Why do you need data governance in 2025? #
- Hidden costs – Weak governance now costs the average firm US $12.9 million a year in fines, re-work, and failed AI projects.
- Regulatory pressure – GDPR fines hit €2.1 billion in 2024 and the EU CSRD will extend strict data-lineage rules to 50 000 companies by 2026 (EDPB 2024).
- AI failure spiral – 70 % of Gen-AI pilots stall for lack of clean, contextual data, burning ≈ US $15 million per project (Gartner 2025).
- Productivity drain – Data teams still lose 30 % of their week to hunting and cleaning datasets instead of building insights (MIT Quest 2025).
Traditional, document-heavy governance can’t keep pace; organisations need automated, lineage-rich controls that scale with today’s data and AI demands. The consequence of inaction is severe.
What are the core aspects of data governance? #
-
Ownership & accountability – One named owner per asset, live RACI matrix in the data catalog, and steward leaderboards that celebrate rapid incident resolution.
-
Common language & standards – Shared business glossary plus null‑rate, freshness and drift thresholds surfaced inline in BI so users see a data trust badge before they click “Run.”
-
Lineage‑driven automation – Column‑level lineage powers impact analysis; policy‑as‑code auto‑tags PII, propagates quality scores downstream and revokes access on breach.
-
Observability & nudges – Trust dashboards update in real‑time; Slack / Teams alerts fire the moment quality or privacy rules break, with a one‑click fix link for stewards.
-
Discovery & collaboration – Google‑like search, in‑context previews and crowd‑sourced wikis turn governance from gate‑keeping into a shared, self‑service knowledge hub.
-
Continuous improvement loop – Quarterly policy reviews use usage analytics and stakeholder feedback to prune dead rules and automate the next 10 % of manual tasks.
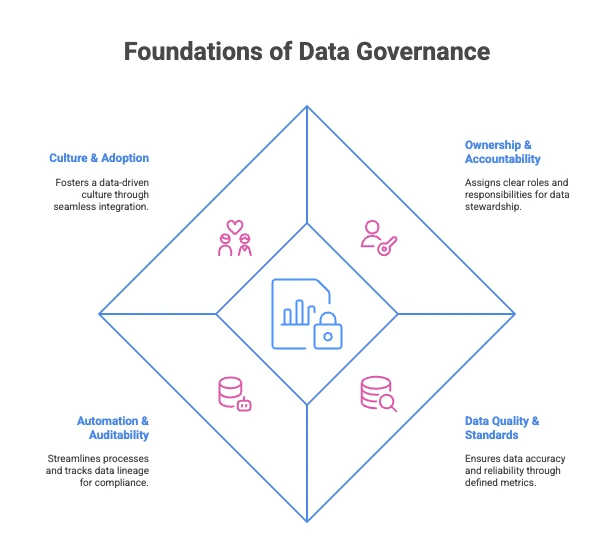
Foundations of Data Governance. Source: Atlan.
What are the goals of data governance? #
These outcomes define success for every modern data governance programme.
