DAMA DMBOK Framework: An Ultimate Guide for 2026
If you’re leading data without a shared framework, you have probably felt the friction. Teams define the same metric differently. Ownership gets blurry, and governance turns into firefighting. This isn’t an isolated experience.
Recent industry research shows 71% of organizations now run formal data governance programs, yet more than half still report governance as a top data challenge. The DAMA DMBOK framework provides a practical structure to address such challenges. It organizes data management into eleven connected knowledge areas with governance at the center. It ensures everyone works from the same playbook.
In this guide, you’ll see what DMBOK actually means, how it works, and how to use it to build data practices that scale with your organization.
Quick facts about the DAMA DMBOK framework
Permalink to “Quick facts about the DAMA DMBOK framework”| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| What it is | Vendor-neutral data management framework with 11 knowledge areas |
| Full name | Data Management Association — Data Management Body of Knowledge (DAMA DMBOK) |
| Publisher | DAMA International |
| Current version | DMBOK 2.0 (DMBOK 3.0 in development, expected 2025) |
| Core structure | Governance at the center, supported by 10 disciplines |
| Best for | Enterprise data governance and regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA) |
| Implementation timeline | 3–6 months for foundation; 18–36 months for enterprise rollout |
Summarize and analyze this article with 👉 🔮 Google AI Mode or 💬 ChatGPT or 🔍 Perplexity or 🤖 Claude or 🐦 Grok (X) .
What does the DAMA DMBOK framework mean?
Permalink to “What does the DAMA DMBOK framework mean?”In practice, the DAMA DMBOK framework gives your organization a shared map for how data should be governed and managed. Instead of ad‑hoc decisions and implied ownership, it spells out which disciplines need to exist, who is accountable, and how those pieces fit together so data work scales without losing alignment.
While leading data governance or architecture, you have probably seen what happens when teams build practices on the fly. Ownership feels implied instead of explicit, and processes evolve unevenly. Nothing collapses overnight, but alignment slowly slips. The DAMA DMBOK framework exists to prevent that drift and delivers a common model for how data should connect.
Instead of prescribing tools, DAMA DMBOK defines what good data management looks like. It defines roles, responsibilities, and activities that scale across environments.
DAMA DMBOK is also the foundation of the Certified Data Management Professional (CDMP) credential. As of 2025, nearly 13,000 professionals worldwide hold CDMP certification, reflecting how widely DMBOK has become a professional reference point for modern data leadership.
What DMBOK is Not
Permalink to “What DMBOK is Not”DAMA DMBOK is often misunderstood because people expect it to behave like a technical manual or a plug-and-play governance solution. It isn’t either of those things.
- It’s not a prescriptive checklist telling you exactly what tools to buy or what buttons to click. DMBOK defines what good data management looks like, not how your specific organization must implement it.
- It’s also not a software product. Adopting DMBOK doesn’t magically install governance. Teams still need ownership, workflows, and operational discipline to bring the model to life.
Some might feel that DMBOK is only for large enterprises or compliance-heavy industries. In reality, its principles scale. Smaller teams simply apply fewer areas at first and grow over time.
Think of it less as a rulebook and more as a shared map, but how you travel that map depends on your goals.
The 11 core knowledge areas of DAMA DMBOK
Permalink to “The 11 core knowledge areas of DAMA DMBOK”DMBOK organizes data management into 11 connected disciplines known as the DAMA Wheel. Data governance sits at the center, linking architecture, quality, metadata, security, and other areas into one operating model. Each knowledge area defines responsibilities, activities, and outcomes, enabling teams to manage data as a coordinated system rather than as isolated projects.
The DAMA Wheel looks simple. Governance in the middle. Ten supporting disciplines around it. But the real value isn’t the diagram; it’s how it changes how teams think about data work.
