Data Compliance Management: Concept, Components, Getting Started in 2024
Share this article
Data compliance management involves implementing policies, procedures, and controls to meet the requirements of various data privacy laws and regulations. Effective compliance management is integral to sustaining long-term business success and fostering a culture of accountability and trust.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Governance – Start Product Tour
There are several aspects related to data compliance management. So, this article will focus on concepts, processes, and tools and discuss considerations for getting started.
Table of Contents #
- What is data compliance management?
- Who is responsible for data compliance management?
- Data compliance management: 6 core components
- Data compliance management: Getting started in 4 steps
- Related Reads
What is data compliance management? #
Data compliance management oversees the practices, processes, and policies involved in the data compliance lifecycle. It ensures that your organization adheres to relevant data protection laws, privacy regulations, industry standards, and internal policies.
It aims to guarantee compliance with various data privacy laws and regulations, such as Europe’s GDPR, California’s CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), or industry-specific standards like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare.
The goal of data compliance management is to protect sensitive data assets, maintain data integrity and security, and avoid legal and financial penalties.
Why does data compliance management matter? #
As humans, we tend to think positively. We don’t buy a house thinking about thieves or take an airplane wondering if the last maintenance was successful. We often assume everything will be all right in our personal lives and how we run our businesses.
However, we must be mindful of potential risks and threats. A 2023 study by Professor Stuart E. Madnick, Ph.D. (supported by Apple), states that data breaches are at an all-time high for US organizations, with a nearly 20% increase in violations in the first nine months of 2023 compared to all of 2022.
Even with precautions and guardrails in place, the same study found that 98% of organizations had a vendor that experienced a data breach in the last two years.
Regulations exist to prevent and mitigate the damage from such threats. Non-compliance can lead to increased data security risks, litigation, fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
Effective data compliance management ensures the ethical, secure, and legal use of data, adhering to regulatory requirements. It also enhances operational efficiency by streamlining data management processes and ensuring data quality.
Organizations can build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to protecting data and upholding ethical standards.
Who is responsible for data compliance management? #
Data compliance management is a collective effort involving various stakeholders, such as DPOs (data protection officers), senior management, legal and compliance officers, and data stewards.
The roles and responsibilities related to data compliance management will vary depending on your organization’s size, industry, and data maturity.
Here’s an illustration that covers the main roles and how they interact in a small organization. It shows the interconnected roles of users, the organization itself, the data protector, the data team, and employees. Each entity has distinct responsibilities:
- The user (in this case, a customer) primarily interacts with the organization by providing consent, requesting access to their data, or asking for data deletion. Their rights are at the heart of data compliance efforts.
- The organization, with the help of the data protector, defines policy guidelines and training programs. It also oversees employee data compliance training programs.
- The data protector (often filled by the DPO) plays a central role in defining policies, conducting risk assessments, and managing incidents.
- The data team is responsible for the technical aspects of data compliance management — cataloging, infrastructure, data governance policy enforcement, and access control.
- Employees adhere to compliance policies, raising access requests with the data team and concerns with the data protector when needed.
