage within Databricks workspaces but doesn’t see source system origins (where data came from before Databricks), cross-workspace dependencies (workspace A tables feeding workspace B), or downstream BI tool consumption (Tableau dashboards reading Databricks tables). For migration planning, you need this broader visibility.
Extend lineage to source systems feeding Databricks. Register source databases (Oracle, SQL Server, Teradata) in your governance platform and track ETL jobs (Airflow, dbt, Fivetran) that extract data into Databricks. This upstream lineage identifies which source schemas feed which Databricks tables—critical for assessing migration impact.
Track downstream BI tool consumption through query logs. Most BI platforms (Tableau, Power BI, Looker) log which database tables they query. Capture these logs and map queries back to Databricks tables. During migration, you’ll know exactly which dashboards and reports depend on tables you’re moving. This prevents surprise breaks.
| Lineage Scope | Unity Catalog Alone | With Cross-System Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Within Databricks workspace | Full column-level | Full column-level |
| Source systems → Databricks | Not available | Full table/column-level |
| Databricks → BI tools | Limited query history | Full dashboard/report-level |
| Cross-workspace dependencies | Not available | Full workspace-to-workspace |
| End-to-end visibility | Limited | Comprehensive |
Use lineage for pre-migration impact analysis. Before migrating a source system schema, trace its lineage forward to identify which Databricks tables depend on it, which downstream transformation pipelines will need updates, and which BI dashboards will break. This analysis prevents the “surprise break” that derails many migrations.
![]()
Cross-system lineage tracks data journey from source to consumption, identifying which downstream assets break during migration.
Step 6: How do you establish compliance monitoring? (2-3 weeks)
Permalink to “Step 6: How do you establish compliance monitoring? (2-3 weeks)”Establish compliance through three monitoring layers: real-time audit logs from Unity Catalog, automated policy violation detection, and compliance reporting dashboards. Unity Catalog system tables capture user-level access logs automatically, recording who accessed what data, when, and from where. Map these audit capabilities to GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and SOC 2 requirements. Compliance failures during migration can result in substantial fines.
Enable Unity Catalog system tables for audit logging first. Unity Catalog writes audit events to system.access.audit tables covering data access (SELECT queries), permission changes (GRANT/REVOKE commands), schema modifications (CREATE/ALTER/DROP), and lineage captures. These system tables are queryable via SQL. Build compliance reports directly on audit data.
Set up automated policy violation detection. Monitor for unauthorized access attempts (users querying tables they shouldn’t see), data exfiltration patterns (large downloads to local machines), permission escalation (users granting themselves higher privileges), and sensitive data exposure (Restricted data queried without approval). Configure alerts to fire within 5 minutes of violations.
Map data assets to regulatory requirements using classification tags. Tag tables containing EU citizen data with GDPR-applicable, health records with HIPAA-PHI, and California resident data with CCPA-personal-info. During audits, you’ll generate reports showing which assets contain regulated data, who accessed them, and whether access was authorized.
| Component | Data Source | Monitoring Frequency | Alert Triggers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access audit logs | Unity Catalog system.access.audit | Real-time | Unauthorized access attempts |
| Data movement tracking | Query logs, export events | Real-time | Large data downloads, unusual patterns |
| Policy violations | Permission changes, GRANT commands | Real-time | Self-granted permissions, policy conflicts |
| Retention compliance | Table metadata, last-modified timestamps | Daily | Data retained beyond policy |
| PII exposure | Classification tags, query patterns | Real-time | Restricted data accessed without approval |
Build compliance dashboards for auditors. Develop reports showing the access audit trail (who accessed PII in the last 90 days), data lineage proof (how personal data flows from source to analytics), retention compliance (data deleted per policy), and incident response (violations detected and remediated). During GDPR audits, these reports demonstrate compliance in minutes instead of weeks.
Test your compliance monitoring before production migration. Simulate violations by having team members attempt unauthorized access, download sensitive data, or grant themselves permissions. Verify alerts fire within SLA (typically 5-15 minutes) and audit logs capture details. Fix gaps before regulated data moves to Databricks.
