What is RACI for data governance roles? #
Summarize and analyze this article with 👉 🔮 Google AI Mode or 💬 ChatGPT or 🔍 Perplexity or 🤖 Claude or 🐦 Grok (X) .
RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) matrices prevent the governance bottlenecks that plague 73% of digital transformation initiatives.
Tip: Review your RACI matrix every 90 days and whenever major org or regulatory shifts occur.
Quick data governance role snapshots (what they actually do) #
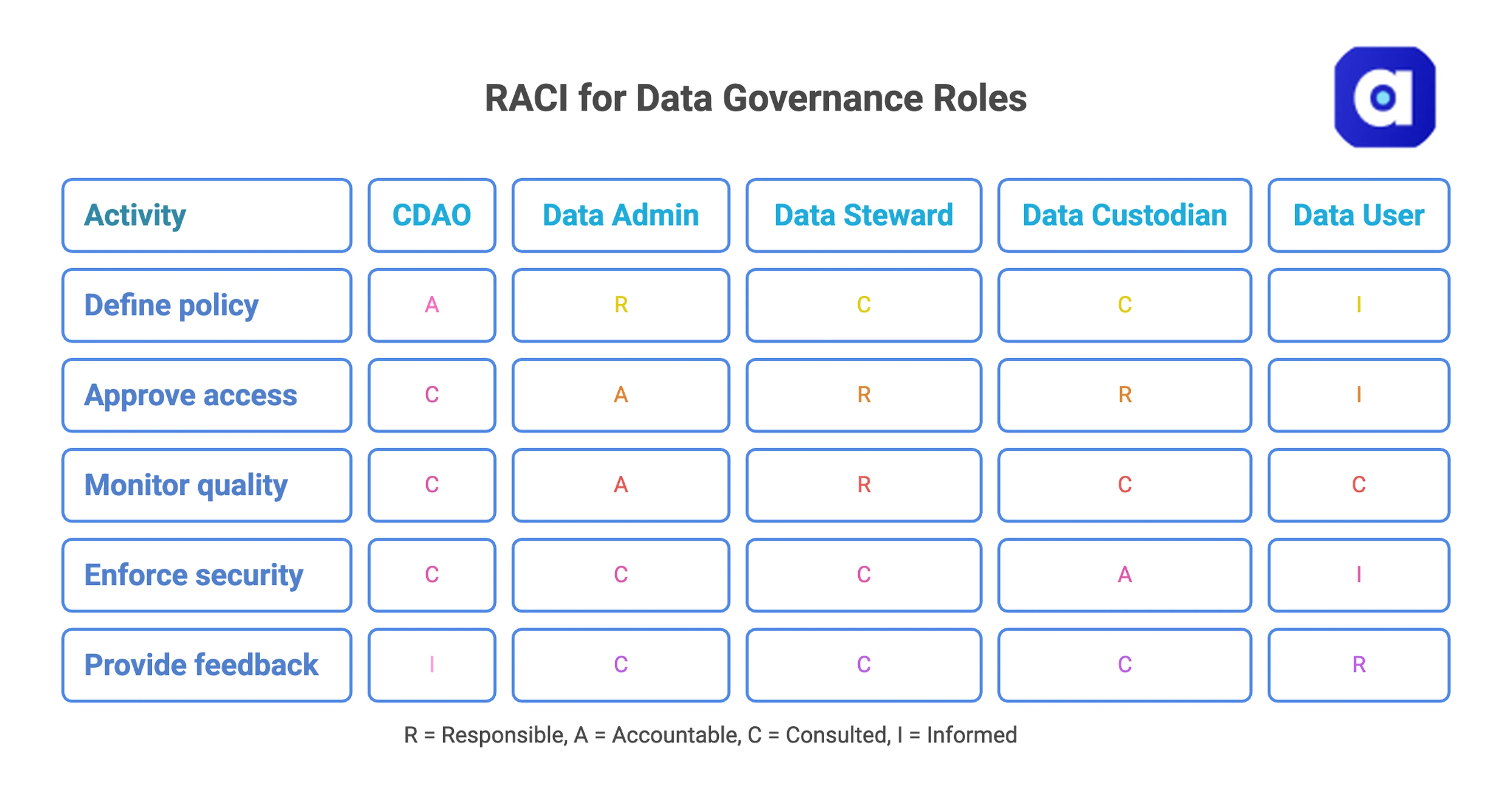
- Data Administrator (Responsible + Accountable): Operates the governance programme end‑to‑end: models data, monitors lineage, resolves conflicts, and publishes policies through automated rule engines.
