Data Catalog Best Practices: Getting The Most Out of Your Investment

Share this article
As the single source of truth for data in your organization, a data catalog can unlock a ton of business value. Data catalogs provide a centralized location to find, document, and use data. They help prevent data from going “dark”, enabling others throughout the company to leverage data assets to drive business value.
However, just installing one isn’t enough. In this article, we’ll discuss data catalog best practices you can use to get the most value out of your investment in the following areas:
- Metadata
- Business usage
- System development
Table of contents #
- Data catalog best practice: Working towards metadata management maturity
- Data catalog best practice: Prioritizing business usage and adoption
- Data catalog best practice: System development
- Conclusion
- Related reads
Data catalog best practice: Working towards metadata management maturity #
Metadata is the data that describes data - who owns it, what purpose it serves, when it was last updated, and so on.
A data catalog enables metadata both through automatic retrieval from external systems and manual enrichment. Users use metadata to understand how best to use data and to verify that it’s trustworthy.
Automated processes can also use metadata to monitor data usage and enforce security and compliance policies. Robust metadata management also makes your data AI-ready, as it accurately captures data source information, which reduces bias and increases trust in AI-derived offerings.
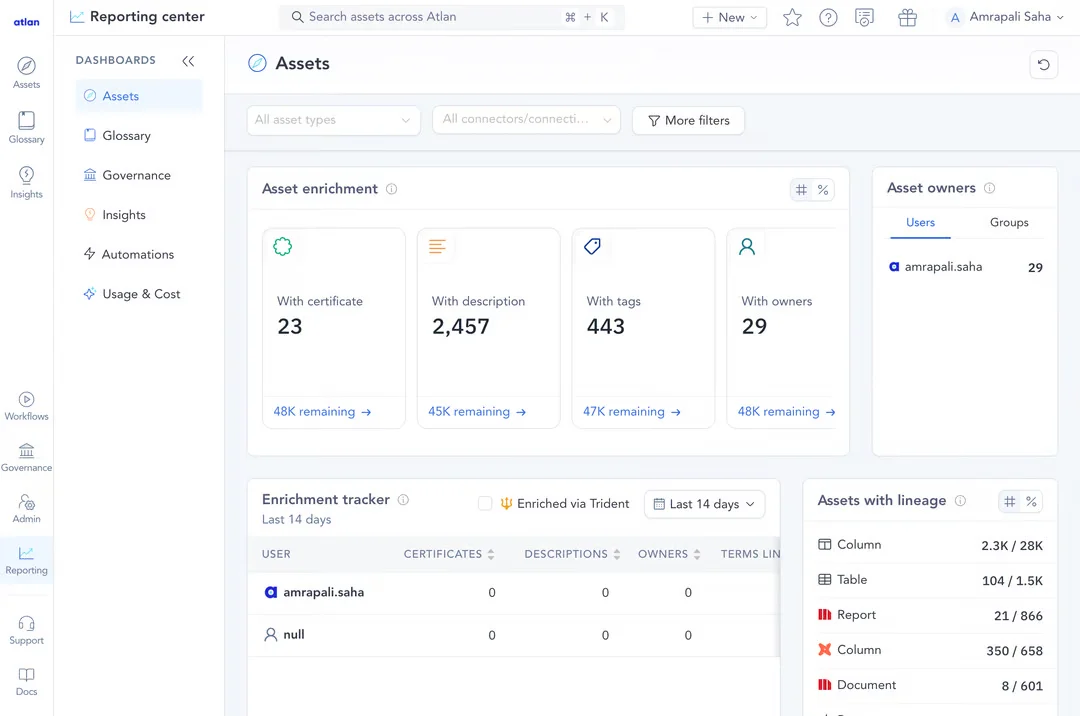
Using a modern data catalog, you can see how much of your data is enriched with metadata - Image by Atlan.
Define business domains #
One of the more fundamental uses of metadata is to break down data into data domains, or areas of ownership and responsibility. For example, you can assign ownership of sales data to the sales team, marketing data to the marketing team, software data to the engineering team, and so on.
Business data domains serve two purposes. First, they assign ownership to the team that best understands that data - and, thus, is best suited to define and maintain it. Second, it breaks down data into navigable spheres, making it easier to discover.
