Intelligent Data Catalog: What Are the 4 Defining Capabilities?

Share this article
An intelligent data catalog leverages automation, AI, and machine learning to support metadata management, data search and discovery, data governance, and observability.
Unlike traditional data catalogs, an intelligent data catalog is proactive and can make working with data more efficient and delightful. It promises to do all the legwork, empowering data practitioners to spend less time doing grunt work and more time making decisions that will impact business.
This article will walk you through the core capabilities of an intelligent data catalog, backed by practical examples to help you understand its value.
Table of contents
Permalink to “Table of contents”- What is an intelligent data catalog?
- Metadata-based automation to scale your workflows
- Better search and discovery to build rich context
- AI-driven security and governance at scale
- Integrated observability to continuously monitor the health of your data estate
- Summary
- Intelligent data catalog: Related reads
What is an intelligent data catalog?
Permalink to “What is an intelligent data catalog?”An intelligent data catalog is a modern data catalog that makes your interactions with data more meaningful by leveraging:
- Metadata-based automation
- Intelligent search and discovery
- AI-driven security and governance
- Integrated observability
According to Michele Goetz, VP, Principal Analyst at Forrester, modern data teams work at the intersection of three patterns — self-service, analytics/BI, and AI (i.e., intelligently automating experiences).
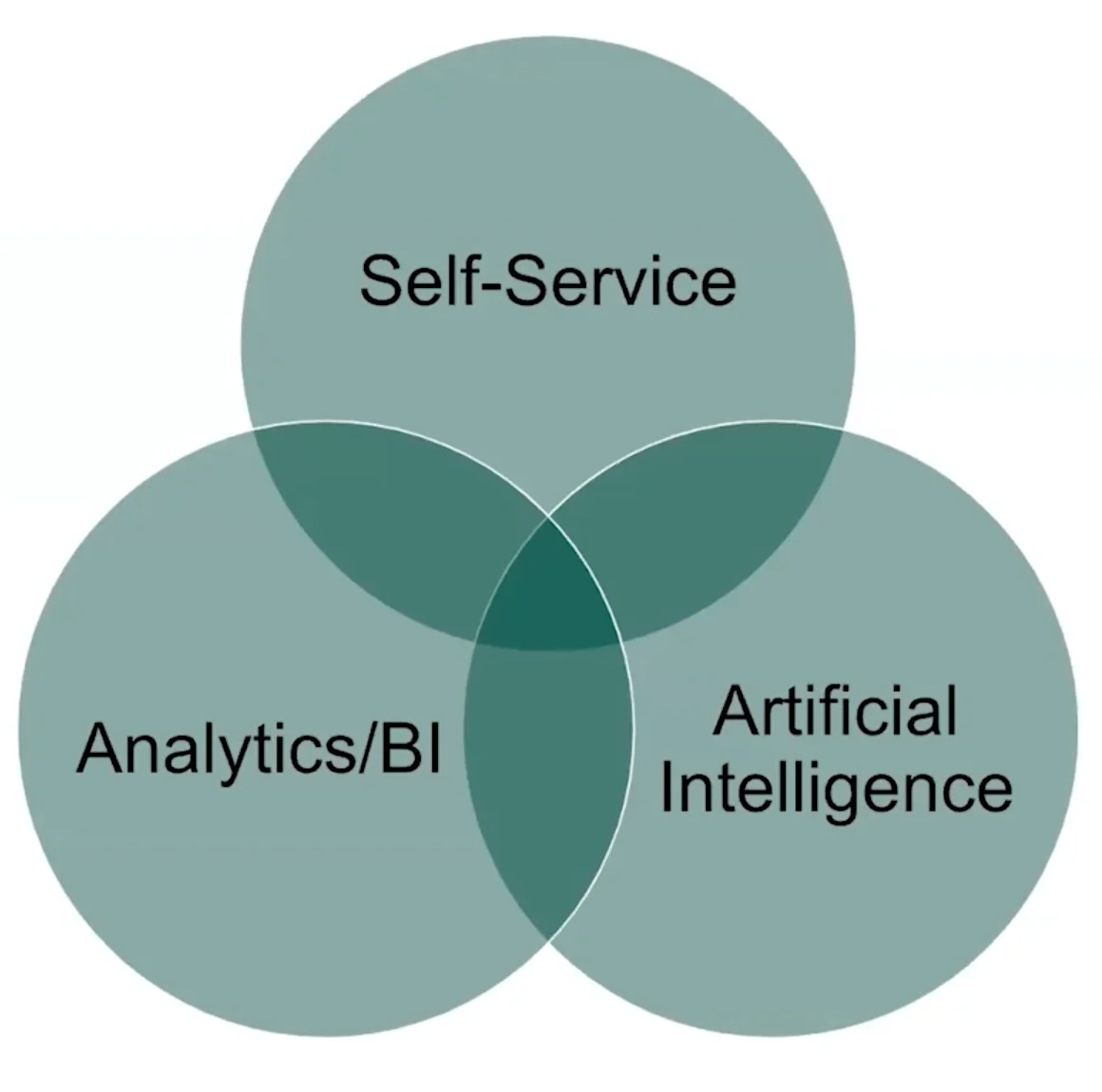
Three patterns that define a new way of working with data. - Image by Michele Goetz.
Intelligent data catalogs can play a vital role in supporting this new way of working with data as they can bring metadata, context, governance, and observability of data assets under one roof.
Let’s explore this further.
Also, read → AI data catalog
Metadata-based automation to scale your workflows
Permalink to “Metadata-based automation to scale your workflows”Intelligent data catalogs can capture, organize, and leverage metadata to automate data asset documentation, classification, and lineage. Let’s see how.
Example 1: Automatic documentation
Permalink to “Example 1: Automatic documentation”Consider a situation where a data scientist creates a new data asset in the catalog. The metadata generated—such as the data type, source, or relevant team—could automatically trigger a documentation process.
The intelligent data catalog acts as your copilot by auto-generating documentation for data asset definitions, descriptions, and READMEs.
All you have to do is review the documentation, make the required edits, and then publish it. This would greatly reduce the manual work of writing documentation from scratch.
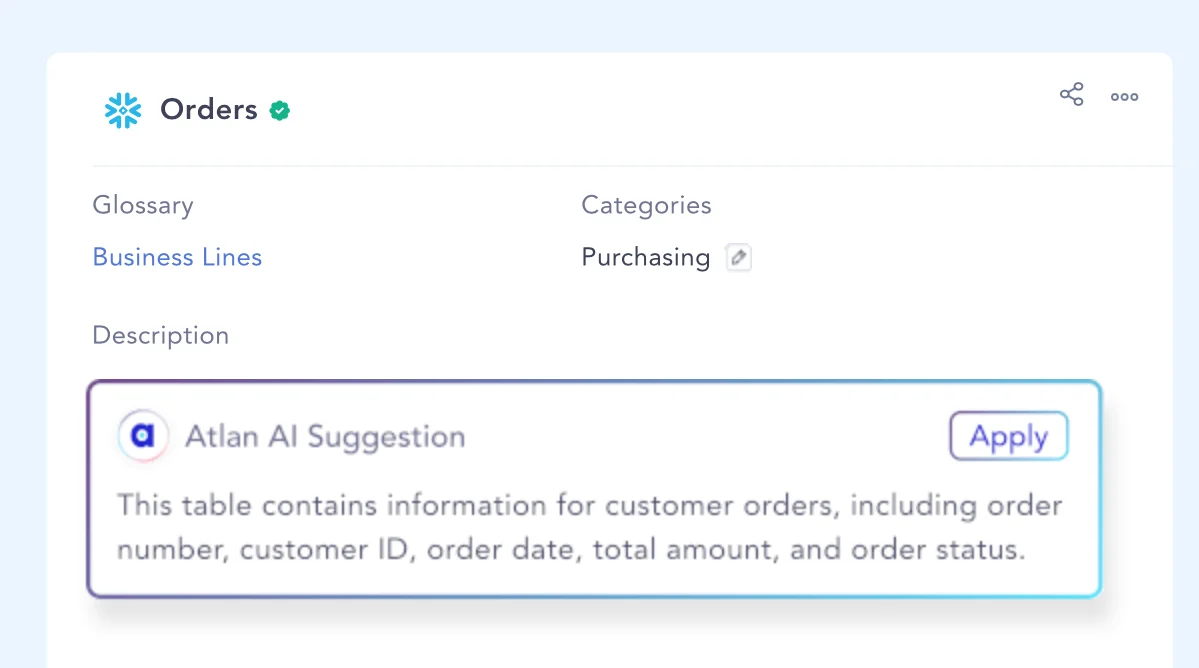
Intelligent documentation for data assets - Image by Atlan.
