How To Build an Effective Data Governance Team in 2025
What are the key responsibilities of a data governance team?
Permalink to “What are the key responsibilities of a data governance team?”Summarize and analyze this article with 👉 🔮 Google AI Mode or 💬 ChatGPT or 🔍 Perplexity or 🤖 Claude or 🐦 Grok (X) .
A data governance team is responsible for translating council-approved policies into day-to-day practices.
Unlike a data governance council (which sets direction and oversight), the team handles the day-to-day operations—from creating policies and frameworks to ensuring compliance, data quality, and adoption across business units.
Their responsibilities typically include:
- Data policy development and enforcement
- Data quality assurance
- Data security and privacy management
- Data literacy
- Collaboration across departments
- Data governance program monitoring and reporting
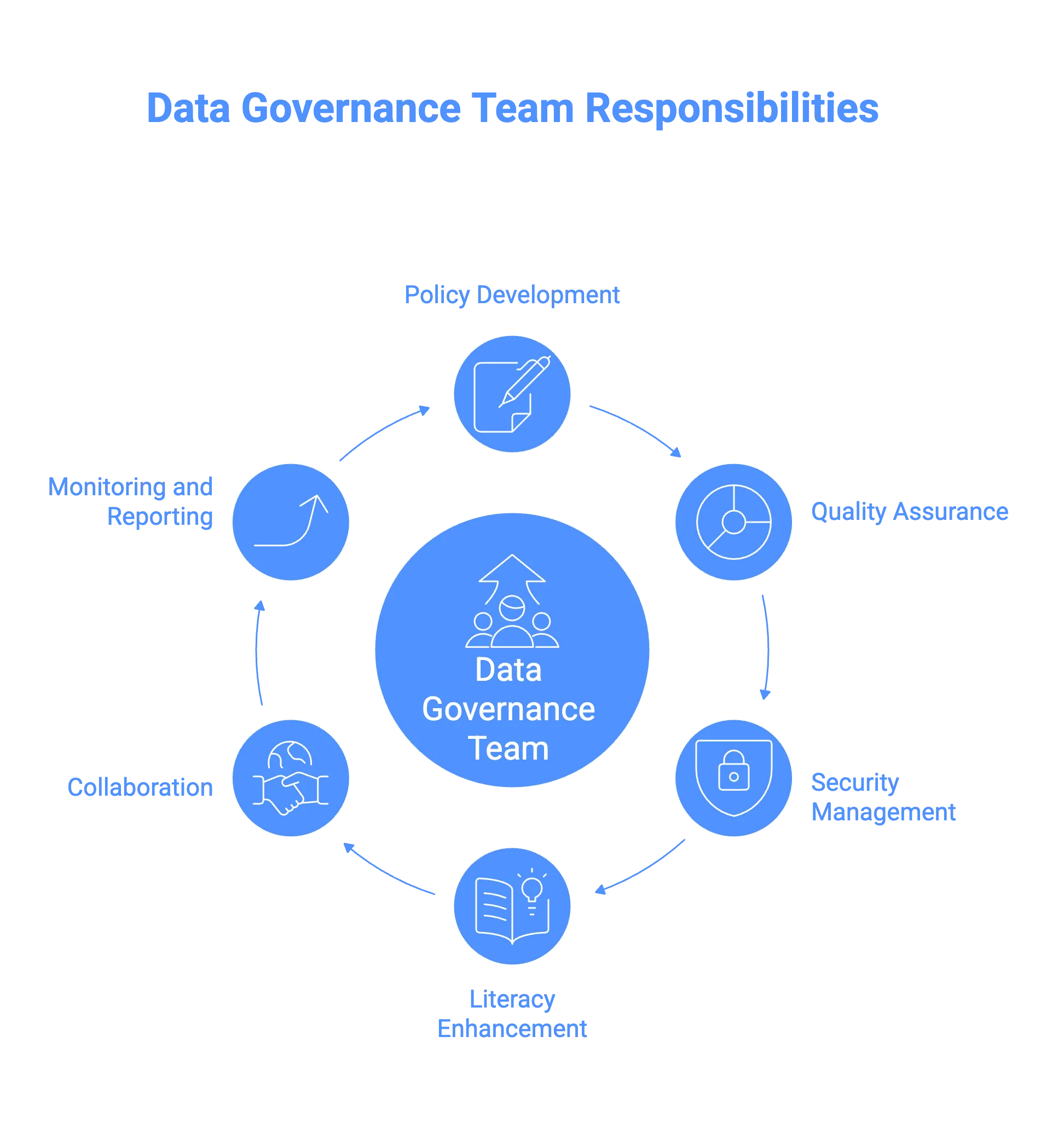
Top responsibilities of the data governance team. Image by Atlan.