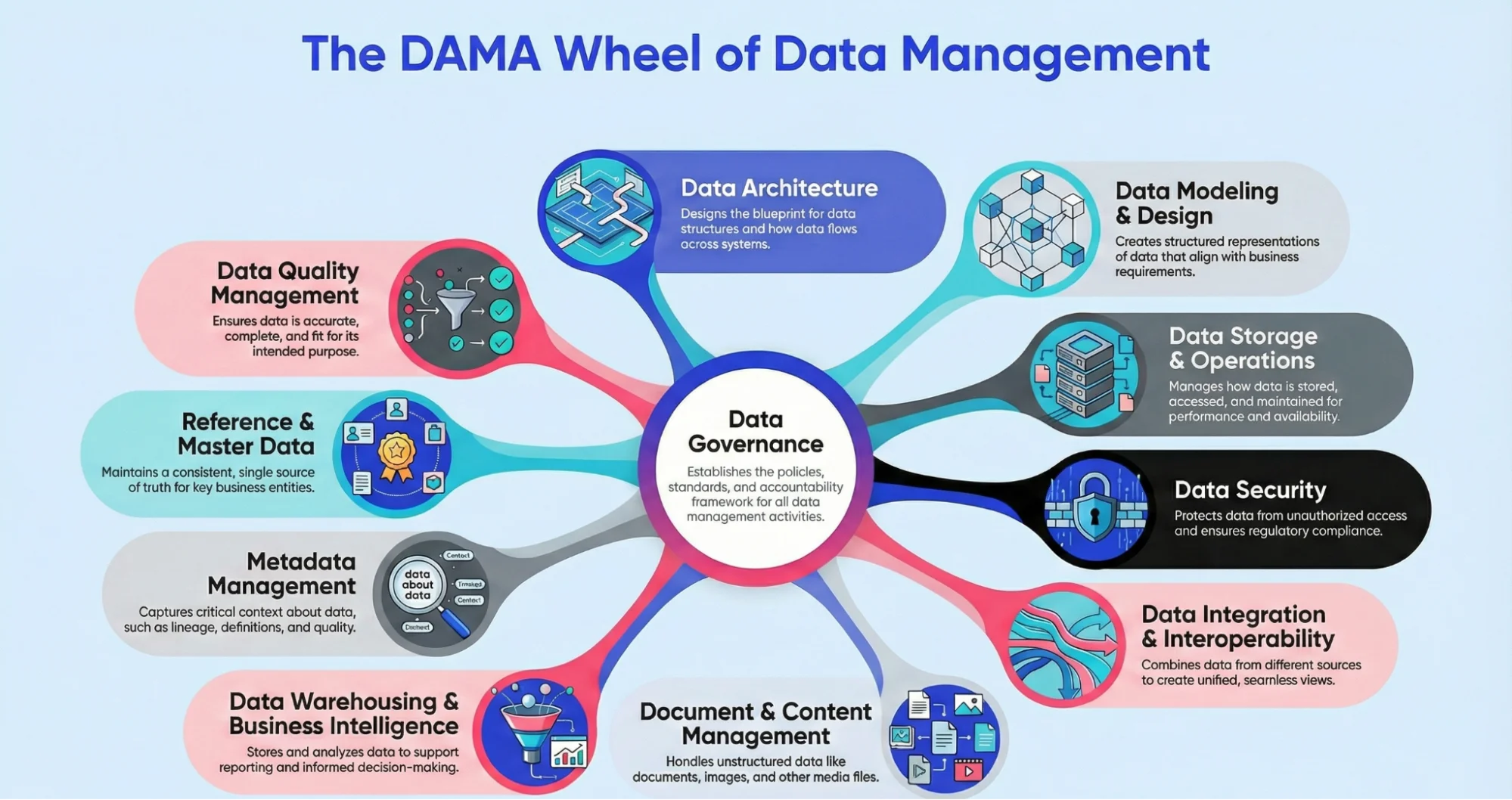
11 core knowledge areas of DAMA DMBOK. Source: Atlan.
Most organizations don’t fail because they lack effort. They fail because efforts don’t connect. The wheel makes those relationships visible. It shows that every discipline influences the others, whether teams recognize it or not.
What are the benefits of the DAMA-DMBOK framework?
Permalink to “What are the benefits of the DAMA-DMBOK framework?”| Knowledge area | When you feel the need for it | What this discipline stabilizes |
|---|---|---|
| Data governance | Decisions stall because ownership is unclear or standards vary. | Establishes who decides what, how policies get enforced, and how accountability flows across teams. |
| Data architecture | Systems don’t align, and data flows feel improvised. | Creates the enterprise blueprint that keeps data movement intentional and scalable. |
| Data modeling and design | Teams argue over definitions or structures that don’t translate cleanly. | Turns business meaning into shared structures everyone can build on. |
| Data storage and operations | Performance issues or lifecycle chaos start appearing. | Keeps stored data reliable, maintained, and managed from creation to retirement. |
| Data security | Access concerns, privacy risks, or audit pressure increase. | Protects sensitive information while ensuring appropriate availability. |
| Data integration and interoperability | Reports don’t reconcile, or pipelines feel fragile. | Aligns how data moves and combines across systems so outputs stay consistent. |
| Document and content management | Unstructured information becomes hard to track or govern. | Brings order and lifecycle control to files, media, and content assets. |
| Reference and master data | Core entities like customers or products don’t match across systems. | Creates a shared truth so business records remain consistent everywhere. |
| Data warehousing and BI | Analytics teams spend more time fixing data than analyzing it. | Delivers trusted, structured data for reporting and decision-making. |
| Metadata management | People don’t know where the data came from or what it means. | Provides lineage and context so information stays understandable and traceable. |
| Data quality management | Confidence in reports drops, or errors repeat. | Monitors and improves fitness-for-use so decisions rest on dependable data. |
How do these knowledge areas connect?
Permalink to “How do these knowledge areas connect?”The wheel is interconnected. Quality depends on modeling discipline and governance ownership.
- Metadata threads through every stage, providing lineage and shared meaning.
- Architecture acts as the master blueprint that guides integration and storage.
- Analytics sits at the usage layer, entirely dependent on trusted upstream practices.
When one area shifts, others feel it. The interdependence is reinforced operationally through context diagrams for each discipline. These diagrams show how outputs from one area become inputs for another.
Nothing exists in isolation.
There are secondary DAMA frameworks that describe the connection between knowledge areas as a hierarchy or progression, such as Aiken’s Pyramid. It suggests that organizations connect these areas in a logical sequence. It starts with a foundation of Modeling, Storage, and Security, moves into Quality, Architecture, and Metadata, and finally integrates Governance to enable advanced practices like Data Warehousing and BI.
Aiken’s Pyramid, also known as DMBOK Pyramid, organizes prioritization into four distinct phases:
- Foundational capabilities: Initial priority is given to basic requirements such as Data Modeling and Design, Data Storage and Operations, and Data Security. Once these are established, the focus shifts to Data Integration and Interoperability to make systems functional.
- Context and quality: As usage grows, organizations must prioritize Data Quality, Metadata Management, and Data Architecture. These areas provide the necessary clarity on how data from disparate systems works together.
- Strategic oversight: Data Governance becomes the priority to provide structural support for all data management activities.
- Advanced practices: Only after the lower levels are established can an organization effectively prioritize the golden pyramid of advanced analytics, data mining, and other high-value capabilities.
