Metadata Management in 2025: Benefits, Importance, Best Practices

Share this article
Metadata management is the process of organizing, cataloging, and governing metadata to improve data accessibility and compliance.
See How Atlan Streamlines Metadata Management – Start Tour
Metadata management is crucial for automating workflows and improving data quality, accessibility as well as enhancing data governance.
Businesses rely on it to streamline operations, improve decision-making, and maintain scalable data systems.
By adopting best practices and leveraging active metadata, organizations can drive automation and future-proof their data catalogs.
Metadata management is the key to making sense of the vast amount of data that exists throughout our increasingly digital world. According to G2, businesses generate approximately two billion gigabytes of data every day. With so much information surrounding us at all times, it can be difficult to find, interpret, or even trust the data we have that is required to get a job done. That’s where metadata management comes into play.
What is metadata management?
Permalink to “What is metadata management?”Metadata management can be defined as a framework of processes, policies, and technologies that are used to catalog information/data assets within your organization throughout their lifecycles.
Metadata management is the practice of cleaning, classifying, and organizing data to ensure its accuracy, integrity, consistency, and usability.
Metadata management is the stepping stone to data discovery, search, collaboration, data quality, and data governance.
It usually refers to enterprise metadata management (EMM), or the business discipline of managing metadata about the information assets of an organization.
Table of contents
Permalink to “Table of contents”- What is metadata management?
- What is metadata?
- What is a metadata management platform?
- Importance of metadata management
- Benefits of metadata management
- Active Metadata: Key to metadata management automation
- Metadata management tools?
- Metadata management best practices
- The future of metadata management and data catalogs
- Atlan: The next generation of metadata management
- How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
- FAQs about Metadata Management
- Metadata Management: Related reads
What is metadata?
Permalink to “What is metadata?”Simply put, metadata is data about data. It describes data and provides important context. Think of an Excel spreadsheet: If the data is the numbers or text contained in the rows and columns, the metadata would be the descriptions of those columns. Metadata helps you understand what your data means or represents.
What are the types of metadata?
Permalink to “What are the types of metadata?”While there are no “official” types of metadata, it can be categorized as one of many different groups:
- Technical metadata (e.g., schemas, data types, data models) provides information on data format and structure.
- Business metadata (e.g., data tags, classifications, mappings) adds business context to data that is created and/or used by an enterprise.
- Operational metadata (e.g., outputs, ETL, lineage metadata) helps you understand when and how data was created or transformed.
- Process metadata (e.g., job execution logs, error logs, audit results) is a type of operational metadata originating from data warehouses and lakes that aids with traceability and lineage mapping.
- Structural metadata (e.g., data element types, table names, record size) is technical information on the physical organization of a data set, which is often used to create data dictionaries.
- Administrative metadata (e.g., access control information, user restrictions) is additional information on the lineage of a data set that helps manage and establish its credibility.
- Rights management metadata (e.g., copyright information, license agreements) is a subset of administrative metadata that refers to intellectual property rights.
- Provenance metadata (e.g., ownership, change logs, versioning records) tracks when something is created, changed, or duplicated.
- Preservation metadata (e.g., technical, rights management, and provenance metadata) helps maintain certain objects and files over time. This includes information that is essentially required for a system to interact with a specific file.
- Social metadata (e.g., author information, content tags, business user knowledge) gives information about the users who create different types of data.
