Data Catalog vs. Data Dictionary: Key Differences & Benefits for 2025

Last Updated on: December 25th, 2024 | 11 min read
Understanding the difference between a data catalog and a data dictionary is vital for effective data management.
A data dictionary captures technical metadata for individual databases, while a data catalog provides a holistic view of all metadata across an organization.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Cataloging – Start Product Tour
This distinction enhances data discovery, governance, and collaboration among data teams, making it crucial for modern data practices.
Quick answer:
In a hurry? We’ve summarized the essence of this article as well as what to expect from it:
- A data dictionary documents technical metadata for a specific database. Meanwhile, a data catalog acts as a unified context and control plane for all metadata.
- In this article, we’ll explore the concepts of a data dictionary and a data catalog, followed by their benefits, core features, and differences. We’ll also compare data catalog vs. data dictionary vs. business glossary.
Data catalog vs. data dictionary: The difference
Permalink to “Data catalog vs. data dictionary: The difference”The main difference between a data catalog and a data dictionary is that a data dictionary documents technical metadata for a specific database, whereas a data catalog acts as a unified context, control, and collaboration layer of all metadata (technical, governance, operational, collaboration, quality, and usage) across your entire data ecosystem.
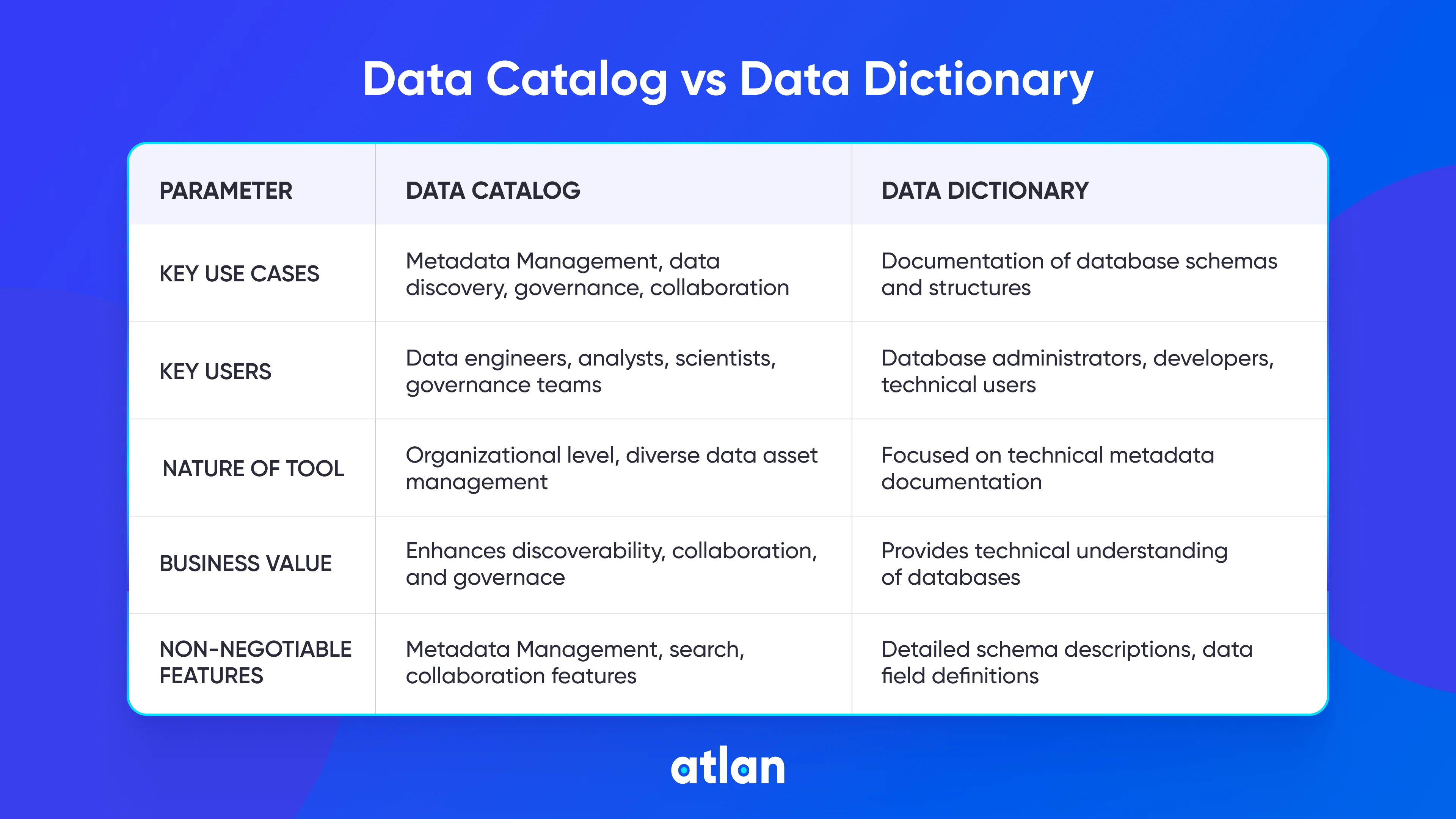
View data catalog vs data dictionary visual representation in full size.
