How do modern catalogs differ from traditional catalogs?
Permalink to “How do modern catalogs differ from traditional catalogs?”Traditional data catalogs emerged in the 1990s as IT-centric tools for documenting database schemas and table structures.
First-generation catalogs from vendors like Informatica required manual metadata entry and served primarily technical users.
A 2024–2025 Modern Data Survey found that data professionals waste 20% of their project time (one full day per week) simply trying to figure out what data to use. Legacy catalogs fail to solve this because they lack business context, with 70% of teams citing “business understanding” as their biggest bottleneck.
Second-generation tools like Alation expanded access to data stewards but still relied heavily on human curation.
Gartner predicts that traditional governance models, which these tools support, are headed for widespread failure. 80% of data and analytics governance initiatives are projected to fail by 2027 if they continue to rely on traditional, passive cataloging methods.
The shift to modern data catalogs stems from four converging pressures. Cloud data platforms like Snowflake and Databricks can spin up in hours, but traditional catalogs take months to implement.
Modern data catalogs address these challenges through architectural shifts. They use active metadata that updates continuously as schemas change and pipelines run. Automated discovery scans databases, warehouses, and BI tools to capture technical specifications without human intervention. Integration with the modern data stack happens through pre-built connectors rather than custom code.
The third generation of catalogs treats metadata as an operational asset rather than documentation. This shift enables data mesh architectures where domain teams own their data while central teams maintain visibility.
According to Gartner, modern data catalog platforms like Atlan have achieved over 90% non-technical user adoption within the first 90 days of deployment.
What are the core capabilities of modern data catalogs?
Permalink to “What are the core capabilities of modern data catalogs?”Modern catalogs combine eight essential capabilities that differentiate them from traditional metadata repositories. Forrester research indicates that organizations evaluate platforms based on how well they deliver across all areas rather than excelling in just one or two.
1. Automated discovery and enrichment
Permalink to “1. Automated discovery and enrichment”Platforms continuously scan data sources to capture schemas, relationships, and technical metadata. Discovery happens automatically through connectors to databases, warehouses, transformation tools, and BI platforms. According to McKinsey, organizations using automated discovery reduce initial cataloging time by 65% compared to manual approaches.
Enrichment layers add context beyond technical specifications. AI-powered classification identifies sensitive data types like PII or financial information without manual tagging. Usage analytics track which datasets analysts query most frequently. Quality scores aggregate freshness, completeness, and validation metrics.
2. End-to-end data lineage
Permalink to “2. End-to-end data lineage”Column-level lineage shows how data moves from source systems through transformations to final reports. Catalogs parse SQL code, read transformation logic from tools like dbt, and trace data flow across the entire stack.
Users can click on any dashboard metric to see upstream dependencies or identify downstream impacts before making changes. Data engineers use lineage to accelerate root cause analysis when data quality issues arise. Compliance teams trace personal data for GDPR requests. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, organizations with automated lineage reduce breach investigation time by an average of 58 days.
Migration projects rely on lineage to understand system dependencies. The catalog updates lineage automatically as pipelines change rather than requiring manual mapping.
3. Intelligent search and discovery
Permalink to “3. Intelligent search and discovery”Search goes beyond keyword matching to understand context and intent. Users can ask “customer revenue by region” and find relevant tables even if they use different terminology. Natural language processing interprets queries while ranking results based on usage patterns, quality scores, and user permissions.
Research from the University of California, Berkeley found that context-aware search reduces data discovery time from an average of 4.2 hours to 12 minutes.
Faceted filters let users narrow results by data source, owner, last update time, or certification status. Search surfaces related assets automatically such as downstream dashboards that use a particular table. Personalization shows each user results most relevant to their role and recent activity.
4. Knowledge graphs and semantic layers
Permalink to “4. Knowledge graphs and semantic layers”Catalogs build knowledge graphs that connect data assets through relationships beyond technical lineage. Business concepts link to the tables that store them. Metrics connect to their calculation logic and source data. Domain models show how entities relate across the organization.