1. Data policy development and enforcement
Permalink to “1. Data policy development and enforcement”This involves defining and applying rules for data handling, access, storage, and usage.
Typical activities include (but aren’t limited to):
- Drafting role-based access policies
- Tagging sensitive data
- Automating policy enforcement in metadata tools
2. Data quality assurance
Permalink to “2. Data quality assurance”Data quality involves implementing processes and controls to maintain accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness of data across systems.
Typical activities include (but aren’t limited to):
- Running data profiling checks
- Resolving duplicates
- Monitoring data quality dashboards
- Correcting records flagged in quality reports
3. Data security and privacy management
Permalink to “3. Data security and privacy management”This involves implementing measures to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with applicable regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, financial mandates).
Typical activities include (but aren’t limited to):
- Conducting access reviews and audits
- Setting up data masking and anonymization for PII
- Maintaining audit trails for sensitive data usage
- Coordinating with security teams on breach prevention and response
4. Data literacy
Permalink to “4. Data literacy”This involves raising awareness of governance practices and their strategic value, and educating employees on how to responsibly use data.
Typical activities include (but aren’t limited to):
- Running onboarding and refresher training sessions
- Publishing data playbooks and glossaries
- Hosting workshops on data ownership and usage policies
- Offering office hours or help desks for governance queries
5. Collaboration across departments
Permalink to “5. Collaboration across departments”This involves bridging the gap between technical, business, legal, and compliance teams to ensure alignment in how data is managed and used.
Typical activities include (but aren’t limited to):
- Facilitating cross-functional meetings or governance forums
- Resolving data ownership disputes
- Aligning KPI definitions across business units
- Working with compliance and legal teams on regulatory reporting
6. Data governance monitoring and reporting
Permalink to “6. Data governance monitoring and reporting”This involves tracking the effectiveness of governance initiatives and providing transparency into progress, policy coverage, quality metrics, risks, and ROI.
Typical activities include (but aren’t limited to):
- Monitoring adherence to policies and standards
- Producing regular governance performance reports
- Tracking lineage and metadata completeness
- Escalating non-compliance issues to the council
What are the key roles within a data governance team?
Permalink to “What are the key roles within a data governance team?”A data governance organization structure brings together technical, business, and compliance expertise to translate governance policies into practice. Key roles within the team include:
- Chief Data Officer (CDO) or Data Governance Lead
- Data Owners
- Data Stewards
- Data Architects and Engineers
- Data Quality Analysts
- Data Security and Privacy Officers
- Business Process Owners
- Legal and Compliance Officers
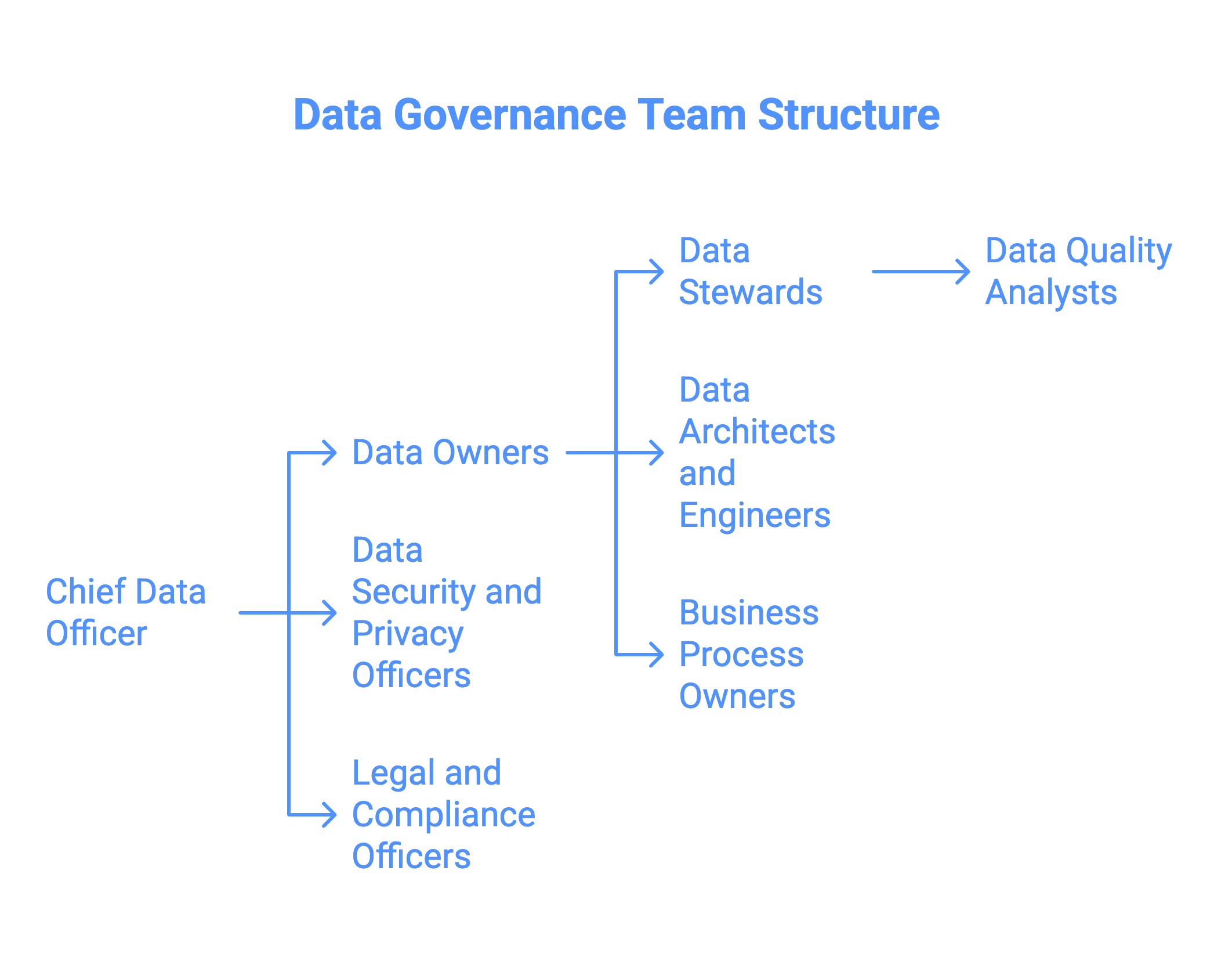
Data governance team structure. Image by Atlan.
Key responsibilities of each role within the data governance team
Permalink to “Key responsibilities of each role within the data governance team”Here’s a breakdown of the key roles within a data governance team structure and their core responsibilities.
| Role | Key responsibilities |