In practice, Context Diagrams formalize these connections. They show that different knowledge areas require the same input and produce deliverables that serve as inputs to other functions.
Why should you adopt DAMA DMBOK?
Permalink to “Why should you adopt DAMA DMBOK?”DAMA DMBOK standardizes data management, reducing risk and increasing value. The framework brings disciplines into a single operating model. It aligns teams around shared terminology and replaces ad hoc decisions with proven practices. Instead of firefighting data issues, you gain structure that supports scaling, governance maturity, and long-term business confidence.
Industry surveys show more than 65% of data leaders now rank governance as their top strategic priority, ahead of analytics modernization and AI initiatives. This shift reflects that advanced analytics depends on disciplined foundations.
You gain much more from adopting DAMA DMBOK, including:
- Strategic value: The framework enables an organization to derive tangible value from its data assets, empowering better decisions.
- Standardization: The multiplicity of definitions and the middle management’s fancy language often lead to miscommunication. DAMA-DMBOK establishes a standard terminology, accelerating collaboration between teams.
- Regulatory compliance and risk mitigation: In heavily regulated sectors such as finance and healthcare, adoption is often driven by the need to meet strict regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, BCBS 239, or CCPA). The framework’s guidance on security, privacy, and accountability makes it easier for organizations to remain compliant.
- Less technical debt: As an organization’s data grows, data-specific technical debt accumulates due to uneven development cycles. The frameworks provide oversight to ensure that SLDC is in accordance with the set standards.
- Accountability: The framework directly addresses hazy assignments of responsibility. It helps people know exactly what is expected of them in relation to data
- Continuous improvement: Using the framework, organizations perform a data management maturity assessment to understand their current state. The framework guides them toward higher efficiency and optimization.
The DAMA-DMBOK 3.0 project further modernizes the framework. It incorporates AI, cloud-native architectures, and modern data platforms to stay relevant while preserving the foundational principles.
How to implement the DAMA DMBOK framework
Permalink to “How to implement the DAMA DMBOK framework”Users implement DAMA DMBOK through a phased roadmap that moves data management from an ad-hoc effort to a sustainable operating model. It starts with assessing maturity. You prioritize high-impact gaps, define ownership, and embed governance into workflows.
Adoption alone isn’t success. Gartner predicts that 80% of data and analytics governance initiatives will fail by 2027 due to a lack of a real or manufactured crisis. To avoid becoming part of that 80%, governance teams must tie their work directly to business outcomes, not just documentation checklists. Implementation structure also determines whether governance becomes an asset or overhead.
Quickly assess your organization’s data governance maturity
Take Assessment →2. Identify gaps and areas for improvement
Permalink to “2. Identify gaps and areas for improvement”Focus on knowledge areas that align with business objectives and present highest risk. Most organizations start with data governance, data quality, or metadata management rather than attempting all areas at once. Prioritization ensures resources target areas with maximum business impact.
3. Develop a roadmap for implementation
Permalink to “3. Develop a roadmap for implementation”This includes setting goals and milestones for implementing DAMA-DMBOK practices and prioritizing areas that have the most significant impact on the organization’s data management capabilities.
Get instant 90 day data governance roadmap to serve as a foundation
Get my data governance roadmap →4. Assign roles and responsibilities
Permalink to “4. Assign roles and responsibilities”Establish clear accountability for each knowledge area. Define data stewardship responsibilities, governance council membership, and escalation paths. Role clarity prevents gaps where no one owns critical data management functions.
5. Provide training and enablement
Permalink to “5. Provide training and enablement”Ensure teams understand DAMA DMBOK principles and have access to necessary tools. Many organizations pursue CDMP certification for key team members. Training investments accelerate adoption and reduce misinterpretation of framework concepts.
6. Monitor progress and iterate
Permalink to “6. Monitor progress and iterate”Track metrics for each knowledge area and adjust approach based on results. Regular assessment ensures continuous improvement rather than one-time compliance. Organizations should review progress quarterly and refine roadmaps based on lessons learned.
However, remember that implementing the DAMA-DMBOK framework does not necessarily mean following it to the letter. Organizations often adapt and customize the framework to fit their specific needs, culture, and industry requirements.
As a result, the extent to which organizations adopt DAMA-DMBOK can vary.
If DMBOK is implemented successfully, it turns scattered data practices into a repeatable system that fits your team’s workflow. It’s more of a guide rather than a prescription. Successful teams treat it as a progression.
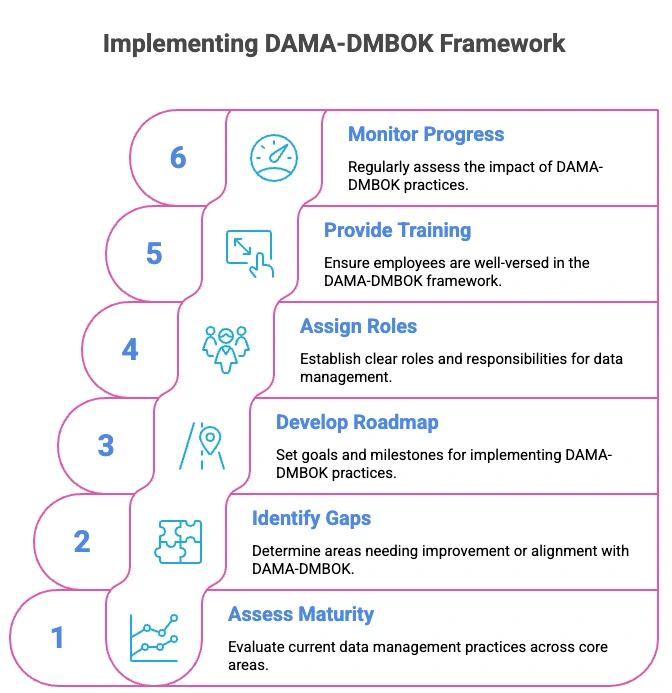
How to implement the DAMA-DMBOK Framework. Source: Atlan.