Example 2: Proactive pipeline management through metadata monitoring
Permalink to “Example 2: Proactive pipeline management through metadata monitoring”Consider a situation where a field changes in your database, potentially breaking your data pipeline.
With an intelligent data catalog as your copilot, these changes are instantly captured. The metadata changes trigger automated workflows and notify the relevant stakeholders to ensure that everyone’s on the same page.
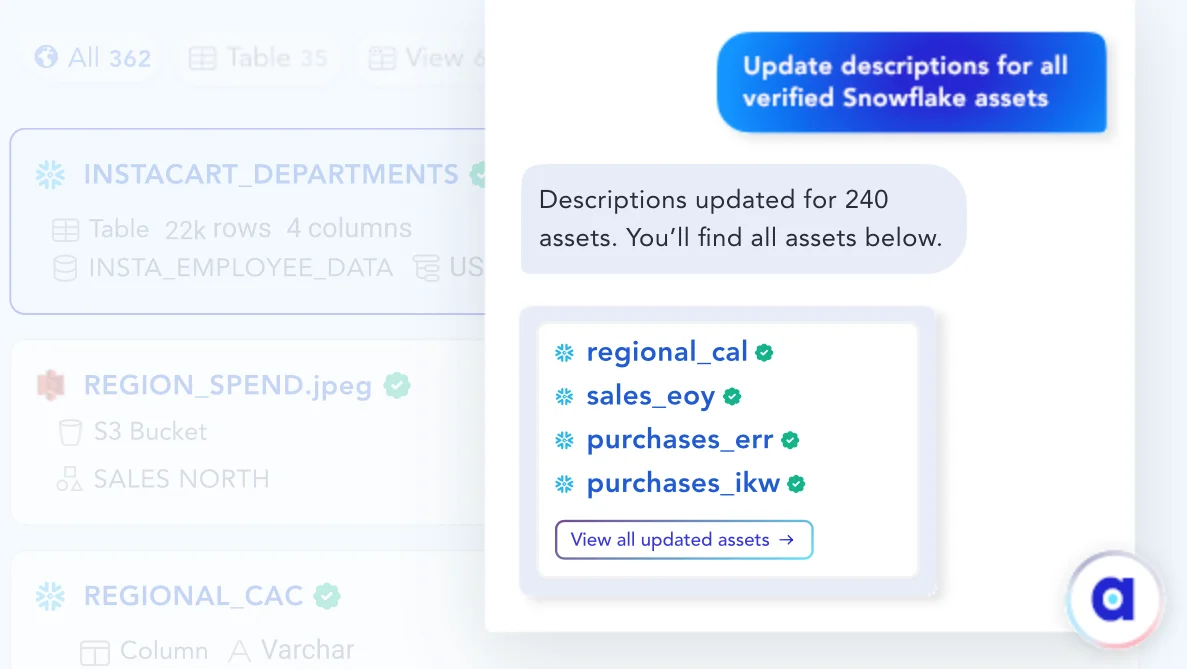
Intelligent updates to asset descriptions - Image by Atlan.
