Dynamic Metadata Management Explained: Key Aspects, Use Cases & Implementation in 2026
Why do you need dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “Why do you need dynamic metadata management?”Modern applications are continually evolving, and so are the underlying data structures and schemas upon which these applications are built.
To ensure that any downstream consumption of this data is accurate and up-to-date, you must incorporate and adapt to changes in the metadata, which is where dynamic metadata management comes into play.
WIth dynamic metadata management, you can enable:
- Real-time and continuous changes in the data sources flow through various ingestion, transformation, modelling, and visualization systems.
- Automated propagation of metadata updates, such as in an event-driven architecture for modern software applications.
- Aspects of built-in governance, compliance, and quality to ensure that the downstream data and data structures are reliable and comply with any laws and regulations.
Metadata activation with dynamic metadata management
Permalink to “Metadata activation with dynamic metadata management”Metadata activation is when you use the metadata changes to push changes to the systems and their behaviours downstream in the following ways:
- Bringing metadata changes to ingestion and ETL workflows
- Having the latest data assets ready to be searched and discovered
- Ensuring governance and compliance rules are propagated and enforced
- Driving better intelligence with the updated metadata
- Improving data quality, availability, and reliability
Active metadata, in these ways, can be used not only as a thread to connect all of your data systems but also keep them up-to-date, especially in scenarios where bi-directional syncing is required. Watch the below video to learn more.
What are the key aspects of dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “What are the key aspects of dynamic metadata management?”Dynamic metadata management creates a continuously updated, enriched, and activated metadata layer that powers discovery, governance, automation, and AI.
The core aspects include:
1. Real-time metadata updates
Permalink to “1. Real-time metadata updates”Continuously captures and refreshes metadata from pipelines, warehouses, and streaming systems, ensuring long-running queries and fast-changing data assets always reflect their current state.
2. Contextual and adaptive enrichment
