What is data fabric according to Gartner?
Permalink to “What is data fabric according to Gartner?”Gartner defines data fabric as a modern architectural approach that simplifies data access in complex, distributed environments.
According to Gartner, the data fabric isn’t a single tool or technology, but rather “a new and evolving data management design” for attaining flexible, reusable, and augmented data integration pipelines. It uses knowledge graphs, semantics and active metadata-based automation for faster data access and sharing.
The concept addresses a fundamental challenge facing enterprises: how to collect, connect, integrate, and deliver data from heterogeneous sources without creating additional silos.
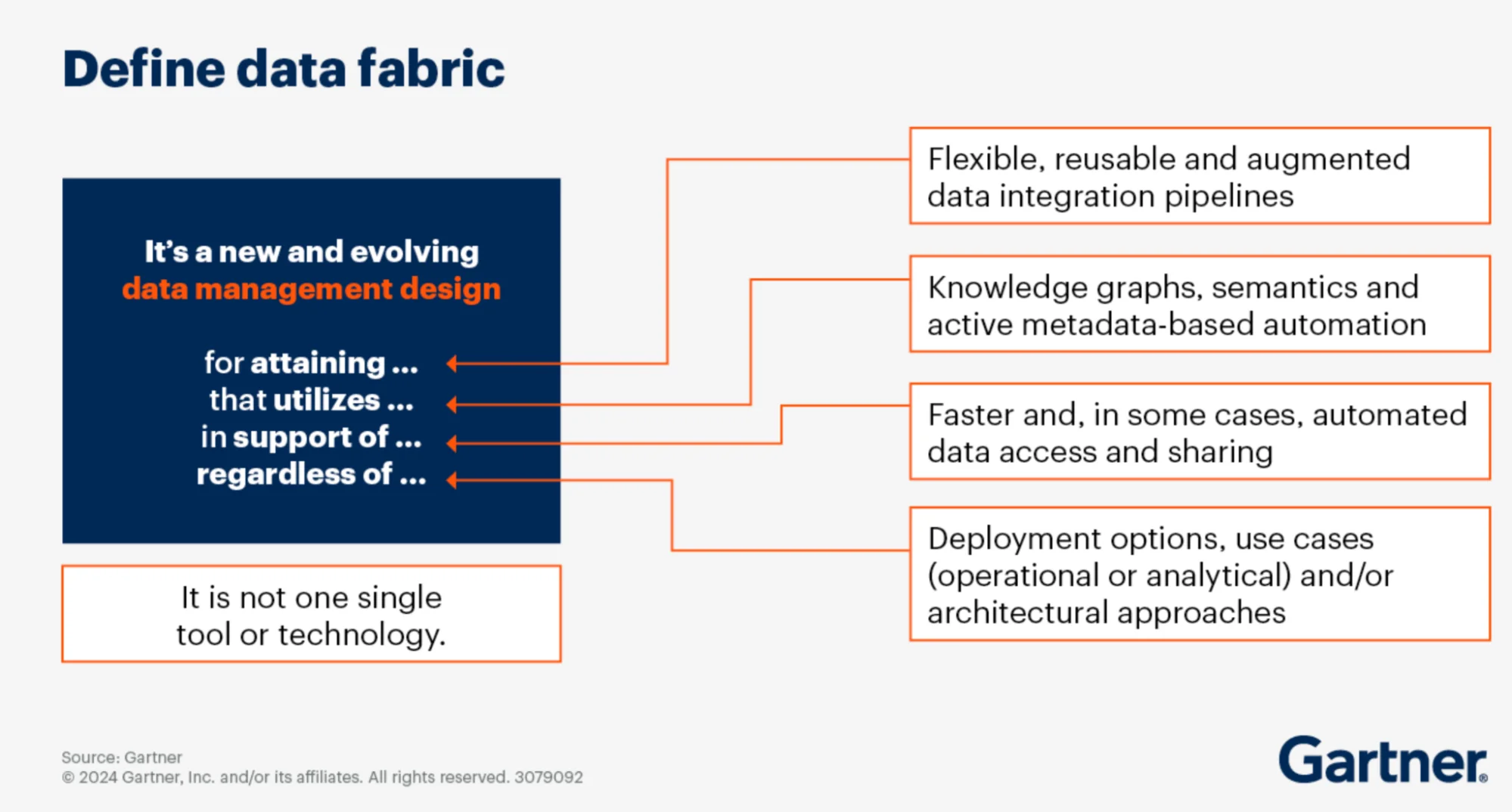
How Gartner defines the data fabric. Source: Gartner.