Learn more → A Comprehensive guide on the types of enterprise metadata
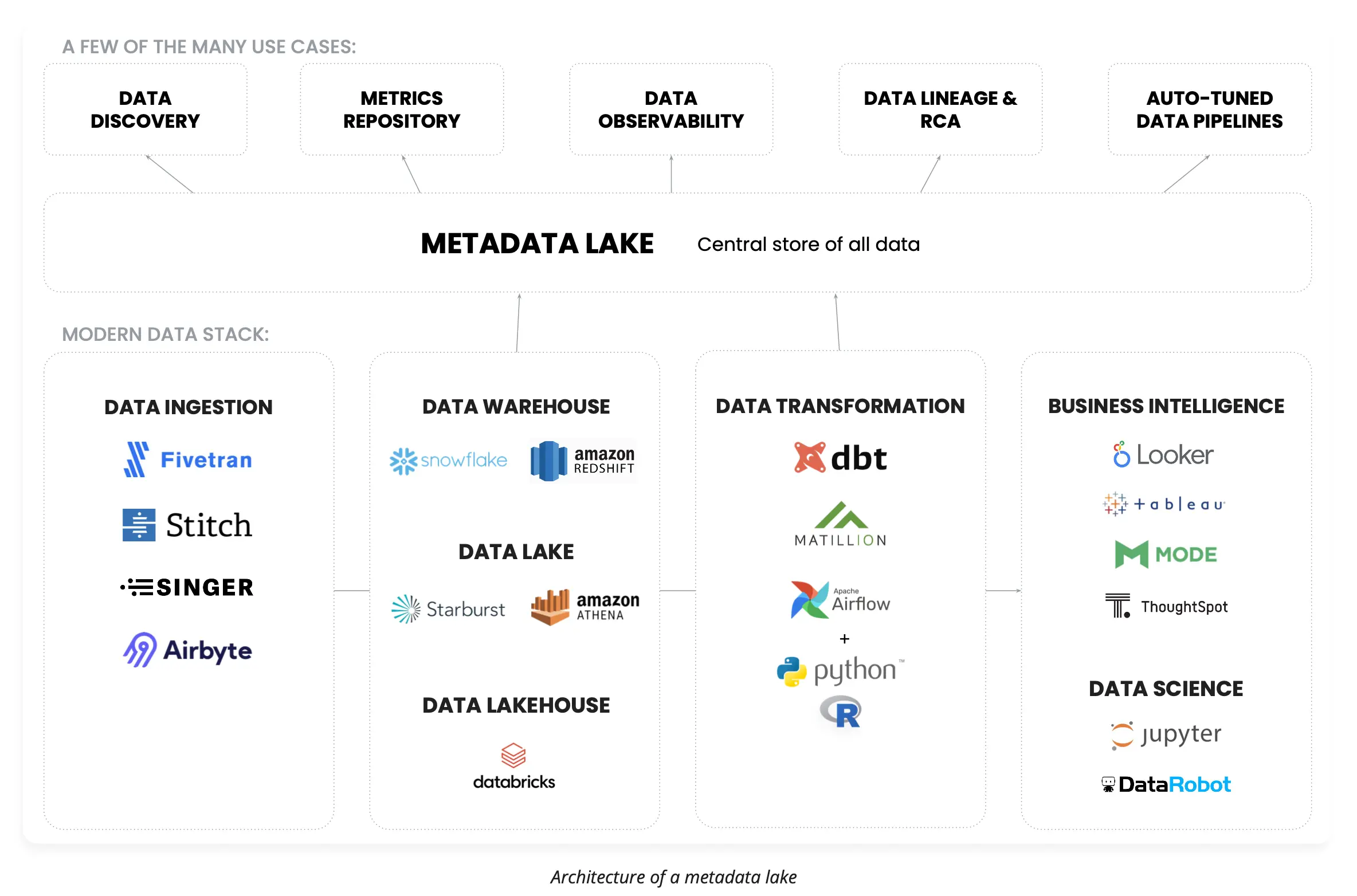
Architecture of enterprise metadata lake: A unified repository for metadata management from disparate data sources. Source: Atlan.
Active Metadata vs Passive Metadata
Permalink to “Active Metadata vs Passive Metadata”All of these types of metadata can be grouped under two broad categories, so we can better understand how they exist within a system:
- Passive metadata: Technical metadata that provides basic data definitions such as schema, data types, models, owner names, etc.
- Active metadata: Descriptive metadata that adds context to data by providing details on everything that happens to the data (e.g. operational, business, and social metadata).