Permalink to “2. Contextual and adaptive enrichment”Adds semantic meaning, relationships, classifications, and usage context—making metadata “smart” so systems and users can adjust in real time based on changing conditions or asset behavior.
3. Cross-system visibility and lineage
Permalink to “3. Cross-system visibility and lineage”Builds unified, end-to-end lineage and dependency maps across diverse platforms, enabling consistent context, trust, and impact analysis.
4. Automation and policy activation
Permalink to “4. Automation and policy activation”Uses active metadata to automate quality checks, policy enforcement, tag propagation, remediation steps, and governance workflows, reducing manual overhead.
5. Scalability for modern data ecosystems
Permalink to “5. Scalability for modern data ecosystems”Supports large, distributed data stacks by using adaptive strategies (e.g., dynamic partitioning, incremental updates) to ensure high performance as metadata volume and complexity grow.
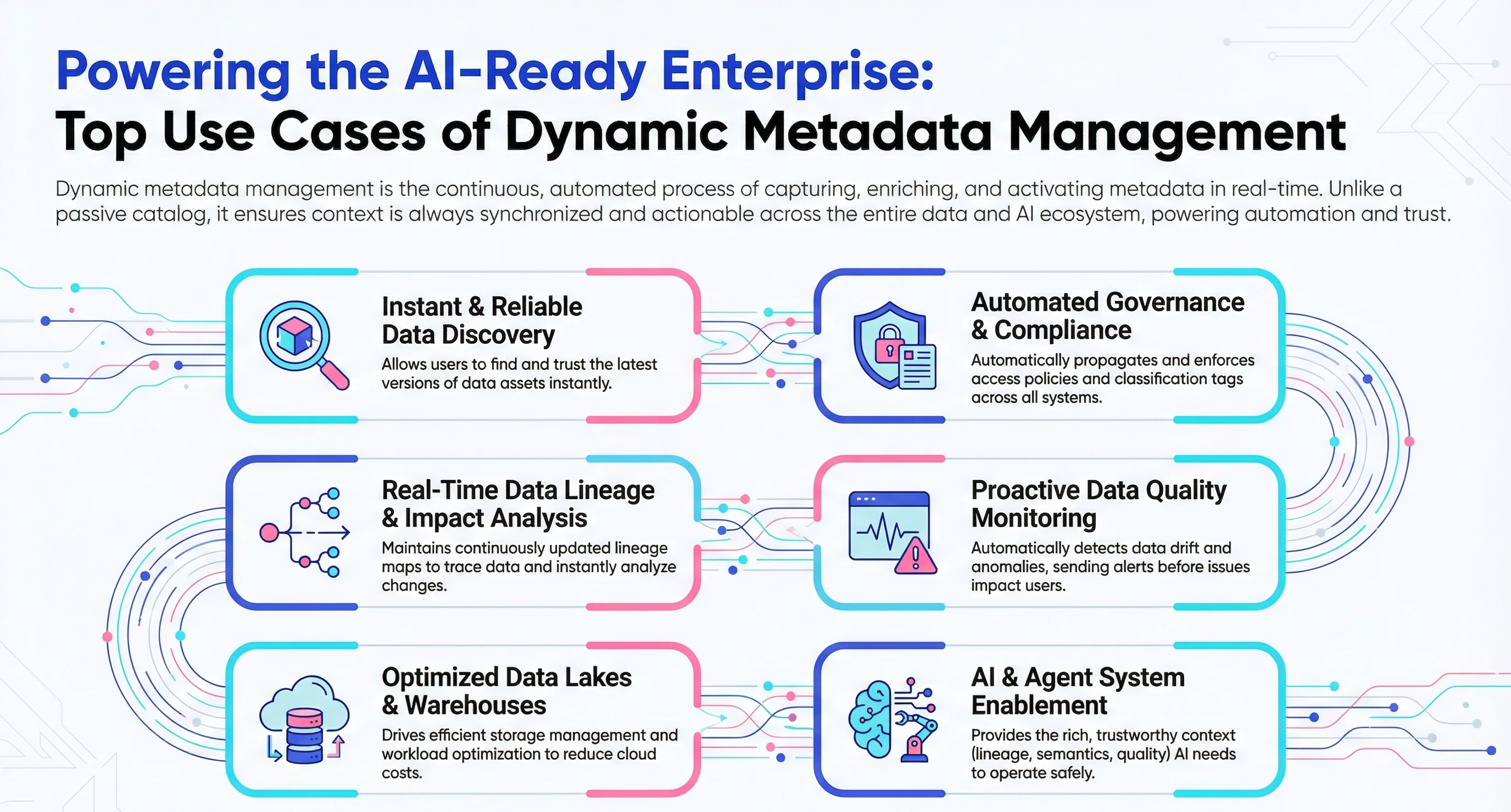
What are the top use cases of dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “What are the top use cases of dynamic metadata management?”Dynamic metadata management drives several high-value use cases across modern data, analytics, and AI ecosystems.
1. Reliable and updated data discovery
Permalink to “1. Reliable and updated data discovery”Data discovery is one of the first use cases that is solved by enabling dynamic metadata management, but you cannot do that without activating the metadata.
When metadata in an upstream data system changes, those changes may be automatically propagated to a downstream system as a one-off activity, for example, by a data ingestion tool.
However, many higher-order processes are triggered after ingestion, one of the primary ones being the maintenance of the data dictionary, cataloging, and discovery engine to keep all critical and auxiliary metadata up to date.
This allows users to search for data assets with the expectation that they’re viewing the latest version of the data asset, in terms of structure, quality, profile, and governance rules, among other factors.
2. Automated data governance and compliance
Permalink to “2. Automated data governance and compliance”Dynamic metadata management also allows metadata activation in governance and compliance by enabling:
- Propagation of rules, conditions, and policies for data access control, sensitive data handling, data sharing, etc.