DAMA DMBOK framework structure and organization
Permalink to “DAMA DMBOK framework structure and organization”DAMA DMBOK organizes its content around the DAMA Wheel, a visual representation of how data management disciplines interconnect. Data governance sits at the center, emphasizing its foundational role. The framework’s structure reflects the reality that effective data management requires coordinated effort across all knowledge areas.
The DAMA Wheel visualization
Permalink to “The DAMA Wheel visualization”The iconic DAMA Wheel places data governance at the hub with 10 knowledge areas arranged around it. This design illustrates that governance underpins every data management activity. Each knowledge area connects to governance while also relating to adjacent areas through shared processes and dependencies.
Functional framework approach
Permalink to “Functional framework approach”DAMA DMBOK provides more than definitions. It includes activities, deliverables, roles, metrics, and maturity models for each knowledge area. This functional framework helps organizations translate principles into practice through concrete implementation guidance.
Context diagrams and relationships
Permalink to “Context diagrams and relationships”The framework documents how knowledge areas depend on and support each other. For example, data quality management relies on both metadata management and data governance. Understanding these interdependencies helps organizations sequence their implementation effectively and avoid isolated initiatives.
Best practices and guidelines
Permalink to “Best practices and guidelines”Each knowledge area includes generally accepted practices gathered from hundreds of data professionals globally. DAMA DMBOK represents consensus knowledge rather than prescriptive mandates. Organizations adapt these practices to their specific contexts, industry requirements, and organizational culture.
Evolution and updates
Permalink to “Evolution and updates”DAMA International released DMBOK2 in 2017 with contributions from 120+ data professionals. The framework continues evolving, with DMBOK 3.0 in development to address emerging technologies like AI and cloud-native architectures. This evolution ensures relevance as the data governance landscape changes with new tools, regulations, and business models.
What are the challenges of the DAMA-DMBOK framework?
Permalink to “What are the challenges of the DAMA-DMBOK framework?”While DAMA DMBOK provides comprehensive guidance, implementation comes with practical considerations that teams should anticipate. The framework’s breadth can feel overwhelming for organizations starting their data governance journey. Understanding these challenges helps teams plan realistic adoption strategies.
Complexity and comprehension curve
Permalink to “Complexity and comprehension curve”With 11 knowledge areas and 600+ pages of content, DAMA DMBOK requires significant investment to master. Teams looking to show early wins may struggle with the framework’s comprehensiveness. Organizations often need to supplement DAMA DMBOK with tactical playbooks for specific tools and platforms.
Strategic guidance vs operational execution
Permalink to “Strategic guidance vs operational execution”DAMA DMBOK excels at outlining principles and roles but provides limited tactical guidance for day-to-day operations. Teams must translate framework concepts into specific processes, tools, and workflows. This translation requires data management expertise and organizational change management capabilities.
Traditional approach in modern environments
Permalink to “Traditional approach in modern environments”The framework predates many cloud-native and AI-driven practices that dominate today’s data landscape. The enterprise data management market is projected to reach $221.6 billion by 2030, driven largely by cloud adoption and AI use cases. Organizations focused on active, automated governance may need to layer modern execution strategies onto DAMA DMBOK’s foundational principles.
Heavy reliance on stewardship
Permalink to “Heavy reliance on stewardship”Effective implementation assumes clear data ownership and active business stewardship. Many organizations lack these cultural foundations and must build them while adopting the framework. This dual transformation increases complexity and extends timelines beyond technical implementation alone.
Tool-agnostic design requires translation
Permalink to “Tool-agnostic design requires translation”While vendor neutrality ensures broad applicability, it also means organizations must determine how to operationalize DAMA DMBOK within their specific technology platforms. The framework doesn’t prescribe which tools to use or how to configure them. Teams need expertise to map DAMA concepts to platform capabilities.
Resource intensity
Permalink to “Resource intensity”Comprehensive DAMA DMBOK adoption requires dedicated personnel, budget, and executive sponsorship. Smaller organizations may struggle to resource all 11 knowledge areas simultaneously. Gartner predicts that by 2027, 60% of organizations will fail to realize AI value due to incohesive governance frameworks, underscoring the importance of proper resourcing.
How modern platforms operationalize DAMA DMBOK principles
Permalink to “How modern platforms operationalize DAMA DMBOK principles”DAMA DMBOK offers a strategic blueprint for managing data, but putting its eleven knowledge areas into practice is often slow and manual. Many teams still document policies in wikis, track lineage in spreadsheets, and manage governance workflows through email. These administrative tasks drain time from strategic decision-making. It’s no surprise that 67 percent of organizations say they lack trust in their data, largely because governance frameworks remain theoretical rather than operational.
From static documentation to living governance systems
Permalink to “From static documentation to living governance systems”Modern data catalog platforms change this dynamic by turning DMBOK guidance into automated, active workflows. Atlan’s Active Governance model replaces manual documentation and coordination with system-driven execution. The platform automatically discovers data assets, infers lineage from real usage, and enforces policies directly within the tools teams already rely on. Metadata becomes active, offering relevant governance context at the exact moment someone is making a decision.
Shifting governance from coordination to strategy
Permalink to “Shifting governance from coordination to strategy”With automation handling routine tasks, governance councils can focus on policy design instead of policy administration. Organizations adopting active governance see faster policy cycles and stronger cross-team engagement. DMBOK provides the structure. Modern data governance platforms supply the operational engine that brings that structure to life at scale.