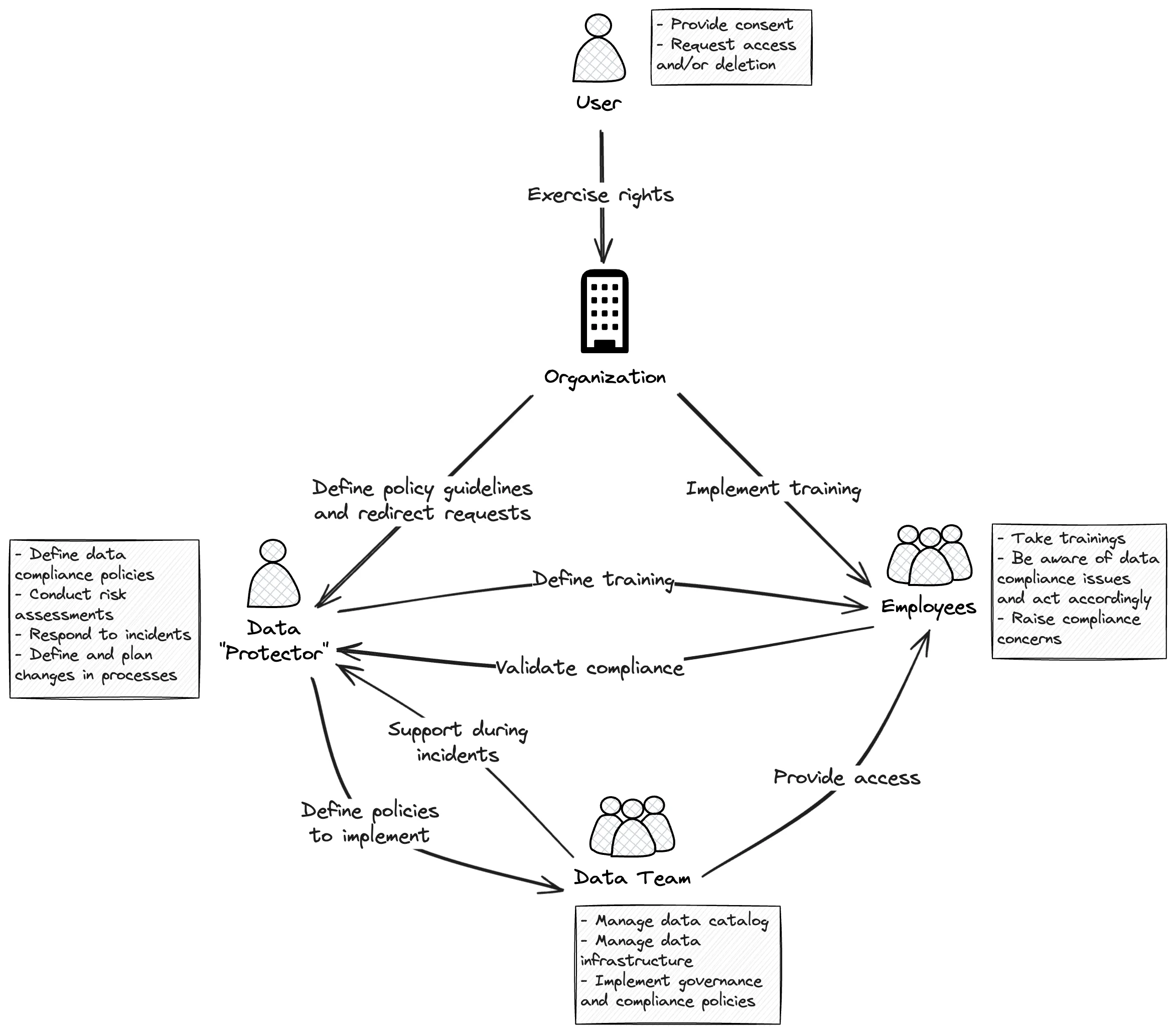
A collaborative approach to data compliance management. - Image by Atlan.
Data compliance management: 6 core components #
Key components of data compliance management include:
- Data catalog for data collection, discovery, and sharing
- Data classification for mitigating risks
- Data storage and processing for compliant handling of data assets
- Monitoring and audit for proper accountability
- Privacy and consent management to manage user consent and data subject rights
- Training and awareness of data compliance policies and procedures
Let’s dig into the specifics.
1. Data catalog for data collection, discovery, and sharing #
Regulations often require maintaining a catalog and recording processing activities. For example, article 30 of GDPR specifies that the organization “shall maintain a record of processing activities under its responsibility”.
That’s why a data catalog is a primary component of data compliance management. It helps you understand the types of data your organization collects, processes, and uses.
A data catalog, a centralized repository of information about data assets, is a cornerstone of effective data compliance management. It serves as a single source of truth, documenting what data an organization collects, processes, and uses, along with essential metadata such as:
The catalog should also contain metadata, such as:
- Details about asset owners and their contact information (for accountability)
- The purpose of processing (to ensure legitimate and ethical use)
- A description of categories of personal data (for transparency)
- Details about data consumers (to track usage)
- Information about the transfer of such information to international organizations (for cross-border compliance)
Dig deeper → Data Catalog: What It Is & How It Drives Business Value
This metadata is crucial for demonstrating compliance with various regulations, not just GDPR. For example, HIPAA requires healthcare organizations to track protected health information (PHI), and CCPA mandates that businesses disclose how they collect and use consumer data.
