How Metadata Lakehouse Activates Governance & Drives AI Readiness in 2026
Traditional catalogs vs. metadata lakehouses: What makes a metadata lakehouse different from a catalog?
Permalink to “Traditional catalogs vs. metadata lakehouses: What makes a metadata lakehouse different from a catalog?”Traditional data catalogs store metadata in proprietary databases optimized for UI rendering and search operations. While effective for discovery, these closed systems create three critical limitations for modern data and AI teams:
- Accessing metadata programmatically requires custom API calls for each query. So, data teams can’t use familiar SQL tools for analytics and governance.
- Metadata remains siloed within the catalog platform, inaccessible to external analytics tools, dashboards, or AI applications without complex integrations.
- Metadata updates flow in just one direction (into the catalog), making it difficult for AI systems to write back enriched context or usage signals.
Metadata lakehouses invert this model by storing metadata in open table formats like Apache Iceberg.
So, any compute engine that supports Iceberg can query the metadata directly using standard SQL:
- Data governance teams can build dashboards tracking completeness by domain.
- Data quality engineers can analyze anomaly patterns across assets.
- Platform architects can identify optimization opportunities through usage analysis.
This architectural shift mirrors how data lakehouses transformed data storage. Just as data lakehouses brought warehouse capabilities to lake storage, metadata lakehouses bring analytics capabilities to metadata management.
According to Gartner’s 2025 MQ on Metadata Management Solutions, a metadata lakehouse is vital for metadata orchestration, so that metadata can flow effortlessly across the enterprise data ecosystem.
“The modern metadata repository is not simply a storage location, but a dynamic “lakehouse” that integrates diverse metadata types — technical, business, operational and social metadata — supporting a holistic view of enterprise data.“ - Gartner Magic Quadrant on Metadata Management Solutions for 2025
With a metadata lakehouse, organizations gain the flexibility of open formats with the governance rigor traditionally associated with proprietary systems.
How does a metadata lakehouse work? 4 foundational architecture components explained.
Permalink to “How does a metadata lakehouse work? 4 foundational architecture components explained.”A metadata lakehouse consists of four integrated layers that work together to make metadata queryable, versioned, and accessible.
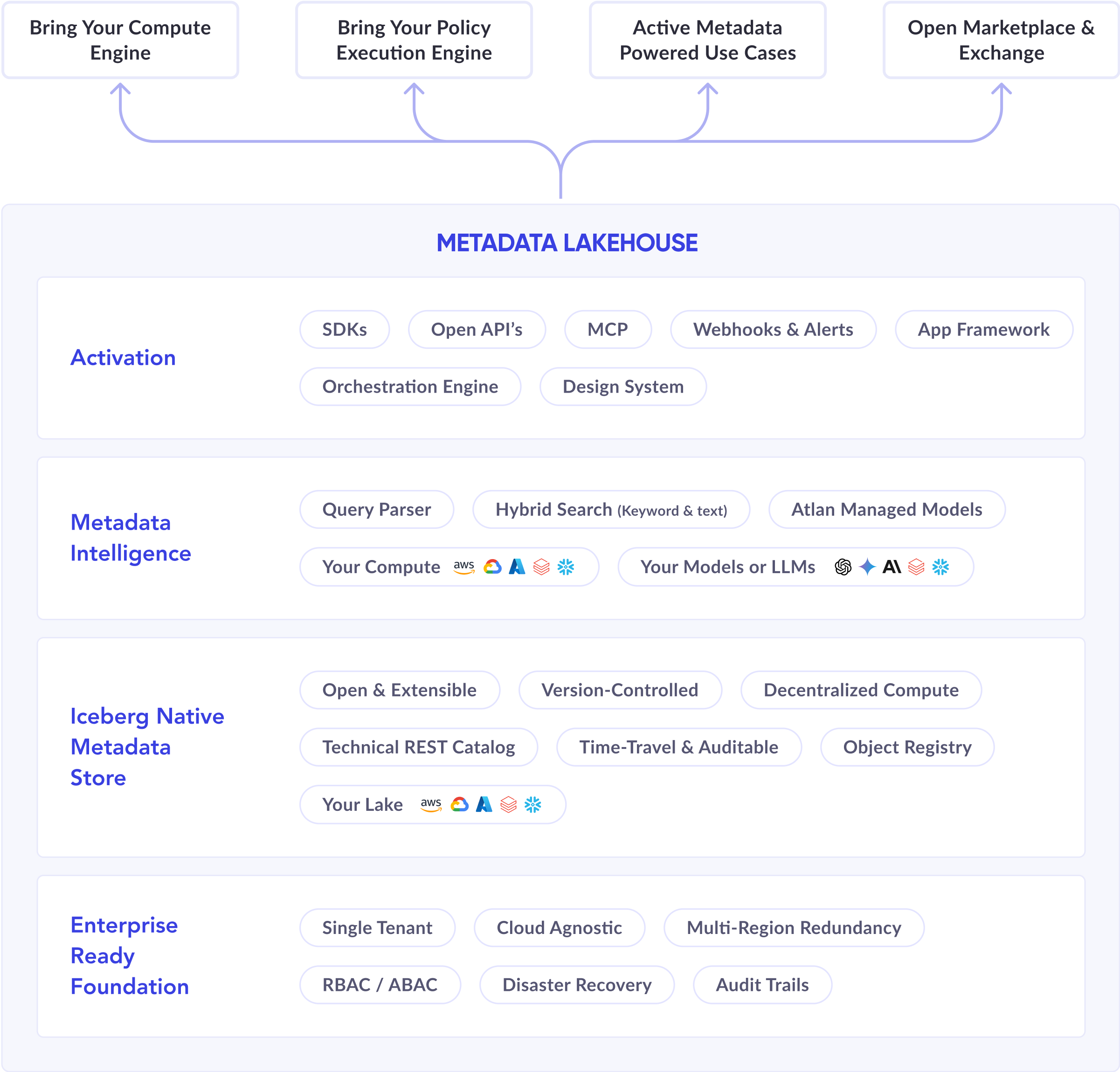
Metadata lakehouse architecture explained. Image by Atlan.
1. Storage layer with open table formats