- Data Steward (Responsible for Domain Excellence): Bridges business and IT: defines metrics, enforces quality rules, and sets access policies directly in the catalog so users can trust what they find.
- Data Custodian (Consulted on Technical Implementation): Owns the technical guardrails: manages encryption, tiered storage, backups, and API‑level access controls from a single console.
- Data User (Informed + Empowered): Any employee or bot that turns data into value: searches, analyses, flags issues, and follows governance training embedded in daily workflows.
What skills do data governance roles require? #
Right skill combinations determine whether governance enables or obstructs data-driven decisions.
Role | Must‑have skills | Nice‑to‑have skills |
|---|---|---|
CDAO | Storytelling, portfolio budgeting, change leadership | Risk management, AI literacy |
Data Admin | Data‑modeling, metadata design, SQL automation | DevOps, cost‑optimisation |
Data Steward | Domain expertise, glossary writing, stakeholder facilitation | Lightweight scripting (SQL/Python) |
Data Custodian | Cloud security, IAM policies, backup & DR | Infrastructure‑as‑code, ABAC/RBAC tooling |
Data User | Analytical thinking, BI tools, basic SQL | Prompt‑engineering for GenAI |
AI Gov Lead | Model cards, bias testing, incident triage | Red‑teaming, regulatory liaison |
Data Product Manager | Product road‑mapping, SLA drafting, customer research | Agile coaching, pricing models |
Tip: For hiring, aim for senior practitioners who pair domain know-how with tool fluency.
How many data governance roles do you need? #
Right-sizing prevents both bottlenecks and governance theater where roles exist without authority.
Company size | Typical staffing pattern |
|---|---|
< 200 employees | 1 CDAO (fractional), 1 Data Admin, part‑time Stewards & Custodians |
200 – 2,000 | Dedicated CDAO, 1–2 Data Admins, 3–5 Stewards, shared Custodians, no PM yet |
> 2,000 / regulated | Full team in every major domain: CDAO + Council, 5–10 Stewards, 3–4 Custodians, 1 AI Gov Lead, 1 Data PM per domain |
As the global data governance market size was estimated at USD 3.35 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.7% from 2024 to 2030, organizations are increasingly recognizing the need for structured governance teams. It is practical to start small but explicit—roles can be “hats” at first. As data products and compliance scope grow, split hats into standalone jobs.
Tip: Formalize roles only when workload or risk justifies—avoid premature hiring.
Gartner’s Inaugural Magic Quadrant for D&A Governance is Here #
In a post-ChatGPT world where AI is reshaping businesses, data governance has become a cornerstone of success. The inaugural report provides a detailed evaluation of top platforms and the key trends shaping data and AI governance.
Read the Magic Quadrant for D&A Governance
What tools do data governance roles need? #
Without strong data governance, companies risk inaccurate insights, siloed systems, and privacy issues, challenges that can derail transformation efforts. Traditional tools often make things worse by spreading cataloging, quality, policy, and collaboration across disconnected platforms. Modern teams need a unified solution like Atlan that enables seamless self-service discovery.
- Data Admins: Set a policy once; Atlan auto‑enforces it across every connected source and surfaces real‑time compliance on a live dashboard.
- Data Stewards: Add business context, trace lineage in one click, and monitor quality KPIs, all inside the catalog.
- Data Custodians: Integrate existing data stacks via APIs to manage encryption, access, and audit logs from one console.
- Data Users: Search Atlan’s Google‑like interface, explore approved datasets, and request access in two clicks.
Why unify? Teams that consolidate onto Atlan see 35 % faster time‑to‑insight and cut governance overhead by 40 %.
Tip: Fewer tools = faster onboarding and clearer ownership.
Real stories from real customers: Implement governance at scale #

Modernized data stack and launched new products faster while safeguarding sensitive data
“Austin Capital Bank has embraced Atlan as their Active Metadata Management solution to modernize their data stack and enhance data governance. Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics, highlighted, ‘We needed a tool for data governance… an interface built on top of Snowflake to easily see who has access to what.’ With Atlan, they launched new products with unprecedented speed while ensuring sensitive data is protected through advanced masking policies.”

Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics
Austin Capital Bank
🎧 Listen to podcast: Austin Capital Bank From Data Chaos to Data Confidence
Curious which components could unlock the same speed for your team?