- Incident reduction: Minimal incident volume, rapid resolution
- Risk mitigation: Proactive breach, privacy, and operational risk control
- Compliance assurance: Continuous GDPR / CCPA / ISO alignment evidence
- Data trust: Verified accuracy, completeness, transparent lineage
- Analytics speed: Instant data discovery, shortened time-to-insight
- AI readiness: Bias-checked, context-rich training datasets
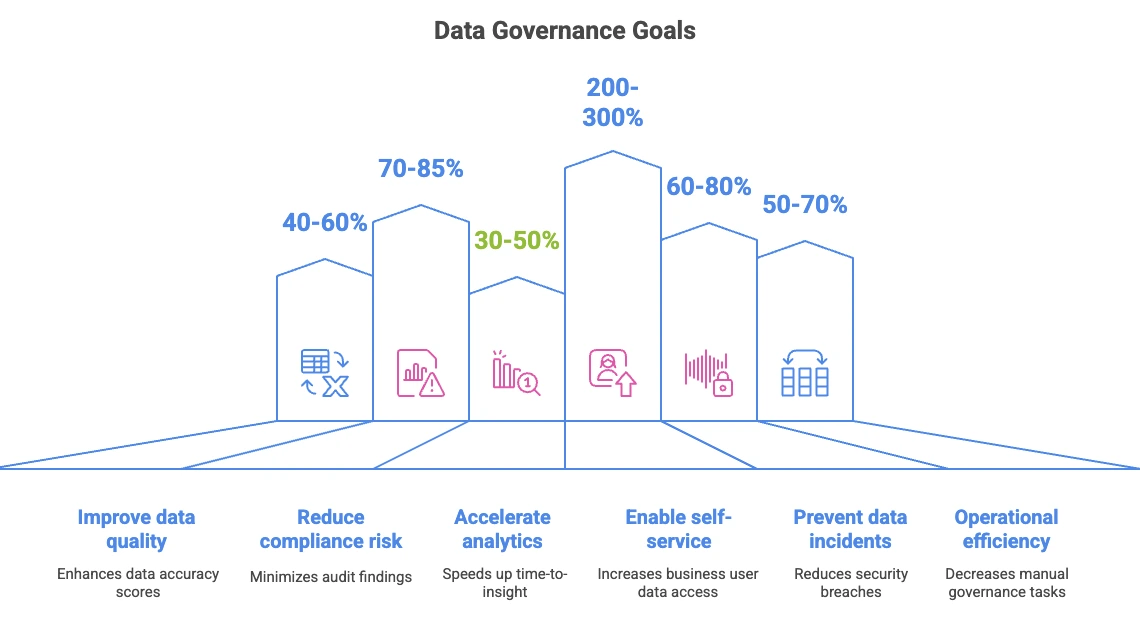
Data Governance Goals. Source: Atlan.
How to implement data governance? #
5-step implementation guide to launch data governance that scales with your data and your team
- Define scope – link 3-5 KPIs to high-risk domains
- Inventory assets – auto-catalog and classify by sensitivity, criticality, usage
- Assign ownership – publish RACI; domain stewards own, central team guides
- Automate controls – policy-as-code for quality, access, retention, alerts
- Monitor & iterate – live cockpit for coverage, incidents, ROI; review quarterly
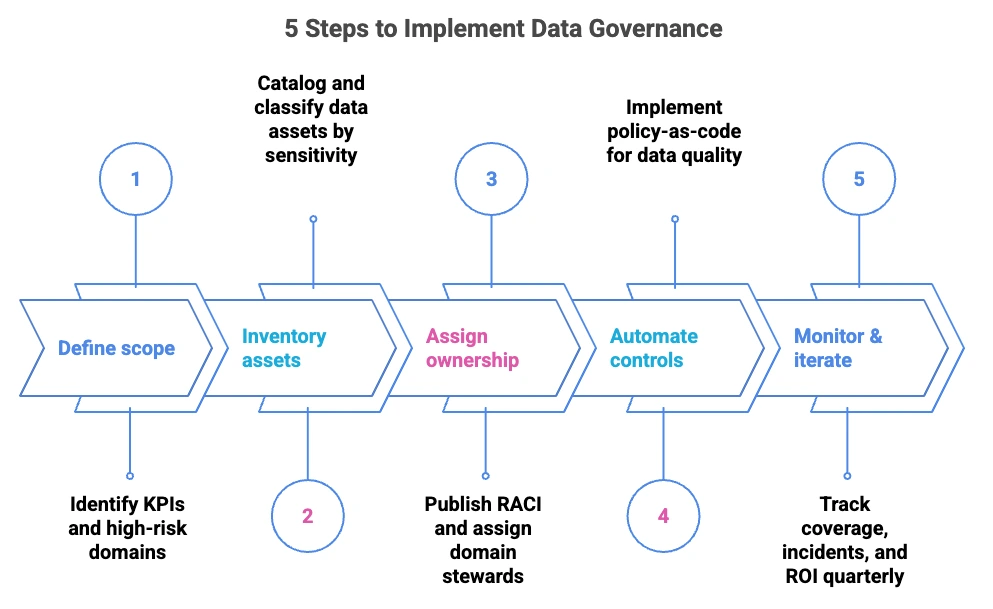
5 Steps to Implement Data Governance. Source: Atlan.
Traditional vs. modern data governance #
The transformation reflects fundamental changes in data architecture complexity. Modern organizations manage thousands of data assets across cloud-native, distributed systems with diverse personas from data engineers to business analysts. Traditional governance approaches designed for centralized data warehouses simply cannot scale to this reality.