These semantic layers enable context-aware experiences. When users search for “revenue,” the catalog understands this business concept and surfaces all related tables, metrics, and reports. According to Gartner’s 2024 Data and Analytics Summit, organizations implementing semantic layers report 43% faster time-to-insight for business users.
Semantic search powered by vector embeddings finds conceptually similar assets even when terminology differs across teams.
5. Embedded catalog experiences
Permalink to “5. Embedded catalog experiences”Platforms embed catalog context directly into tools where data work happens. Chrome extensions surface data definitions and lineage within BI tools. Slack integrations enable catalog search and notifications without leaving conversations.
API access lets developers build catalog context into custom applications. This embedded approach drives adoption by meeting users where they work rather than requiring context switching.
6. Collaborative workflows
Permalink to “6. Collaborative workflows”Platforms embed collaboration directly into the catalog interface. Users can ask questions about datasets, share knowledge through annotations, and document tribal knowledge that would otherwise remain siloed.
Discussions happen in context on specific tables or columns rather than in separate channels. Integration with tools like Slack enables notifications when data owners respond to questions or when quality checks fail.
Workflows for data access requests, certification approvals, and ownership assignments keep governance processes moving. The catalog becomes the system of record for data-related decisions and context.
7. Governance and compliance automation
Permalink to “7. Governance and compliance automation”Automated policy enforcement applies access controls, data masking, and retention rules based on metadata classifications. When the catalog identifies a new table containing PII, policies automatically apply appropriate restrictions.
Tag propagation ensures classifications flow downstream through transformations. Audit trails document who accessed sensitive data and why. Certification workflows let stewards validate dataset quality and approve assets for production use.
According to industry research, organizations with automated governance reduce compliance violations by 67% and cut audit preparation time by 52%.
The catalog provides compliance evidence for regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Modern platforms support federated governance where domain teams own classification while central teams define policies.
8. Open API architecture
Permalink to “8. Open API architecture”Catalogs expose comprehensive APIs that enable bidirectional metadata flow. External tools can read metadata to enrich their interfaces or write metadata back when users make changes. This openness prevents vendor lock-in and allows organizations to build custom workflows.
API-first design supports metadata orchestration across the entire data stack. Quality tools write validation results to the catalog. BI platforms read lineage to show impact analysis. Transformation tools publish data definitions.
Active vs passive metadata approaches
Permalink to “Active vs passive metadata approaches”The fundamental difference between modern and traditional catalogs lies in how they handle metadata. This distinction determines whether catalogs scale with data growth or become outdated documentation that teams ignore.
Aspect | Passive Data Catalog | Active Data Catalog |
|---|---|---|
Update method | Manual documentation by data stewards | Automated discovery and continuous monitoring |
Accuracy | Degrades over time as data changes | Maintains currency through real-time synchronization |
Automation | Limited, relies on human effort | Extensive AI-powered classification and enrichment |
Users | Primarily data engineers and stewards | Serves technical and business users across all roles |
Workflows | Separate tool requiring context switching | Embedded into BI tools, Slack, and daily workflows |
Governance | Manual policy application | Automated policy enforcement based on classifications |
Scalability | Breaks down beyond hundreds of tables | Handles millions of assets across hundreds of sources |
Passive approaches rely on data stewards to document tables, add descriptions, and maintain accuracy. This works for small data estates but breaks down at scale. Metadata becomes outdated within weeks as schemas change and pipelines evolve. Users lose trust when descriptions don’t match reality. Organizations spend resources maintaining catalogs rather than deriving value.
Active metadata systems invert this model. They continuously monitor source systems and capture changes in real time. When a developer adds a table to the warehouse, the catalog discovers it automatically. When transformation logic changes, lineage updates reflect the new flow.
According to Gartner research on active metadata management, metadata must be continuously captured, analyzed, and applied in real time to support AI-driven intelligence. Organizations using active approaches report metadata accuracy rates above 90% compared to 60-70% with passive documentation.
Active catalogs also drive automation beyond documentation. They trigger alerts when quality thresholds are breached. They recommend similar datasets to users based on analysis patterns. They enforce governance policies automatically when sensitive data is discovered.