So, inventorying your data, along with relevant metadata, in a data catalog is central to your data compliance management efforts.
Note: The data inventory is a related concept. Both serve as assets for metadata management, and the difference lies in the objective. The data catalog is usually built with search and discovery in mind, whereas the data inventory is for data compliance.
Read more → Data inventory vs. data catalog
2. Data classification for mitigating risks #
Data classification is critical to ensuring data compliance and mitigating risks. By categorizing data based on sensitivity levels, organizations gain a granular understanding of their data landscape, enabling them to tailor access controls and security measures accordingly.
Since regulations require an organization to respond to protect its customers from threats, a helpful way to define priorities for policy implementation is to classify data assets based on their sensitivity — public, internal, confidential, and restricted.
Organizations can customize access and security policies for encryption, access restrictions, monitoring, and more, depending on the classification.
Dig deeper → Data Classification and Tagging: How to Marie Kondo Your Data Catalog and Spark Joy
If your organization already has a data catalog in place, you can use it to streamline data classification by propagating classifications and tags through lineage mapping. If not, the ability to automate the process via lineage should be a key consideration when evaluating data cataloging solutions.
3. Data storage and processing for compliant handling of data assets #
Storage is a crucial aspect of data compliance management. Regulations often dictate where data can be stored (data residency) and how it’s processed.
With the rise of cloud-native tools and remote work, organizations should prioritize storage and processing solutions that offer:
- Access control (users and roles with different access levels)
- Logging access history, data processing and transformation
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Firewalls to regulate access (especially for remote/hybrid workspaces with BYOD policies)
4. Monitoring and audit for proper accountability #
Effective monitoring and auditing are essential to a robust data compliance management strategy. Setting this up requires deploying a combination of tools and processes, such as:
- Automated monitoring systems that track data usage and access patterns
- Observability tools that provide a record of data activities, essential for audits
- Compliance dashboards that offer a centralized view of compliance status, metrics, and reports
Organizations must guarantee that both technology and processes are auditable. They should maintain up-to-date documentation and conduct regular internal reviews to assess the effectiveness of compliance measures.
5. Privacy and consent management for user consent and data subject rights #
Privacy and consent management are fundamental to building trust and maintaining ethical data practices.
Here’s how the GDPR characterizes consent:
“Consent must be freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous. In order to obtain freely given consent, it must be given on a voluntary basis. The element “free” implies a real choice by the data subject. Any element of inappropriate pressure or influence which could affect the outcome of that choice renders the consent invalid.”
Besides this, there are other rights that different regulations (like CCPA, LGPD in Brazil, PIPEDA in Canada) cover:
- Right to opt-out from third-party data sales
- Right to be informed about how the organization is processing personal data
- Right to access personal data organization stores and processes (sometimes in a structured, machine-readable format)
- Right to erasure or “to be forgotten” refers to the complete removal of personal information within the organization
- Right of rectification, to correct any inaccurate data about a person
There are several consent management platforms available that allow you to log and track consent collection across applications and platforms. Marketing platforms often incorporate consent management features to align data storage and processing permissions with targeted customer interactions.
You can use data cataloging and governance platforms to manage consent by incorporating it into different aspects of the data management lifecycle. For instance, data retention policies can be linked to consent records, ensuring that data is deleted when consent expires.
6. Training and awareness of data compliance policies and procedures #
Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report reveals that 74% of breaches involved the human element — social engineering attacks, errors, or misuse. It also observes that internal actors caused 19% of data breaches.
Technology, like Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools, can help, but it’s not insufficient.
Training and awareness are crucial to empower your people. Regulations often mandate specific training. For example, in California, organizations must provide information security and privacy training and awareness programs.