Example 3: Data lineage propagation
Permalink to “Example 3: Data lineage propagation”An intelligent data catalog can propagate access control policies via lineage and auto-suggest owners by studying metadata from similar assets.
Imagine that your product team has added a new data source. This new source includes marketing information, such as conversion rate and acquisition cost for a specific region.
The intelligent data catalog, i.e., your copilot, will notice that the new data assets are similar to other marketing assets already labeled and maintained by other teams.
Based on the lineage and metadata of similar assets, the intelligent data catalog understands that this kind of data will be classified under the same tag and require similar access control policies.
It will also identify downstream data products using this data and then propagate the access control policies.
Better search and discovery to build rich context
Permalink to “Better search and discovery to build rich context”Another advantage of an intelligent data catalog is better search and discovery.
With the automatic enrichment of data assets with documentation and lineage, search and discovery will get more intuitive and easy to use.
Example 1: Contextual search and recommendations
Permalink to “Example 1: Contextual search and recommendations”Let’s imagine a scenario where a data analyst is looking for a specific type of sales data, but is unsure of the exact dataset name.
The intelligent data catalog can understand the context of their search and recommend datasets with similar metadata.
For instance, you can type search queries, such as “What table should I use for churn analysis?” or “What table should I use to calculate CAC?”
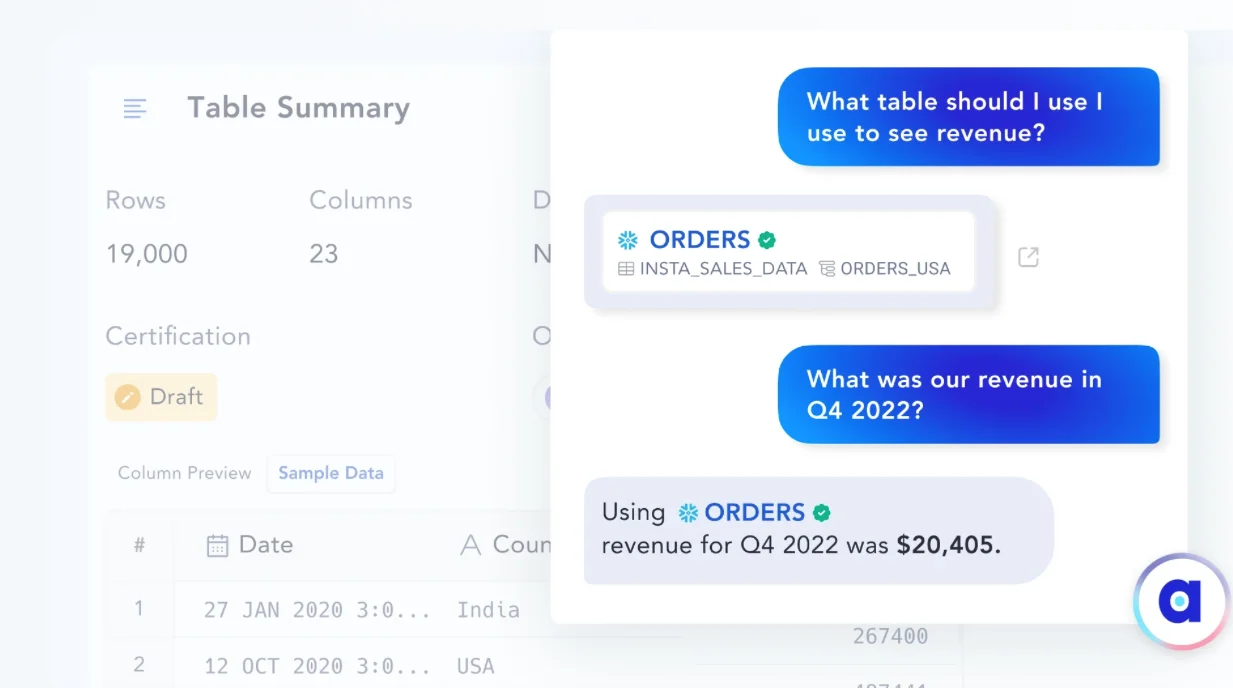
Looking for datasets without knowing the exact name using natural language search - Image by Atlan.