See how Atlan operationalizes DAMA DMBOK principles through automated governance and active metadata.
Quickly assess your organization's data governance maturity
Take Assessment →Below are different phases of implementing the DAMA-DMBOK framework.
| Phase | What you focus on | Why it matters | Success signals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assess maturity | Evaluate practices across the 11 knowledge areas | Establishes a realistic baseline instead of assumptions | Clear view of strengths, gaps, and risk areas |
| Prioritize gaps | Target governance, quality, or metadata issues with business impact | Prevents trying to fix everything at once | Focused improvement plan tied to business outcomes |
| Build the roadmap | Translate priorities into projects, milestones, and ownership | Connects governance intent to execution | Documented plan aligned with enterprise architecture |
| Establish roles | Define stewardship, ownership, and governance authority | Removes ambiguity and escalation loops | Decisions resolve faster with clear accountability |
| Operationalize policies | Create standards, glossaries, and workflow rules | Turns governance into daily behavior | Teams follow consistent processes |
| Monitor and iterate | Track KPIs and refine practices quarterly | Keeps governance adaptive and value-driven | Measurable improvement in trust and efficiency |
You shouldn’t implement all 11 knowledge areas at once. Adoption typically unfolds in layers.
How Do You Assess Data Management Maturity With DAMA DMBOK?
Permalink to “How Do You Assess Data Management Maturity With DAMA DMBOK?”You can measure data management maturity using DAMA DMBOK, but not in the way many people expect. DMBOK itself is not a scoring model. It doesn’t assign maturity levels or grades. Instead, it defines what areas of data management should exist. You then use a maturity framework, such as CMMI or DCAM, to evaluate how well those areas perform. Together, they create a structured, practical way to understand where your data management stands.
DAMA DMBOK shows how well your organization actually manages data. Data Management Maturity Assessment (DMMA) lets you see where governance is working, where gaps exist, and how consistent your data practices really are.
While DMBOK itself isn’t a maturity model, it defines what good data management includes. Maturity models such as CMMI or DCAM provide scoring systems. Together, they give you both structure and evaluation.
Each DMBOK knowledge area gets evaluated separately.
Common maturity levels used in assessment
Permalink to “Common maturity levels used in assessment”| Maturity level | What it looks like in practice |
|---|---|
| Initial | Data work is reactive and inconsistent. Success depends on individuals. Governance is unclear. |
| Managed | Basic repeatable processes exist. Ownership begins to form. Standards emerge. |
| Defined | Processes are documented and followed consistently. Governance roles are clear. |
| Quantitatively managed | Metrics guide decisions. Quality and performance are tracked. |
| Optimizing | Continuous improvement and automation support scaling governance. |
DMBOK’s knowledge areas act as the evaluation lens. After scoring, teams compare results to a target state, often aiming for the Defined level as a realistic milestone. The gap becomes a roadmap for improvement, prioritized by business impact.
The goal isn’t to be perfect, it’s about providing clarity. When you understand your maturity level, you stop reacting to data problems and start improving deliberately.
How does DAMA DMBOK compare to COBIT, TOGAF, and other frameworks?
Permalink to “How does DAMA DMBOK compare to COBIT, TOGAF, and other frameworks?”DAMA DMBOK defines what good data management looks like across 11 disciplines. Other frameworks focus on IT governance, architecture, maturity scoring, or compliance. You don’t replace those with DMBOK; you layer it alongside them. The right choice depends on whether you’re solving for data depth, enterprise alignment, risk control, or operational maturity.
DMBOK is often called a standard, but it’s better understood as a functional backbone. It explains which disciplines are required to manage data as an enterprise asset. Other frameworks solve adjacent problems: IT controls, architecture modeling, maturity benchmarking, or regulatory alignment.
The decision is rarely either/or. Mature programs combine frameworks intentionally. You use each one for what it does best, instead of stretching a single model to cover everything.
How DMBOK fits alongside other frameworks
Permalink to “How DMBOK fits alongside other frameworks”| Framework | Primary focus | When to use it | How it complements DMBOK |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAMA DMBOK | Functional data management discipline | You need a complete operating model for governance, quality, metadata, and lifecycle management | Serves as the core structure for managing data as a strategic asset |
| COBIT | Enterprise IT governance and controls | You’re making decisions about IT investments, risk, or infrastructure governance | DMBOK adds depth for data-specific policies and stewardship inside COBIT governance |
| ISO standards (8000, 11179) | Compliance and formal data standards | Regulatory environments demand measurable adherence to international standards | DMBOK provides the operational framework to implement those standards in daily workflows |
| SAM / AIM | Strategic business–IT alignment | You’re mapping enterprise strategy to technology capabilities | DMBOK translates alignment into concrete data roles and operating practices |
| DCAM | Data capability maturity assessment | You want structured scoring of governance maturity and interdependencies | DMBOK defines what activities exist; DCAM measures how well you execute them |
| Zachman Framework | Enterprise modeling ontology | You’re defining enterprise perspectives and structural models | DMBOK guides the actual data modeling work identified in Zachman views |
| TOGAF | Enterprise architecture planning | You’re aligning business and technology architecture systematically | DMBOK specializes the data architecture domain within broader EA programs |
| CMMI | Process maturity benchmarking | You need to evaluate repeatability and optimization of practices | DMBOK outlines activities; CMMI grades their maturity level |
| Data Management at Scale | Cloud-native engineering practices | You want pragmatic, modern implementation patterns | DMBOK provides a governance structure; this adds tactical execution detail |
| DaLiF | Government data lifecycle governance | Public-sector ecosystems demand transparency and lifecycle control | DMBOK expands lifecycle discipline into broader enterprise governance |
| NIST frameworks | Privacy and cybersecurity controls | Legal or operational risk drives a strict security posture | DMBOK integrates those controls into enterprise data management workflows |
Here’s the simple way to think about it:
- If you’re defining how data should be governed and managed, start with DMBOK
- If you’re managing enterprise IT risk and controls, bring in COBIT
- If compliance or standards drive requirements, align with ISO or NIST
- If maturity benchmarking matters, pair with DCAM or CMMI
- If architecture planning dominates, integrate TOGAF or Zachman
Each framework answers a different question. Together, they create a layered system in which governance, architecture, compliance, and maturity reinforce one another rather than compete.
