What is data fabric?
Permalink to “What is data fabric?”Data fabric represents a shift from traditional centralized data management to distributed intelligence. Rather than moving data to a single location, data fabric architectures connect existing data sources through an intelligent integration layer powered by metadata and automation.
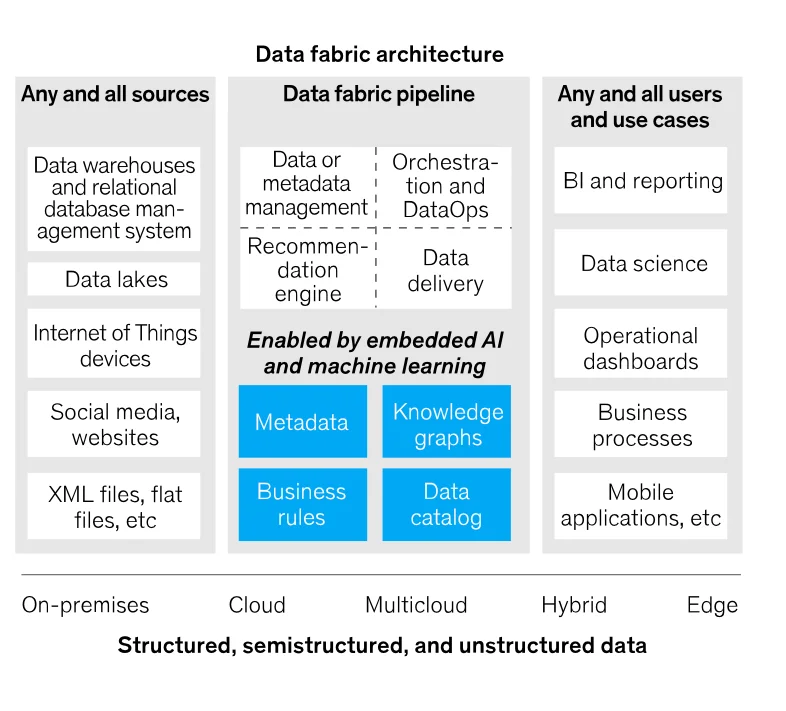
Data fabric explained. Source:McKinsey
According to research from Fortune Business Insights, the global data fabric market reached $2.29 billion in 2023 and projects growth to $12.91 billion by 2032, reflecting a 21.2% CAGR.
It’s important to note that data fabric is composable, not a single product. Organizations assemble components based on their specific integration, governance, and analytics requirements.
Modern data fabric implementations leverage several core patterns:
- Metadata-driven automation discovers and classifies data sources
- Knowledge graphs map relationships between distributed assets
- Semantic layers provide consistent business meaning across systems
- Policy engines enforce governance rules automatically based on metadata signals
What challenges does a data fabric architecture solve?
Permalink to “What challenges does a data fabric architecture solve?”A data fabric saves on data processing and movement costs while future-proofing your architecture to add more data sources and siloed data. This helps in addressing three fundamental challenges organizations face.
1. Data silos across systems
Permalink to “1. Data silos across systems”Enterprise data lives in hundreds of repositories from legacy databases to modern cloud platforms. Traditional approaches require moving data to warehouses or lakes, creating latency and compliance issues.
Data fabric connects sources in place through virtualization and federation patterns.
2. Manual integration overhead
Permalink to “2. Manual integration overhead”Point-to-point integrations don’t scale. Each new source requires custom pipelines.
Data fabric uses active metadata and machine learning to discover integration patterns automatically, reducing development time from weeks to hours.
3. Governance at scale
Permalink to “3. Governance at scale”As data volume grows, manual governance fails.
Data fabric embeds governance through metadata-driven policies that execute automatically. Access controls, quality checks, and compliance measures become native to how data flows through systems.
What are the key components of data fabric architecture?
Permalink to “What are the key components of data fabric architecture?”Data fabric architectures combine multiple technical components into unified platforms. While implementations vary based on organizational needs, successful deployments share the following core capabilities.