The defining characteristic of Gartner’s data fabric concept is its use of continuous metadata analytics.
Unlike traditional integration approaches that require manual mapping and maintenance, data fabrics leverage machine learning to automatically discover patterns in metadata. This enables the system to suggest optimal integration paths and adapt as data environments evolve.
Gartner uses the analogy of a self-driving car to illustrate how the data fabric operates.
“Just as an autonomous vehicle uses advanced technology to perceive its environment and navigate without human intervention, a data fabric employs machine learning capabilities to autonomously access, consolidate, and manage data.” - Gartner on how the data fabric operates
What are the three core characteristics of the data fabric, emphasized by Gartner?
Permalink to “What are the three core characteristics of the data fabric, emphasized by Gartner?”1. Intelligent automation: The architecture employs AI and machine learning to automate data profiling, schema discovery, and pipeline creation. These capabilities reduce the manual effort traditionally required from data engineers.
2. Unified semantic layer: Data fabric creates consistent meaning across disparate systems. Business users can access data using familiar terminology rather than needing to understand technical implementations.
3. Adaptive integration: As new data sources emerge or existing sources change, the fabric adapts integration patterns automatically. This reduces the technical debt that accumulates in traditional integration architectures.
According to Gartner’s research framework, organizations implementing the data fabric aim to simplify integration infrastructure while reducing the time deficit between data requests and fulfillment. The architecture supports both batch and real-time integration styles across on-premises and cloud environments.
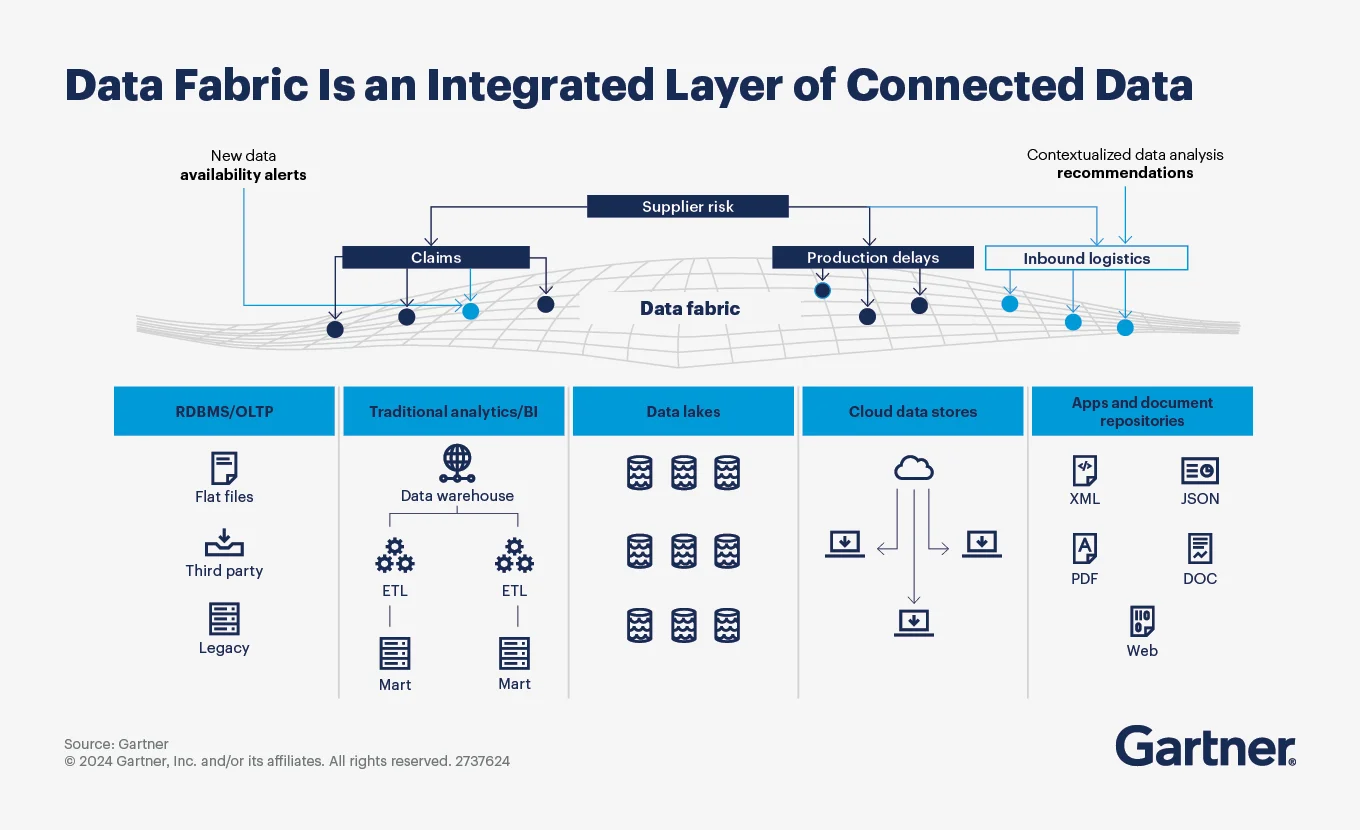
How the data fabric architecture can establish an integrated layer of connected data. Source: Gartner.
Why does Gartner position the data fabric as strategically critical?
Permalink to “Why does Gartner position the data fabric as strategically critical?”Gartner’s research identifies data fabric as a solution to mounting organizational challenges in data management. The strategic importance stems from measurable efficiency gains and fundamental shifts in how organizations can operate with data.