What are the types of modern data catalogs
Permalink to “What are the types of modern data catalogs”Organizations evaluate multiple catalog approaches based on their data architecture, vendor relationships, and governance requirements. Understanding the landscape helps teams make informed decisions.
1. Enterprise data catalogs
Permalink to “1. Enterprise data catalogs”Enterprise data catalogs provide comprehensive coverage across the entire data estate. These platforms like Atlan connect to hundreds of data sources through pre-built connectors and offer advanced capabilities for governance, collaboration, and AI readiness.
According to research, you can reduce your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) by as much as 40% by migrating your business to the public cloud. Enterprise catalogs excel at multi-cloud and multi-platform environments. They provide unified visibility across Snowflake, Databricks, cloud warehouses, on-premise databases, and BI tools.
This breadth makes them ideal for organizations with diverse technology stacks or those undergoing cloud migration.
2. Platform-native catalogs
Permalink to “2. Platform-native catalogs”Cloud data platforms increasingly offer native catalog capabilities. Unity Catalog from Databricks, Microsoft Purview, and Google Dataplex provide basic cataloging for assets within their ecosystems. These native catalogs integrate tightly with their respective platforms and often come at no additional cost.
Platform-native catalogs work well for organizations standardized on a single platform. However, they create challenges in multi-cloud or hybrid environments where metadata remains siloed across platforms.
Teams cannot see lineage or govern policies consistently when data flows between platforms. EA Journals research found that 79% of data leaders cite cross-platform visibility as their top challenge.
3. Layered catalog architectures
Permalink to “3. Layered catalog architectures”Many organizations layer enterprise catalogs over platform-native capabilities to get benefits of both approaches. Platform-native catalogs handle basic discovery and access control within their ecosystem. Enterprise catalogs provide cross-platform visibility, advanced governance, and collaboration features.
This layered approach makes sense when organizations use Horizon Data Catalog or Unity Catalog or Purview for operational governance but need unified discovery across multiple platforms. Atlan integrates with platform-native catalogs through bidirectional metadata sync, creating a unified control plane without replacing existing investments.
4. Open source data catalogs
Permalink to “4. Open source data catalogs”Open source alternatives like Apache Atlas, Amundsen, and DataHub offer free catalog capabilities with full code access. These projects work well for organizations with engineering resources to customize and maintain them.
Open source catalogs provide flexibility but require significant investment in deployment, configuration, and ongoing maintenance. A survey by The New Stack revealed that organizations spend an average of 2.3 FTE years annually maintaining open source data infrastructure.
Organizations should evaluate total cost of ownership including engineering time versus licensing costs for commercial platforms that include support and automated updates.
Quantify productivity gains and governance efficiency for your organization.
Calculate Data Catalog ROI →How do modern catalogs enable AI readiness?
Permalink to “How do modern catalogs enable AI readiness?”AI and machine learning initiatives create new requirements for data catalogs beyond traditional discovery and governance. Modern catalogs evolve to support the entire AI lifecycle from training data discovery to model governance.
1. AI asset registration and cataloging
Permalink to “1. AI asset registration and cataloging”Catalogs extend beyond data assets to catalog ML models, features, and embeddings. Organizations can register ML models alongside the datasets that train them. Feature stores connect to show which features feed which models. This unified view enables teams to understand AI assets with the same rigor as data assets.
Model metadata includes training data lineage, performance metrics, deployment status, and ownership. Teams can search for models by use case, understand dependencies, and track model drift over time. According to Gartner’s AI Governance survey, only 29% of organizations currently catalog AI assets, creating significant governance gaps.
This governance prevents shadow AI where teams build models outside visibility and control.
2. Training data lineage for transparency
Permalink to “2. Training data lineage for transparency”AI regulations like the EU AI Act require transparency into training data sources and quality. Modern catalogs provide end-to-end lineage showing which datasets trained which models. Teams can trace model predictions back to source data for explainability and bias detection.
Lineage also helps teams understand when training data changes affect model performance. If source data quality degrades or schemas change, the catalog alerts model owners to potential impacts. This proactive monitoring prevents model drift and maintains AI system reliability.
