What is a Data Catalog? The Complete Guide
Without a data catalog, teams waste substantial time hunting for data across scattered systems. Research shows data teams spend up to half their time simply trying to find, interpret, and validate data. A data catalog solves this by creating a searchable inventory of your data assets enriched with metadata about ownership, quality, and lineage. It reduces discovery time from hours to minutes, enables governance at scale, and provides the foundation for AI initiatives. Below, we’ll explore how catalogs work, key features, use cases by role, and when your organization needs one.
What exactly is a data catalog?
| What It Is | What It Does | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized inventory of data assets enriched with metadata | Helps teams find, understand, and trust data through search, context, and governance | Automated discovery, metadata management, data lineage, intelligent search, collaboration features |
This definition provides the foundation. Now let’s explore how catalogs work in practice.
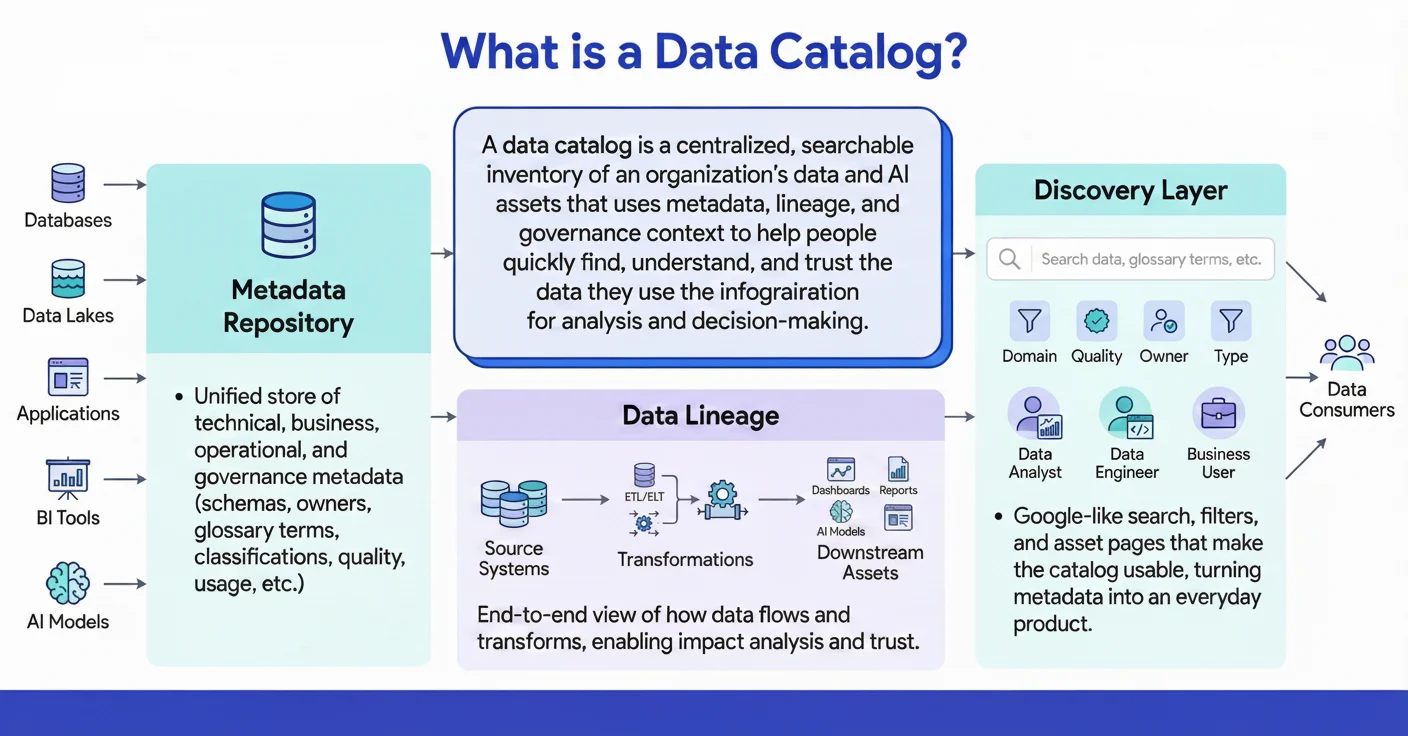
How a data catalog works
Permalink to “How a data catalog works”Summarize and analyze this article with 👉 🔮 Google AI Mode or 💬 ChatGPT or 🔍 Perplexity or 🤖 Claude or 🐦 Grok (X) .
