Data Governance Councils in 2025: Responsibilities, Benefits, Tooling & Setup Guide
What does a data governance council do?
Permalink to “What does a data governance council do?”Summarize and analyze this article with 👉 🔮 Google AI Mode or 💬 ChatGPT or 🔍 Perplexity or 🤖 Claude or 🐦 Grok (X) .
“The Data Governance Council manages data governance initiatives, issues, and escalations in an effort to improve and promote data quality and integrity, appropriate and ethical use of data, compliance, and data literacy and awareness.” - University of Wisconsin-Madison on the purpose of a data governance council
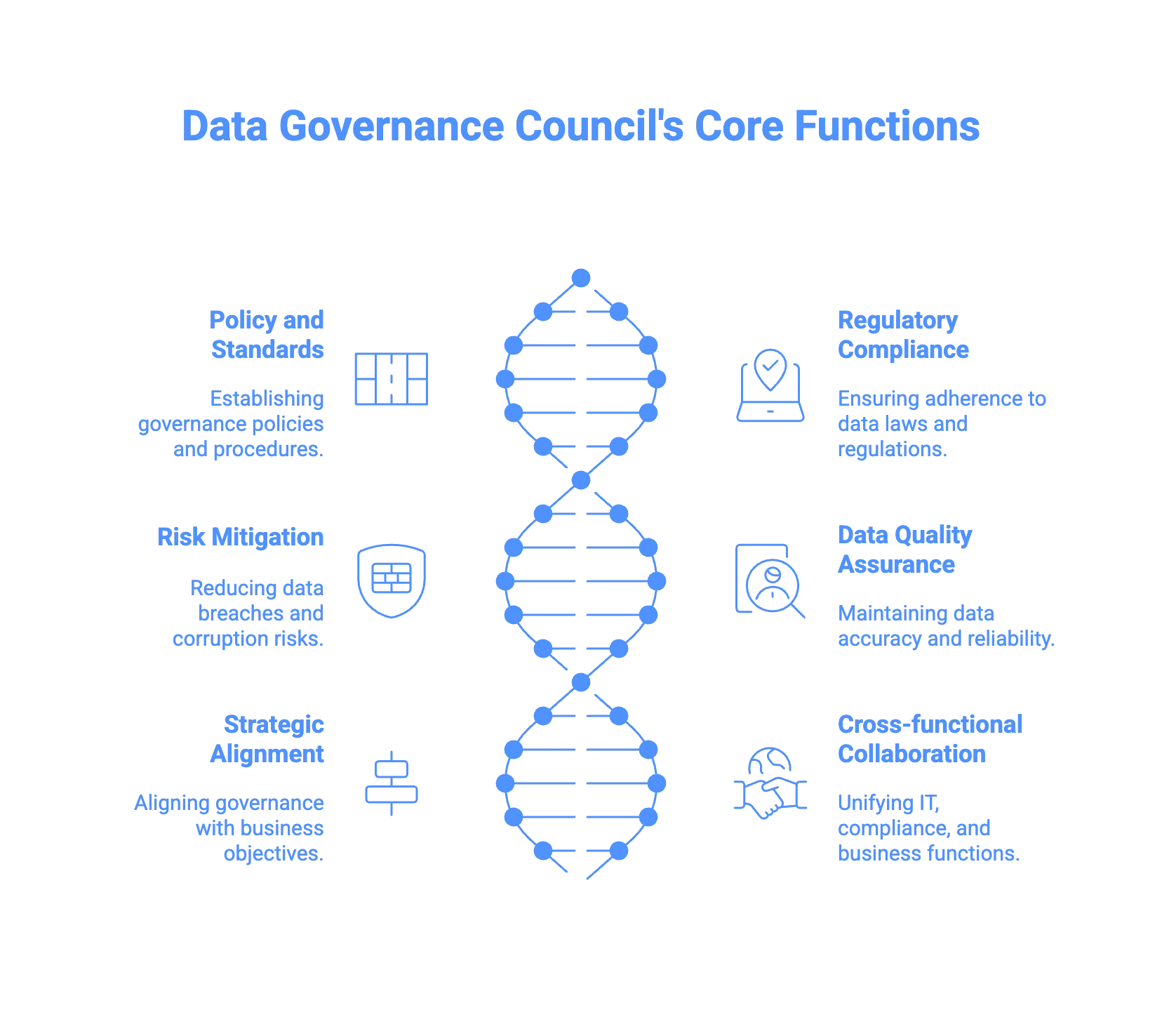
In other words, the Data Governance Council (DGC) oversees and manages your organization’s data as a strategic asset. The six vital purposes of a data governance council are:
- Policy and standards setting: Establishing governance policies, procedures, and standards that align with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring compliance with data-specific laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other industry regulations through continuous monitoring and adaptation.