Permalink to “1. Storage layer with open table formats”The foundation uses cloud object storage (Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage) to hold metadata in Apache Iceberg tables. This open format ensures that metadata remains accessible independent of any specific vendor platform.
Iceberg provides ACID transactions, schema evolution, and time travel capabilities. Organizations can query historical metadata states, understand how assets evolved, and audit changes over time. The format’s partitioning and indexing optimize query performance even when metadata volume reaches billions of rows.
2. Compute layer for analysis
Permalink to “2. Compute layer for analysis”Any Iceberg-compatible compute engine can query metadata lakehouse tables. Organizations typically use their existing infrastructure—Snowflake, Databricks, Spark, Trino, or Presto—eliminating the need for specialized metadata query tools.
This compute flexibility enables teams to analyze metadata using tools they already know.
So, data engineers write SQL queries in their preferred notebooks, business analysts build dashboards in their BI platforms, and ML engineers integrate metadata directly into model training pipelines.
3. Metadata integration and enrichment
Permalink to “3. Metadata integration and enrichment”The integration layer continuously captures metadata from source systems and writes it to Iceberg tables. Modern implementations refresh metadata every 15 minutes, ensuring dashboards and applications work with current information.
Beyond basic technical metadata (schemas, lineage, statistics), the layer enriches assets with:
- Operational metadata (query patterns, performance metrics)
- Social metadata (usage frequency, user ratings)
- Governance metadata (classifications, policies, ownership)
This comprehensive context enables sophisticated analysis and automation.
4. Activation layer for consumption
Permalink to “4. Activation layer for consumption”The activation layer exposes metadata to applications, dashboards, and AI systems. Unlike traditional catalogs where metadata consumption happens only through vendor UIs, metadata lakehouses enable unlimited consumption patterns.
For example, governance teams can build compliance dashboards, platform engineers can create cost optimization reports, and AI systems can retrieve context for retrieval-augmented generation.
This ensures metadata serves as infrastructure rather than just documentation.
What can you do with metadata lakehouses? 5 top use cases explained.
Permalink to “What can you do with metadata lakehouses? 5 top use cases explained.”Storing metadata in queryable format unlocks use cases impossible with traditional catalog architectures.
1. Track governance maturity across domains
Permalink to “1. Track governance maturity across domains”Organizations implementing data mesh or federated governance need visibility into how different domains maintain their data products.