A data catalog automatically discovers your data assets, enriches them with metadata about ownership and quality, then surfaces this context through search and embedded interfaces. Think of it like a library system that not only locates data but tells you what it means, who owns it, and whether you can trust it.
A helpful way to understand a data catalog is to compare it to a library catalog. In a library, you can search for books by title, author, genre, or subject. The catalog tells you where the book is located, whether it’s available, and provides a brief summary so you know what you’re getting before you check it out.
A data catalog works the same way for your organization’s data. Instead of books, it indexes databases, tables, dashboards, and reports. Instead of author or genre, you filter by data owner, domain, sensitivity, or freshness. Instead of a short summary, you see context such as lineage, quality signals, and who uses the data.
The Three-Stage Process:
Modern data catalogs operate through three connected stages that turn scattered technical details into actionable knowledge:
| Stage | What Happens | Automation Level | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingest | Scans databases, warehouses, BI tools for metadata without impacting performance | Fully automated | Complete, continuously updated inventory |
| Enrich | Adds business context, quality scores, automated classification, and human curation | Automated + human stewardship | Searchable, meaningful metadata |
| Surface | Delivers context via search and embeds directly in tools like Slack, Tableau, SQL editors | Automated | Fast, trusted discovery where work happens |
This three-stage model ensures your catalog stays current as data landscapes change. From there, teams can discover data in seconds rather than hours.
Why do you need a data catalog?
Permalink to “Why do you need a data catalog?”Organizations need catalogs to solve four core problems: teams waste hours finding data, scattered assets become data swamps, governance demands grow, and AI initiatives fail from poor data quality. Catalogs centralize knowledge, prevent duplication, enable compliance, and provide trusted training data for machine learning.
Data catalogs address challenges that intensify as data volumes and complexity grow. Here’s why organizations invest in catalogs:
1. Reduce wasted time and break down silos
Permalink to “1. Reduce wasted time and break down silos”Data teams spend substantial time simply trying to find, interpret, and validate data before they can analyze it. A catalog centralizes knowledge so teams can discover the right data faster, understand the data they discovered, and avoid recreating existing datasets. This shift means analysts spend more time analyzing and less time hunting.
2. Prevent the data swamp problem
Permalink to “2. Prevent the data swamp problem”Organizations with strong metadata practices achieve significantly faster time-to-insight because teams can locate trusted data and align on consistent definitions. A catalog helps by consolidating scattered data across warehouses, lakes, and SaaS tools, reducing duplication and conflicting metrics, and making data quality issues easier to detect.
3. Meet growing governance and compliance demands
Permalink to “3. Meet growing governance and compliance demands”Weak data governance and unclear ownership increase compliance risk and make it harder to satisfy regulators and internal risk teams. A data catalog gives governance teams the visibility needed to automatically identify and classify sensitive data, trace lineage for GDPR and CCPA reporting, and see who accessed what data and when.
4. Prepare for AI and machine learning initiatives
Permalink to “4. Prepare for AI and machine learning initiatives”Most AI projects struggle without strong data quality and governance. A data catalog strengthens AI readiness by enabling teams to find high-quality, well-documented training datasets, understand lineage and transformations behind model features, and rely on quality checks and trust signals during model development.
Modern catalogs also increasingly bring automated context, workflows, and collaboration into the tools where data work already happens, making it far easier for teams to find, understand, and use data confidently.
Quantify productivity gains and governance efficiency for your organization
Calculate Data Catalog ROI →Passive vs Active data catalogs: The evolution
Permalink to “Passive vs Active data catalogs: The evolution”Passive catalogs are static inventories requiring manual updates that quickly become outdated. Active catalogs continuously monitor systems, automatically enriching metadata and surfacing context where people work. The shift from passive to active is essential for scaling data operations without adding manual overhead.
The market is shifting from passive documentation tools to active metadata platforms that automate context, governance, and decision-making. This evolution reflects lessons learned from failed catalog implementations.
Passive catalogs are static inventories that rely on manual updates. They quickly become outdated and erode trust as data changes faster than teams can document it. Teams invest months cataloging assets, only to watch accuracy degrade within weeks.
Active catalogs invert this model by continuously monitoring systems, capturing changes in real-time, and surfacing context where people work. Automation drives enrichment, quality signals, lineage updates, and governance enforcement, keeping metadata accurate and usable without manual effort.
| Aspect | Passive Catalog | Active Catalog |
|---|---|---|
| Updates | Manual, quickly outdated within months | Automated, real-time as data changes |
| Metadata | Static documentation requiring steward effort | Continuously enriched through automation |
| Discovery | Search only, requires knowing what to look for | Recommendations + proactive surfacing based on usage |
| Governance | Manual policy enforcement and tagging | Automated classification with real-time controls |
| Adoption | Low (requires separate login and context switching) | High (embedded in Slack, BI tools, SQL editors) |
Industry analysts highlight this shift as foundational to modern data practices. Modern catalogs increasingly use intelligence to anticipate user needs, recommend trusted datasets, and surface context before teams even search for it.