Book a Personalized Demo →
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
“Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, ‘Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.’ With Atlan’s integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate.”

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare’s Data Renaissance with Atlan
What are common data governance pitfalls? #
Pitfall | Warning Signs | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
Over-Centralization | Request resolution >2 weeks, shadow IT solutions, "bureaucracy" complaints | User frustration, governance avoidance, policy violations | Federated model: 80% decisions at steward level, clear escalation paths |
Authority Without Accountability | Roles exist on charts but lack budget/decision rights | Governance theater, ignored policies, false security | Document RACI matrix, provide budget authority, tie to performance reviews |
Tool Sprawl | Multiple data inventories, user confusion, no unified visibility | Information silos, duplicated effort, inconsistent enforcement | Unified platform or strong API integration between existing tools |
Governance Theater | Meetings without decisions, acknowledged but unfollowed policies | Audit risk, cultural cynicism, wasted resources | Link performance to business outcomes, executive enforcement of decisions |
Role Boundary Confusion | Issues falling between roles, finger-pointing during incidents | Accountability gaps, duplicated work, slow resolution | Detailed RACI scenarios, regular cross-role collaboration, shared dashboards |
Top reported benefits of data governance programs include improved quality of data analytics and insights (58%), improved data quality (58%), and increased collaboration (57%). Achieving these outcomes starts with building the right team to lead and sustain governance efforts.
Tip: Run a semi‑annual “tool audit” to retire redundant platforms before they create confusion.
How does AI transform data governance roles? #
AI shifts governance from reactive compliance to predictive risk management and automated enforcement.
- New accountability layer – AI Governance Lead owns model cards, bias audits, incident playbooks.
- Hybrid human‑AI workflows – Bots classify data and draft policies; humans validate edge cases.
- Prompt governance – Stewards curate sanctioned prompts, just as they curate metrics.
- Continuous monitoring – Custodians stream model‑telemetry into the observability stack for real‑time drift alerts.
- Value acceleration – Product Managers package governed data + co mpliant models as revenue‑ready “data products.”
By 2025, AI will play a bigger role in data governance, with ethics and explainability at the forefront. As data volume triples from 2020 levels, traditional systems will strain. Future‑ready teams view GenAI as an amplifier, not a threat: automate the toil, elevate the talent.
Ready to define your governance team? #
While each team member has a distinct role, these data governance roles depend on each other. Everyone must collaborate effectively to help their organization achieve its business and data goals. Despite their unique skill sets, these roles within the data governance team achieve the best results through collaboration, sharing, and transparent communication.
Set up your data governance team with expert help
Book a Personalized Demo →FAQs about data governance roles #
What is a data governance role? #
A data governance role refers to a specific position within an organization responsible for managing, protecting, and ensuring the quality of data. Key roles include data admin, data steward, data custodian, and data user, each with distinct responsibilities that contribute to effective data governance.
What are the 4 pillars of data governance? #
The four pillars of data governance typically include data quality, data management, data security, and compliance. These pillars ensure that data is accurate, accessible, secure, and used in accordance with regulatory requirements, fostering a culture of accountability and trust.
What is the role of IT in data governance? #
The IT department plays a critical role in data governance by implementing technical solutions for data management, security, and compliance. IT professionals collaborate with data stewards and custodians to ensure that data governance policies are enforced and that data systems are secure and efficient.
Who should be in charge of data governance? #
Data governance should ideally be overseen by a dedicated data governance team, which may include a Chief Data Officer (CDO) or a data governance committee. This team is responsible for establishing policies, standards, and practices that ensure effective data management across the organization.
Can one person handle multiple data governance roles? #
Yes, especially in smaller organizations. Senior data professionals often combine Administrator and Custodian duties, while business analysts serve as both Stewards and Users. Key is documenting which responsibility applies to each decision.
How do governance roles differ from data engineering roles? #
Governance focuses on policy, quality, compliance while engineering builds technical infrastructure. Governance provides “what and why” through business context, engineering delivers “how” through technical implementation.
What’s the biggest governance implementation mistake? #
Creating accountability without authority. Roles need decision power, budget allocation, executive backing to drive change. Governance theater—roles existing only for audits, increases risk through false confidence.
How often should data governance role definitions be updated? #
Annually or during major changes: new regulations, technology adoption, organizational restructuring. AI advancement may accelerate to semi-annual reviews as automation capabilities evolve rapidly.