- Risk mitigation: Reducing risks of breaches, loss, or corruption with strong governance frameworks.
- Data quality assurance: Maintaining accuracy, consistency, and reliability across organizational data.
- Strategic alignment: Ensuring governance supports long-term business goals and growth.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Bringing IT, compliance, and business functions together for unified practices.
What does a data governance council do? - Image by Atlan.
Who are the key members of a data governance council?
Permalink to “Who are the key members of a data governance council?”“The Data Governance Council consists of designated officials who have planning, policy-level, and management responsibility for data within their functional areas.” - University of Wisconsin-Madison on who is a part of a data governance council
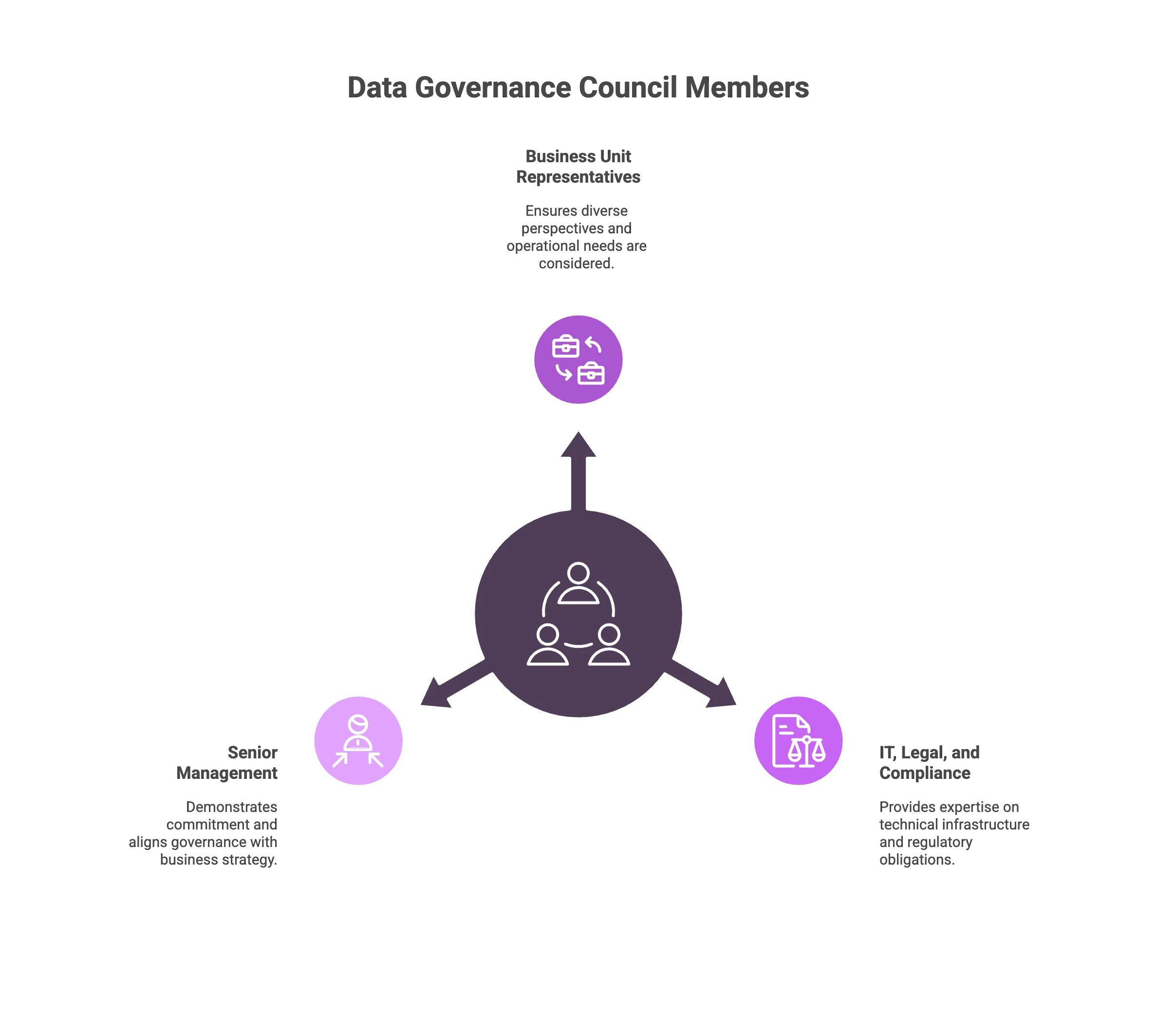
In other words, a Data Governance Council should bring together senior leaders and domain experts who can provide authority, oversight, and cross-functional alignment. Key members typically include:
-
Representatives from various business units: Ensures diverse perspectives and operational needs are considered in governance decisions.