In practice, active catalogs detect downstream impacts instantly, notify stakeholders automatically, and recommend trusted datasets based on usage patterns. These behaviors define the next generation of data cataloging.
What are the key features of a modern data catalog?
Permalink to “What are the key features of a modern data catalog?”Modern catalogs combine automated discovery across your data stack, intelligent search with natural language, and end-to-end lineage showing data flow. They add governance controls for security and compliance, plus embedded collaboration that surfaces context in your daily tools. These capabilities transform catalogs from static inventories into active platforms.
Modern data catalogs combine multiple capabilities that transform them from simple inventories into comprehensive data intelligence platforms. Here’s what distinguishes today’s leading catalogs:
| Capability | What It Does | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Discovery | Scans databases, warehouses, BI tools for metadata without manual cataloging | Keeps inventory current as data landscape changes daily |
| Intelligent Search | Natural language search with filters by freshness, owner, sensitivity, domain | Non-technical users find data in seconds instead of hours |
| Data Lineage | End-to-end visibility showing data flow from source to dashboard | Enables impact analysis before changes and accelerates troubleshooting |
| Governance & Security | Automated classification of sensitive data with policy enforcement and access controls | Scales compliance without adding manual overhead to teams |
| Embedded Collaboration | Context surfaces in Slack, SQL editors, BI tools where work already happens | Drives adoption by eliminating tool switching and separate logins |
These capabilities work together to reduce discovery time, improve data trust, and enable governance at scale. The result is faster analytics, reduced risk, and better decisions.
Discovery and search
Modern catalogs automatically index all data assets across databases, files, streams, models, and BI tools. They support both technical and business-friendly search, including natural language queries. Machine learning interprets intent and personalizes results based on usage patterns. Faceted filters let you narrow by freshness, sensitivity, popularity, or domain.
Lineage and impact analysis
Catalogs offer real-time, end-to-end lineage across pipelines, dashboards, and models. Column-level visibility provides precise dependency and transformation insights. This identifies downstream impacts of upstream changes to prevent incidents and accelerates troubleshooting and migrations through complete dependency maps.
Governance, security, and quality
Catalogs automatically detect and classify sensitive data for consistent policy enforcement. They support certification workflows for trusted, high-quality datasets. Quality metrics are monitored continuously, with alerts sent when data degrades. Real-time policy checks can block downstream use of low-quality data.
Collaboration and productivity
Catalogs centralize shared knowledge through user-added context and documentation. They enable questions, discussions, and expertise sharing around data assets. Collaboration embeds in tools like Slack, Jira, and GitHub to reduce context switching. Personalized recommendations and ratings guide users to reliable data.
What are the top data catalog use cases in 2026?
Permalink to “What are the top data catalog use cases in 2026?”Catalogs deliver value across roles and scenarios. Analysts discover trusted datasets faster. Engineers trace lineage for debugging. Governance teams enforce compliance. AI teams find quality training data. Real implementations show substantial time savings in discovery and significantly faster incident resolution across organizations.
Data catalogs deliver value across diverse roles and scenarios, from operational efficiency to strategic initiatives.
How do data analysts use data catalogs?
Permalink to “How do data analysts use data catalogs?”Analysts use catalogs to find trusted customer, product, and operational data in seconds instead of hours. Self-service discovery with quality scores and lineage reduces dependence on engineers and accelerates dashboard creation. This means more time analyzing and less time hunting for the right tables.
Use cases:
- Self-service discovery – Fast search helps analysts find trusted datasets for dashboards without engineering support
- Faster customer and campaign analytics – Quality scores and lineage guide analysts to the right customer and order tables immediately
Example: A leading capital markets firm uses its data catalog as a primary window into its modern data platform, cutting discovery time substantially and boosting confidence in trading and market data analytics.
How do data engineers use data catalogs?
Permalink to “How do data engineers use data catalogs?”Engineers rely on lineage to trace impacts before changes, debug pipeline failures, and onboard new team members. Automated schema capture eliminates manual documentation, cutting implementation time substantially. When something breaks, lineage shows exactly where to look.