To understand the differences between data catalog and data dictionary, read on.
Table of Contents
Permalink to “Table of Contents”- What is a data dictionary?
- What are the benefits of a data dictionary?
- What is a data catalog?
- 4 Fundamental features of a data catalog
- Data catalog vs. data dictionary vs. business glossary
- Data catalogs vs. data dictionaries in the real world
- How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
- FAQs about Data Catalog vs Data Dictionary
- Related reads
Data Catalog Vs Data Dictionary: Which one do you need?
What is a data dictionary?
Permalink to “What is a data dictionary?”A data dictionary provides information and insights about your database. Consider a data dictionary to be a documentation for databases.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Cataloging – Start Product Tour
A data dictionary provides insights on
Permalink to “A data dictionary provides insights on”- Data source (data warehouse, data lakes, databases, applications)
- Tables names and descriptions
- Table relationships
- Column name and descriptions
- Permissible values for a field
- Data types
- Column nullability
- Referential constraints — foreign keys and primary keys
- Column statistics — missing values, min-max values, and histogram distribution.
- Data and time when the property was created or changed
- Data owner
- Data freshness
- Classifications (PII, GDPR, HIPAA)
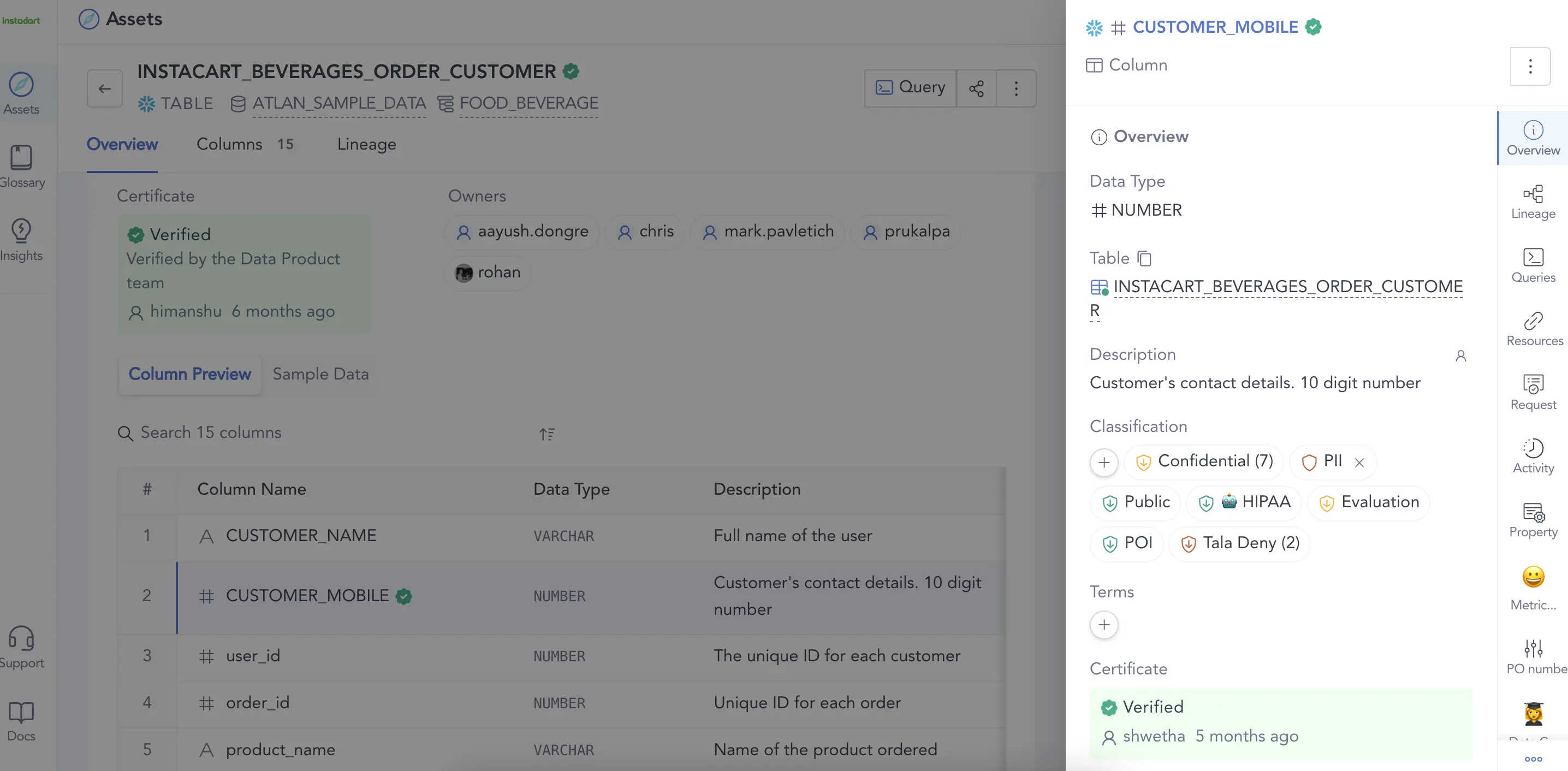
A data dictionary provides information about the database’s structure, data elements, constraints, and relationships. Image by Atlan.
What are the benefits of a data dictionary?
Permalink to “What are the benefits of a data dictionary?”The number of benefits your organization can have from a robust data dictionary is endless. Yet, let’s have a look at the top seven benefits of a data dictionary that acts as the interpreter for your databases:
- A data dictionary links physical data assets to business terms/concepts/metrics. This helps data users to understand and trust data better (improves data validity and credibility).
- Enables quick detection of anomalies and errors and hence helps keep a check on data quality.
- Checks how and where a field is referenced across the entire database.
- Provides a framework for programming and database standards to maintain data integrity.
- Helps evaluate data consistency during security and compliance audits.
- A data dictionary acts as self-serve documentation for new engineers/analysts. This greatly reduces onboarding time.
- Data dictionaries can be accessed externally through APIs for reporting and cataloging purposes.
And to learn more about each benefit in detail, check out the key benefits of a data dictionary.
What is a data catalog?
Permalink to “What is a data catalog?”A data catalog is an inventory of data assets across all your data sources in your enterprise. It helps organizations discover, understand, and consume data better — all in one place.
A data catalog helps find answers to:
Permalink to “A data catalog helps find answers to:”- What data do we have?
- Where does it come from?
- Who is the owner?
- How clean is the data & are there any gaps?
- How is it classified?
- Is the data good enough for running analysis?
4 fundamental features of a data catalog
Permalink to “4 fundamental features of a data catalog”Fundamentally, what are the features of a data catalog? A data catalog reduces the time to insight for data users. It ensures:
- Data is made readily accessible
- Context is provided
- The data lifecycle is visible
- Access permissions are defined
Watch a demo of Atlan data catalog
1. Data catalogs make data accessible
Permalink to “1. Data catalogs make data accessible”A data catalog automatically crawls, identifies, inventories, and classifies data assets from multiple sources. Data catalog tools allow you to run a search across data lakes, data warehouses, databases, tables, columns, SQL queries, and business glossaries.