Examples: Finance, Operations, Marketing, Product, Customer Success leaders
-
IT, legal, and compliance representatives: Provides expertise on technical infrastructure, security, and regulatory obligations.
Examples: CIO/CTO delegates, data architects, legal counsel, compliance officers, risk/security leaders
-
Senior management or executives: Demonstrates commitment, secures resources, and aligns governance with business strategy.
Examples: Chief Data Officer, COO, CFO, or a designated executive sponsor
Members of a data governance council - Image by Atlan.
What are the eight key responsibilities of a data governance council?
Permalink to “What are the eight key responsibilities of a data governance council?”The Data Governance Council (DGC) sets direction and provides oversight, ensuring that data is governed responsibly and strategically across the enterprise.
In essence, the DGC acts as the steward and strategist of data, positioning it as both a protective shield and a propellant for organizational success.
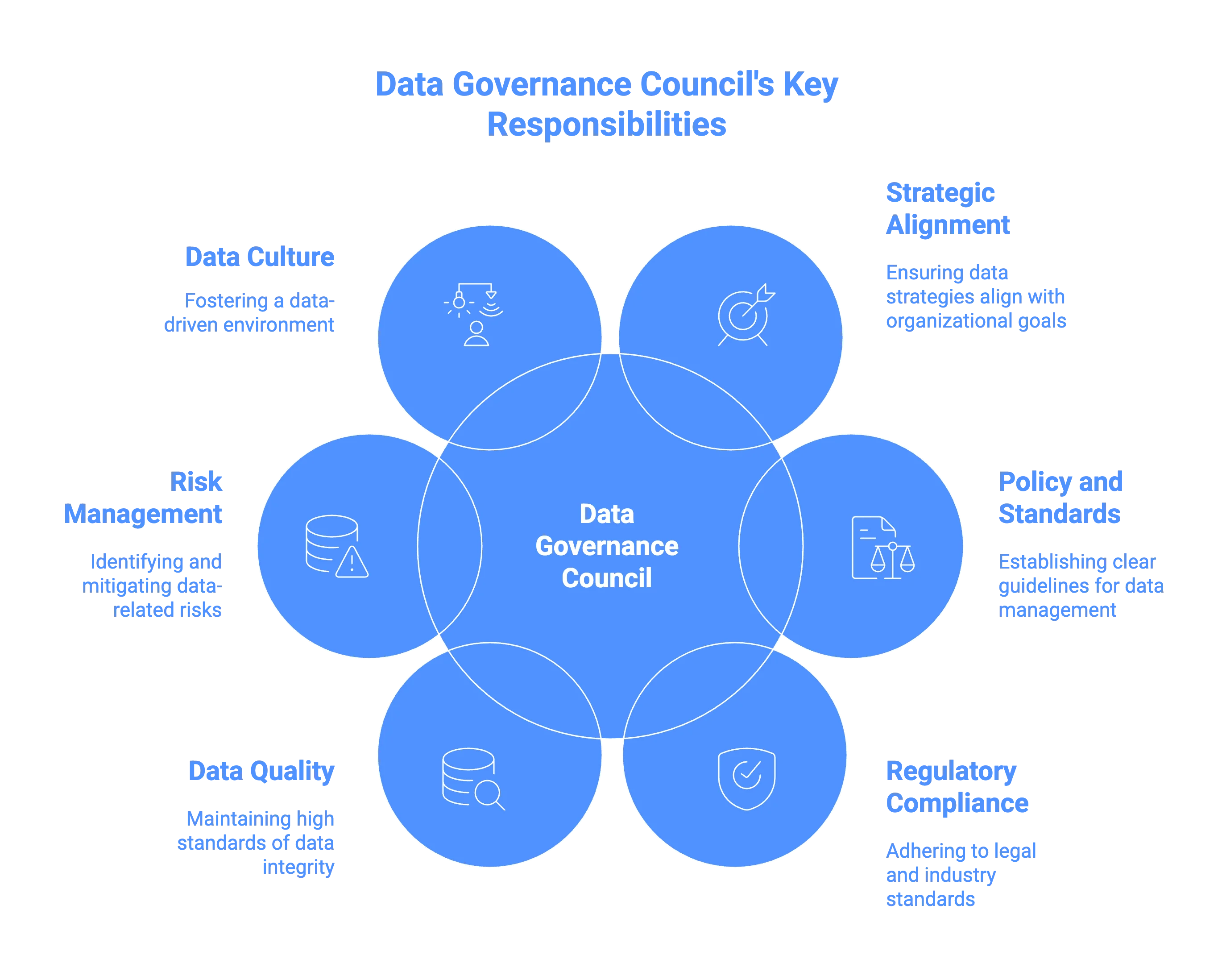
Its eight key responsibilities include:
- Strategic alignment and innovation
- Comprehensive guidelines for data management and governance
- Policy and standards setting
- Regulatory compliance and risk management
- Data quality and integrity
- Supervision of various governance initiatives
- Management of data-related risks
- Establishment of a data-driven culture
8 key responsibilities of a data governance council - Image by Atlan.
1. Strategic alignment and innovation
Permalink to “1. Strategic alignment and innovation”The DGC ensures that data governance is not an isolated function but is intrinsically linked to the organization’s broader goals. This alignment helps in leveraging data as a strategic asset to drive growth and innovation.
Since AI use has become mainstream, the council should also ensure that AI initiatives support business priorities, by asking questions, such as:
- Does this AI use case align with strategy?
- Is it compliant and ethical?
- Does it unlock business value without undermining customer trust?
2. Comprehensive guidelines for data management and governance
Permalink to “2. Comprehensive guidelines for data management and governance”The Data Governance Council (DGC) formulates overarching guidelines that detail how data is to be collected, processed, stored, and shared.
This involves understanding the organization’s specific needs, industry requirements, and legal obligations, and creating policies that reflect these nuances.
3. Policy and standards setting