Use cases:
- Impact analysis and debugging – Lineage reduces breakages and shortens incident resolution significantly
- Automated onboarding – Automated schema capture and lineage shrink implementation cycles
Example: A global software company used its data catalog as the backbone of a data mesh, enabling dozens of domain teams to publish data products and powering more than forty self-service use cases within two years.
For Governance teams
Permalink to “For Governance teams”Governance teams use catalogs to automatically classify sensitive data, enforce access policies, and maintain consistent definitions. Automated tagging and glossaries reduce manual effort while ensuring compliance. This means governance scales without adding headcount.
Use cases:
- PII governance and compliance – Automated tagging and controls simplify GDPR and similar requirements substantially
- Definitions and policy consistency – Glossaries reduce metric confusion across teams
Example: A global industrial manufacturer built an organization-wide business glossary, creating a single place for definitions, ownership, and rules, and sharply reducing the time teams spent resolving terminology questions and inconsistent metrics.
How do AI teams use data catalogs?
Permalink to “How do AI teams use data catalogs?”AI teams discover high-quality training datasets, track feature lineage for model explainability, and extend governance across ML pipelines. Catalogs provide the data foundation AI initiatives need to succeed without the risks of unmanaged models.
Use cases:
- AI-ready training data – Teams quickly locate high-quality, documented datasets for model training
- Unified governance across ML pipelines – Catalogs extend visibility and control beyond platform-native tools
Example: A leading automotive AI team paired a platform-native catalog with an enterprise data catalog to gain visibility from cloud to on-premises, centralizing governance across ML workflows and avoiding the risks of unmanaged AI.
Across roles, data catalogs consistently reduce time to insight, lower operational risk, and improve trust in data.
Types of data catalogs and tools
Permalink to “Types of data catalogs and tools”The catalog market includes cloud platform catalogs from AWS, Azure, and Google, enterprise platforms like Atlan connecting diverse sources, open source projects like DataHub and Apache Atlas, and AI-native catalogs using machine learning for automation. Choose based on your infrastructure complexity, governance maturity, and need for multi-cloud support.
The data catalog market includes several categories serving different needs and deployment preferences:
Cloud platform catalogs are built-in options from major cloud providers that offer tight ecosystem integration but can be limiting for multi-cloud or hybrid setups. Examples include AWS Glue Data Catalog, Google Cloud Data Catalog, and Azure Purview.
Enterprise catalog platforms are enterprise-grade platforms that connect to diverse data sources, support advanced governance workflows, and scale across complex environments. Examples include Atlan, Alation, and others designed for organizations needing cross-platform visibility.
Open source catalogs are projects like Apache Atlas, DataHub, and Amundsen that provide flexible, license-free options for engineering-heavy teams. They require more hands-on maintenance but offer customization freedom.
AI-native catalogs are newer catalogs that use machine learning for natural language search, automated classification, recommendations, and anomaly detection. They reduce manual effort as data complexity grows by using intent recognition, behavioral signals, and automated insights to guide users to the highest quality data.
Data catalog vs related concepts
Permalink to “Data catalog vs related concepts”Data catalogs often get confused with adjacent tools. A data catalog provides enterprise-wide discovery and governance. A data dictionary documents single database schemas. A business glossary defines business terms. Metadata management is the underlying infrastructure. These tools complement each other rather than compete.
Understanding how data catalogs differ from adjacent tools helps organizations build complementary capabilities rather than redundant systems.
The four-way comparison
Permalink to “The four-way comparison”| Aspect | Data Catalog | Data Dictionary | Business Glossary | Metadata Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Searchable inventory for discovery & governance | Technical schema documentation | Business term definitions | Metadata infrastructure |
| Scope | Enterprise-wide across all tools and platforms | Single database or application | Cross-functional business terminology | Technical platforms and systems |
| Audience | All data users from analysts to engineers | DBAs, developers, technical teams | Business users, stewards, analysts | Architects, platform teams |
| Primary Output | Search results, lineage views, asset profiles | Schema documentation with field specs | Term definitions, synonyms, ownership | Metadata pipelines and synchronization |
Data catalog vs Data dictionary
Permalink to “Data catalog vs Data dictionary”Data dictionaries document the structure of a single dataset with field names, data types, and formats. Data catalogs span the entire data landscape, combining technical details with business context, usage patterns, and relationships. Modern catalogs often include dictionary-level metadata but go far beyond it to connect data across systems.
Data catalog vs Business glossary
Permalink to “Data catalog vs Business glossary”A business glossary defines shared terms, KPIs, and metric rules that create common language. A data catalog connects these definitions to the actual tables, fields, and dashboards that implement them. The glossary provides meaning while the catalog shows where that meaning lives in data.