|---|---|
| CDO/Data Governance Lead | 1. Work with the Data Governance Council to define data governance goals and objectives 2. Approve and review data governance policies and standards 3. Allocate resources and budget 4. Monitor progress |
| Data Owners | 1. Define data quality requirements and standards for the data domain 2. Determine data access and security policies 3. Assign data stewards to manage specific data sets 4. Collaborate with data stewards to resolve data governance issues |
| Data Stewards | 1. Monitor and maintain data quality within their domain 2. Implement data governance policies and standards 3. Define and maintain metadata, data lineage, business glossary and data catalogs 4. Collaborate with other data stewards and data owners to ensure data consistency across the organization According to Gartner, 67% of organizations have formally established one or more data governance stewards to enforce policies and procedures. |
| Data Architects and Engineers | 1. Design and maintain the data infrastructure 2. Ensure systems support governance requirements such as lineage tracking and metadata capture 3. Integrate governance tools into pipelines 4. Collaborate with stewards and analysts on implementing quality and access rules |
| Data Quality Analysts | 1. Develop and execute data quality checks and controls 2. Profile datasets for accuracy, completeness, and consistency 3. Monitor dashboards and reports for anomalies 4. Escalate recurring data issues to stewards or owners |
| Data Security and Privacy Officers | 1. Define and enforce data protection measures 2. Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) 3. Conduct risk assessments and security audits 4. Train data governance team members on privacy and security best practices 5. Collaborate with legal and compliance teams to stay informed about relevant regulations |
| Business Process Owners | 1. Align governance requirements with operational workflows 2. Ensure business processes comply with governance standards 3. Support change management when policies impact processes 4. Provide feedback on data usability within operations |
| Legal and Compliance Officers | 1. Monitor evolving regulatory requirements 2. Advise on legal implications of governance policies 3. Validate compliance documentation for audits 4. Work with CDO and security officers to ensure legal alignment |
RACI for a typical data governance team
Permalink to “RACI for a typical data governance team”RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) matrices prevent the governance bottlenecks and improve overall team function. Here’s a legend for the RACI matrix:
- R = Responsible (does the work)
- A = Accountable (final authority, owns the outcome)
- C = Consulted (provides input/expertise)
- I = Informed (kept in the loop)
Responsibility | CDO / Governance Lead | Data Owners | Data Stewards | Data Architects & Engineers | Data Quality Analysts | Data Security & Privacy Officers | Business Process Owners | Legal & Compliance Officers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Define governance policies | A/R | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
Enforce governance policies | A | R | R | C | C | C | C | C |
Ensure data quality | C | A | R | C | R | C | C | I |
Manage data security & privacy | C | C | C | C | I | A/R | I | C |
Align data with business strategy | A | R | C | C | I | C | R | I |
Regulatory compliance & audit readiness | C | I | C | I | I | R | I | A |
Cross-functional collaboration | R | R | R | C | C | C | R | C |
Program monitoring & reporting | A | C | R | C | R | C | C | C |
What skills do data governance teams require?