“Organizations can leverage data fabrics to augment (or completely automate) data integration design and delivery, while capitalizing on sunk costs in existing data lakes and data warehouses.” - Gartner on the benefits of implementing the data fabric
The seven biggest strategic benefits include:
- Eliminating data siloes by providing unified, integrated access regardless of where data physically resides or its original format.
- Converting passive metadata into active metadata, continuously exposing connections between your organization’s varied data assets and their users.
- Enabling nontechnical business users to quickly find, integrate, analyze and share data–subject matter experts can use semantic search to better understand data.
- Providing productivity advantages through automated data access and integration for data management teams.
- Increasing engineering agility (from automated integration design and delivery) empowering data engineers to act quickly on data requests.
- Delivering faster time to insight and improved utilization of data assets for D&A use cases.
- Reducing infrastructure costs with more effective data design, delivery, and use.
Attending Gartner Summit Orlando? Don't miss the sessions that matter most to you
Build Personalized AgendaWhat are the key challenges in data fabric adoption?
Permalink to “What are the key challenges in data fabric adoption?”Gartner acknowledges that implementing data fabric involves significant organizational and technical challenges. Understanding these obstacles helps organizations prepare realistic implementation plans.
1. Securing stakeholder support
Permalink to “1. Securing stakeholder support”Data fabric implementation requires shifts in both technology and organizational culture. Success depends on buy-in from multiple levels:
- Executive sponsors who commit budget and strategic priority
- Data platform teams who maintain and evolve the architecture
- Domain experts who contribute business context and metadata
- End users who adopt new access patterns and tools
Without broad support, data fabric initiatives risk becoming isolated IT projects that fail to deliver business value.