Permalink to “3. Policy and standards setting”The DGC works to establish common terminologies, definitions, and processes that prevent miscommunication and misunderstanding.
The council defines governance rules and standards to ensure there’s consistency and reliability in organization-wide data handling practices.
The council should extend its guidelines to cover AI-specific data use — for example:
- Defining acceptable use of AI/ML models (training, validation, deployment).
- Setting standards for explainability, fairness, and bias mitigation.
- Establishing rules for what data can or cannot be fed into AI systems.
4. Regulatory compliance and risk management
Permalink to “4. Regulatory compliance and risk management”The council ensures that organizational policies align with relevant data protection laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, industry-specific mandates, and AI-related regulations.
It provides oversight to guarantee that compliance requirements are reflected in governance frameworks.
With rising AI use, the council is also responsible for ensuring data used in AI models complies with privacy, security, and ethical standards. This requires ongoing monitoring and enforcement workflows to be set up.
5. Data quality and integrity
Permalink to “5. Data quality and integrity”The council sets expectations for data accuracy, consistency, and reliability across the enterprise.
It defines what “fit-for-purpose” data looks like, guiding teams in implementing quality checks and integrity controls to keep data trustworthy.
6. Supervision of various governance initiatives
Permalink to “6. Supervision of various governance initiatives”The council monitors the progress of governance programs, ensuring they stay aligned with business priorities. It doesn’t execute projects directly but holds teams accountable for delivery, outcomes, and alignment with strategic goals.
7. Management of data-related risks
Permalink to “7. Management of data-related risks”The council identifies potential risks such as data breaches, misuse, or loss, and establishes policies to mitigate them. It provides oversight on risk posture, while operational teams implement the technical and procedural safeguards.
The council will also oversee setting risk management policies for AI outputs (e.g., avoiding opaque black-box decisions in critical areas like finance or healthcare).
8. Establishment of a data-driven culture
Permalink to “8. Establishment of a data-driven culture”The DGC champions data literacy and awareness, encouraging stakeholders across business, IT, and compliance to use data responsibly.