3. Model Context Protocol (MCP) support
Permalink to “3. Model Context Protocol (MCP) support”The Model Context Protocol enables AI agents and assistants to access catalog metadata dynamically. Modern catalogs expose MCP servers that let LLMs retrieve data definitions, lineage, and quality metrics on demand. This connectivity makes AI agents more accurate by grounding responses in actual metadata.
MCP integration allows developers to build AI agents that understand your data landscape. Agents can answer questions about data availability, recommend relevant datasets, and even generate queries based on catalog metadata. This makes data more accessible through conversational interfaces.
4. RAG governance and semantic search
Permalink to “4. RAG governance and semantic search”Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) applications need governed access to organizational knowledge. Modern catalogs provide semantic search over metadata using vector embeddings. This enables RAG systems to find relevant context even when search terms don’t exactly match metadata.
AI governance capabilities ensure RAG applications access only data users have permissions for. The catalog enforces the same access policies for AI agents as for human users. This prevents data leakage through AI interfaces while enabling self-service question answering.
5. Vector search and embedding management
Permalink to “5. Vector search and embedding management”Organizations building semantic search or recommendation systems need to manage vector embeddings alongside traditional metadata. Modern catalogs store embeddings, track which models generated them, and provide vector search capabilities for similarity-based discovery.
This enables advanced use cases like finding conceptually similar datasets even when column names differ. Teams can search for “customer demographics” and discover relevant tables even if they use terms like “user attributes” or “subscriber profiles.”
Typical implementation timeline of a modern data catalog
Permalink to “Typical implementation timeline of a modern data catalog”Implementation timelines vary significantly based on deployment model, data estate complexity, and organizational readiness. Understanding typical patterns helps teams set realistic expectations.
SaaS deployments: 2-4 weeks for initial value