2. An off-the-shelf solution doesn’t exist
Permalink to “2. An off-the-shelf solution doesn’t exist”Organizations cannot purchase a complete data fabric as a packaged product. Gartner frames data fabric as a composable design pattern rather than a single technology.
The composable nature means each organization’s data fabric looks different based on specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and maturity level.
Implementation requires selecting and integrating multiple components like data catalogs, integration tools, and metadata management platforms. Organizations must evaluate which existing investments can be leveraged and where new capabilities are needed.
3. Metadata scarcity and quality
Permalink to “3. Metadata scarcity and quality”The data fabric depends on comprehensive, high-quality metadata to function effectively.
Many organizations face significant gaps:
- Technical metadata may be incomplete or inconsistent across systems.
- Business metadata defining meaning and context often exists only in tribal knowledge.
- Operational metadata about usage patterns and performance requires instrumentation many organizations lack.
- Social metadata such as ownership, endorsements, comments, and usage signals is fragmented or missing, making it hard to understand trust, relevance, and collaboration around data.
Collecting, managing, and continuously updating metadata represents substantial work. Organizations must establish processes for metadata governance, quality assurance, and enrichment as part of data fabric implementation.
4. Specialized skill requirements
Permalink to “4. Specialized skill requirements”Building and maintaining data fabrics requires expertise in emerging technologies. Organizations need skills in:
- Graph databases and knowledge graph construction
- Machine learning model development and operations
- API design and microservices architecture
- Cloud-native data platform engineering
The talent market for these specialized skills remains competitive. Organizations must invest in training existing staff or compete for scarce external talent.
What are Gartner’s six implementation principles for data fabric?
Permalink to “What are Gartner’s six implementation principles for data fabric?”In their comprehensive guide “Data and Analytics Essentials: How to Define, Build, and Operationalize a Data Fabric,” Gartner provides detailed recommendations for successful implementation.
These six principles form the foundation of effective data fabric architectures.
Step 1. Gather and analyze all metadata types
Permalink to “Step 1. Gather and analyze all metadata types”“For an effective data fabric implementation, start with metadata.” - Gartner on data fabric implementation
Comprehensive metadata collection forms the foundation of data fabric functionality. Organizations must capture and analyze multiple metadata categories:
- Technical metadata describes schemas, data types, and system configurations.
- Business metadata provides definitions, ownership, and business rules.
- Operational metadata tracks usage patterns, performance metrics, and data quality measures.
- Social metadata captures context, such as asset owners, certifications, comments, ratings, endorsements, and collaboration activity that indicate trust and relevance.
Step 2. Shift from passive to active metadata
Permalink to “Step 2. Shift from passive to active metadata”Gartner emphasizes transforming passive metadata documentation into active metadata that drives automation.
Passive metadata simply records information about data—its source, creation date, or format. Active metadata provides context, relationships, and lineage that enable intelligent automation.
This transformation represents a fundamental shift in metadata management:
- Visualization: Make metadata relationships visible through knowledge graphs.
- Metrics generation: Derive quantitative measures from metadata patterns.
- AI enablement: Feed metadata to machine learning algorithms that improve over time.
- Continuous updates: Keep metadata current through automated discovery and inference.
Organizations implementing active metadata can automate tasks that previously required manual analysis and decision-making.
Step 3. Build and maintain knowledge graphs
Permalink to “Step 3. Build and maintain knowledge graphs”Knowledge graphs model relationships between data assets, creating a semantic network across the organization. These graphs connect datasets, business terms, applications, and people to show how everything relates.
Creating knowledge graphs requires:
- Identifying entities and relationships worth modeling.
- Establishing ontologies that define connection types.
- Ingesting metadata from source systems.
- Enriching graphs with business context and usage patterns.
Curating knowledge graphs represents ongoing work rather than one-time implementation. As new data sources emerge and relationships evolve, the graph requires updates to maintain accuracy and completeness.