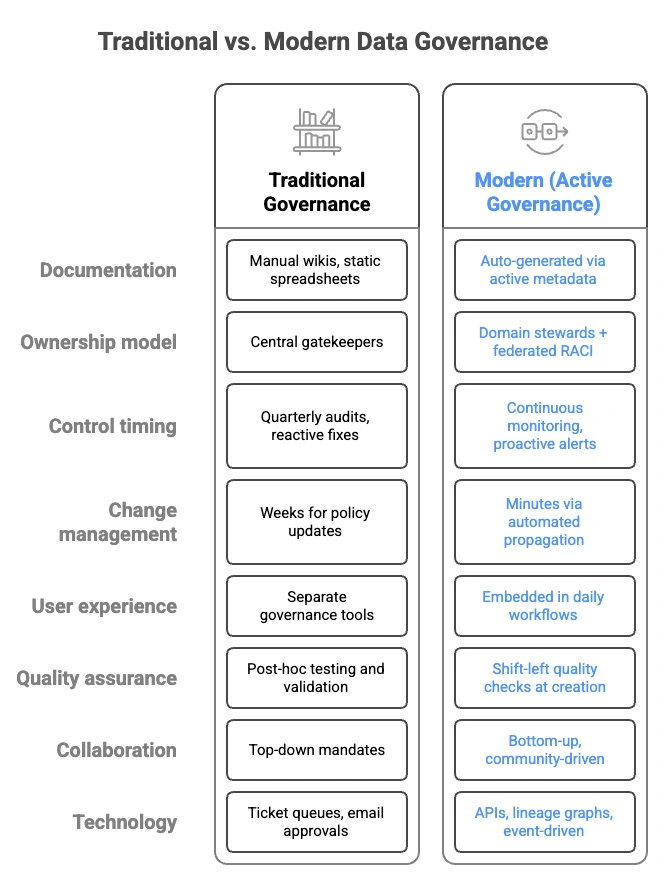
Traditional vs. Modern Data Governance. Source: Atlan.
What are the common data governance challenges? #
-
Challenge: Distinguishing data governance from data management. #
Solution: Data governance establishes the “what and who”—the policies, standards, and accountability frameworks. Data management executes the “how and when”—the daily operations, technical implementations, and process execution. Modern platforms increasingly blur this distinction through automation, embedding governance decisions directly into data management workflows to eliminate friction between policy and practice.
-
Challenge: Determining the timeframe for data governance implementation. #
Solution: Initial framework and pilot domains typically take 3-6 months. Full enterprise maturity can take 18-24 months. Success depends on starting with business-critical use cases and expanding gradually. Organizations that begin with compliance-focused initiatives often achieve faster stakeholder buy-in, while those starting with AI readiness see higher long-term value creation.
-
Challenge: Operating when the organization lacks dedicated data stewards. #
Solution: Modern governance distributes stewardship across domain experts rather than requiring dedicated full-time roles. Automation handles routine tasks like classification and quality monitoring, while business users contribute context through embedded workflows. Leading platforms enable over 80% governance coverage with minimal dedicated resources through intelligent automation and community-driven collaboration.
-
Challenge: Measuring the return on investment (ROI) of governance initiatives. #
Solution: Track direct cost avoidance (e.g., compliance fines, breach remediation), operational efficiency gains (e.g., reduced analyst search time, automated quality checks), and business value creation (e.g., faster time-to-insight, AI initiative success rates). Organizations typically see a 3-5x ROI within 18 months, with average annual savings of $2.4 million through reduced compliance costs and operational efficiency.