- Enforcement of the said rules, conditions, and policies within and outside the organization.
- Tagging, classification, and enrichment of data assets based on business use cases and organizational hierarchies.
- Building of end-to-end lineage based on how and when the metadata is changing for any given asset and how it impacts upstream and downstream data assets.
dynamic metadata management explained. Source: Atlan.
3. Automated, cross-system data lineage and impact analysis
Permalink to “3. Automated, cross-system data lineage and impact analysis”You can maintain continuously updated lineage maps that reflect schema drift, pipeline changes, and new transformations with dynamic metadata management. This supports faster root-cause analysis, safer deployments, and audit readiness.
4. Data quality monitoring and anomaly detection
Permalink to “4. Data quality monitoring and anomaly detection”Dynamic metadata continuously feeds freshness metrics, volume patterns, schema changes, and statistical signals into data quality and observability systems. This enables automated anomaly detection, early identification of drift, and real-time alerts when pipelines break or data deviates from expected norms.
By pairing operational metadata with contextual lineage, teams can diagnose issues faster and prioritize fixes based on downstream impact.
5. Optimize data lakes and warehouses
Permalink to “5. Optimize data lakes and warehouses”Dynamic metadata management supports asset classification, partitioning strategies, workload optimization, and lifecycle management. This helps data teams manage large-scale storage ecosystems efficiently and cut cloud costs.
6. AI/ML and agentic system enablement
Permalink to “6. AI/ML and agentic system enablement”Dynamic metadata management provides the contextual metadata (lineage, semantics, usage patterns, provenance) needed for:
- AI feature stores
- Model governance
- AI explainability
- Agentic AI decision workflows
Without dynamic metadata, AI systems cannot safely navigate or interpret enterprise data.
What are some of the key challenges in implementing dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “What are some of the key challenges in implementing dynamic metadata management?”Dynamic metadata management comes with the challenges related to the variousness of systems, complexity of architectures, and lack of metadata-related standards, which results in the following:
- Siloed and disjointed metadata stored in individual technical data catalogs of individual systems.
- Inconsistent handling of metadata, which results in unavailability of data assets for search and discovery, and bad quality, among other things.
- Difficulty in implementing reliable security, governance, and compliance rules.
All of these factors result in operational inefficiencies in the data production and consumption lifecycle, while also contributing to an inconsistent and unintuitive user experience for searching, discovering, accessing, and using data assets across the organization.
This is where the need for a metadata control plane arises.
A metadata control plane aggregates and standardizes metadata from all systems that plug into it, while also possessing all the key ingredients for handling dynamic metadata and activating it with automation.
Atlan is a metadata activation platform built on the foundation of a metadata control plane.
How does a metadata control plane enable dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “How does a metadata control plane enable dynamic metadata management?”Atlan’s unified metadata control plane is built on the premise of integrating all of your organization’s metadata in place, from where it can be managed, activated, and put to use for automation.
It thrives on (and gets you the most out of the platform) dynamic, constantly changing metadata. This gives you a chance to use as many of Atlan’s metadata activation features as possible, which include, but are not limited to:
- Automatic tagging, classification, and their propagation and bi-directional syncing to and from other systems.
- Data governance and compliance policy enforcement, along with data contract enforcement using source-aligned rules.
- Ease of discovery of data assets using a wealth of metadata, which is not only cleansed and organized, but also enriched and contextualized.
- Unlocking operational efficiencies by enabling the teams to focus on building and consuming data products rather than worrying about the metadata.
All in all, Atlan’s unified control plane and its metadata activation approach extract the most out of dynamic metadata in terms of automation, while also managing it effectively.
Let’s examine how some of Atlan’s customers have found it useful in this context.
Real stories from real customers: Driving dynamic metadata management with Atlan
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Driving dynamic metadata management with Atlan”
From Hours to Minutes: How Aliaxis Reduced Effort on Root Cause Analysis by almost 95%
“A data product owner told me it used to take at least an hour to find the source of a column or a problem, then find a fix for it, each time there was a change. With Atlan, it’s a matter of minutes. They can go there and quickly get a report.”