Step 4. Establish robust data integration backbone
Permalink to “Step 4. Establish robust data integration backbone”Here’s how Gartner distinguishes between data ingestion and data integration:
- Ingestion moves data into systems.
- Integration consolidates data from various sources into unified, consistent views that enable analysis.
A robust integration backbone supports multiple integration patterns:
- Batch processing for large-scale transformations
- Real-time streaming for continuous data flows
- CDC (change data capture) for incremental updates
- Virtualization for logical integration without data movement
The backbone must handle both structured data from databases and unstructured content from documents, images, and other sources. Flexibility across integration methods enables organizations to choose appropriate patterns for different use cases.
Step 5. Adopt open standards and protocols
Permalink to “Step 5. Adopt open standards and protocols”Implementing data fabric requires embracing standards that enable interoperability. Gartner recommends protocols like Open Data Discovery that facilitate metadata exchange across systems.
Adopting open API architectures enables seamless integration between applications. APIs provide programmatic access to data fabric capabilities, allowing developers to embed functionality into workflows and applications. This architectural approach promotes flexibility and prevents vendor lock-in.
Step 6. Invest in augmented data catalogs
Permalink to “Step 6. Invest in augmented data catalogs”Gartner identifies augmented data catalogs as essential infrastructure for data fabric implementations. These catalogs serve as centralized metadata repositories with advanced capabilities powered by machine learning.
Augmented catalogs go beyond basic metadata storage to provide:
- Intelligent search that understands context and intent
- Automated classification of data assets
- Recommendations for relevant datasets based on usage patterns
- Impact analysis showing downstream effects of changes
“The augmented data catalog uses AI/ML to connect to different data sources and find, tag and annotate them. The resulting data catalog curates an inventory of distributed data assets and their associated passive metadata.” - Gartner on data fabric implementation
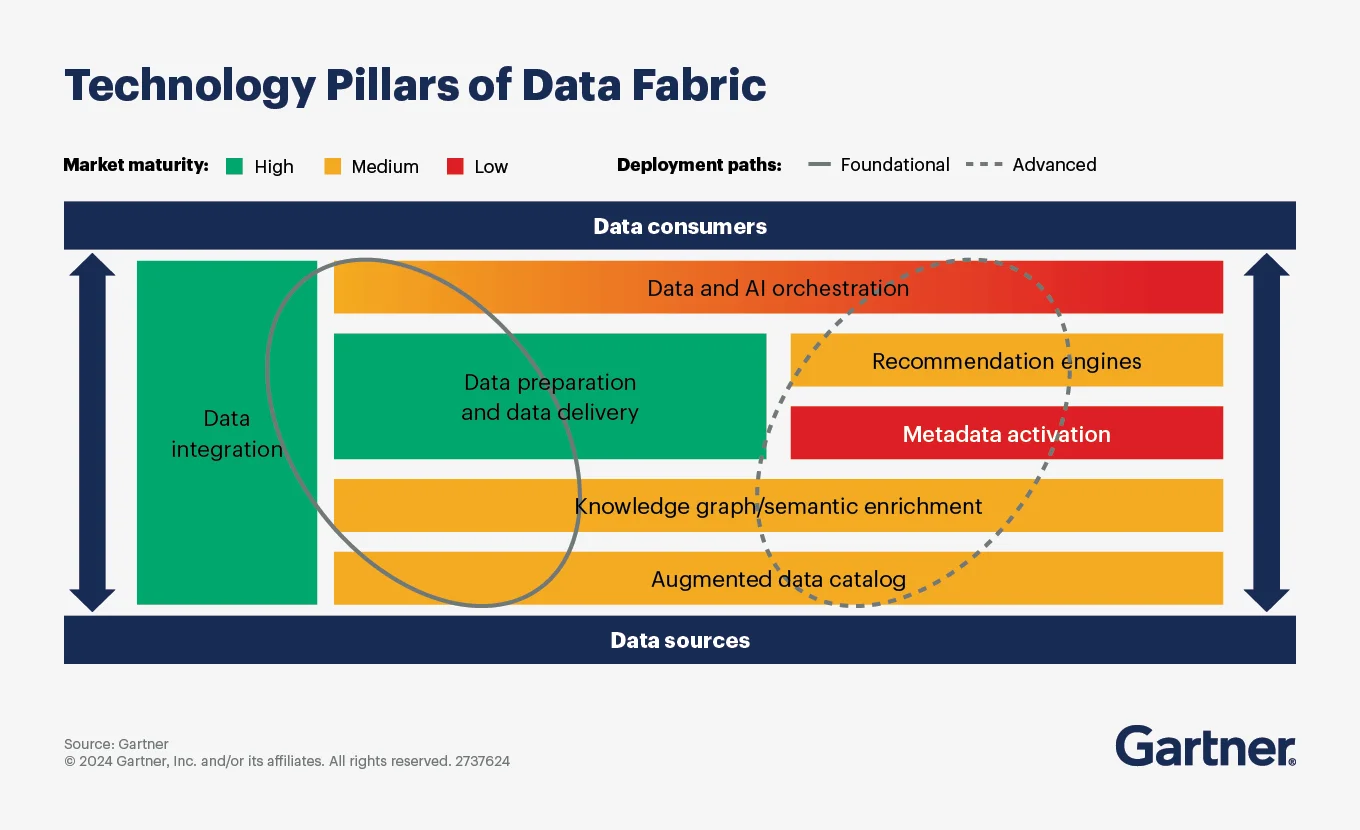
The augmented data catalog is central to implementing the data fabric architecture. Source: Gartner.
How do modern platforms enable Gartner’s data fabric vision?
Permalink to “How do modern platforms enable Gartner’s data fabric vision?”Implementing Gartner’s data fabric principles requires platforms purpose-built for active metadata management and intelligent automation. Traditional data management tools weren’t designed for the continuous analytics and adaptation that data fabrics demand.
Modern metadata management platforms like Atlan address this gap by centralizing metadata from across the data stack. Rather than metadata existing in isolated silos within individual tools, these platforms create unified repositories that enable cross-system intelligence.