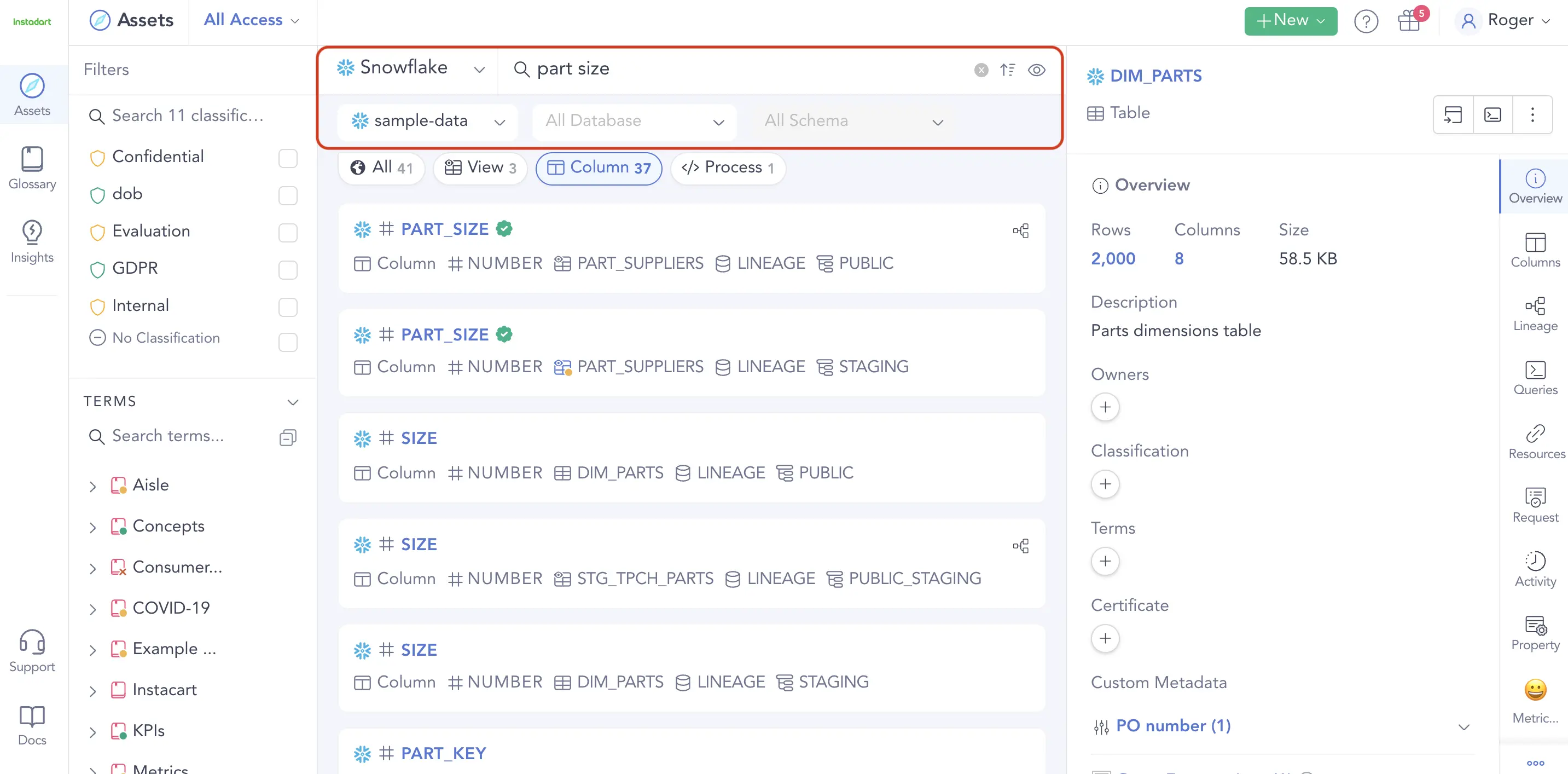
Modern data catalogs have google-like search interfaces that respond to text-based searches for data assets. Image by Atlan
2. Data catalogs provide context
Permalink to “2. Data catalogs provide context”People with no context of the data can learn more about it to decide if they have the right data.
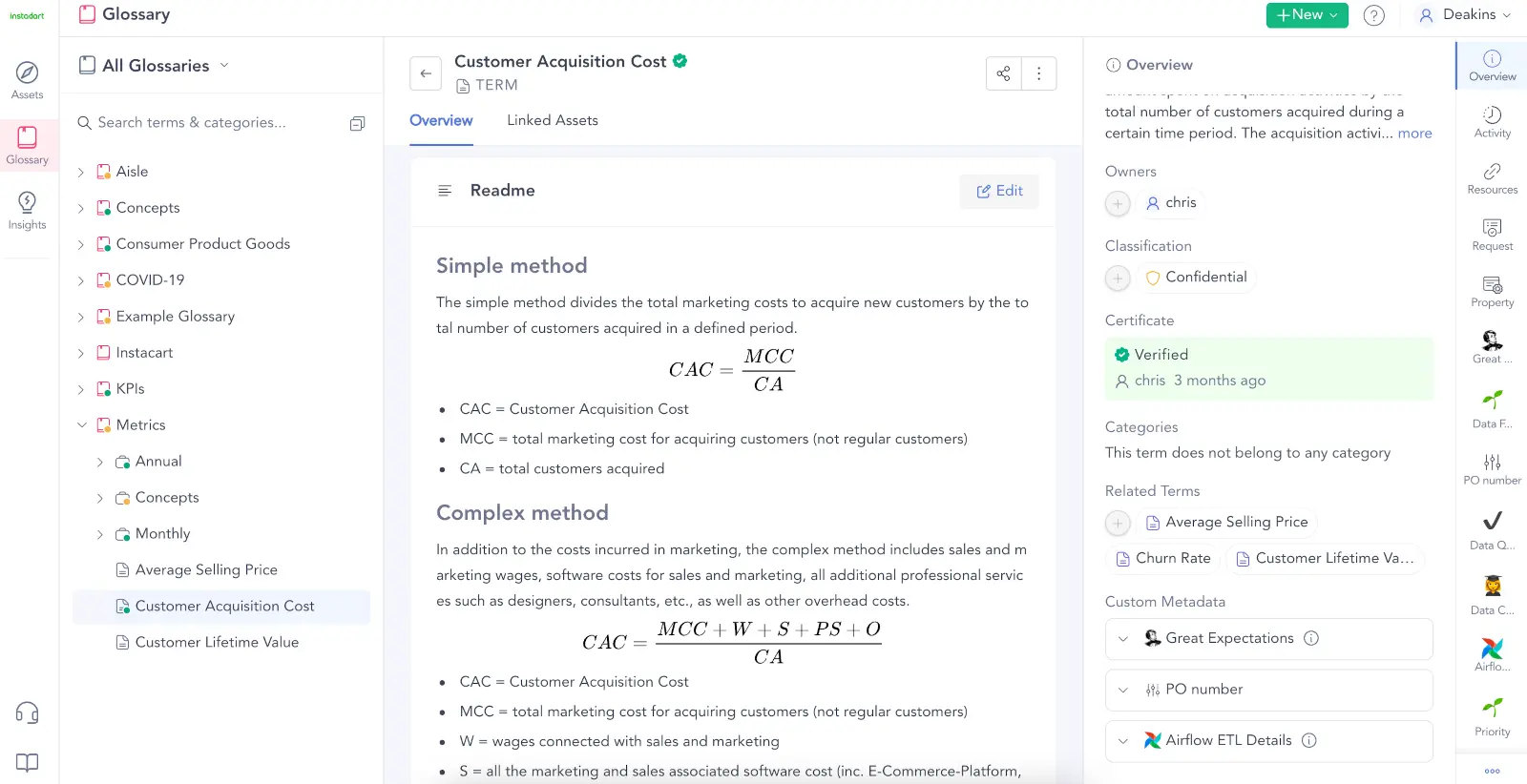
Modern data catalogs come with in-built business glossaries to ensure a common understanding of data assets and their usage across the organization. Image by Atlan
3. Data catalogs help visualize data lifecycle
Permalink to “3. Data catalogs help visualize data lifecycle”Data catalogs enable you to visualize the complete lifecycle of a data asset, its transformation, and its dependency both upstream and downstream.