A metadata lakehouse enables measuring completeness, quality, and adoption metrics for each domain using SQL queries that aggregate across thousands of assets. So, platform teams can identify which domains have high-quality metadata (descriptions, ownership, classifications) and which need support.
2. Optimize cloud data warehouse costs
Permalink to “2. Optimize cloud data warehouse costs”Cloud data warehouses charge for both storage and compute. Metadata lakehouses reveal which tables consume significant storage but receive little or no query activity, highlighting candidates for archival or deletion.
For example, you can quickly spot which tables haven’t been queried in 90 days, or highlight duplicate/near-duplicate tables across projects. This can reduce warehousing costs significantly, without impacting active workloads.
3. Feed context to AI applications
Permalink to “3. Feed context to AI applications”AI models and agents need context about data assets to answer questions accurately.
Metadata lakehouses serve as knowledge bases for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, providing semantic context when users ask “which revenue table should I trust?” or “where can I find customer churn data?”
Moreover, the open architecture enables bidirectional flow. So, AI systems not only read metadata for context but also write back generated insights—suggested descriptions, inferred relationships, usage patterns.
This closed-loop feedback continuously improves metadata quality through AI-assisted enrichment.
4. Measure AI readiness and adoption
Permalink to “4. Measure AI readiness and adoption”As organizations deploy AI applications, leadership needs visibility into which data assets support AI workloads versus which remain unavailable due to quality or governance issues.
Metadata lakehouses enable tracking metrics like percentage of datasets with verified quality, assets with complete lineage, and adoption rates for AI-governed data products.
These metrics inform strategic decisions about AI investments and identify bottlenecks preventing broader AI adoption across the enterprise.
5. Enable metadata-driven automation
Permalink to “5. Enable metadata-driven automation”Modern data platforms use metadata to automate workflows—triggering data quality checks when schemas change, notifying stakeholders when lineage breaks, or automatically classifying sensitive data based on content patterns.
With metadata in a lakehouse format, automation logic can be expressed as SQL queries evaluated continuously. Rather than building custom code for each automation scenario, teams define rules declaratively and let the platform execute them against real-time metadata.
How can you implement a metadata lakehouse for your enterprise? Building vs. buying metadata lakehouse solutions.
Permalink to “How can you implement a metadata lakehouse for your enterprise? Building vs. buying metadata lakehouse solutions.”Organizations considering metadata lakehouses face a build-versus-buy decision similar to other infrastructure investments.
Metadata lakehouse implementation approach #1: Building in-house
Permalink to “Metadata lakehouse implementation approach #1: Building in-house”Building in-house requires:
- Choosing a table format (typically Iceberg)
- Designing a schema for diverse metadata types
- Implementing continuous extraction from source systems
- Creating tooling for analysis and activation
While the open-source foundations are well-documented, the process is time and resource intensive:
- Organizations that built early metadata warehouses report spending 6-12 months reaching production quality.
- Ongoing maintenance–schema evolution, performance optimization, new integrations–require dedicated engineering teams.
Metadata lakehouse implementation approach #2: Buying managed platforms
Permalink to “Metadata lakehouse implementation approach #2: Buying managed platforms”Managed metadata lakehouse platforms handle infrastructure, integration, and optimization.
Atlan’s metadata lakehouse provides Iceberg-native storage with built-in capabilities for automated metadata extraction, enrichment, and activation.
This approach has become the AI and automation ecosystem at GM, powering conversational interfaces for natural-language discovery, enterprise-wide metadata search, data contracts, and more.
As a result, time to value drops from months to weeks. Key capabilities include:
- Pre-built connectors handle extraction from 100+ source systems.
- Automatic compaction and maintenance optimize performance.
- Native dashboards serve common governance and operational use cases out of the box.
How to evaluate metadata lakehouse solutions: 3 essential factors to consider
Permalink to “How to evaluate metadata lakehouse solutions: 3 essential factors to consider”The key evaluation criteria for metadata lakehouse solutions include:
- Openness of the underlying storage format (ensuring no vendor lock-in)
- Breadth of source system integrations, performance at scale (billions of assets)
- Richness of activation capabilities beyond basic querying
How do modern platforms like Atlan streamline metadata lakehouse operations?
Permalink to “How do modern platforms like Atlan streamline metadata lakehouse operations?”Operating metadata lakehouses at scale requires solving several technical challenges that most organizations prefer not to tackle in-house.