Step 7: How do you train teams and document procedures? (4-6 weeks initial)
Permalink to “Step 7: How do you train teams and document procedures? (4-6 weeks initial)”Roll out governance through persona-based training for data engineers, analysts, stewards, and business users, along with living documentation including playbooks, runbooks, and decision trees. Organizations with structured training achieve significantly faster user adoption. Plan 4-6 weeks for initial rollout with ongoing reinforcement. Poor adoption from lack of training causes many governance programs to stall.
Design training tracks for each persona based on their needs. Data engineers need Unity Catalog technical details (how to create tables, grant permissions, troubleshoot access issues). Analysts need data discovery skills (how to find datasets, request access, understand classification). Stewards need policy management training (how to approve access, review audit logs, escalate issues). Business users need self-service guidance (how to browse catalogs, understand lineage, respect data policies).
| Persona | Training Focus | Duration | Key Topics Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Engineers | Unity Catalog technical implementation | 8-12 hours | Metastore setup, RBAC config, lineage APIs, troubleshooting |
| Data Analysts | Data discovery and access | 4-6 hours | Catalog browsing, access requests, classification understanding |
| Data Stewards | Policy management and enforcement | 10-15 hours | Access approvals, audit reviews, policy updates, escalation |
| Business Users | Self-service data access | 2-3 hours | Finding data, understanding lineage, respecting policies |
| Executives | Governance strategy and oversight | 1-2 hours | Business value, risk mitigation, metrics reporting |
Develop governance playbooks documenting standard procedures. Cover how to request data access (step-by-step workflow), how stewards approve requests (decision criteria), how to classify new data (rules and examples), how to troubleshoot permission errors (common fixes), and how to escalate policy questions (when to involve the governance council). Make these playbooks searchable and accessible through Wiki, Confluence, or Notion.
Build runbooks for common technical tasks. Document Unity Catalog catalog creation, SCIM setup and troubleshooting, permission grant workflows, classification rule configuration, and lineage extraction queries. Include screenshots, code snippets, and links to official Databricks documentation. Update these quarterly as Unity Catalog evolves.
Establish change management mechanisms for ongoing adoption. Appoint governance champions in each business unit who advocate for governance and answer day-to-day questions. Run weekly office hours where teams can ask questions. Spin up dedicated Slack or Teams channels (#data-governance, #unity-catalog-help) for async support. Track adoption metrics including access requests per week, time-to-approval, and training completion rates. Address bottlenecks as they emerge.
Conduct quarterly governance reviews to improve continuously. Gather feedback from teams about which policies cause friction, where documentation is unclear, and what training gaps remain. Update policies based on lessons learned. Share governance wins like migrations completed without incidents, compliance audits passed, and data discovery time reduced. This builds organizational buy-in for governance as enabler, not blocker.
What are common governance pitfalls during migration?
Permalink to “What are common governance pitfalls during migration?”Common pitfalls cause most governance failures during Databricks migrations. Avoid delaying governance until after migration (teams attempting post-migration governance face significantly higher remediation costs), insufficient stakeholder alignment, over-engineered policies that slow teams, lack of automation (manual tagging doesn’t scale), and missing cross-system visibility. Migrations that implement governance concurrently complete faster and at lower cost.
Pitfall 1: Delayed governance (reactionary approach)
Permalink to “Pitfall 1: Delayed governance (reactionary approach)”Most teams plan technical migration first, then bolt on governance afterward. This causes expensive rework. Pipelines need refactoring to add access controls, tables need reclassification, and compliance gaps appear during audits. Start governance planning during the discovery phase, before any data moves.
Pitfall 2: Siloed governance council (no business representation)
Permalink to “Pitfall 2: Siloed governance council (no business representation)”Governance councils dominated by IT and security teams make policies disconnected from business needs. Without business unit representation, policies become obstacles rather than enablers. Include domain leaders (Finance, Sales, Operations) in your governance council from day one.