For instance, Gartner calls the data fabric architecture an approach that “takes in metadata from participating systems and users, analyzes it, and produces alerts and recommendations highlighting how data could be better organized, integrated, given meaning and used to improve the user experience and business outcomes.”
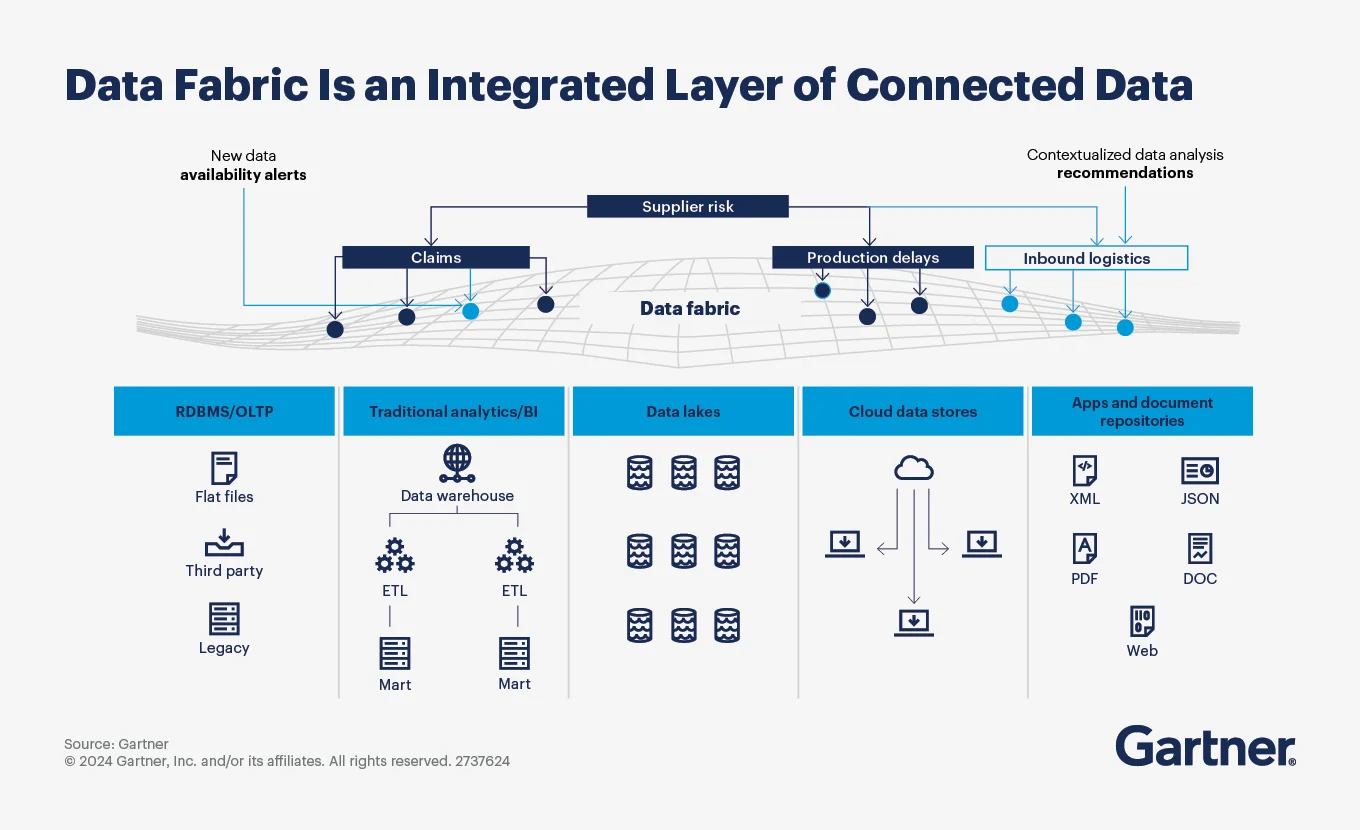
Gartner's perspective on the data fabric architecture. Source:Gartner
1. Active metadata management system
Permalink to “1. Active metadata management system”Active metadata management is the foundation of data fabric. Active metadata continuously captures technical, operational, business, and social metadata from across the data ecosystem. Unlike passive catalogs that require manual updates, active systems analyze metadata in real-time to detect changes, suggest classifications, and trigger automated workflows.