Design and publish data products #
A data product is a specialized application or software tool that’s designed to generate, process, or provide data as a service. Using metadata, teams can describe and package a unit of data to give it clear ownership, description, version, and other attributes. A team can release new versions of its data products over time, providing new capabilities and features while also preserving backward compatibility.
Data products can range from simple dashboards and visualizations to complex machine learning models or analytics data services. Data products can take raw data and transform it into actionable insights, useful information, or valuable services.
Business value:
- Enables teams to package, version, and manage their own data in a way that others can easily find and consume
- Makes it easier for users to reuse the same data in their own apps and reports
- Prevents breakages: Since data products are versioned, data producers can release updates without breaking existing data pipelines or reports on which crucial business decisions depend
Standardize terminology #
Another data catalog best practice is to enforce common terminology and definitions across all teams within an organization.
For example, what distinguishes a “user” and a “customer”? How are metrics around monthly sales calculated? Without a clear, written definition, different teams may use different formulas in different reports. That can lead to confusion, bad business decisions, and a breakdown in cross-team communication.
Business value:
- Eliminates confusion and miscommunications caused by conflicting definitions of similar-sounding terms
- Makes it easier to onboard new team members, as these terms are now defined in a centralized location instead of existing only in other team members’ heads
- Facilitates collaboration by enabling clearer communication and defining terms and metrics that can be used cross-team
Data catalog best practice: Prioritizing business usage and adoption #
A data catalog isn’t of much use if users can’t figure out how to use it.
Early versions of data catalogs were mainly technical tools utilized by data engineers and other IT staff. Then came the cloud computing era and data exploded in growth. A Matillion and IDG study says most enterprises are sourcing data from an average of 400 different sources.
In this environment, limiting data catalogs to tech staff no longer scales. The modern data catalog needs to enable self-service operation across both technical and business users.
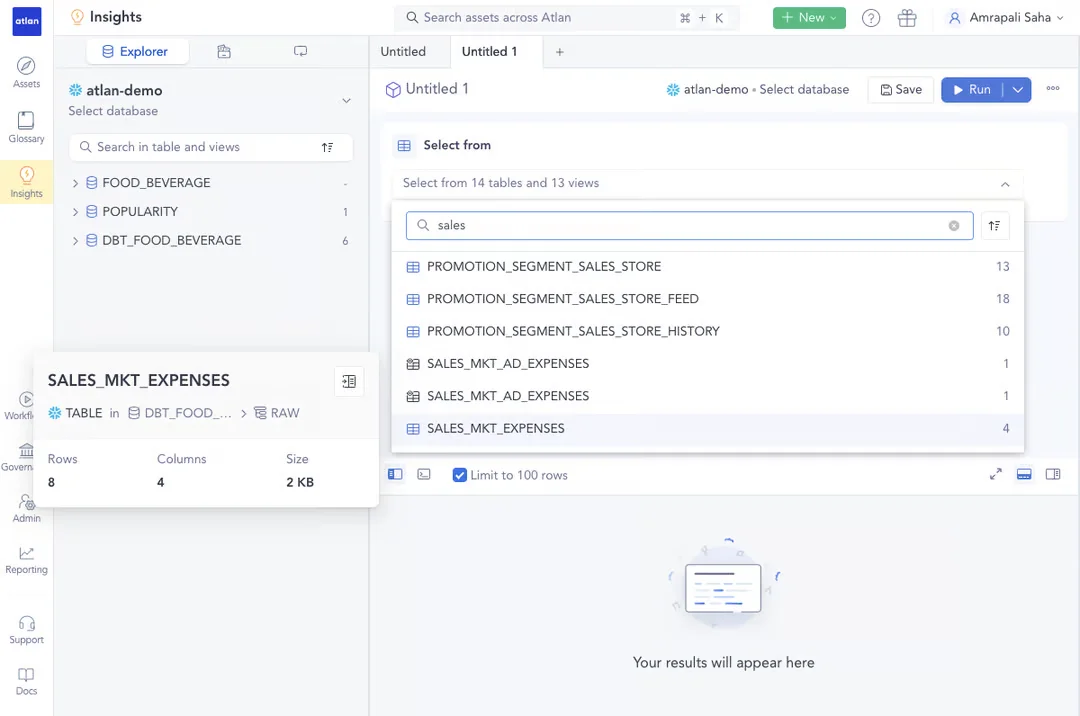
With a visual query builder in modern data catalogs, business users can find the data they need without needing to master SQL. - Image by Atlan.