Permalink to “What skills do data governance teams require?”Here’s a breakdown of the key skills that each member of the data governance team should have to fulfill their responsibilities.
Role | Must-Have Skills | Nice-to-Have Skills |
|---|---|---|
Chief Data Officer / Governance Lead | Strategic leadership, regulatory awareness, stakeholder management | Change and risk management, AI governance knowledge |
Data Owners | Domain expertise, accountability for data quality, collaboration | Understanding of metadata tools and dashboards |
Data Stewards | Metadata management, data quality monitoring, glossary setup and maintenance, collaboration | Scripting (SQL, Python) and automation setup |
Data Architects & Engineers | Data modeling, ETL pipeline design, system integration | Cloud architecture, lineage automation |
Data Quality Analysts | Data profiling, anomaly detection, dashboard reporting | Predictive analytics, ML-driven quality checks |
Data Security & Privacy Officers | Data classification, regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA), risk assessment | Zero-trust architecture, privacy-by-design |
Business Process Owners | Process optimization, cross-department alignment | Lean/Six Sigma, automation tool experience |
Legal & Compliance Officers | Regulatory interpretation, audit documentation, policy advisory | Experience with RegTech platforms, AI regulation awareness |
Why is it important to have a data governance team?
Permalink to “Why is it important to have a data governance team?”A data governance team is critical because it brings council-approved policies to life through execution and accountability. Without a dedicated team, governance efforts risk remaining high-level directives with no operational impact.
The biggest benefits of having a data governance team are:
- Improved decision-making: High-quality, well-managed data enables better analysis, more reliable insights, and confident business strategies.
- Reduced risks: Proper handling of data minimizes errors, fraud, and non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Enhanced operational efficiency: Streamlined processes for data quality, security, and access help teams work faster and more productively.
- Increased trust in data: By ensuring accuracy, consistency, and compliance, governance builds organizational confidence in data as a reliable asset.
What tools do data governance teams need?
Permalink to “What tools do data governance teams need?”Data governance teams can’t succeed with fragmented tools. Separate platforms for catalogs, lineage, quality, and access controls only create silos and inefficiencies.
Modern governance needs a unified, metadata-driven control plane like Atlan, where policies, quality, and context live together and flow across the data stack.
For instance, with Atlan, here’s how your team would function:
- Data Governance Leads: Define policies once; Atlan auto-applies them across connected systems and tracks compliance in real time.
- Data Stewards: Enrich datasets with business context, trace lineage instantly, and monitor quality KPIs within the same workspace.
- Data Architects & Engineers: Connect APIs, enforce encryption, and manage audit logs in a central console.
- Business Users: Search and explore approved datasets through Atlan’s Google-like interface, request access in two clicks, and trust that data is compliant and high-quality.
Teams consolidating onto Atlan see 35% faster time-to-insight and cut governance overhead by 40%, making governance both scalable and impactful.
Real stories from real customers: Scaling data governance programs
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Scaling data governance programs”
Implemented data governance strategy and roadmap using Atlan
“Our objective was to improve Aliaxis’ maturity around Data Governance, and we wanted to ensure that whatever tool we picked not only fit nicely with our tech stack, but that users didn’t feel intimidated, or felt that it was a huge organizational shift. Atlan’s user-friendliness seemed so simple and its capabilities gave us room to grow and mature as an organization without too many restrictions.”