Active metadata platforms enable data fabric setups to understand data lineage, track quality metrics, and map dependencies automatically. For instance, when a source system schema changes, the metadata layer detects the impact and alerts downstream consumers before issues occur.
2. Intelligent data catalog
Permalink to “2. Intelligent data catalog”Catalogs serve as the interface where users search for data, understand its context through lineage and documentation, and request access through governance workflows. The ideal catalog integrates with source systems bidirectionally, pushing enriched metadata back to where data teams work daily.
An intelligent data catalog automates and scales discovery and governance across distributed sources. Modern catalogs use machine learning to automatically tag, classify, and organize data assets. This helps in creating business semantic layers that connect organizational terminology with technical data structures.
In a data fabric, the data catalog becomes the first touchpoint for data consumers and makes the data available to them. This means that the data consumers can search, understand, and access business data using a single interface.
3. Knowledge graph engine
Permalink to “3. Knowledge graph engine”A knowledge graph engine maps relationships between data assets, users, and business concepts.
Knowledge graphs reveal hidden connections like which datasets share common attributes or which teams use similar data. This enables intelligent recommendations and automated data product creation.
Graph technology powers semantic search, allowing users to find data using business terms rather than technical names. For instance, when someone searches for “customer revenue,” the knowledge graph understands this connects to sales tables, CRM systems, and financial databases.
4. Integration and orchestration plane
Permalink to “4. Integration and orchestration plane”One of the primary offerings of a data fabric is a way to seamlessly integrate heterogeneous, spread-out, and often siloed data sources. By using concepts like cross-platform data sharing, clean rooms, and CDC (Change Data Capture), a data fabric can weave your data sources together to fit on a single data plane.
The integration and orchestration plane of a data fabric handles actual data movement and transformation through multiple delivery patterns:
- Batch processing for historical loads
- Change data capture for near real-time replication
- Streaming for continuous data flows
- Data virtualization for federated queries without movement
- API-based access for application integration
The layer adapts the delivery method to use case requirements automatically. Real-time dashboards get streaming data while analytical workloads receive optimized batch loads.
5. Data quality and observability framework
Permalink to “5. Data quality and observability framework”This framework monitors data health across the fabric continuously. Quality rules execute automatically based on metadata classifications. When sensitive data moves through the system, the framework verifies encryption and access controls.
Data observability is an overarching theme that covers data reliability, availability, quality, security, governance, and more. It extends beyond traditional monitoring by tracking data freshness, completeness, and usage patterns. Teams receive alerts when quality degrades or compliance violations occur, enabling proactive issue resolution.
Building observability into your enterprise data ecosystem using a data fabric also automatically builds trust in the system. The data fabric, through its virtualization layer, makes it very easy for you to look at any component of the system and see what it is doing, not just after an incident or a raised bug, but in real time.
6. Policy and governance engine
Permalink to “6. Policy and governance engine”The policy and governance engine enforces rules through metadata-driven automation. Instead of separate governance layers, policies embed into integration workflows. When data classified as “customer PII” moves between systems, the engine automatically applies required controls.
This approach shifts governance from manual reviews to automated enforcement. Access requests, quality checks, and retention policies execute based on metadata signals rather than human intervention.
How does data fabric work?
Permalink to “How does data fabric work?”Data fabric operates through continuous metadata analysis rather than physical data movement. Understanding this operational model reveals why organizations report significant efficiency gains.
Discovery and cataloging phase
Permalink to “Discovery and cataloging phase”Modern data fabrics begin with automated discovery across the data estate. Connectors scan databases, cloud platforms, and applications to identify available data assets. Machine learning classifies content based on structure, values, and usage patterns.