The automation capabilities Gartner emphasizes become practical through several technical approaches:
- Automated lineage tracking maps data flows from source through transformation to consumption without manual documentation. This visibility enables root cause and impact analysis.
- Machine learning-driven classification automatically tags data based on content, usage patterns, and relationships. Classification that once required armies of data stewards now happens continuously as new data emerges.
- Policy enforcement through metadata allows governance rules to execute automatically. When sensitive data moves or combines in ways that violate policies, the system detects and responds without human monitoring.
Organizations implementing these capabilities report significant outcomes. Teams reduce time spent searching for data by 40-60%. Policy compliance becomes proactive rather than reactive. Data quality issues surface earlier when automated lineage connects quality metrics to root causes.
The shift to active metadata also changes how organizations approach data governance. Rather than governance as a separate layer imposed on top of data operations, metadata-driven governance embeds into workflows. Access controls, quality checks, and compliance measures become native to how data moves through systems.
See how Atlan’s active metadata platform helps organizations implement Gartner’s data fabric principles at scale. Book a demo
Real stories from real customers: Future-proofing your data ecosystem for modern architectures and AI use cases
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Future-proofing your data ecosystem for modern architectures and AI use cases”From siloed systems to unified access: How Dropbox streamlined data governance and built the foundation for their data fabric approach
Permalink to “From siloed systems to unified access: How Dropbox streamlined data governance and built the foundation for their data fabric approach”“We needed a platform that could handle our scale while keeping data accessible and governed. The ability to automate lineage and see real-time impact across our entire data ecosystem changed how our teams work together.” — Data Engineering Leader, Dropbox
Atlan's impact on Dropbox's data governance efforts
Watch HowFrom complex in-house systems to governed AI, future-proof your data stack
Permalink to “From complex in-house systems to governed AI, future-proof your data stack”“Atlan is built on Open API architecture, which gives us extensibility across the data stack. That was a game changer.” — Mihir Modi, Data Governance Manager, Fox
Extensibility across Fox's data stack with Atlan's open API architecture
Watch How
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
"Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. 'Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,' Kiwi.com shared. Atlan's intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams."