The catalog can also offer suggestions on similar data assets that you aren’t even aware of, making data discovery intuitive and efficient.
Example 2: Enhanced data understanding through integrations with collaboration tools
Permalink to “Example 2: Enhanced data understanding through integrations with collaboration tools”Another example is when a user has found a dataset but needs more information to understand it fully.
The intelligent data catalog can integrate with collaboration tools like Slack and analyze discussions around data to capture additional context.
For instance, if an analyst mentions on Slack that they’ve found an inconsistency in a specific column of the dataset, the intelligent data catalog adds a note against this asset about this issue.
Similarly, if the data science team discusses a transformation they’ve applied to the data asset and the results they’ve achieved, the intelligent data catalog can capture this tribal knowledge and add it to the data asset’s metadata.
So, all users can understand what transformations have been tried before, what worked, and what didn’t.
AI-driven security and governance at scale
Permalink to “AI-driven security and governance at scale”An intelligent data catalog automatically tags and classifies data based on the teams using it, its owners, or the clearance level required to access it.
It can also automatically identify personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), and other compliance-related data that needs to either be masked or restricted.
For instance, when a new patient record data source is connected to the data catalog, it automatically scans the metadata to identify any PHI. If it detects PHI, the catalog will tag the data as sensitive and apply the necessary access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can access it.
It can also automatically mask certain elements of the data to protect individual identities—replacing real social security numbers with pseudonymous placeholders, for instance.
In such situations, all you have to do is review the auto-classifications and masking and make sure that it’s accurate. This helps you implement and oversee your organization’s data governance program at scale.