Data Governance Team
Aliaxis
🎧 Listen to AI-generated podcast: How Aliaxis Reduced Effort on Root Cause Analysis
How Atlan helps to setup a connected data ecosystem
Book a Personalized Demo →
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan
Ready to use dynamic metadata management to activate your data and AI estate?
Permalink to “Ready to use dynamic metadata management to activate your data and AI estate?”Dynamic metadata, in contrast to static metadata, is constantly changing. This brings both challenges and opportunities for an organization.
The challenges are related to the variety and complexity of the metadata and the opportunities are related to automation and the betterment of all the processes in the data production and consumption lifecycle.
In the absence of a tool that provides consistency of metadata in terms of structure, organization, user interface, and metadata movement, it isn’t easy to enable efficient dynamic metadata management. That’s where the need for a unified metadata control plane and a tool like Atlan that is built upon its foundation arises.
Atlan is a metadata activation platform designed to leverage ever-changing and dynamic metadata, utilizing various automation workflows for data discovery, lineage, quality, governance, security, and other purposes.
How Atlan helps to setup a connected data ecosystem
Book a Personalized Demo →FAQs about dynamic metadata management
Permalink to “FAQs about dynamic metadata management”1. What is dynamic metadata management? How does it relate to metadata activation?
Permalink to “1. What is dynamic metadata management? How does it relate to metadata activation?”Dynamic metadata management involves the handling and effective utilization of constantly changing metadata related to data structure, governance, compliance, quality, lineage, and other aspects.
Metadata activation is the automated use of dynamic data to facilitate further automation in data production and consumption workflows.
2. What is dynamic metadata propagation?
Permalink to “2. What is dynamic metadata propagation?”Dynamic metadata propagation is the process of propagating or transmitting changes in metadata from one system to another, while retaining the meaning of the metadata changes throughout the process.
Some examples of this are propagation of policy changes, tags, classification, certification, among other things.
3. What are the key challenges in implementing dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “3. What are the key challenges in implementing dynamic metadata management?”Several challenges, including siloed data systems and the lack of metadata storage and exchange standards, among others, are key issues. However, the most important is the absence of infrastructure and architecture to enable dynamic metadata management and metadata activation.
4. What are some key examples of dynamic metadata in action?
Permalink to “4. What are some key examples of dynamic metadata in action?”Some key examples of adaptive metadata in action include governance policy changes, which management at the source should translate into all downstream systems to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Another example is changing hierarchies or ownership of data assets, which you want to reflect in your live systems as soon as the changes are made.
5. What are the different approaches to managing metadata?
Permalink to “5. What are the different approaches to managing metadata?”There are two broad approaches to managing dynamic or constantly changing metadata:
- Manual metadata management: While you may have systems to incorporate changes, you need to manually run scripts or have manual oversight on every step of the way
- Automated metadata management:Updates in the metadata flow through various systems in an automated manner, while ensuring that the flow of the downstream systems don’t break.
Manual metadata management is the traditional way of bringing the changes in the metadata of the upstream systems to the downstream systems.
However, the pace of development and consumption of data in modern applications does not allow for the time required or the potential errors associated with manual metadata management.
This is why you need to take an automated approach to dynamic metadata management, which also then becomes foundational for metadata activation.
6. How can you make your organization’s metadata AI-ready?
Permalink to “6. How can you make your organization’s metadata AI-ready?”You can make your organization’s metadata AI-ready by first ending your reliance on manual or passive processes for metadata management and, second, by enabling a dynamic metadata management workflow that allows you to activate changes to metadata to manage your data workflows in an automated fashion.