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan
Ready to move forward with your data fabric implementation?
Permalink to “Ready to move forward with your data fabric implementation?”Data fabric represents a fundamental shift from rigid integration architectures to flexible, intelligent systems that adapt to change.
Gartner’s framework provides organizations with concrete principles for implementation—from comprehensive metadata management to automated integration patterns. The six core principles work together to create architectures that reduce manual effort while improving data accessibility and governance.
Success requires commitment beyond technology adoption. Organizations must secure stakeholder buy-in, address metadata quality systematically, and invest in building necessary capabilities.
The composable nature of data fabric means each organization’s implementation reflects specific needs and constraints. Modern platforms that embrace active metadata management and intelligent automation make Gartner’s vision practical for enterprises ready to move beyond traditional approaches.
Atlan helps organizations implement data fabric principles with automated metadata management and governance.
Let's help you build it
Book a Personalized DemoFAQs about Gartner data fabric
Permalink to “FAQs about Gartner data fabric”1. What is Gartner’s definition of data fabric?
Permalink to “1. What is Gartner’s definition of data fabric?”The data fabric is an emerging data management design that uses metadata to automate data management tasks and eliminate manual data integration tasks.
Unlike traditional approaches, data fabric creates a unified layer of interconnected data that adapts as data environments change without requiring constant manual reconfiguration.
2. How does data fabric differ from traditional data integration?
Permalink to “2. How does data fabric differ from traditional data integration?”Traditional integration requires manual mapping between systems and breaks when source systems change.
Data fabric uses active metadata and machine learning to discover integration patterns automatically. The architecture adapts to changes in source systems without manual intervention.
Traditional approaches also separate integration from governance, while data fabric embeds governance through metadata-driven policies.
3. What are the main benefits of implementing data fabric according to Gartner?
Permalink to “3. What are the main benefits of implementing data fabric according to Gartner?”Gartner research indicates data fabric can reduce time spent on data management tasks by up to 50%. Organizations achieve faster time to insight by eliminating bottlenecks in data access. Business users gain self-service capabilities without depending on IT for every integration need.
The architecture also reduces technical debt by replacing brittle point-to-point integrations with adaptive patterns.
4. Is data fabric the same as data mesh?
Permalink to “4. Is data fabric the same as data mesh?”No, it’s not. Data fabric and data mesh represent independent architectural approaches. Data mesh emphasizes decentralized ownership where domain teams manage their own data products.
Data fabric focuses on creating unified access across distributed systems through intelligent integration of existing tools and platforms.
Organizations can implement aspects of both approaches—using mesh principles for ownership while leveraging fabric capabilities for integration.
5. What role do data catalogs play in Gartner’s data fabric framework?
Permalink to “5. What role do data catalogs play in Gartner’s data fabric framework?”Gartner identifies augmented data catalogs as foundational infrastructure for the data fabric. Modern catalogs use machine learning to classify data, recommend connections, and maintain knowledge graphs.
Such a catalog would serve as the centralized metadata repository that enables automated discovery and integration. It provides the semantic layer that translates between business terminology and technical implementations.
6. How long does it take to implement a data fabric?
Permalink to “6. How long does it take to implement a data fabric?”Implementation timelines vary based on organizational size, existing infrastructure maturity, and scope. Gartner recommends phased approaches starting with specific use cases rather than enterprise-wide deployments.
Organizations typically see initial value within 3-6 months by focusing on high-impact domains. Full enterprise implementation typically spans 18-36 months as organizations expand coverage and mature capabilities.
Share this article



