The system builds an inventory of every table, file, and API endpoint. Business context gets added through crowdsourced annotations where domain experts provide definitions. Automated classification tags sensitive data like personally identifiable information without manual review.
Discovery runs continuously rather than as a one-time setup. When new data sources appear, the fabric automatically incorporates them into the catalog and applies appropriate policies based on detected classifications.
Semantic layer creation
Permalink to “Semantic layer creation”The fabric creates unified views across disparate sources through semantic modeling. When customer data exists in CRM, billing, and support systems, the semantic layer connects these representations into a single logical entity.
Business users query “customers” through the semantic interface without knowing data spans three different databases. The fabric translates logical queries into physical operations against appropriate sources and combines results transparently.
This abstraction enables business-focused data products rather than technical table structures. Domain teams publish curated views that hide complexity while maintaining governance controls.
Integration pattern automation
Permalink to “Integration pattern automation”Data fabric uses metadata to identify optimal integration patterns automatically. When analysts need historical customer purchase data, the system recognizes this requires batch ETL from the transaction database. Real-time fraud detection triggers streaming integration from payment systems.
The fabric recommends delivery methods based on data characteristics, freshness requirements, and historical usage. Teams approve recommendations rather than designing custom pipelines from scratch. This reduces integration development from weeks to days.
Integration jobs self-heal when source schemas change. The metadata layer detects structural modifications and adjusts downstream transformations automatically. Data engineers receive notifications about changes rather than discovering broken pipelines through failed jobs.
Governance enforcement
Permalink to “Governance enforcement”Policies execute through metadata rather than manual checks. When data classified as “restricted” moves between systems, the fabric enforces encryption, logs access, and validates user permissions automatically.
This metadata-driven approach enables consistent governance across hybrid environments. The same policy protecting customer data in cloud storage also protects it in on-premises databases. Rules follow data rather than requiring separate implementations per platform.
Compliance becomes continuous rather than periodic. Audit trails capture every data access and transformation in real-time. Compliance teams query the metadata layer to prove controls rather than manually collecting evidence.
What are the benefits of implementing data fabric?
Permalink to “What are the benefits of implementing data fabric?”Organizations implementing data fabric architectures report measurable improvements across multiple dimensions.
Reduced time to insight
Permalink to “Reduced time to insight”Data fabric eliminates traditional bottlenecks in data access. Business users discover and access approved data through self-service interfaces without IT involvement for each request. Automated integration patterns deploy in hours rather than weeks.
The combination of automated discovery, semantic abstraction, and governance workflows accelerates time from business question to actionable answer.
Lower operational costs
Permalink to “Lower operational costs”By eliminating redundant data copies and manual integration work, data fabric reduces infrastructure and labor costs. Organizations leverage existing investments in data lakes, warehouses, and applications rather than replacing them.
Improved data quality and trust
Permalink to “Improved data quality and trust”Continuous quality monitoring identifies issues before they impact business decisions. Automated lineage shows exactly where data originates and how it transforms, building user confidence.
When quality problems occur, lineage enables root cause analysis in minutes rather than days. Teams trace issues back to source systems and quantify downstream impact automatically through metadata relationships.
Scalable governance
Permalink to “Scalable governance”Metadata-driven governance scales with data growth without proportional staffing increases. Policies that took weeks to implement manually now execute instantly through automation.
Organizations manage hundreds of data sources with smaller governance teams by eliminating manual processes. Compliance teams spend time defining policies rather than chasing evidence during audits.
Enhanced data democratization
Permalink to “Enhanced data democratization”Business users access data through intuitive semantic layers rather than complex technical structures. Natural language search finds relevant datasets using business terminology. This democratization enables data-driven decisions across organizations rather than limiting insights to technical teams.
Data fabric use cases across industries
Permalink to “Data fabric use cases across industries”Data fabric architectures enable specific use cases that traditional approaches struggle to support at scale.