In addition, consider educating everyone about common threats like phishing and social hacking, and internal data governance policies and best practices.
When you foster awareness of your internal data governance program and practices, everyone understands best practices and their role in maintaining compliance.
Now that you’re familiar with data compliance management and its core components, let’s understand how to implement it.
Data compliance management: Getting started in 4 steps #
Here are the key steps to get started with data compliance management:
- Identify and catalog your data assets: Before managing compliance, you need to know what data assets your organization handles, both directly and through third-party vendors. This includes everything from customer information to internal financial data.
- Research relevant data regulations for your industry: Different industries and regions have varying data protection laws. Research the specific regulations that apply to your organization based on your location, industry, and the types of data you collect and process. Familiarize yourself with how Data Protection Authorities (DPAs) typically assess compliance — proactive audits, investigations following complaints or breaches, and reviews of compliance documentation and practices.
- Focus compliance efforts based on risk assessment findings: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to your data. This includes understanding the likelihood and impact of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other risks. Use this assessment to prioritize your compliance efforts, focusing on the most critical areas first.
- Establish robust data governance policies and processes: Data governance policies ensure that data is responsibly managed as an asset. Some aspects to consider include developing a sound data security approach, defining access policies, deploying the right tools, and maintaining detailed audit logs.
- Monitor, adapt, and improve continuously: Data compliance is an ongoing process. So, continuously monitor your data environment for changes, vulnerabilities, and emerging threats. Adjust your policies and procedures to stay ahead of evolving regulatory requirements and technological advancements. Regularly review and improve your data governance framework based on lessons learned and stakeholder feedback.
By following this streamlined action plan, organizations can lay a strong foundation for data compliance management, safeguarding their data assets and mitigating potential risks.
Wrapping up #
Data regulations exist to protect individuals and organizations against the harm that data misuse can cause, and complying with them can help organizations in many ways.
We’ve explored the first steps to get started with data compliance management and the crucial aspects to consider. Data security, privacy, and integrity are vital to getting trustworthy outcomes from your data while minimizing legal and financial risks.

Connect with Bruno Gonzalez here.
Data Compliance Management: Related Reads #
- Data Governance in Action: Community-Centered and Personalized
- Data Governance Framework — Examples, Templates, Standards, Best practices & How to Create One?
- Data Governance Tools: Importance, Key Capabilities, Trends, and Deployment Options
- Data Governance Tools Comparison: How to Select the Best
- Data Governance Tools Cost: What’s The Actual Price?
- Data Governance Process: Why Your Business Can’t Succeed Without It
- Data Governance and Compliance: Act of Checks & Balances
- Data Governance vs Data Compliance: Nah, They Aren’t The Same!
- Data Compliance Management: Concept, Components, Getting Started
- Data Governance for AI: Challenges & Best Practices
- A Guide to Gartner Data Governance Research: Market Guides, Hype Cycles, and Peer Reviews
- Gartner Data Governance Maturity Model: What It Is, How It Works
- Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities: A Round-Up
- Data Governance in Banking: Benefits, Implementation, Challenges, and Best Practices
- Data Governance Maturity Model: A Roadmap to Optimizing Your Data Initiatives and Driving Business Value
- Open Source Data Governance - 7 Best Tools to Consider in 2024
- Federated Data Governance: Principles, Benefits, Setup
- Data Governance Committee 101: When Do You Need One?
- Data Governance for Healthcare: Challenges, Benefits, Core Capabilities, and Implementation
- Data Governance in Hospitality: Challenges, Benefits, Core Capabilities, and Implementation
- 10 Steps to Achieve HIPAA Compliance With Data Governance
- Snowflake Data Governance — Features, Frameworks & Best practices
- Data Governance Policy: Examples, Templates & How to Write One
- 7 Best Practices for Data Governance to Follow in 2024
- Benefits of Data Governance: 4 Ways It Helps Build Great Data Teams
- Key Objectives of Data Governance: How Should You Think About Them?
- The 3 Principles of Data Governance: Pillars of a Modern Data Culture
Share this article