1. Continuous metadata extraction across systems
Permalink to “1. Continuous metadata extraction across systems”Modern platforms handle continuous metadata extraction across diverse source systems without manual pipeline building. They automatically discover schema changes, track lineage evolution, and capture operational metrics in near-real-time.
2. Performance optimization across billions of metadata records
Permalink to “2. Performance optimization across billions of metadata records”Performance optimization happens transparently through intelligent compaction, partitioning, and indexing strategies tuned for metadata workloads. Organizations query billions of metadata records without performance degradation, even as the estate grows.
3. Governance-ready infrastructure within weeks
Permalink to “3. Governance-ready infrastructure within weeks”The activation layer provides governance-ready dashboards, AI-ready APIs, and integration with popular BI tools without custom development.
Teams can immediately start analyzing metadata completeness, building compliance reports, or feeding context to AI applications rather than spending months building activation infrastructure.
4. Operational support to ensure regulatory compliance
Permalink to “4. Operational support to ensure regulatory compliance”Platform-managed metadata lakehouses also handle operational concerns like backup and recovery, access control integration with existing identity systems, and audit logging for compliance requirements.
These capabilities, while essential for production systems, represent undifferentiated heavy lifting that diverts engineering resources from value-creating work.
Organizations using managed platforms report achieving their governance and AI enablement goals 3-4x faster than teams building internally, with significantly lower total cost of ownership when accounting for engineering time and infrastructure expenses.
See how Atlan’s metadata lakehouse can accelerate your organization’s data governance and AI initiatives.
Real stories from real customers: Metadata-driven governance at scale
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Metadata-driven governance at scale”From complex in-house systems to governed AI, future-proof your data stack
Permalink to “From complex in-house systems to governed AI, future-proof your data stack”“Atlan is built on Open API architecture, which gives us extensibility across the data stack. That was a game changer.” - Mihir Modi, Data Governance Manager, Fox
Extensibility across Fox’s data stack with Atlan’s open API architecture
Watch How →Unify Every Type of Metadata in an Iceberg Native Meta Store
Permalink to “Unify Every Type of Metadata in an Iceberg Native Meta Store”“Atlan gave us end-to-end visibility and lineage from the cloud all the way back to our on-prem.” - Brian Ames, Sr. Manager, Production AI & Data Products, General Motors
General Motors built a strong metadata foundation through governance
Watch How →Ready to implement a metadata lakehouse that unifies and governs every type of metadata at scale?
Permalink to “Ready to implement a metadata lakehouse that unifies and governs every type of metadata at scale?”Metadata lakehouses represent a fundamental shift in how organizations manage and activate metadata. By storing metadata in open, queryable formats, teams gain unprecedented flexibility to analyze governance maturity, optimize infrastructure costs, feed context to AI systems, and automate metadata-driven workflows.
The approach mirrors the broader industry movement toward open architectures, ensuring organizations maintain control over their metadata assets without vendor lock-in.
While building metadata lakehouses in-house remains possible, managed platforms like Atlan accelerate time to value by handling operational complexity and providing pre-built integrations.
As AI adoption accelerates, metadata lakehouses will become essential infrastructure for organizations seeking to govern data at scale while enabling autonomous agents and intelligent applications.
Atlan’s metadata lakehouse can transform your metadata infrastructure.
Let’s help you build it
Book a Personalized Demo →FAQs about metadata lakehouse
Permalink to “FAQs about metadata lakehouse”1. How does a metadata lakehouse differ from a traditional data catalog?
Permalink to “1. How does a metadata lakehouse differ from a traditional data catalog?”Traditional data catalogs store metadata in proprietary databases optimized for UI search and browsing.
Metadata lakehouses store metadata in open table formats like Apache Iceberg, making it queryable through standard SQL by any compatible compute engine.
2. What table formats work with metadata lakehouses?
Permalink to “2. What table formats work with metadata lakehouses?”Apache Iceberg is the most common choice for metadata lakehouses due to its maturity, broad ecosystem support, and features like time travel and schema evolution.
The key requirement is that the format supports ACID transactions, versioning, and interoperability across multiple compute engines.
Others include Delta Lake and Apache Hudi.