Here are a few things you can do to integrate your data catalog better into your daily business practices:
Provide accessible search #
Choose a data catalog UI that enables searching for data using a variety of interface languages. It should, at a minimum, support:
- SQL for technical/business analyst users
- Natural language queries
- Visual query builders to simplify the query creation process and assist first-time users
- Filtering by metadata (e.g., business domain, owner, etc.)
A data catalog that incorporates machine learning can provide enhanced search capabilities by using ML, context clues, and search history to make intelligent recommendations to users on results that might be relevant to them.
Business value:
- Enables users from various domains to find the data they need without filing a support ticket to the data engineering team
- Enables self-service - e.g., by giving analysts the ability to find and immediately use the data they need for a report or a new data product
- Eliminates data silos by making data easier to discover
Enable collaboration #
Configure collaboration for your data catalog so that your teams can use tools such as Slack, Teams, Jira, and others to deal with data-related issues with their colleagues. Ideally, these tools can be integrated directly with your data catalog to provide seamless, inline collaboration.
For example, assume that a business user finds a field without a data classification tag identifying whether or not it contains sensitive information. Using collaboration tools, they can discuss the field with their team on Slack and figure out how best to proceed. If the issue requires a deeper dive, they can directly open a Jira ticket from within the data catalog tool and assign it to a team member for resolution.
Business value:
- Lowers the barriers to team members and teams sharing and discussing information
- Accelerates development time by reducing friction in communication about data assets
- Provides a written record around discussions about data assets that other team members can reference for clarity
Automate compliance #
Failure to comply with local regulations surrounding data can erode customer trust and carry hefty fines. For example, in 2022, Danske Bank incurred a hefty fine when the European Union found it failed to delete data that no longer had any business value - a violation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
As data growth skyrockets, ensuring and enforcing compliance across all data assets becomes increasingly difficult. You can alleviate the burden by appropriately classifying data and using automated processes to enforce classification rules - e.g., by enforcing role-based access control (RBAC) to limit data exposure or automatically purging data after a set time period.
Business value:
- Increases business by reassuring customers that you’re taking every measure possible to keep their data safe and secure
- Reduces fines and expenses associated with noncompliance or data breaches
- Reduces the cost and accuracy of compliance by replacing manual effort with automated processes
Data catalog best practice: System development #
“System development” refers to the processes and standards that your organization sets to increase the quality and the impact of your data catalog over time. Creating a system development plan is crucial for both measuring the impact of your data catalog as well as increasing user engagement and increasing asset value.
Define KPIs and OKRs #
A Key Performance Indicators (KPI) is a type of metric tied to a specific performance goal - either individual, team, or corporate. Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are organizational goals against which a company benchmarks itself every quarter.
Both KPIs and OKRs can be broken down into sets of quantitative and qualitative goals. Common KPIs for data initiatives may include elements such as data quality scores or user engagement metrics. OKRs may include larger initiatives, such as an effort to implement compliance with GDPR right to deletion requests via a single button click.
Business value:
- Shows to all stakeholders and senior leadership the direct impact that the data catalog is having on data quality, compliance, and overall revenue
- Aligns data catalog goals with larger business objectives
- Enables making targeted improvements in data catalog usage
Test, automate, and audit data quality #
When data is split across hundreds of data stores, there is usually no single, uniform approach to ensuring that data is clean and accurate. As the single source of truth for data company-wide, you can leverage your data catalog to define data quality standards across the org.
You can use trust and verification scores in your data catalog to monitor and improve the data quality of your data products over time.