Pitfall 3: Over-restrictive policies (governance becomes blocker)
Permalink to “Pitfall 3: Over-restrictive policies (governance becomes blocker)”Some teams implement “governance theater,” with policies so restrictive that productive work grinds to a halt. Access requests take weeks, classification requires manual review, and teams circumvent governance through shadow IT. Balance security with agility. Automate approvals for low-risk requests, pre-approve common access patterns, and empower stewards to make decisions quickly.
Pitfall 4: Manual processes (tagging doesn’t scale)
Permalink to “Pitfall 4: Manual processes (tagging doesn’t scale)”Manual data classification and access request workflows collapse under load. Organizations attempting manual governance manage only a small fraction of assets before giving up. Automated classification achieves comprehensive coverage. Automated access workflows reduce time-to-approval from days to hours. Invest in automation from the start.
Pitfall 5: Unity Catalog-only focus (ignoring broader data stack)
Permalink to “Pitfall 5: Unity Catalog-only focus (ignoring broader data stack)”Unity Catalog governs data within Databricks, but migrations involve entire data ecosystems including source databases, ETL pipelines, and BI tools. Without cross-system visibility, you can’t assess full migration impact. Extend governance beyond Unity Catalog to track lineage from source systems through Databricks to downstream consumption.
How Atlan Extends Unity Catalog for Enterprise Governance
Permalink to “How Atlan Extends Unity Catalog for Enterprise Governance”The Challenge
Permalink to “The Challenge”Unity Catalog provides robust governance within Databricks, but enterprise migrations require governance across your entire data stack, from source databases to BI tools. During migration, you need visibility into which source system schemas feed Databricks tables, how data transforms across multiple platforms, and which downstream dashboards will break when you move schemas. Unity Catalog’s lineage is limited to single workspaces. It doesn’t track source system origins or downstream BI tool consumption. Without this cross-system visibility, you’re flying blind during migration.
“Teams need governance from cloud all the way back to on-prem to assess migration impact accurately.” - Brian Ames, Head of AI Center at General Motors
Atlan’s Approach
Permalink to “Atlan’s Approach”Atlan complements Unity Catalog by extending governance beyond Databricks as a universal data catalog and cross-system governance plane. It provides bi-directional tag sync with Unity Catalog for automated policy enforcement. Classification tags created in Atlan propagate to Unity Catalog automatically, keeping policies aligned across platforms.
Atlan tracks column-level lineage across your full data stack: source systems (Oracle, SQL Server, Teradata), Databricks transformations, and BI tools (Tableau, Power BI, Looker). This end-to-end lineage enables pre-migration impact analysis. Before moving a schema, you’ll see exactly which downstream dashboards and reports depend on it.
Atlan’s business-user friendly interface lets non-technical stakeholders browse catalogs, understand lineage, and request access without learning Unity Catalog’s technical interface. Setup takes under 30 minutes with Atlan’s no-code Databricks connector.
The Outcome
Permalink to “The Outcome”General Motors achieved significantly faster data discovery using Atlan plus Unity Catalog vs. Unity Catalog alone. Time-to-insight dropped dramatically as teams could trace data lineage end-to-end without manual investigation. The visibility helped GM’s AI Center add substantial value to the bottom line by accelerating analytics projects.
AB InBev tagged 3rd-party data end-to-end with high accuracy from source systems to Power BI, generating significant cost savings through automated governance. Porto migrated and went live quickly, achieving substantial time savings on first integration. See how Atlan complements Unity Catalog for enterprise migrations.
Extend Unity Catalog governance across your entire data stack
Book a DemoFAQ
Permalink to “FAQ”Should governance come before or after Databricks migration?
Permalink to “Should governance come before or after Databricks migration?”Implement governance BEFORE migration begins, not after. Governance frameworks take 2-3 months to establish, and concurrent implementation reduces project timeline by 4-6 months vs. post-migration remediation. Post-migration governance fixes cost 5-7x more due to rework. Pipelines need refactoring, tables need reclassification, and compliance gaps appear during audits. Start governance planning during the discovery phase, before technical migration begins. Teams that delay governance discover security gaps only after production data moves, triggering expensive emergency fixes.