Permalink to “SaaS deployments: 2-4 weeks for initial value”Modern SaaS catalogs like Atlan deliver value within weeks. Day one starts with connector setup to scan initial data sources. Week one provides basic discovery as automated scanning captures technical metadata. Week two adds business context through bulk imports or initial curation. Week three onboards early adopters and establishes feedback loops.
Organizations see immediate benefits from search and lineage even before comprehensive enrichment. Technical users gain visibility into schemas and dependencies. This quick time-to-value builds momentum for broader rollout and justifies continued investment.
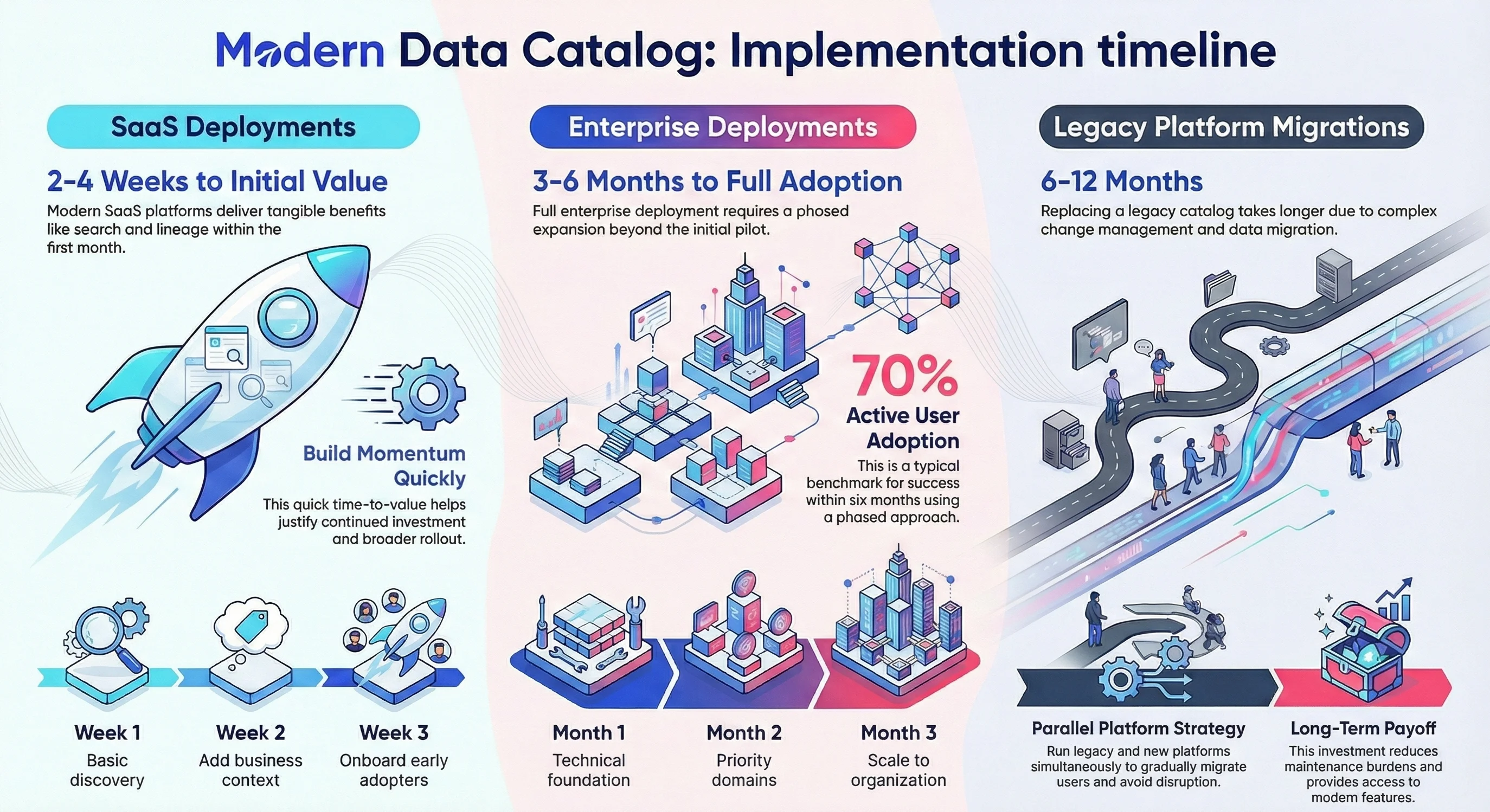
Typical implementation timeline of a modern data catalog. Source: Atlan.
Enterprise deployments: 3-6 months for full adoption
Permalink to “Enterprise deployments: 3-6 months for full adoption”Full enterprise deployment requires phased expansion beyond initial pilots. Month one focuses on technical foundation with core systems connected and governance framework defined. Month two expands to priority domains with stewards trained and workflows established. Month three scales to full organization with self-service enablement and change management.
Success metrics evolve through phases. Early wins focus on technical metadata completeness and search usage. Later phases measure business adoption, governance compliance, and reduced time to insight. Organizations report reaching 70% active user adoption within six months using phased approaches.
Legacy platform migrations: 6-12 months
Permalink to “Legacy platform migrations: 6-12 months”Organizations replacing legacy catalogs face longer timelines due to change management and metadata migration. These projects require careful planning to avoid disrupting existing workflows. Teams typically run platforms in parallel while gradually migrating users and content.
Migration strategies include bulk metadata export from legacy systems, gradual cutover by domain or use case, and user training on new capabilities. Organizations report this investment pays off through reduced maintenance burden and access to modern features that legacy platforms cannot provide.
Modern data catalog evaluation matrix
Permalink to “Modern data catalog evaluation matrix”Organizations should evaluate data catalogs across six core dimensions. Each dimension reflects a capability that directly impacts adoption, governance effectiveness, and long term scalability.