1. 360-degree customer view
Permalink to “1. 360-degree customer view”Enterprises maintain customer data across dozens of systems from sales to support to billing. Data fabric connects these sources into unified customer profiles without centralizing data physically.
The semantic layer maintains a single “customer” definition even as underlying systems use different identifiers and structures. Changes in one system automatically update the unified view through integration patterns.
So, retail organizations can combine online behavior, in-store purchases, loyalty programs, and support interactions in real-time. Service representatives can access complete customer history regardless of which system originally captured each interaction.
2. Real-time fraud detection
Permalink to “2. Real-time fraud detection”Financial institutions need instant access to transaction data, account history, and external risk signals to identify fraud as it occurs. Data fabric enables real-time queries across operational databases, data warehouses, and third-party services.
The architecture supports both high-volume streaming ingestion and complex analytical queries simultaneously.
3. Supply chain visibility
Permalink to “3. Supply chain visibility”Manufacturing and retail organizations track products through complex global supply chains spanning hundreds of suppliers and logistics partners. Data fabric integrates data from procurement, manufacturing, shipping, and inventory systems.
Operations teams query unified views showing product location, expected arrival, and current status. The fabric translates logical queries into physical operations against appropriate systems whether internal databases or partner APIs.
When disruptions occur, automated lineage identifies affected shipments and downstream impact. Procurement teams quickly assess which products and customers face delays based on complete supply chain visibility.
4. Regulatory compliance automation
Permalink to “4. Regulatory compliance automation”Healthcare and financial services organizations face complex compliance requirements across multiple regulations. Data fabric automates compliance through metadata-driven policies that identify sensitive data and enforce required controls automatically.
When patient health information moves between systems, the fabric verifies encryption, validates access permissions, and logs activity for audit trails. Compliance teams define rules once and they execute consistently across all platforms.
The metadata layer maintains complete documentation of data processing activities required by regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Audit reports generate automatically from metadata rather than manual evidence collection.
How do modern platforms enable data fabric implementation?
Permalink to “How do modern platforms enable data fabric implementation?”Implementing data fabric principles requires platforms purpose-built for active metadata management and intelligent automation. Traditional data management tools weren’t designed for the continuous analytics and adaptation that data fabrics demand.