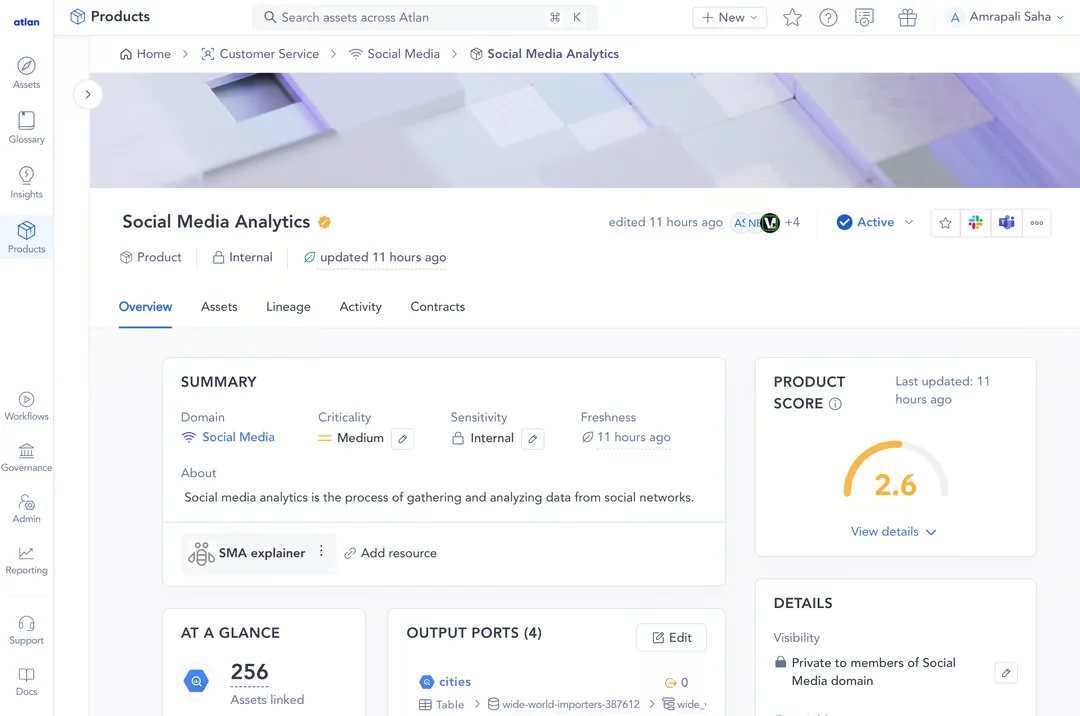
Data catalogs can enable a product score for all of your data products so that you can improve data product quality by making sure they’re discoverable, understandable, addressable, secure, interoperable, and trustworthy. - Image by Atlan.
Business value:
- Improves data trust, user engagement, and communication between teams
- Reduces time spent manually checking and enforcing data quality across hundreds of data sources
Establish domain-specific standards #
By utilizing business data domains and data products, you can enforce global data quality standards while also enabling teams to enforce their own domain-specific data rules. Domain owners can leverage the data catalog to define rules surrounding their data to ensure that any data sourced from upstream producers conforms to the team’s understanding and expectations.
Business value:
- Provides for implementing global standards while also granting local control
- Enables experts in a given data set to set data quality criteria based on their knowledge and experience
Conclusion #
Getting maximum value from your data catalog requires more than just wiring it up. By following the best practices above, you can ensure that data in your organization is clean, discoverable, and safe. And using KPIs and OKRs, you can demonstrate objectively that your efforts are having a positive impact on the company’s bottom line.
Implementing these best practices is easier with the right foundation. Atlan Data Catalog provides the support for collaboration, automation, ease of use, and security that you need to deliver business value.
Want to learn more? Contact us for a demo today.
Data catalog best practices: Related reads #
- Data Catalog Guide
- Build vs. Buy Data Catalog: What Should Factor Into Your Decision Making?
- Build vs. Buy: Why Fox Chose Atlan
- Data Catalog Requirements in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide
- Open-Source Modern Data Stack: 5 Steps to Build
- Data Catalog Demo 101: What to Expect, Questions to Ask, and More
- Data catalogs in 2024
- 5 Main Benefits of a Data Catalog
- Data Cataloging Process: Challenges, Steps, and Success Factors
- Data Catalog Business Value: Assessment Factors, Benefits, and ROI Calculation
- Who Uses a Data Catalog & How to Drive Positive Outcomes?
- 15 Essential Features of Data Catalogs to Look for in 2024
- Data Catalog Adoption: What Limits It and How to Drive It Effectively
Share this article