The strongest data programs build a framework ecosystem, using DMBOK as the anchor that keeps data management coherent while adjacent models handle specialization.
What are the challenges in implementing DAMA DMBOK? (+ Solutions)
Permalink to “What are the challenges in implementing DAMA DMBOK? (+ Solutions)”When you implement DMBOK, resistance shows up first. Culture pushes back, and complexity feels intimidating. Translating principles into real work takes effort. But the solution isn’t to retreat; it’s to move deliberately, get leadership behind the change, and automate wherever possible. That’s when governance starts supporting work instead of slowing it down.
Every framework looks clean on paper. Real organizations aren’t.
When teams begin implementing DMBOK, friction shows up; not because the model is wrong, but because it introduces discipline where informal habits once lived. Most challenges fall into four categories: culture, complexity, execution, and risk. They’re predictable and solvable.
Here’s an overview of the common implementation challenges and their practical solution:
| Challenge you’ll hit | Why it happens | Practical solution |
|---|---|---|
| Culture shock | DMBOK introduces formal structure into environments used for improvisation | Treat governance as change management. Secure executive sponsorship and run a formal OCM program so teams understand why discipline matters |
| Unclear ownership | Responsibilities evolve organically, leaving gaps and escalation loops | Define data owners, stewards, and custodians early. Establish a governance council to resolve conflicts quickly |
| Governance is seen as overhead | Leadership doesn’t see immediate ROI | Tie governance goals to measurable outcomes. |
| Framework overwhelm | 11 knowledge areas feel too big for quick adoption | Start modular. Focus on 2–3 high-impact areas first (often quality, metadata, governance) before expanding |
| Vendor-neutral gap | Principles exist, but teams lack tactical guidance | Pair DMBOK with platform-specific playbooks and automation tools that operationalize workflows |
| IT-only mindset | Governance gets siloed inside technical teams | Reframe governance as a business discipline. Let data needs drive technology decisions |
| Technical debt and fragile pipelines | Legacy architecture evolved without coordination | Prioritize architecture and enterprise modeling to stabilize data flow before scaling analytics |
| Hard-to-measure data value | Data ROI feels abstract compared to financial assets | Use valuation models tied to replacement cost, decision impact, and revenue potential |
| Fragmented environments | Hybrid systems create disconnected lineage and visibility | Standardize integration patterns and use active metadata for cross-system transparency |
| Ethical and security exposure | Governance lags behind AI or privacy risks | Embed ethics reviews, bias checks, and privacy-by-design into governance workflows |
Many implementation struggles share the same root cause: trying to deploy governance as a static framework instead of an evolving operating model.
Teams aim for completeness instead of momentum. They build policies before ownership exists. Phased adoption solves this.
Stabilize foundations and expand governance as trust grows. When teams see early wins in the form of cleaner reporting, faster issue resolution, resistance drops, and adoption accelerates.
Automation changes the equation
Permalink to “Automation changes the equation”Manual governance doesn’t scale.
Modern tooling reduces friction by embedding lineage, policy enforcement, and metadata capture directly into workflows. Teams operationalize rules where work actually happens, shifting governance from a compliance exercise to a daily habit.
The opportunity is significant. Analysts expect generative AI to accelerate time-to-value in governance by up to 40%. However, it would only happen if the foundational structure already exists. Automation amplifies disciplined governance; it doesn’t replace it.
The implementation challenges aren’t signs that DMBOK is too heavy. They’re signals that governance is moving from theory to practice.
DMBOK 3.0: What’s changing in the framework?
Permalink to “DMBOK 3.0: What’s changing in the framework?”DMBOK 3.0 is a major modernization effort that keeps the framework’s core principles intact while updating it for AI, cloud-native architectures, and modern data platforms. It doesn’t replace what works; the framework evolves to keep governance practical and usable in modern data environments.
DMBOK has always been a living reference, not a frozen rulebook. The 3.0 project, launched in 2025, reflects that philosophy. Data ecosystems include AI pipelines, hybrid cloud architectures, and platform-driven workflows that didn’t exist when earlier versions were written. The update ensures the framework continues to guide real-world practice instead of lagging behind it.
The foundational disciplines remain. Governance, architecture, quality, and lifecycle thinking don’t disappear; they expand to cover new realities.
What’s evolving in DMBOK 3.0
Permalink to “What’s evolving in DMBOK 3.0”Rather than introducing entirely new principles, the update deepens how existing disciplines operate in modern environments:
- AI governance becomes explicit: Guidance addresses model lifecycle management, bias detection, and responsible AI use. Governance expands beyond datasets to include algorithmic oversight.
Cloud-native thinking gets embedded: Storage, architecture, and lifecycle practices adapt to distributed, hybrid infrastructures instead of assuming on-prem environments. - Modern data platforms are recognized: The framework reflects how data products, lakehouses, and platform ecosystems change ownership, integration, and stewardship patterns.