Data catalog vs Metadata management
Permalink to “Data catalog vs Metadata management”Metadata management collects and stores metadata across systems at the infrastructure level. A data catalog sits on top of this foundation, turning metadata into an accessible product with search, context, collaboration, and governance workflows that serve all users.
How to choose the right data catalog
Permalink to “How to choose the right data catalog”Choose a catalog by matching it to your data landscape—single-cloud versus multi-cloud—governance maturity, user experience needs, automation depth, and total cost including implementation. Prioritize catalogs that embed context in your existing tools. Adoption depends on surfacing metadata where people work rather than requiring separate logins.
Selecting a data catalog requires evaluating multiple factors aligned to your organization’s specific needs and maturity.
1. Match the catalog to your data landscape
Single-cloud stacks may suit platform catalogs, while multi-cloud or hybrid environments usually require enterprise-level connectivity and scale. Consider whether your data lives primarily in one cloud provider or spans multiple platforms.
2. Align with governance maturity
New programs need simplicity and quick value. Mature teams need automated classification, policy enforcement, and audit-ready lineage. Choose a catalog that fits today and grows with you as governance matures.
3. Prioritize user experience and adoption
A catalog only works if people use it. Ensure interfaces fit analysts, engineers, and business users. Confirm it integrates with daily tools like Slack, BI platforms, and SQL editors. Platforms that bring context into the tools teams already use tend to see substantially higher adoption than separate catalog applications.
4. Evaluate automation and AI depth
Manual upkeep fails at scale. Prioritize automated discovery, classification, enrichment, and recommendations. Continuous active metadata updates deliver the most value as data landscapes grow.
5. Consider total cost and implementation
Account for licensing, data volume, connectors, deployment, training, and support. Validate vendor timelines with similar organizations to set realistic expectations. Implementation can range from weeks for simple deployments to months for complex environments.
Organizations succeed when they start with clear pain points—discovery problems, governance gaps, or AI readiness—rather than treating catalogs as infrastructure projects.
Check your data catalog maturity instantly
Take Assessment →When a data catalog isn’t the right solution
Permalink to “When a data catalog isn’t the right solution”Not every organization needs a catalog. Teams with fewer than 50 assets, no governance mandate, or single-platform environments may not justify the investment. Data quality tools, ETL platforms, or simple documentation may better solve your specific problem. Start with clear pain points before investing.
Not every organization needs a data catalog. The decision depends on your data landscape size, governance maturity, and the specific problems you need to solve.
Data catalogs deliver value when you manage dozens of assets across multiple platforms, when teams struggle to find trusted data, or when compliance demands visibility. Simpler alternatives work better in other scenarios.
Scenario | Why Catalog May Not Fit | Better Alternative |
|---|---|---|
Small team with fewer than 50 data assets | Overhead exceeds value; tribal knowledge still works | Shared documentation, wiki, or spreadsheet inventory |
No governance mandate or executive sponsorship | Catalogs need organizational commitment to maintain | Build the governance case first; catalog comes after |
Primary need is data quality or observability only | Catalog solves discovery; quality tools solve data health | Purpose-built data quality or observability platform |
Looking for an ETL or data integration solution | Catalogs document data; they don't move or transform it | Data integration or orchestration tool |
Single-platform environment (all in Snowflake/Databricks) | Native catalog features may suffice for basic needs | Evaluate native capabilities first; catalog for multi-platform growth |
When lightweight alternatives work:
Teams with straightforward environments and strong informal coordination can start with simpler tools. Single-platform shops where native features handle basic needs may not need enterprise catalogs immediately. Organizations focused exclusively on data quality issues should prioritize quality tools first.
When catalogs become essential:
Teams ask “where is our customer data?” or “which dashboard should I trust?” frequently. Multi-cloud or hybrid environments create discovery challenges that simple documentation can’t solve. Regulatory requirements demand lineage and access tracking that spreadsheets can’t provide. Distributed teams need shared understanding of data assets that informal coordination can’t maintain.
Start with your pain points. Discovery, trust, or governance challenges signal catalog readiness. Simpler needs call for foundational practices first.
How do you implement a data catalog successfully?
Permalink to “How do you implement a data catalog successfully?”Successful implementations start with high-value use cases, establish ownership early, automate progressively, and measure adoption continuously. Common failures stem from manual approaches that don’t scale, lack of executive sponsorship, and trying to catalog everything at once. Focus on quick wins first.
Successful catalog implementations follow structured approaches while avoiding predictable traps.