-
Challenge: Implementing data governance across hybrid cloud environments. #
Solution: Modern platforms provide unified control through metadata-driven approaches that abstract physical storage locations. Focus on consistent policy enforcement via API-driven integrations rather than tool consolidation. Leading implementations achieve seamless governance across on-premises, multi-cloud, and SaaS environments through active metadata layers that sync policies in real-time.
How does data governance keep AI models reliable? #
AI fundamentally changes governance requirements, demanding new approaches to traditional challenges while introducing novel risk categories that require proactive management.
-
Bias detection – fairness dashboards
AI governance traces lineage down to raw features and runs automated bias checks on every prediction. Dashboards flag demographic skew the moment source data drifts and can auto-trigger a retraining workflow, adding fairness metrics and parity checks to the traditional data-quality rule set. -
Drift alerts – performance guardrails
Live input data is continually compared with the model’s training baseline. When the distribution shifts, the system creates an incident ticket and pings model owners, ensuring that feature stores, model artefacts and deployment configs stay within performance bounds. -
Audit snapshots – explainability compliance
Every model deploy stores a “model card” that captures the exact training dataset, feature list and hyper-parameters. These snapshots give regulators and stakeholders a full lineage trail—from raw data to final prediction—meeting emerging AI audit and explainability rules. -
Input validation – continuous QA
Governance pipelines run schema, freshness and outlier checks on every incoming batch before inference. Catching bad data upstream prevents silent corruption of production models and shifts quality assurance left in the ML lifecycle.
McKinsey’s 2024 research confirms that 70% of top-performing companies face challenges integrating data into AI models, making robust governance frameworks essential for AI initiative success. Organizations with mature data governance report 60% higher AI project success rates and 40% faster time-to-deployment for ML models.
What does successful data governance look like? #

Modernized data stack and launched new products faster while safeguarding sensitive data
“Austin Capital Bank has embraced Atlan as their Active Metadata Management solution to modernize their data stack and enhance data governance. Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics, highlighted, ‘We needed a tool for data governance… an interface built on top of Snowflake to easily see who has access to what.’ With Atlan, they launched new products with unprecedented speed while ensuring sensitive data is protected through advanced masking policies.”

Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics
Austin Capital Bank
🎧 Listen to podcast: Austin Capital Bank From Data Chaos to Data Confidence

53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
“Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, ‘Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.’ With Atlan’s integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate.”

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare’s Data Renaissance with Atlan
Ready to implement data governance? #
Data governance is not just about control. It is how modern teams build trust in their data, decisions, and business.
Whether you are just getting started or scaling fast, the right framework can turn intent into impact.
Let us help you build it
Book a Personalized Demo →FAQs on data governance #
What is the main goal of data governance? #
The core goal is to make data trustworthy and usable for everyone who needs it. Governance assigns clear ownership, sets quality and security rules, and puts automated checks in place. When done well, teams can find, understand, and use data without second-guessing its accuracy.
Who should own data governance in a company? #
A Chief Data Officer (or equivalent senior leader) usually sponsors the program. Day-to-day responsibility sits with domain stewards—people closest to the data—while a small central team sets standards and provides tooling. This federated model balances control with agility.
How do we measure the success of data governance? #
Track a small set of KPIs: data-quality incident MTTR, policy-violation rate, time-to-first-query, and data-consumer satisfaction (NPS). Improvements in these metrics translate directly into faster insights, lower risk, and higher trust. Fewer audit findings and reduced re-work are additional ROI signals.
Does data governance slow down innovation? #
Modern governance is designed to speed things up, not slow them down. Automated policies and self-service access mean engineers spend less time chasing approvals and fixing data issues. The result is quicker experimentation and delivery of data-driven products.
How is data governance different from data management? #
Governance defines the rules—who owns data, what quality thresholds apply, and how access is granted. Data management is the day-to-day execution of those rules: collecting, storing, transforming, and delivering data. Think of governance as the playbook and management as game-time execution.
How does governance impact AI and machine learning? #
AI raises the stakes because model quality depends on the underlying data. Governance now must track lineage to training data, monitor bias and drift, and log every dataset version used in a model. These controls help you meet emerging AI regulations and maintain model trust over time.