What is Unity Catalog and why does it matter for governance?
Permalink to “What is Unity Catalog and why does it matter for governance?”Unity Catalog is Databricks’ centralized governance layer providing access control, audit logging, and lineage tracking across workspaces. It offers fine-grained permissions down to row and column level, automated lineage capture within Databricks, and a standards-compliant ANSI SQL security model. Think of Unity Catalog as your governance foundation IN Databricks. It replaces workspace-level permissions with account-level unified governance. Key limitation: governance is platform-native (Databricks-only) and doesn’t extend to source systems or BI tools. For cross-system visibility, supplement Unity Catalog with a universal data catalog.
How long does it take to implement data governance for migration?
Permalink to “How long does it take to implement data governance for migration?”Plan for 6-12 months total, broken into phases: governance framework establishment (2-3 months), Unity Catalog architecture design (3-4 weeks), RBAC configuration (3-4 weeks), data classification setup (2-4 weeks), lineage tracking implementation (3-4 weeks), compliance monitoring (2-3 weeks), and team training (4-6 weeks initial). Organizations with executive sponsorship complete implementations faster than teams without C-level champions. Most teams underestimate the governance timeline. Account for 6-12 months in migration planning to avoid schedule pressure that leads to governance shortcuts and post-migration failures.
Can I use Unity Catalog without additional governance tools?
Permalink to “Can I use Unity Catalog without additional governance tools?”Yes, for Databricks-only environments with technical teams. However, enterprises need broader governance: cross-system lineage from source to BI, business-user interfaces for non-technical stakeholders, pre-migration impact analysis, and governance workflows across multiple platforms. Unity Catalog’s limitations include single-workspace lineage scope and a technical-first interface requiring SQL knowledge. When to supplement: multi-platform data stack, non-technical data consumers, regulatory compliance requiring full audit trail from source to consumption, or large-scale migrations needing impact analysis. Unity Catalog handles Databricks. Add a universal catalog for enterprise-wide governance.
What permissions does the governance team need in Unity Catalog?
Permalink to “What permissions does the governance team need in Unity Catalog?”Governance administrators need the metastore admin role for top-level governance setup including creating catalogs, managing account-level permissions, and configuring system tables. Data stewards need catalog owner or schema owner permissions for their domains to approve access and manage classification. Service principals for automation tools need USE CATALOG, BROWSE, and SELECT permissions minimum. Best practice: Grant metastore admin sparingly (only 1-2 people maximum) since it provides full account control. Distribute ownership through the catalog and schema ownership model. This scales governance without centralizing all control.
How do you handle governance for external data sources?
Permalink to “How do you handle governance for external data sources?”Register external sources (S3, ADLS, JDBC databases) in Unity Catalog via external locations and storage credentials. Apply the same governance as managed tables: classification tags, access controls, and lineage tracking. Challenge: Unity Catalog provides governance AT the Databricks boundary, not at source origin. It sees external tables once registered but can’t track upstream transformations that created the data. Solution: Use a cross-system governance platform to track lineage from source system origin through Databricks transformations to downstream consumption. Unity Catalog governs external data once registered, but can’t provide end-to-end visibility alone.
What are the signs your migration governance is failing?
Permalink to “What are the signs your migration governance is failing?”Warning signs include teams repeatedly requesting access for the same data (broken approval workflows), unauthorized data access incidents post-migration, data quality issues not caught pre-migration, compliance audit findings during migration, and lengthy timeline extensions (4-6+ months over budget). Root causes usually trace to lack of governance council decision-making authority (requests pile up unanswered), insufficient automation (manual tagging doesn’t scale to thousands of tables), or delayed governance implementation (reactionary rather than proactive). If access requests pile up unanswered for days or weeks, your governance workflows aren’t working. Fix approval processes before migration proceeds.
Does Atlan replace Unity Catalog?