Implementation steps
Permalink to “Implementation steps”| Step | Action | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Prioritize | Identify 3-5 high-value data sources first | Clear use case alignment, stakeholder agreement |
| 2. Establish Ownership | Assign stewards and admins before launch | Roles documented, responsibilities clear |
| 3. Automate Discovery | Connect priority systems, validate metadata capture | >90% automated coverage, minimal manual effort |
| 4. Set Governance | Define certification criteria and quality rules | Policies documented, workflows established |
| 5. Launch with Training | Train users on search, showcase real use cases | >50% team engagement within first month |
| 6. Measure & Iterate | Track usage metrics, time saved, adoption rates | Monthly metrics reviewed, adjustments made |
Start small with high-value assets rather than attempting comprehensive coverage immediately. Expand gradually as you prove value and refine processes.
Common pitfalls
Permalink to “Common pitfalls”| Pitfall | Why It Fails | How to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Manual documentation | Can’t scale beyond ~100 assets, accuracy degrades quickly | Choose platforms with strong automation from day one |
| No ownership model | Catalog becomes outdated without steward accountability | Assign stewards before launch with clear responsibilities |
| Big bang rollout | Teams overwhelmed, adoption stalls from complexity | Start with 1-2 high-impact use cases, expand iteratively |
| Governance misalignment | Policies don’t match actual workflows, creating friction | Co-design governance with data teams, not for them |
Modern platforms reduce these risks through built-in workflows, automation, and strong adoption patterns learned from hundreds of implementations.
Why data catalogs fail (and how to avoid it)
Permalink to “Why data catalogs fail (and how to avoid it)”Most catalogs fail because manual tagging can’t scale. Organizations launch with enthusiasm, assign stewards to document assets manually, then watch accuracy degrade as data changes faster than teams can update metadata. Automation, clear ownership, embedded workflows, continuous improvement, and executive sponsorship prevent these failures.
Most catalogs fail because manual tagging cannot scale. If you rely on humans to tag columns, your catalog will become outdated within months.
Organizations launch with enthusiasm, assign stewards to document assets, and watch accuracy degrade as data changes faster than teams can update metadata. Research shows catalog implementations struggle with metadata decay within the first year when manual processes dominate.
1. Manual metadata decay
Permalink to “1. Manual metadata decay”The problem: Data stewards cannot manually tag thousands of columns across dozens of systems while keeping up with continuous changes. Comprehensive inventories become outdated and untrusted within months.
How to avoid it: Prioritize automated discovery, classification, and enrichment from day one. Modern active metadata platforms continuously monitor systems and update catalogs as schemas, lineage, and usage patterns change. Automation handles scale; humans focus on business context and certification.
2. No clear ownership model
Permalink to “2. No clear ownership model”The problem: Catalogs without stewardship programs become ghost towns. When no one owns data quality, documentation, or user support, the catalog degrades into an unreliable reference teams stop consulting.
How to avoid it: Establish a governance operating model before launching. Assign data owners and stewards with specific responsibilities for domains or assets. Make stewardship part of job expectations, not volunteer work. Modern platforms include workflows that make stewardship tasks manageable rather than overwhelming.
3. Disconnected from workflows
Permalink to “3. Disconnected from workflows”The problem: Catalogs that exist as standalone destinations see adoption rates below 20%. Analysts, engineers, and scientists won’t context-switch to a separate portal when they can work in familiar BI tools, SQL editors, or notebooks.
How to avoid it: Select platforms that embed metadata directly into tools like Tableau, Looker, dbt, and Slack. Context should surface where work happens. Integrations that bring lineage and quality signals into familiar interfaces drive 3-5x higher adoption than separate catalog applications.
4. Treating it as a one-time project
Permalink to “4. Treating it as a one-time project”The problem: Organizations that “launch and leave” see rapid value decay. Teams that treat implementation as a project with a finish line rather than a continuous capability fail to realize sustained value.
How to avoid it: Plan for catalog operations from the start. Budget for ongoing training, stewardship time, connector updates, and process refinement. Measure adoption and value quarterly, adjusting based on usage patterns. Continuous improvement is essential.
5. Lack of executive sponsorship
Permalink to “5. Lack of executive sponsorship”The problem: Without CDO or VP of Data support, governance initiatives stall. When leadership doesn’t prioritize data governance, teams lack resources, authority, and incentives to maintain the catalog effectively.
How to avoid it: Secure executive sponsorship before launching. Build a business case showing time saved, risk reduced, and decisions improved. Connect catalog success to strategic priorities like AI readiness, regulatory compliance, or faster analytics. Executive champions ensure sustained attention and resources.