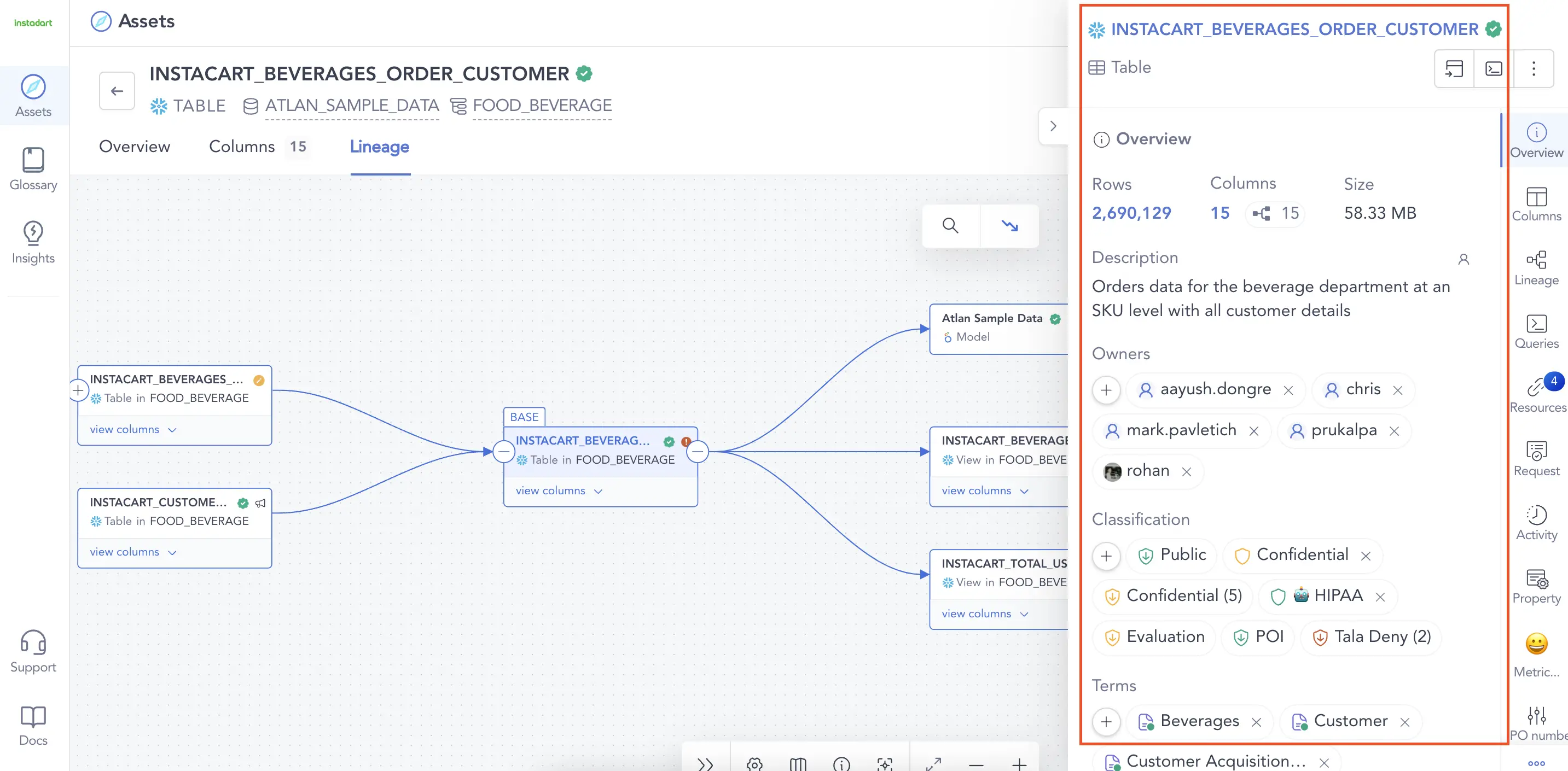
The best of modern data catalogs auto-construct the visual lineage of data to give an understanding of how data has evolved through its lifecycle and how changing the data will impact downstream. Image by Atlan
4. Data catalogs enable data governance
Permalink to “4. Data catalogs enable data governance”A data catalog helps enforce robust access control policies as guard rails to help you protect confidentiality and comply with various data protection regulations.
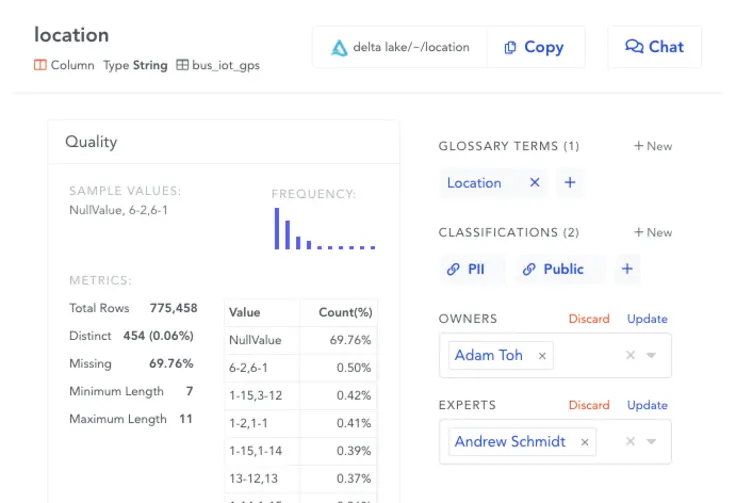
Modern data catalogs help deploy best-in-class data access governance without compromising on data democratization. Image by Atlan
Data catalog vs. data dictionary vs. business glossary
Permalink to “Data catalog vs. data dictionary vs. business glossary”While evaluating the need for data catalogs and data dictionaries, people often stumble upon business glossaries. Here’s how the three are primarily different.
The main difference between data catalog, data dictionary and business glossary is that A data dictionary holds the technical metadata for a database, a business glossary pulls together a common understanding of business terms and concepts, whereas a data catalog is a unified access, control, and collaboration layer that spans all metadata across your data estate.