- Weight each dimension based on your maturity and priorities. For example AI heavy teams should weight AI and ML support higher
- Score vendors per dimension rather than by feature count
- Validate claims through hands on testing with your actual stack and scale
Dimension | What to Evaluate | Key Questions to Ask | What "Good" Looks Like |
|---|---|---|---|
Integration breadth and depth | Coverage across your data stack and quality of metadata flow | Does it natively connect to our warehouses, transformation tools, and BI platforms? Is metadata bidirectional or scan only? | Native integrations with Snowflake, Databricks, dbt, Tableau, etc. Automatic, real time metadata flow as pipelines and dashboards change |
Automation capabilities | How much manual work the catalog eliminates | Does it only scan tables or actively enrich metadata? What is automated vs user driven? | ML powered classification, automated lineage, quality signals, and policy enforcement with minimal manual setup |
AI and ML support | Support for modern AI driven data use cases | Can we register ML models? Track training data lineage? Integrate with AI agents or MCP style protocols? | Unified visibility of data assets and AI assets so models, features, and datasets are governed together |
Governance and security | Depth of policy enforcement and compliance support | How are access controls handled? Do tags and policies propagate back to the warehouse? | Automated PII detection, policy based masking, certification workflows, and audit ready compliance evidence |
User experience and adoption | Ease of use across different personas | Can engineers, analysts, and business users all succeed without training? | Fast, intuitive search. Easy documentation. Context surfaced directly in BI tools, SQL editors, and Slack |
Scalability and performance | Ability to handle large, complex data estates | How does performance change as sources, tables, and users grow? | Cloud native architecture that supports millions of tables and high concurrent search without latency issues |
How Atlan enables modern data cataloging
Permalink to “How Atlan enables modern data cataloging”Modern data moves fast. Atlan was built to keep up. By pioneering the active metadata approach, Atlan turns the catalog from static documentation into a living system of context, governance, and collaboration.
Active metadata, always current
Permalink to “Active metadata, always current”Atlan continuously captures technical metadata, usage signals, and quality indicators as data changes. With 100 plus native integrations across warehouses, transformation tools, and BI platforms, metadata updates automatically. Machine learning classifies sensitive data, enriches descriptions, and surfaces quality issues, enabling teams to catalog at scale with minimal manual effort.
Built for real teams and real workflows
Permalink to “Built for real teams and real workflows”Atlan delivers tailored experiences for engineers, analysts, and leaders without forcing context switching. Deep lineage for technical users, intuitive discovery for analysts, and governance visibility for executives all live in one platform. Browser extensions and Slack integration bring catalog context directly into BI tools and SQL editors.
AI native and governance first
Permalink to “AI native and governance first”Atlan catalogs AI assets alongside data, with end to end lineage from training data to models. Semantic search and MCP support enable AI agents to safely consume metadata, while access policies apply consistently across humans and machines.
Federated governance, enterprise trust
Permalink to “Federated governance, enterprise trust”Domain teams own their data while central policies enforce automatically. Bidirectional tag sync with Snowflake and Databricks enables tag once, enforce everywhere governance. Enterprise grade security, audit trails, and certifications like SOC 2 and ISO 27001 ensure compliance at scale.
Real stories from real customers: Modern data cataloging in action
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Modern data cataloging in action”
From Weeks to Hours: How Tide Automated GDPR Compliance
"We needed to tag personally identifiable information across our entire data estate to strengthen GDPR compliance for 500,000 customers. Manual processes would have taken 50 days. Using automated rule-based workflows, we completed the tagging in just five hours."
Data Team
Tide (UK Digital Bank)
🎧 Listen to the podcast: Tide's active governance journey

From 6 Weeks to Launch: How Porto Built Their Modern Data Catalog
"We launched Datapedia, our self-service data catalog, in less than six weeks. Our 5-person governance team now automates governance for over 1 million data assets, saving 40% of our time that we can reinvest in strategic initiatives."
Data Governance Team
Porto
🎧 Listen to the podcast: Porto is revolutionizing data literacy

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
"Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, 'Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.' With Atlan's integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate."

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare's Data Renaissance with Atlan
Key takeaways
Permalink to “Key takeaways”Modern data catalogs mark a shift from static documentation to active metadata platforms that power discovery, governance, and collaboration at scale. As organizations move to the cloud, they need catalogs built for modern stacks with automated discovery, AI driven enrichment, and workflows embedded where teams already work.
With AI becoming core to business strategy, catalogs now extend beyond data discovery to support the full AI lifecycle. Capabilities like training data lineage, model registration, and secure AI agent access through protocols such as MCP are no longer optional. Modern catalogs provide the foundation for AI readiness without compromising governance or compliance.
The right catalog delivers impact fast. Cloud native platforms typically show value within weeks and reach broad adoption in months, not years.
Atlan’s Modern data cataloging accelerates data governance and AI readiness.