The pattern for success: Organizations that succeed treat catalogs as living platforms supported by automation, clear ownership, embedded workflows, and executive commitment. Modern active metadata approaches address the scale problems that defeated earlier catalogs. When automation handles heavy lifting and governance embeds in daily work, catalogs deliver lasting value.
Where a data catalog tool like Atlan fits in
Permalink to “Where a data catalog tool like Atlan fits in”Organizations struggle with catalogs that require manual maintenance, create separate login friction, and can’t keep pace with modern data platform changes. Traditional catalogs become outdated within months, fail to drive adoption, and add governance overhead instead of reducing it. Teams need catalogs that continuously monitor systems, automatically enrich metadata, and surface context directly in the tools where work happens. The shift toward active metadata platforms addresses these scale problems that caused earlier catalog implementations to fail.
Atlan operates as an active metadata platform that continuously monitors your data systems, automatically enriching metadata without manual effort. Context embeds directly in tools teams already use—Tableau, Looker, Slack, SQL editors—eliminating separate logins and reducing friction. Machine learning classifies sensitive data, suggests ownership based on usage patterns, and recommends trusted datasets to users. Governance policies apply automatically when new data appears, ensuring consistent controls at scale. Column-level lineage tracks dependencies across your entire stack, from raw sources through transformations to dashboards and models. This automation-first approach means catalogs stay current as data landscapes evolve.
Teams using Atlan reduce central engineering workload by over 50%, improve data user satisfaction by 20%, and cut discovery time substantially. Nasdaq uses Atlan as their “window into their modern data stack.” Kiwi.com consolidated thousands of assets into 58 governed data products. The results consistently show automation drives adoption while reducing operational burden on data teams.
Real customers, real stories: Modern data catalog in action
Permalink to “Real customers, real stories: Modern data catalog in action”
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
“Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, ‘Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.’ With Atlan’s integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate.”

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare’s Data Renaissance with Atlan
FAQs about data catalogs
Permalink to “FAQs about data catalogs”1. What is a data catalog?
Permalink to “1. What is a data catalog?”A data catalog is a centralized inventory of an organization’s data assets that uses metadata to help users discover, understand, and manage data. It functions like a library system, organizing information about databases, tables, reports, and other data resources into a searchable format. Modern catalogs combine automated discovery, rich metadata, data lineage, and collaborative features to make data findable and trustworthy.
2. How does a data catalog work?
Permalink to “2. How does a data catalog work?”Data catalogs work through automated discovery that scans data sources, metadata enrichment that adds business context and classifications, and intelligent surfacing that makes information accessible through search and embedded interfaces. Connectors continuously monitor databases, warehouses, and BI tools to capture technical specifications, usage patterns, and relationships. Machine learning classifies sensitive data and suggests relevant tags while users contribute descriptions, ratings, and knowledge.
3. Why is a data catalog important?
Permalink to “3. Why is a data catalog important?”Data catalogs are important because they reduce the time teams spend finding and understanding data, enable governance at scale, support regulatory compliance, and provide the foundation for AI initiatives. Without catalogs, organizations struggle with data silos, duplicated efforts, unclear data quality, and difficulty enforcing access controls. Research shows data teams spend 30% of their time on discovery activities that catalogs can accelerate dramatically.
4. Who uses a data catalog?
Permalink to “4. Who uses a data catalog?”Data analysts use catalogs to discover datasets for analysis projects. Data engineers rely on lineage for impact analysis and troubleshooting. Governance teams enforce policies and demonstrate compliance. Business users search for trusted metrics and reports. Data scientists find features for machine learning models. Essentially, anyone who works with data benefits from catalog capabilities tailored to their role.
5. What metadata does a data catalog manage?
Permalink to “5. What metadata does a data catalog manage?”Data catalogs manage technical metadata including schemas, data types, and table structures; business metadata like descriptions, ownership, and glossary terms; operational metadata such as usage statistics and access patterns; and governance metadata including classifications, quality scores, and compliance tags. Comprehensive catalogs unify all these metadata types into a single, searchable interface.
6. What is the difference between a data dictionary and a data catalog?
Permalink to “6. What is the difference between a data dictionary and a data catalog?”A data dictionary defines the structure of individual datasets with field names, data types, and formats, focusing on a single database or application. A data catalog provides enterprise-wide visibility across all data assets, combining technical specifications with business context, lineage, and usage patterns. Dictionaries look inward at one system while catalogs look outward across the entire data landscape.
7. What is the difference between a data catalog and a data lake
Permalink to “7. What is the difference between a data catalog and a data lake”A data lake stores large volumes of raw data in its native format. A data catalog does not store data. Instead, it provides searchable metadata and context about the data stored in lakes, warehouses, and other systems. The two are complementary because the catalog helps users understand and trust the data inside the lake.