Think of it this way, a data dictionary helps understand and trust data in databases better, a business glossary provides a common language for the organization when it comes to business concepts and metrics, and a data catalog helps find, understand, trust, and collaborate on data.
And to explore more about how a business glossary differs from the other two, check out the business glossary vs. data catalog.
When does an organization need a data catalog?
Permalink to “When does an organization need a data catalog?”It’s safe to say, deploying a data catalog is a right of passage for an organization to be truly data-driven. As a business, you can collect all the data that you want and set up best-in-class infrastructure to store that data, but data in itself is nothing. Just numbers.
You need the right data to reach the right person at the right time - for it to really move the needle on your business. Modern Data Catalogs are being designed to ensure that the complexities and scale of data do not deter “non-data” folks from using data in their day-to-day work.
→ Read in-depth about data catalogs.
Data catalogs vs. data dictionaries in the real world
Permalink to “Data catalogs vs. data dictionaries in the real world”As more and more data teams are feeling the need for and adopting data catalogs, the difference between a catalog and a dictionary is fast vanishing—and becoming more complementary—because catalog tools now crawl and inventory data dictionaries for metadata. Data dictionaries are now an integral part of a data catalog.
Just in case, if you are evaluating a data catalog, data dictionary, and metadata management for your team, do take Atlan for a spin.
Atlan is a modern data catalog built on the premise of embedded collaboration that is key in today’s modern workplace, borrowing principles from GitHub, Figma, Slack, Notion, Superhuman, and other modern tools that are commonplace today.
How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
Permalink to “How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan”The recently published Forrester Wave report compared all the major enterprise data catalogs and positioned Atlan as the market leader ahead of all others. The comparison was based on 24 different aspects of cataloging, broadly across the following three criteria:
- Automatic cataloging of the entire technology, data, and AI ecosystem
- Enabling the data ecosystem AI and automation first
- Prioritizing data democratization and self-service
These criteria made Atlan the ideal choice for a major audio content platform, where the data ecosystem was centered around Snowflake. The platform sought a “one-stop shop for governance and discovery,” and Atlan played a crucial role in ensuring their data was “understandable, reliable, high-quality, and discoverable.”
For another organization, Aliaxis, which also uses Snowflake as their core data platform, Atlan served as “a bridge” between various tools and technologies across the data ecosystem. With its organization-wide business glossary, Atlan became the go-to platform for finding, accessing, and using data. It also significantly reduced the time spent by data engineers and analysts on pipeline debugging and troubleshooting.
A key goal of Atlan is to help organizations maximize the use of their data for AI use cases. As generative AI capabilities have advanced in recent years, organizations can now do more with both structured and unstructured data—provided it is discoverable and trustworthy, or in other words, AI-ready.
Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes
Permalink to “Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes”- Tide, a UK-based digital bank with nearly 500,000 small business customers, sought to improve their compliance with GDPR’s Right to Erasure, commonly known as the “Right to be forgotten”.
- After adopting Atlan as their metadata platform, Tide’s data and legal teams collaborated to define personally identifiable information in order to propagate those definitions and tags across their data estate.
- Tide used Atlan Playbooks (rule-based bulk automations) to automatically identify, tag, and secure personal data, turning a 50-day manual process into mere hours of work.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization in establishing and scaling data governance programs.
FAQs about Data Catalog vs Data Dictionary
Permalink to “FAQs about Data Catalog vs Data Dictionary”1. What is the difference between a data catalog and a data dictionary?
Permalink to “1. What is the difference between a data catalog and a data dictionary?”A data catalog serves as a comprehensive inventory of all data assets across an organization, facilitating data discovery and governance. In contrast, a data dictionary documents technical metadata for specific databases, detailing data elements and their relationships.
2. How can a data catalog improve data discovery in an organization?
Permalink to “2. How can a data catalog improve data discovery in an organization?”A data catalog enhances data discovery by providing a unified view of all data assets, enabling users to search and access relevant data quickly. It organizes metadata, making it easier for teams to find and utilize data effectively.
3. What are the key features of a data dictionary?
Permalink to “3. What are the key features of a data dictionary?”Key features of a data dictionary include documentation of data sources, table names, column descriptions, permissible values, data types, and referential constraints. It serves as a reference for understanding the structure and relationships within a database.
4. How do data catalogs support data governance and compliance?
Permalink to “4. How do data catalogs support data governance and compliance?”Data catalogs support data governance by enforcing access control policies and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. They provide visibility into data lineage and usage, helping organizations maintain data integrity and security.