3. Can metadata lakehouses integrate with existing data catalogs?
Permalink to “3. Can metadata lakehouses integrate with existing data catalogs?”Yes, metadata lakehouses complement rather than replace catalogs. The lakehouse serves as the queryable storage layer while catalogs provide UI experiences for discovery and collaboration.
Modern platforms bidirectionally sync metadata between lakehouse storage and catalog interfaces, ensuring teams can both analyze metadata through SQL and discover assets through familiar catalog UIs. This hybrid approach delivers the best of both architectural patterns.
4. What compute engines can query metadata lakehouses?
Permalink to “4. What compute engines can query metadata lakehouses?”Any engine supporting Apache Iceberg can query metadata lakehouses, including Snowflake, Databricks, Amazon Athena, Trino, Presto, and Apache Spark.
Teams choose the engine that best fits their skills and existing platform investments, then connect it to the metadata lakehouse through standard Iceberg REST catalog APIs.
5. How often does metadata refresh in a lakehouse architecture?
Permalink to “5. How often does metadata refresh in a lakehouse architecture?”Refresh frequency depends on platform implementation and organizational needs. Leading platforms update metadata every 15 minutes, balancing freshness with processing overhead.
For time-sensitive use cases like AI agent context or anomaly detection, some platforms support sub-minute refresh intervals for critical metadata types.
6. What are the primary use cases driving metadata lakehouse adoption?
Permalink to “6. What are the primary use cases driving metadata lakehouse adoption?”Four use cases dominate early adoption:
- Governance maturity tracking for federated data architectures
- Cloud cost optimization through usage analysis
- AI context provision for retrieval-augmented generation systems
- Metadata-driven automation for quality checks and policy enforcement
Organizations implementing data mesh or scaling AI deployments find metadata lakehouses essential for maintaining visibility and control as data estates grow more distributed and complex.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
Metadata lakehouse: Related reads
Permalink to “Metadata lakehouse: Related reads”- Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Metadata Management Solutions 2025: Key Shifts & Market Signals
- The G2 Grid® Report for Data Governance: How Can You Use It to Choose the Right Data Governance Platform for Your Organization?
- Data Governance in Action: Community-Centered and Personalized
- Data Governance Framework — Examples, Templates, Standards, Best practices & How to Create One?
- Data Governance Tools: Importance, Key Capabilities, Trends, and Deployment Options
- Data Governance Tools Cost: What’s The Actual Price?
- Data Governance Process in 8 Steps: Why Your Business Can’t Succeed Without It
- Data Compliance Management: Concept, Components, Getting Started
- Data Governance for AI: Challenges & Best Practices
- A Guide to Gartner Data Governance Research: Market Guides, Hype Cycles, and Peer Reviews
- Gartner Data Governance Maturity Model: What It Is, How It Works
- Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities: A Round-Up
- How to Choose a Data Governance Maturity Model in 2026
- Open Source Data Governance: 7 Best Tools to Consider in 2026
- Data Governance Committee 101: When Do You Need One?
- Snowflake Data Governance: Features, Frameworks & Best Practices
- Data Governance Policy: Examples, Templates & How to Write One
- 12 Best Practices for Data Governance to Follow in 2026
- Benefits of Data Governance: 4 Ways It Helps Build Great Data Teams
- 8 Key Objectives of Data Governance: How Should You Think About Them?
- The 10 Foundational Principles of Data Governance: Pillars of a Modern Data Culture
- Collibra Pricing: Will It Deliver a Return on Investment?
- AI Data Catalog: Exploring the Possibilities That Artificial Intelligence Brings to Your Metadata Applications & Data Interactions
- 7 Top AI Governance Tools Compared | A Complete Roundup for 2026
- Dynamic Metadata Discovery Explained: How It Works, Top Use Cases & Implementation in 2026
- 9 Best Data Lineage Tools: Critical Features, Use Cases & Innovations
- Data Lineage Solutions: Capabilities and 2026 Guidance
- 12 Best Data Catalog Tools in 2026 | A Complete Roundup of Key Capabilities
- Data Catalog Examples | Use Cases Across Industries and Implementation Guide
- 5 Best Data Governance Platforms in 2026 | A Complete Evaluation Guide to Help You Choose
- Data Lineage Tracking | Why It Matters, How It Works & Best Practices for 2026
- Dynamic Metadata Management Explained: Key Aspects, Use Cases & Implementation in 2026



