- Existing disciplines are refined: Core knowledge areas evolve to match current industry practice rather than remaining anchored to older operating assumptions.
A shift in how the framework is delivered
Permalink to “A shift in how the framework is delivered”The biggest changes are structural. DMBOK 3.0 is being paired with a digital content platform designed for accessibility and interaction.
This matters because governance frameworks lose relevance when updates lag behind technology cycles. A digital delivery model keeps the framework closer to operational reality.
The modernization effort follows a collaborative governance structure often described as a Triple Helix:
- Editorial leadership ensures coherence and practical clarity
- Expert peer review maintains rigor and professional standards
- Global practitioner input grounds the framework in real-world use
The intent is to let the framework evolve with the profession, not above it.
How does Atlan operationalize DAMA DMBOK?
Permalink to “How does Atlan operationalize DAMA DMBOK?”Atlan turns DMBOK from a reference framework into an automated operating model. Instead of relying on manual documentation and disconnected workflows, governance runs inside the systems teams already use. Discovery, lineage, stewardship, and policy enforcement become embedded processes, reducing overhead while making DMBOK practical at scale.
Traditional DMBOK implementations often stall because governance lives in documents while work happens elsewhere. Policies sit in wikis, ownership is tracked in spreadsheets, and lineage gets mapped manually. Over time, maintenance becomes the real workload.
Atlan approaches the framework differently. The goal isn’t to reinterpret DMBOK, it’s to operationalize it. Governance becomes system-driven, visible, and automated so the 11 knowledge areas function as part of daily data work rather than separate administrative exercises.
The operating model: Unify, collaborate, and activate
Permalink to “The operating model: Unify, collaborate, and activate”Atlan structures DMBOK execution around three practical motions that map directly to how modern data teams work:
- Unify to create a system-wide visibility: Atlan acts as a control plane across your data ecosystem. Automated discovery and column-level lineage surface how assets connect, supporting the DMBOK disciplines of architecture and metadata. It helps you understand where data comes from and how it moves.
- Collaborate to embed ownership into workflows: Stewardship and accountability live inside the platform instead of external documents. Teams define ownership and coordinate governance decisions where work happens. It reduces escalation loops and clarifies responsibility.
- Activate to deliver governance in real time: Governance context doesn’t stay passive. Active Metadata pushes lineage, definitions, and policy signals directly into analytics and operational tools. Users see trusted context at the moment of decision, which turns governance into an enabler instead of a gate.
A core pillar of Atlan’s approach is Active Governance, which is automation that moves policies from documentation into execution. Metadata automation continuously captures and enriches lineage and context, supporting discoverability without manual upkeep. Additionally, policy workflows enforce rules inside everyday tools, allowing governance councils to focus on strategy instead of administration.
This automation aligns closely with DMBOK’s metadata and governance disciplines. It empowers teams to operate from a living context that updates as systems evolve.
Real stories from real customers: Governance frameworks in action
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Governance frameworks in action”“Atlan is much more than a catalog of catalogs. It’s more of a context operating system… Atlan enabled us to easily activate metadata for everything from discovery in the marketplace to AI governance to data quality to an MCP server delivering context to AI models.” — Sridher Arumugham, Chief Data and Analytics Officer, Workday
Governance is an active semantic layer not a passive documentation
Watch Workday’s story →
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
“Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, ‘Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.’ With Atlan’s integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate.”

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare’s Data Renaissance with Atlan
Key takeaways on DAMA DMBOK framework
Permalink to “Key takeaways on DAMA DMBOK framework”The DAMA DMBOK framework offers a solid, vendor-neutral foundation for enterprise data management through its eleven knowledge areas. Its value comes from adapting the guidance to your organization’s realities, not following it rigidly. The strongest implementations begin with an honest capability assessment, focus on the knowledge areas that matter most to current business priorities, and expand in manageable phases.
While the framework’s principles remain reliable, effective execution now relies on platforms that automate governance workflows and deliver real-time context to data users. Teams that pair DAMA’s strategic structure with modern operational tooling are best positioned to treat data as the strategic asset it is.
Atlan enables organizations to put DAMA DMBOK principles into practice in today’s data environments.
FAQs: Common questions about the DAMA DMBOK framework
Permalink to “FAQs: Common questions about the DAMA DMBOK framework”1. What is the DAMA Wheel?
Permalink to “1. What is the DAMA Wheel?”The DAMA Wheel is a visual model of the framework. Data governance sits at the center, with ten supporting knowledge areas arranged around it. The design highlights that governance provides direction and accountability while architecture, quality, metadata, and analytics operate as connected disciplines, not isolated activities.
2. What are the 11 core knowledge areas?
Permalink to “2. What are the 11 core knowledge areas?”DMBOK organizes data management into governance, architecture, modeling, storage, security, integration, content management, master/reference data, analytics, metadata, and quality. Together, these disciplines ensure they support real business use rather than living in disconnected systems.
3. How long does DAMA DMBOK implementation take?
Permalink to “3. How long does DAMA DMBOK implementation take?”DMBOK implementation typically takes 3-6 months for foundational governance, 6-12 months for pilot adoption across priority knowledge areas, and 18-36 months for full enterprise rollout. Most organizations implement iteratively, starting with high-impact areas like data quality, metadata management, and governance before expanding to all 11 disciplines.
4. Is DAMA DMBOK a prescriptive “how-to” guide?
Permalink to “4. Is DAMA DMBOK a prescriptive “how-to” guide?”No. DMBOK defines what good data management looks like, not exactly how to execute it. It’s vendor-neutral and adaptable. Organizations interpret the framework based on their culture, tooling, and industry needs.