8. Is a data catalog available as open source
Permalink to “8. Is a data catalog available as open source”Yes. Several open source projects provide catalog and metadata capabilities. These tools offer flexibility and customization but often require strong engineering resources to deploy, integrate, and maintain at scale.
9. What should be included in a data catalog
Permalink to “9. What should be included in a data catalog”A complete catalog should include technical metadata such as schemas, data types, and lineage. It should also include business metadata like definitions, owners, glossary terms, quality signals, and usage patterns. The goal is to give users a full understanding of what the data is, how it is used, and whether it can be trusted.
10. How do you build a data catalog
Permalink to “10. How do you build a data catalog”Most organizations build a catalog by connecting it to databases, warehouses, BI tools, and pipelines through automated connectors. Automated discovery collects metadata from these systems continuously and stewards enrich it with definitions, ownership, and business context. Over time, usage patterns, quality checks, and governance rules complete the catalog and keep it reliable as data landscapes evolve.
11. When does an organization need a data catalog?
Permalink to “11. When does an organization need a data catalog?”You need a catalog when teams frequently ask where customer data lives or which dashboard to trust. Multi-cloud or hybrid environments create discovery challenges that simple documentation cannot solve. Regulatory requirements demanding lineage and access tracking also signal catalog readiness. Organizations with fewer than 50 assets or strong informal coordination may not justify the investment yet.
12. How long does it take to implement a data catalog?
Permalink to “12. How long does it take to implement a data catalog?”Implementation time depends on data landscape complexity and governance maturity. Small deployments take two to three months while enterprise rollouts span six to twelve months. Modern platforms with automated discovery and pre-built connectors accelerate timelines significantly. Starting with high-value use cases and expanding iteratively typically delivers fastest time to value rather than comprehensive big-bang deployments.
What’s next for data catalogs in 2026?
Permalink to “What’s next for data catalogs in 2026?”Data catalogs have evolved from passive documentation tools into active metadata platforms that continuously automate discovery, governance, and collaboration. The future accelerates this shift as AI-native features become standard, embedded experiences replace separate logins, and catalogs extend beyond traditional data to govern AI models and GenAI applications.
The organizations succeeding with catalogs share common patterns. They start with clear pain points rather than treating catalogs as infrastructure projects. They prioritize automation over manual effort, knowing that manual tagging cannot scale. They embed governance in daily workflows rather than creating separate compliance processes. They treat catalogs as living platforms requiring continuous improvement rather than one-time implementations.
If your teams ask “where is our customer data?” or “which dashboard should I trust?” you’re ready for a catalog. Start by cataloging high-value assets that solve immediate problems. Establish ownership and stewardship before launch. Expand as adoption grows and value becomes clear. The investment pays back quickly—teams save hours daily, governance becomes scalable without adding headcount, and AI initiatives launch on trusted, well-documented data rather than hoping for the best.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
Data catalog: Related reads
Permalink to “Data catalog: Related reads”- What Is a Data Lake and Why It Needs a Data Catalog
- Top data catalog tools — Compare the top data catalog tools of 2026
- Data Lineage Tracking | Why It Matters, How It Works & Best Practices for 2026
- Data Catalog Examples | Use Cases Across Industries and Implementation Guide
- Data Lineage Solutions| Capabilities and 2026 Guidance
- Features of Machine Learning Data Catalog - 2026 Guide
- 7 Top AI Governance Tools Compared | A Complete Roundup for 2026
- Best Data Governance Tools in 2026 — A Complete Roundup of Key Capabilities
- Can Metadata Catalogs Enhance Data Discovery & Access?
- 5 Best Data Governance Platforms in 2026 | A Complete Evaluation Guide to Help You Choose
- Modern Data Catalogs: What They Are, How They’ve Changed
- Data Catalog vs. Data Dictionary: Benefits & Business Value
- Data Catalog for Data Fabric: 5 Essential Features to Consider
- Business Glossary vs. Data Catalog: Definition, Differences & Examples
- 5 Data Catalog Benefits: Data Governance, Quality & More
- How Enterprise Data Catalogs Drive Business Value
- 11 Best Data Governance Software in 2026 | A Complete Roundup of Key Strengths & Limitations
- The Modern Data Catalog Platform: More Value and a Better UX
- Data Catalog Evaluation Checklist to Boost Business Value
- AI Data Catalog: It’s Everything You Hoped For & More
- Semantic Layers: The Complete Guide for 2026



