The council sets the tone for cultural change by emphasizing the strategic value of data and supporting education initiatives. To this end, it can organize workshops, provide resources, and build transparent communication practices.
What are the biggest benefits of setting up a data governance council?
Permalink to “What are the biggest benefits of setting up a data governance council?”A data governance council strengthens how organizations manage, protect, and use their data. Its biggest benefits include:
- Improved data quality and reliability: Trusted, accurate data that powers better insights.
- Reduced data-related risks and lower costs: Strong governance minimizes breaches, inefficiencies, and compliance penalties.
- Enhanced decision-making: High-quality data enables leaders to make informed strategic and operational choices.
- Increased business value from data assets: Unlocks data’s potential for innovation, new opportunities, and competitive advantage.
- Strategic alignment: Ensures governance initiatives directly support organizational goals.
- Customer and stakeholder trust: Builds confidence with regulators, partners, and customers.
- Innovation and competitive advantage: High-quality, accessible data fuels faster experimentation and growth.
How does AI transform data governance councils?
Permalink to “How does AI transform data governance councils?”AI strengthens the oversight role of Data Governance Councils by giving them real-time visibility, predictive insights, and automated monitoring capabilities.
It equips councils with sharper tools to oversee compliance, safeguard trust, and extend governance into the AI era.
Key areas of impact:
- Automated compliance monitoring: AI systems can continuously scan data flows for privacy risks, sensitive data exposure, or non-compliant activity.
- Data quality oversight: AI augmented data governance platforms can detect anomalies, missing values, or inconsistencies faster than manual checks
- Risk assessment: AI-driven analytics help identify hidden risks, such as unusual access patterns or potential bias in datasets.
- Decision support: By surfacing trends, predictions, and simulations, AI-augmented platforms can equip councils with evidence-based insights, enabling them to align governance decisions with business goals more quickly.
- AI governance: Councils also have an expanded mandate – overseeing the responsible use of AI. This includes extending traditional data governance into the AI space, ensuring that the data fueling AI systems (and their outputs) remain trustworthy, compliant, and aligned with organizational values.
How to create a data governance council: A 7-step approach
Permalink to “How to create a data governance council: A 7-step approach”Establishing a Data Governance Council (DGC) requires planning, sponsorship, and cross-functional collaboration. These seven steps provide a practical roadmap.
Step 1: Assess organizational needs
Permalink to “Step 1: Assess organizational needs”Define the scope and goals of the council. Identify challenges such as compliance gaps or data quality issues, and determine the resources required — people, budget, and technology.
Step 2: Secure leadership buy-in
Permalink to “Step 2: Secure leadership buy-in”Build a strong business case that highlights benefits like reduced risk and improved decision-making. Gain executive sponsorship to ensure organizational priority.
Step 3: Define structure and membership
Permalink to “Step 3: Define structure and membership”Outline the council’s structure, roles, and reporting lines. Select members from IT, business, legal, compliance, and operations to ensure diverse perspectives.
Step 4: Develop policies and guidelines
Permalink to “Step 4: Develop policies and guidelines”Draft governance policies and standards that reflect regulatory requirements and business objectives. Define KPIs and metrics to track effectiveness.
Step 5: Establish communication and collaboration channels
Permalink to “Step 5: Establish communication and collaboration channels”Create clear communication pathways across teams. Hold regular meetings and workshops to encourage collaboration and consistent data practices.
Step 6: Provide training and education
Permalink to “Step 6: Provide training and education”Offer training programs to council members and stakeholders to build awareness, improve data literacy, and ensure alignment with governance policies.
Step 7: Monitor and evaluate performance
Permalink to “Step 7: Monitor and evaluate performance”Track performance against defined KPIs, conduct periodic reviews, and refine policies as needed. Continuous improvement ensures the council remains effective and relevant.
What tools do data governance councils need?
Permalink to “What tools do data governance councils need?”Councils rely on tools that give them visibility and control across the data lifecycle—catalogs, lineage, quality checks, access governance, and compliance monitoring.
For instance, data cataloging and metadata management help councils understand what data exists, where it lives, and how it is being used. They provide lineage, classification, and context to support policy-setting and monitoring.
Meanwhile, data access governance helps control who has access to what data, monitor permissions, and enforce role-based or policy-based access aligned with compliance requirements.