5. Can DAMA DMBOK work with frameworks like COBIT or TOGAF?
Permalink to “5. Can DAMA DMBOK work with frameworks like COBIT or TOGAF?”Yes. DMBOK complements other frameworks. COBIT handles enterprise IT governance, TOGAF guides architecture strategy, and ISO standards address compliance. DMBOK adds deep, data-specific discipline inside those broader structures.
6. What’s the difference between DMBOK 2.0 and DMBOK 3.0?
Permalink to “6. What’s the difference between DMBOK 2.0 and DMBOK 3.0?”DMBOK 2.0 is the current standard focused on core data management disciplines. DMBOK 3.0, launched in 2025, modernizes the framework for AI governance, cloud-native environments, and contemporary data platforms. The foundations remain the same; the update expands how those principles apply to modern ecosystems.
7. Is certification required to use the framework?
Permalink to “7. Is certification required to use the framework?”No certification is required to adopt DMBOK. Any organization can implement its principles. However, many professionals pursue CDMP certification to validate their understanding and establish a shared baseline of governance knowledge across teams.
8. How does DMBOK address modern data technologies like AI and cloud?
Permalink to “8. How does DMBOK address modern data technologies like AI and cloud?”DMBOK remains technology-agnostic, so its governance principles apply across platforms. The evolving 3.0 version explicitly addresses AI lifecycle oversight, bias awareness, and cloud-native architecture, helping teams apply familiar governance discipline to emerging technologies.
9. What are the main criticisms of DAMA DMBOK?
Permalink to “9. What are the main criticisms of DAMA DMBOK?”Teams sometimes find the framework complex, abstract, or light on tactical execution guidance. DMBOK excels at defining structure but requires operational playbooks and tooling to bring concepts into daily workflows.
10. Is DAMA DMBOK only for large enterprises?
Permalink to “10. Is DAMA DMBOK only for large enterprises?”No. The framework scales. Smaller organizations typically focus on essential governance and quality disciplines first, expanding over time. Because DMBOK is modular, teams implement what delivers immediate value without needing full enterprise adoption on day one.
11. Do I need the DAMA DMBOK book to implement it?
Permalink to “11. Do I need the DAMA DMBOK book to implement it?”The full reference provides depth and context, especially for formal programs. But many teams begin with summaries and practical guides to understand core principles before committing to the full material. Implementation success depends more on disciplined execution than documentation volume.
Ready to implement DAMA DMBOK in your organization?
Permalink to “Ready to implement DAMA DMBOK in your organization?”DAMA DMBOK provides a clear blueprint for treating data as a real business asset. Implementation isn’t a big-bang project. It’s a progression. Strong teams start with the basics and build from there. The framework helps you focus on what matters first. That way, you don’t chase advanced analytics before your foundation is stable. Leadership support keeps the effort moving.
DMBOK 3.0 adds guidance for AI and cloud environments. But the bigger shift is operational. Governance can’t sit in documents anymore. It has to live inside everyday workflows.
Modern governance platforms make it possible. They turn DMBOK principles into automated, working systems.
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. A control plane that stitches together your disparate data infrastructure and activates DAMA-aligned policies, lineage, and context where teams actually work.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
DAMA-DMBOK: Related reads
Permalink to “DAMA-DMBOK: Related reads”- What is data governance & why does it matter?
- 11 Best Data Governance Software in 2026 | A Complete Roundup of Key Strengths & Limitations
- Data Governance Framework: Examples, Standards & Templates
- 7 Top AI Governance Tools Compared | A Complete Roundup for 2026
- 7 Best Practices for Data Governance to Follow in 2026
- Benefits of Data Governance : 4 Ways It Helps Build Great Data Teams
- Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities: A Quick Round-Up
- Data Governance Policy: Examples, Templates & How to Write One
- Key Objectives of Data Governance: How Should You Think About Them?
- 5 Popular Data Governance Certifications & Trainings in 2026
- 8 Best Data Governance Books Every Data Practitioner Should Read in 2026
- Automated Data Governance: How Does It Help You Manage Access, Security & More at Scale?
- Top data catalog tools — Compare the top data catalog tools of 2026
- Snowflake Data Catalog: Importance, Benefits, Native Capabilities & Evaluation Guide
- AI Data Catalog: Exploring the Possibilities That Artificial Intelligence Brings to Your Metadata Applications & Data Interactions
- Data Lineage Tracking | Why It Matters, How It Works & Best Practices for 2026
- Data Lineage Solutions| Capabilities and 2026 Guidance
- Data Catalog Market: Current State and Top Trends in 2026
- Build vs. Buy Data Catalog: What Should Factor Into Your Decision Making?
- How to Set Up a Data Catalog for Snowflake? (2026 Guide)
- Data Catalog Pricing: Understanding What You’re Paying For
- Data Catalog Comparison: 6 Fundamental Factors to Consider
- Best Data Governance Tools in 2026 — A Complete Roundup of Key Capabilities
- 5 Best Data Governance Platforms in 2026 | A Complete Evaluation Guide to Help You Choose
- Data Catalog Demo 101: What to Expect, Questions to Ask, and More
- Data Mesh Catalog: Manage Federated Domains, Curate Data Products, and Unlock Your Data Mesh
- Best Data Catalog: How to Find a Tool That Grows With Your Business
- How to Build a Data Catalog: An 8-Step Guide to Get You Started
- The Forrester Wave™: Enterprise Data Catalogs, Q3 2024 | Available Now
- How to Pick the Best Enterprise Data Catalog? Experts Recommend These 11 Key Criteria for Your Evaluation Checklist




