Nestor Jarquin, Global Data & Analytics Lead
Aliaxis
🎧 Listen to podcast: Aliaxis’s global data journey with Atlan
Join Data Leaders Scaling with Automated Data Governance
Book a Personalized Demo →
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
“Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. ‘Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,’ Kiwi.com shared. Atlan’s intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams.”
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan
Join Data Leaders Scaling with Automated Data Governance
Book a Personalized Demo →Ready to build a world-class data governance team?
Permalink to “Ready to build a world-class data governance team?”With clear roles, defined responsibilities, and the right tools, your data governance team can safeguard data quality, reduce risks, and unlock greater business value from every dataset.
If you’re ready to move beyond policies on paper and into execution, start by aligning the right people, processes, and technology. Done right, your governance team will turn data into a trusted asset that drives growth and innovation across the business.
Join Data Leaders Scaling with Automated Data Governance
Book a Personalized Demo →FAQs about data governance team
Permalink to “FAQs about data governance team”What is a data governance team?
Permalink to “What is a data governance team?”A data governance team is responsible for implementing policies, frameworks, and processes that ensure data is accurate, secure, and compliant throughout its lifecycle.
Who leads data governance?
Permalink to “Who leads data governance?”Data governance is typically led by a Chief Data Officer (CDO) or a Data Governance Lead, who provides leadership, ensures alignment with business goals, and reports to senior management.
What is the data governance team’s structure?
Permalink to “What is the data governance team’s structure?”The structure usually includes:
- CDO or Data Governance Lead
- Data Owners for domains
- Data Stewards for quality and metadata
- Data Architects and Engineers
- Data Quality Analysts
- Data Security and Privacy Officers
- Business Process Owners
- Legal and Compliance Officers
What are the key responsibilities of a data governance team?
Permalink to “What are the key responsibilities of a data governance team?”Their responsibilities include enforcing data policies, ensuring data quality, managing security and privacy, promoting data literacy, collaborating across departments, and monitoring program effectiveness.
How does a data governance team differ from a data governance council?
Permalink to “How does a data governance team differ from a data governance council?”A data governance council sets the direction and oversight (policies, principles, alignment). Meanwhile, the data governance team executes daily operations (policy enforcement, data quality checks, compliance, training).
Why is a data governance team important?
Permalink to “Why is a data governance team important?”The data governance team improves decision-making with high-quality data, reduces risks like breaches and compliance failures, enhances operational efficiency, builds trust in data, and increases business value from data assets.
What tools do data governance teams use?
Permalink to “What tools do data governance teams use?”Data governance teams need metadata-driven platforms like Atlan, which unify cataloging, lineage, quality, security, and collaboration in one control plane, cutting governance overhead and speeding time-to-insight.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
Data governance team: Related reads
Permalink to “Data governance team: Related reads”- What Does a Data Governance Team Do?
- Who is a Chief Data Officer & What Can They Do For You?
- Data Governance Roles and Their Responsibilities: A Complete Round Up
- What Is Data Governance? Its Importance, Principles & How to Get Started
- Data Governance 101: Principles, Examples, Strategy & Programs
- What Is Data Lineage & Why Is It Important?
- What Is a Data Catalog? & Why Do You Need One in 2025?
- Data Governance Committee 101: When Do You Need One?
- Data Governance Councils in 2025: Responsibilities, Benefits, Tooling & Setup Guide
- Data Governance and Compliance: Act of Checks & Balances
- Data Governance Framework — Guide, Examples, Template
- Data Governance Tools Comparison: How to Select the Best
- Data Governance Tools Cost: What’s The Actual Price?
- Data Governance Process: Why Your Business Can’t Succeed Without It
- Data Governance for AI: Challenges & Best Practices
- Data Governance Maturity Model: A Roadmap to Optimizing Your Data Initiatives and Driving Business Value
- Federated Data Governance: Principles, Benefits, Setup
- Data Governance Committee 101: When Do You Need One?
- Data Governance Policy: Examples, Templates & How to Write One
- 7 Best Practices for Data Governance to Follow in 2025
- Benefits of Data Governance: 4 Ways It Helps Build Great Data Teams
- Key Objectives of Data Governance: How Should You Think About Them?
- The Principles of Data Governance: Pillars of a Modern Data Culture
- 7 Must-Have Data Governance Certifications for 2025




