A unified, metadata-driven control plane like Atlan consolidates all of these capabilities under one roof. As a result, teams see 35 % faster time-to-insight and cut governance overhead by 40 %, making governance more efficient and scalable.
Tip: Fewer tools = faster onboarding and clearer ownership.
Real stories from real customers: Scaling data governance programs
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Scaling data governance programs”
Modernized data stack and launched new products faster while safeguarding sensitive data
“Austin Capital Bank has embraced Atlan as their Active Metadata Management solution to modernize their data stack and enhance data governance. Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics, highlighted, ‘We needed a tool for data governance… an interface built on top of Snowflake to easily see who has access to what.’ With Atlan, they launched new products with unprecedented speed while ensuring sensitive data is protected through advanced masking policies.”

Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics
Austin Capital Bank
🎧 Listen to podcast: Austin Capital Bank From Data Chaos to Data Confidence

53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan
Join Data Leaders Scaling with Automated Policy Controls
Book a Personalized Demo →Ready to define your data governance council?
Permalink to “Ready to define your data governance council?”A Data Governance Council is the backbone of trusted, compliant, and high-value data practices.
By setting clear policies, aligning with business goals, and overseeing governance efforts, the council ensures your data becomes a strategic advantage rather than a liability.
If your organization is ready to reduce risks, improve data quality, and unlock the full value of its data assets, defining your Data Governance Council is the first step.
The right framework will give your teams the clarity and accountability they need to steward data responsibly while driving innovation and growth.
Discover how a modern data governance platform drives real results
Book a Personalized Demo →FAQs about data governance council
Permalink to “FAQs about data governance council”What is the role of a data governance council?
Permalink to “What is the role of a data governance council?”The role of a Data Governance Council is to set policies, define standards, and provide oversight for how data is managed, accessed, and protected across the organization. It ensures that data is treated as a strategic asset.
What is the purpose of a data governance council?
Permalink to “What is the purpose of a data governance council?”The purpose of the Data Governance Council is to align data governance with business goals, reduce risks, ensure compliance, improve data quality, and maximize the value of data assets for decision-making and innovation.
Who should be in a data governance council?
Permalink to “Who should be in a data governance council?”A Data Governance Council should include senior leaders and cross-functional stakeholders from IT, business, legal, compliance, and operations. Executive representation ensures strategic alignment and authority.
How does a data governance council differ from a data governance team?
Permalink to “How does a data governance council differ from a data governance team?”The council defines the what and why—policies, priorities, and oversight—while the data governance team handles the how by executing those policies and managing day-to-day governance tasks.
What are the benefits of having a data governance council?
Permalink to “What are the benefits of having a data governance council?”Benefits include improved data quality and reliability, reduced risks and costs, enhanced decision-making, stronger compliance, and greater business value from data.
How often should a data governance council meet?
Permalink to “How often should a data governance council meet?”Most councils meet quarterly or monthly, depending on the organization’s size, regulatory environment, and data priorities. Regular meetings ensure oversight and accountability.
How does AI impact data governance councils?
Permalink to “How does AI impact data governance councils?”AI enhances councils by automating compliance monitoring, improving data classification, detecting risks faster, and supporting responsible AI governance to maintain transparency and fairness.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
Data governance council: Related reads
Permalink to “Data governance council: Related reads”- What is Data Governance? Its Importance & Principles
- Data Governance and Compliance: Act of Checks & Balances
- Data Governance Framework — Guide, Examples, Template
- Data Governance Tools Comparison: How to Select the Best
- Data Governance Tools Cost: What’s The Actual Price?
- Data Governance Process: Why Your Business Can’t Succeed Without It
- Data Governance for AI: Challenges & Best Practices
- Data Governance Maturity Model: A Roadmap to Optimizing Your Data Initiatives and Driving Business Value
- Federated Data Governance: Principles, Benefits, Setup
- Data Governance Committee 101: When Do You Need One?
- Data Governance Policy: Examples, Templates & How to Write One
- 7 Best Practices for Data Governance to Follow in 2025
- Benefits of Data Governance: 4 Ways It Helps Build Great Data Teams
- Key Objectives of Data Governance: How Should You Think About Them?
- The 3 Principles of Data Governance: Pillars of a Modern Data Culture
- 7 Must-Have Data Governance Certifications for 2025




