5. What types of metadata are included in a data catalog?
Permalink to “5. What types of metadata are included in a data catalog?”A data catalog includes various types of metadata, such as technical metadata, business metadata, operational metadata, and governance metadata. This comprehensive view helps organizations manage and utilize their data assets effectively.
6. How do data catalogs and data dictionaries complement each other in data management?
Permalink to “6. How do data catalogs and data dictionaries complement each other in data management?”Data catalogs and data dictionaries complement each other by providing different perspectives on data. While a data dictionary focuses on technical details of specific databases, a data catalog offers a broader view of all data assets, enhancing overall data management and usability.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
Data dictionary vs. Data catalog: Related reads
Permalink to “Data dictionary vs. Data catalog: Related reads”- Business Glossary vs. Data Catalog — Fundamentals, Use Cases, Examples & More
- Data Inventory vs. Data Catalog: Definitions, Differences, and Examples
- Data Dictionary: Examples, Components, Benefits, How To Create One, and Available Tools
- Explore the Top 6 Benefits of a Data Dictionary
- Data Dictionary vs. Business Glossary: Definitions, Examples & Why Do They Matter?
- Best Alation Alternative: 5 Reasons Why Customers Choose Atlan
- Best Collibra Alternative — 8 Reasons Why Future-Focused Data Teams Are Choosing Atlan
- Data Catalog: What It Is & How It Drives Business Value
- What Is a Metadata Catalog? - Basics & Use Cases
- Modern Data Catalog: What They Are, How They’ve Changed, Where They’re Going
- Open Source Data Catalog - List of 6 Popular Tools to Consider in 2025
- 5 Main Benefits of Data Catalog & Why Do You Need It?
- Enterprise Data Catalogs: Attributes, Capabilities, Use Cases & Business Value
- The Top 11 Data Catalog Use Cases with Examples
- 15 Essential Features of Data Catalogs To Look For in 2025
- Data Catalog vs. Data Warehouse: Differences, and How They Work Together?
- Snowflake Data Catalog: Importance, Benefits, Native Capabilities & Evaluation Guide
- Data Catalog vs. Data Lineage: Differences, Use Cases, and Evolution of Available Solutions
- Data Catalogs in 2025: Features, Business Value, Use Cases
- AI Data Catalog: Exploring the Possibilities That Artificial Intelligence Brings to Your Metadata Applications & Data Interactions
- Amundsen Data Catalog: Understanding Architecture, Features, Ways to Install & More
- Machine Learning Data Catalog: Evolution, Benefits, Business Impacts and Use Cases in 2025
- 7 Data Catalog Capabilities That Can Unlock Business Value for Modern Enterprises
- Data Catalog Architecture: Insights into Key Components, Integrations, and Open Source Examples
- Data Catalog Market: Current State and Top Trends in 2025
- Build vs. Buy Data Catalog: What Should Factor Into Your Decision Making?
- How to Set Up a Data Catalog for Snowflake? (2025 Guide)
- Data Catalog Pricing: Understanding What You’re Paying For
- Data Catalog Comparison: 6 Fundamental Factors to Consider
- Alation Data Catalog: Is it Right for Your Modern Business Needs?
- Collibra Data Catalog: Is It a Viable Option for Businesses Navigating the Evolving Data Landscape?
- Informatica Data Catalog Pricing: Estimate the Total Cost of Ownership
- Informatica Data Catalog Alternatives? 6 Reasons Why Top Data Teams Prefer Atlan
- Data Catalog Implementation Plan: 10 Steps to Follow, Common Roadblocks & Solutions
- Data Catalog Demo 101: What to Expect, Questions to Ask, and More
- Data Mesh Catalog: Manage Federated Domains, Curate Data Products, and Unlock Your Data Mesh
- Best Data Catalog: How to Find a Tool That Grows With Your Business
- How to Build a Data Catalog: An 8-Step Guide to Get You Started
- The Forrester Wave™: Enterprise Data Catalogs, Q3 2024 | Available Now
- How to Pick the Best Enterprise Data Catalog? Experts Recommend These 11 Key Criteria for Your Evaluation Checklist
- Collibra Pricing: Will It Deliver a Return on Investment?
- Data Lineage Tools: Critical Features, Use Cases & Innovations
- OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Compare Architecture, Capabilities, Integrations & More
- Automated Data Catalog: What Is It and How Does It Simplify Metadata Management, Data Lineage, Governance, and More
- Data Mesh Setup and Implementation - An Ultimate Guide
- What is Active Metadata? Your 101 Guide


