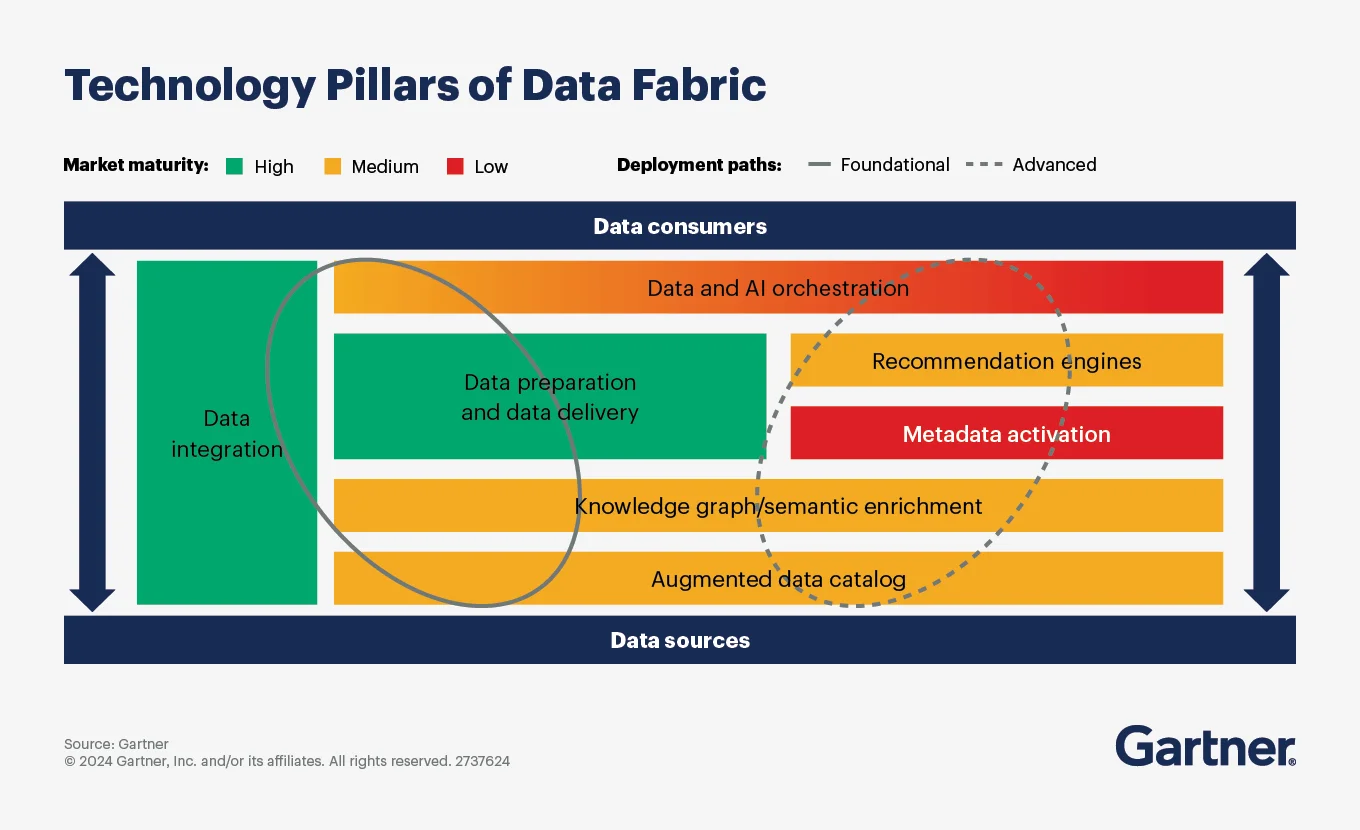
Technology requirements for implementing the data fabric. Source:Gartner
Centralized metadata repository
Permalink to “Centralized metadata repository”Modern metadata platforms centralize metadata from across the data stack. Rather than metadata existing in isolated silos within individual tools, unified repositories enable cross-system intelligence.
Atlan creates this foundation by connecting to data warehouses, BI tools, orchestration platforms, and business applications. Metadata flows bidirectionally so enrichment in the central catalog propagates back to source systems where teams work daily.
Automated classification and tagging
Permalink to “Automated classification and tagging”Machine learning-driven classification automatically tags data based on content, usage patterns, and relationships. Classification that once required armies of data stewards now happens continuously as new data emerges.
Platforms scan table contents, analyze column names, and examine actual values to detect sensitive information. When personally identifiable information appears in new tables, systems automatically apply appropriate security classifications and governance policies.
Intelligent lineage and impact analysis
Permalink to “Intelligent lineage and impact analysis”Automated lineage tracking maps data flows from source through transformation to consumption without manual documentation. This visibility enables root cause analysis when issues occur and impact assessment before changes deploy.
When source system schemas change, lineage-aware platforms identify every downstream report, dashboard, and model affected. Data teams can proactively address impact rather than discovering broken dependencies through user complaints.
Policy-driven governance
Permalink to “Policy-driven governance”Governance rules execute automatically through metadata signals rather than manual enforcement. When data classified as sensitive moves between systems, platforms verify appropriate controls throughout the asset’s lifecycle without human monitoring.
Here’s a snapshot of how that would look in practice. Access requests follow approval workflows based on data sensitivity and user roles. Quality checks run automatically against datasets tagged as critical. Retention policies trigger based on metadata rather than separate systems.
Collaborative data marketplace
Permalink to “Collaborative data marketplace”Modern platforms enable domain teams to publish curated data products with embedded context and governance. Business users discover and access approved datasets through self-service interfaces.
Crowdsourced enrichment allows knowledge workers to contribute definitions, tags, and documentation. This collective intelligence builds institutional knowledge that scales with organizational growth.