Let's help you build it
Book a demo →FAQs about modern data catalogs
Permalink to “FAQs about modern data catalogs”1. What is the difference between a modern and traditional data catalog?
Permalink to “1. What is the difference between a modern and traditional data catalog?”Modern data catalogs use active metadata that updates continuously through automated discovery and monitoring. Traditional catalogs rely on manual documentation that data stewards must maintain. Modern platforms integrate across the entire data stack through APIs and provide AI-powered automation for classification and enrichment. Traditional catalogs focus primarily on database schemas and require months of manual setup. The key difference is automation that scales with data growth versus manual processes that create bottlenecks as data estates expand.
2. How long does it take to implement a modern data catalog?
Permalink to “2. How long does it take to implement a modern data catalog?”SaaS deployments deliver initial value within 2-4 weeks as automated discovery captures technical metadata from connected sources. Full enterprise adoption typically takes 3-6 months including domain expansion, user training, and change management. Organizations see immediate benefits from search and lineage even before comprehensive enrichment. Legacy platform replacements require 6-12 months due to migration complexity and user transition planning. Modern cloud-native catalogs deploy 3-4x faster than traditional on-premise platforms that required 12-18 months.
3. Do modern data catalogs support AI and ML workflows?
Permalink to “3. Do modern data catalogs support AI and ML workflows?”Modern catalogs extend beyond data assets to catalog ML models, features, and embeddings alongside traditional data. They provide training data lineage showing which datasets trained which models for transparency and compliance. Catalogs support Model Context Protocol (MCP) enabling AI agents to access metadata dynamically for grounded responses. Semantic search using vector embeddings helps find conceptually similar assets even when terminology differs. AI governance features ensure RAG applications and agents respect the same access policies as human users, preventing data leakage through AI interfaces.
4. What ROI can organizations expect from a modern data catalog?
Permalink to “4. What ROI can organizations expect from a modern data catalog?”Organizations report 30-50% reduction in time spent searching for and understanding data. Teams using modern catalogs document 60-70% fewer manual hours for metadata maintenance through automation. Data discovery time drops from hours or days to minutes through intelligent search and automated documentation. Governance compliance improves as automated policy enforcement reduces manual oversight by 40-60%. Organizations also see 20-40% improvements in data user satisfaction scores and reduced duplicate analysis efforts when teams can find existing work.
5. How do modern data catalogs handle multi-cloud environments?
Permalink to “5. How do modern data catalogs handle multi-cloud environments?”Modern catalogs connect to data regardless of location through cloud-agnostic connector architecture. They scan cloud warehouses like Snowflake and Databricks alongside on-premise databases and SaaS applications. The catalog provides unified search and lineage across all platforms in one interface. This becomes critical during cloud migrations when data spans multiple environments. Organizations can track dependencies and govern policies consistently even when data moves between AWS, Azure, and GCP. Hybrid deployments are common as teams gradually migrate from on-premise to cloud infrastructure.
6. What makes a data catalog “active” vs “passive”?
Permalink to “6. What makes a data catalog “active” vs “passive”?”Active catalogs continuously monitor source systems and capture metadata changes in real time without human intervention. When schemas change or new tables are added, active catalogs update automatically within minutes. They drive automated workflows for quality monitoring, policy enforcement, and impact analysis. Passive catalogs require data stewards to manually document changes and maintain accuracy. Metadata in passive systems becomes outdated within weeks as data estates evolve. Active approaches maintain 90%+ metadata accuracy versus 60-70% for passive documentation through automation that scales with data growth.
7. How do modern catalogs integrate with data mesh architectures?
Permalink to “7. How do modern catalogs integrate with data mesh architectures?”Modern catalogs enable federated data mesh governance where domain teams own their data while central teams maintain visibility and policy consistency. Domain owners classify and document their data products within the catalog. Central governance teams define policies that apply automatically across all domains based on classifications. The catalog provides a unified marketplace where domains can discover and consume each other’s data products. Cross-domain lineage shows dependencies between data products. This federated approach scales governance without creating central bottlenecks that slow domain autonomy.
Share this article



