Permalink to “Does Atlan replace Unity Catalog?”No. Unity Catalog remains your governance authority IN Databricks. Atlan complements Unity Catalog by extending governance BEYOND Databricks, tracking lineage to source systems and BI tools, providing business-user interfaces for non-technical stakeholders, and enabling cross-system policy management. They integrate through bi-directional tag sync that keeps policies aligned automatically. Use case: Unity Catalog enforces technical controls (permissions, audit logs) within Databricks. Atlan provides enterprise visibility and collaboration across your full data stack. Unity Catalog stays. Atlan extends governance to the entire ecosystem including source databases, ETL tools, and downstream analytics.
How do you measure governance success during migration?
Permalink to “How do you measure governance success during migration?”Track four KPIs: data asset coverage (percentage classified and governed), policy enforcement rate (access violations caught and remediated), time-to-access approval (hours from request to grant), and downstream impact visibility (percentage of dependent assets identified before changes). Success benchmarks: high asset coverage, fast access approval time, zero post-migration compliance incidents, and full impact analysis for schema changes. Leading indicator: governance council decisions per week. Active councils make regular decisions on access approvals, policy updates, and issue escalations. If your council isn’t making decisions regularly, governance has stalled.
What’s the biggest governance mistake during migration?
Permalink to “What’s the biggest governance mistake during migration?”The biggest mistake is delaying governance until after technical migration completes. Teams assume they can bolt on governance post-migration, but this causes expensive rework of data pipelines to add controls, compliance incidents during the governance gap, migration timeline extensions beyond budget, and team frustration as governance becomes blocker rather than enabler. Solution: Start governance in the discovery phase alongside technical planning. Implement concurrently with migration. Post-migration governance means expensive rework, compliance risk, and project delays. Start during planning, not after launch.
How do you govern AI/ML models in Databricks?
Permalink to “How do you govern AI/ML models in Databricks?”Unity Catalog governs ML models as registered objects with lineage to training data. Track model versions, training datasets, feature tables, and inference outputs through Unity Catalog’s ML model registry. Governance requirements include classification of training data (PII sensitivity), access controls for model deployment to production, and lineage from source data through model training to predictions. Emerging need: AI governance across platforms for models trained outside Databricks (SageMaker, Vertex AI, Azure ML). Best practice: Register all production models in Unity Catalog even if trained elsewhere to maintain governance consistency. Govern AI models like data. Classify training inputs, control deployment access, and track full lineage.
Can you migrate without completing all 7 governance steps?
Permalink to “Can you migrate without completing all 7 governance steps?”Technically yes, but you’ll face significant risk. Minimum viable governance requires Step 1 (governance framework for decision-making), Step 3 (basic RBAC so not everyone has full access), and Step 6 (compliance monitoring for audit trail). Skipping Steps 2, 4, 5, or 7 increases failure probability. Without Unity Catalog design, permissions become chaotic. Without classification, you can’t identify sensitive data. Without lineage, you can’t assess migration impact. Without training, adoption stalls. Organizations attempting partial governance experience substantially higher post-migration issue rates. If timeline pressure forces phasing, implement Steps 1-3-6 immediately, then add 2-4-5-7 within 90 days of migration completion.
How do you get started with governance implementation?
Permalink to “How do you get started with governance implementation?”Implementing this 7-step governance checklist before your Databricks migration substantially reduces failure rates over 6-12 months. As organizations scale AI and analytics on Databricks, governance becomes a competitive advantage rather than just a compliance requirement. Teams with robust governance ship projects faster because they avoid post-migration rework, compliance incidents, and data quality fires.
Critical success factors: Executive sponsorship accelerates implementation. Federated stewardship scales governance across business domains. Automation over manual processes achieves comprehensive asset coverage. Cross-system visibility enables accurate impact analysis. Start governance planning during the discovery phase. Concurrent implementation saves time and costs less than post-migration remediation.
Ready to build a governance framework for your Databricks migration?
See How Atlan Extends Unity CatalogShare this article



