Integrated observability to continuously monitor the health of your data estate
Permalink to “Integrated observability to continuously monitor the health of your data estate”Observability is central to any data platform and is the ability to monitor, track, and triage incidents to prevent data downtime.
Observability within the data catalog means that you’ll be able to look at data workflows related to the data assets in the data catalog, such as data quality and profiling.
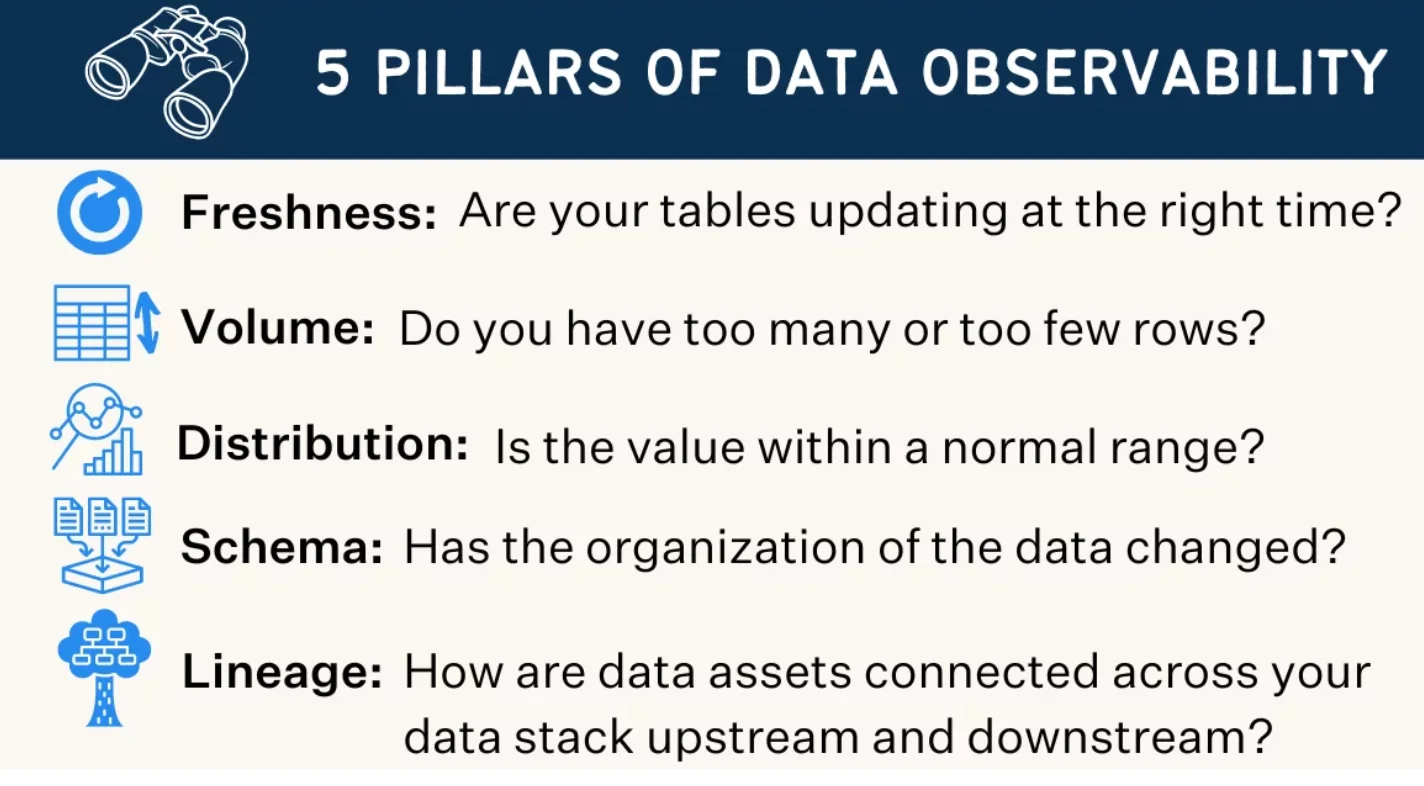
The pillars of data observability - Source: Monte Carlo Data.
Data observability will not only report the success or failure of a data asset load or update, but it will also tell you about the freshness or staleness of data along with a number of other data profiling and quality metrics.
It’s like having your AI copilot keep an eye on your data landscape, monitor its health, and notify you whenever it notices anomalies that need further inspection or fixing.
Also, read → Data Observability 101
Summary
Permalink to “Summary”We’ve walked through the world of intelligent data catalogs together, exploring how automation, AI-driven context-building, governance, and observability can transform your data operations.
Ultimately, the intelligent data catalog should take over the grunt work, freeing up your data users to focus more on solving business problems with data.
Intelligent data catalog: Related reads
Permalink to “Intelligent data catalog: Related reads”- What Is a Data Catalog? & Do You Need One?
- AI Data Catalog: Exploring the Possibilities That Artificial Intelligence Brings to Your Metadata Applications & Data Interactions
- 8 Ways AI-Powered Data Catalogs Save Time Spent on Documentation, Tagging, Querying & More
- 15 Essential Data Catalog Features to Look For in 2023
- What is Active Metadata? — Definition, Characteristics, Example & Use Cases
- Data catalog benefits: 5 key reasons why you need one
- Open Source Data Catalog Software: 5 Popular Tools to Consider in 2023
- Data Catalog Platform: The Key To Future-Proofing Your Data Stack
- Top Data Catalog Use Cases Intrinsic to Data-Led Enterprises
- Business Data Catalog: Users, Differentiating Features, Evolution & More
Share this article


