Real stories from real customers: Building data fabric foundations with unified metadata
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Building data fabric foundations with unified metadata”
From siloed systems to unified governance: How Tide automated GDPR compliance
"With Atlan, technical and non-technical users could find the right data asset for their needs, quickly and intuitively, reducing the time it once took to find, explore, and use data across tools. Tide used Atlan to support a wide array of users and business units, from Legal and Privacy, to Data Science, Engineering, Governance, and BI colleagues."
Hendrik Brackmann, Data Governance
Tide
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Tide achieved GDPR readiness
Let's help you build it
Book a Personalized Demo
Scaling discovery across distributed systems: How Autodesk built a data mesh with unified metadata
"We wanted something that was very accessible, something that had API access that we could enrich with our own metadata as well as getting data back out. We also wanted something with a much stronger user experience, so folks could come in and leverage the catalog almost as a data portal. It could be the primary starting point to find the data they need and immediately start using it."
Mark Kidwell, Chief Data Architect
Autodesk
🎧 Listen to podcast: Why Autodesk chose Atlan to activate its Snowflake data mesh
Ready to move forward with data fabric implementation?
Permalink to “Ready to move forward with data fabric implementation?”Data fabric architectures address fundamental challenges in modern data management through intelligent metadata automation and distributed integration patterns.
Organizations achieve this through active metadata automation, composable architecture, and policy-driven governance rather than physical data consolidation. The platforms you choose determine whether your fabric delivers automation and scale or simply creates another integration project.
Focus on continuous metadata analysis, automated discovery and classification, and governance that embeds into workflows rather than sitting as a separate layer.
Atlan enables data fabric implementation through active metadata automation and intelligent governance.
Let's help you build it
Book a Personalized DemoFAQs about data fabric
Permalink to “FAQs about data fabric”1. What is the difference between data fabric and data warehouse?
Permalink to “1. What is the difference between data fabric and data warehouse?”Data warehouses centralize structured data for analytics through ETL processes. Data fabric provides an integration layer across distributed sources including warehouses, lakes, and operational systems.
Organizations use both together: warehouses for analytical workloads, fabric for unified access and governance across all systems.
2. How does data fabric differ from data mesh?
Permalink to “2. How does data fabric differ from data mesh?”Data mesh emphasizes decentralized domain ownership with data treated as products. Data fabric focuses on integration architecture that connects distributed sources through metadata and automation.
Many organizations combine both: mesh for organizational model, fabric for technical implementation enabling discovery and governance across domains.
3. What technologies are required to implement data fabric?
Permalink to “3. What technologies are required to implement data fabric?”Core requirements to implement a data fabric include active metadata management platforms, data catalog with automated discovery, integration tools supporting multiple patterns (batch, streaming, virtualization), policy engines for governance, and knowledge graph technology for semantic relationships.
Organizations typically assemble these components rather than deploying single monolithic products.
4. How long does data fabric implementation take?
Permalink to “4. How long does data fabric implementation take?”Implementation timelines vary based on organizational size, existing infrastructure maturity, and scope. Organizations should start with specific use cases rather than enterprise-wide deployments.
Initial implementations delivering value typically take 3-6 months. Full organizational coverage evolves over 12-24 months as additional sources and use cases integrate.
5. What are the main challenges in adopting data fabric?
Permalink to “5. What are the main challenges in adopting data fabric?”Common challenges include organizational change management for distributed ownership models, technical complexity integrating diverse systems, metadata quality and standardization across sources, and skillset gaps in modern integration patterns.
Success requires executive sponsorship, phased implementation focusing on business value, and investment in metadata management capabilities.
6. How does data fabric support AI and machine learning?
Permalink to “6. How does data fabric support AI and machine learning?”Data fabric accelerates AI by providing governed access to training data across distributed sources, automated feature engineering through semantic layers, lineage tracking for model explainability, and policy enforcement ensuring ethical AI practices.
The architecture makes diverse data discoverable and accessible to data science teams without manual data engineering overhead.
Share this article



