7. How can AI help with dynamic metadata management?
Permalink to “7. How can AI help with dynamic metadata management?”Two aspects of AI relate to dynamic metadata management. The first is related to how AI can power dynamic metadata management, and the second is about how metadata can be better prepared for AI use further downstream. Both aspects feed into each other.
In practice, AI can help with better dynamic metadata management by:
- Improving tagging, classification, and enrichment of data assets by reading existing metadata in relation to the incoming updates.
- Enforcing policies in real-time by tracking changes to governance and compliance metadata for data assets.
- Bettering search and discovery by finding hidden relationships, filling gaps in lineage, among other things.
Once you start incorporating AI in any one of the two aspects mentioned earlier, the other one will be much easier to handle. For example, AI-enriched, human-validated metadata is significantly more beneficial for subsequent data use than otherwise.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
Dynamic metadata management: Related reads
Permalink to “Dynamic metadata management: Related reads”- Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Metadata Management Solutions 2025: Key Shifts & Market Signals
- Best Data Governance Tools in 2026 — A Complete Roundup of Key Capabilities
- Gartner Data Catalog Research Guide — How To Read Market Guide, Magic Quadrant, and Peer Reviews
- A Guide to Gartner Data Governance Research — Market Guides, Hype Cycles, and Peer Reviews
- Gartner Active Metadata Management: Concept, Market Guide, Peer Insights, Magic Quadrant, and Hype Cycle
- The G2 Grid® Report for Data Governance: How Can You Use It to Choose the Right Data Governance Platform for Your Organization?
- The G2 Grid® Report for Machine Learning Data Catalog: How Can You Use It to Choose the Right Data Catalog for Your Organization?
- The Forrester Wave™: Enterprise Data Catalogs, Q3 2024 | Available Now
- Data Catalog: What It Is & How It Drives Business Value
- What Is a Metadata Catalog? - Basics & Use Cases
- Modern Data Catalog: What They Are, How They’ve Changed, Where They’re Going
- Enterprise Data Catalogs: Attributes, Capabilities, Use Cases & Business Value
- The Top 11 Data Catalog Use Cases with Examples
- 15 Essential Features of Data Catalogs To Look For in 2026
- Data Catalog vs. Data Warehouse: Differences, and How They Work Together?
- Snowflake Data Catalog: Importance, Benefits, Native Capabilities & Evaluation Guide
- Data Catalog vs. Data Lineage: Differences, Use Cases, and Evolution of Available Solutions
- Data Catalogs in 2025: Features, Business Value, Use Cases
- AI Data Catalog: Exploring the Possibilities That Artificial Intelligence Brings to Your Metadata Applications & Data Interactions
- Build vs. Buy Data Catalog: What Should Factor Into Your Decision Making?
- Data Catalog Pricing: Understanding What You’re Paying For
- Data Catalog Comparison: 6 Fundamental Factors to Consider
- Informatica Data Catalog Pricing: Estimate the Total Cost of Ownership
- Data Catalog Demo 101: What to Expect, Questions to Ask, and More
- Best Data Catalog: How to Find a Tool That Grows With Your Business
- How to Build a Data Catalog: An 8-Step Guide to Get You Started
- How to Pick the Best Enterprise Data Catalog? Experts Recommend These 11 Key Criteria for Your Evaluation Checklist
- Collibra Pricing: Will It Deliver a Return on Investment?
- Data Lineage Tools: Critical Features, Use Cases & Innovations
- Data Mesh Setup and Implementation - An Ultimate Guide
- What is Active Metadata? Your 101 Guide
- Data Lineage Solutions: Capabilities and 2026 Guidance
- 12 Best Data Catalog Tools in 2026 | A Complete Roundup of Key Capabilities
- Data Catalog Examples | Use Cases Across Industries and Implementation Guide
- 5 Best Data Governance Platforms in 2026 | A Complete Evaluation Guide to Help You Choose
- Data Lineage Tracking | Why It Matters, How It Works & Best Practices for 2026



