Read more →Active metadata management: The key building block of a modern data stack.
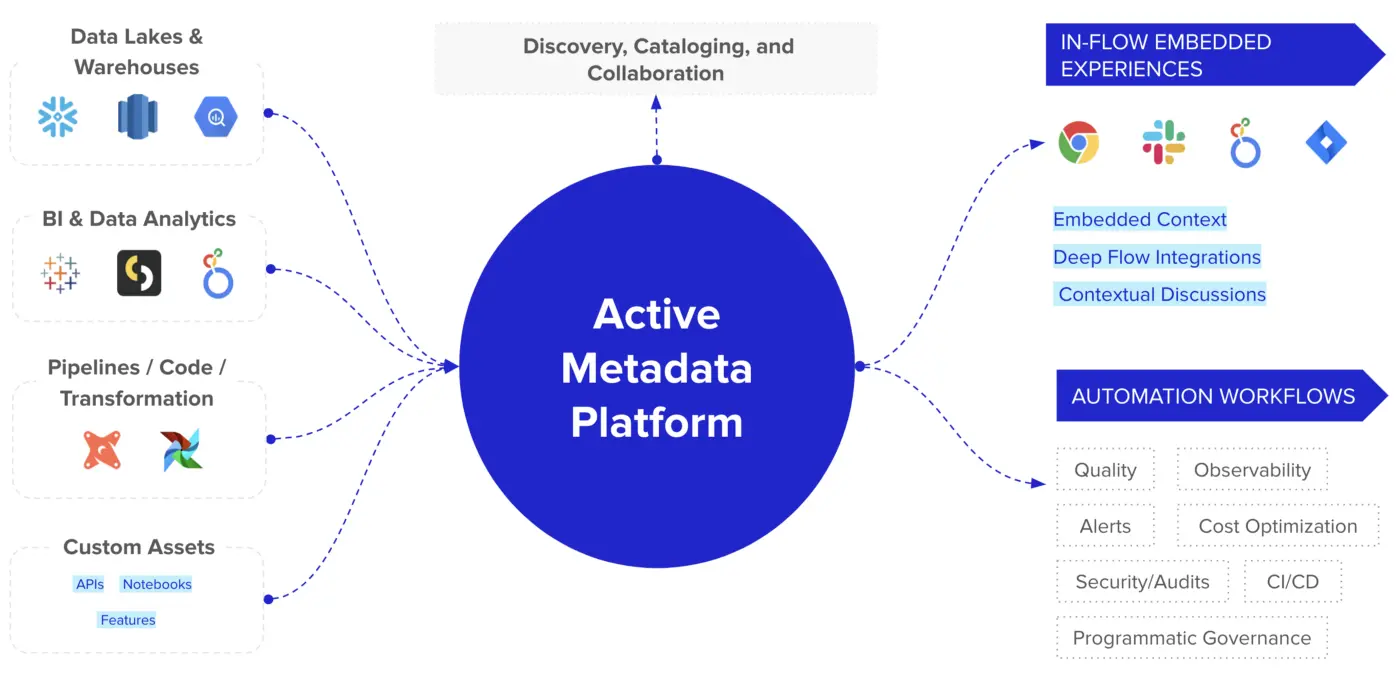
Key components of an enterprise metadata management data stack. Source: Atlan.
[ebook] → Building a Business Case for Metadata Management & Data Catalog
Download ebook
What is a metadata management platform?
Permalink to “What is a metadata management platform?”A metadata management tool is a technology, often a SaaS product used to store, organize, track, and edit every type of metadata within a business. A metadata management platform should enable diverse data users to surface relevant metadata when and where they need it.
Traditional metadata management solutions are typically static and rely on humans to curate and document information. However, a new generation of technology — the active metadata management platform — not only aggregates metadata in a single store (such as a metadata lake), it also leverages orchestration to make relevant metadata available to users as seamlessly as possible.
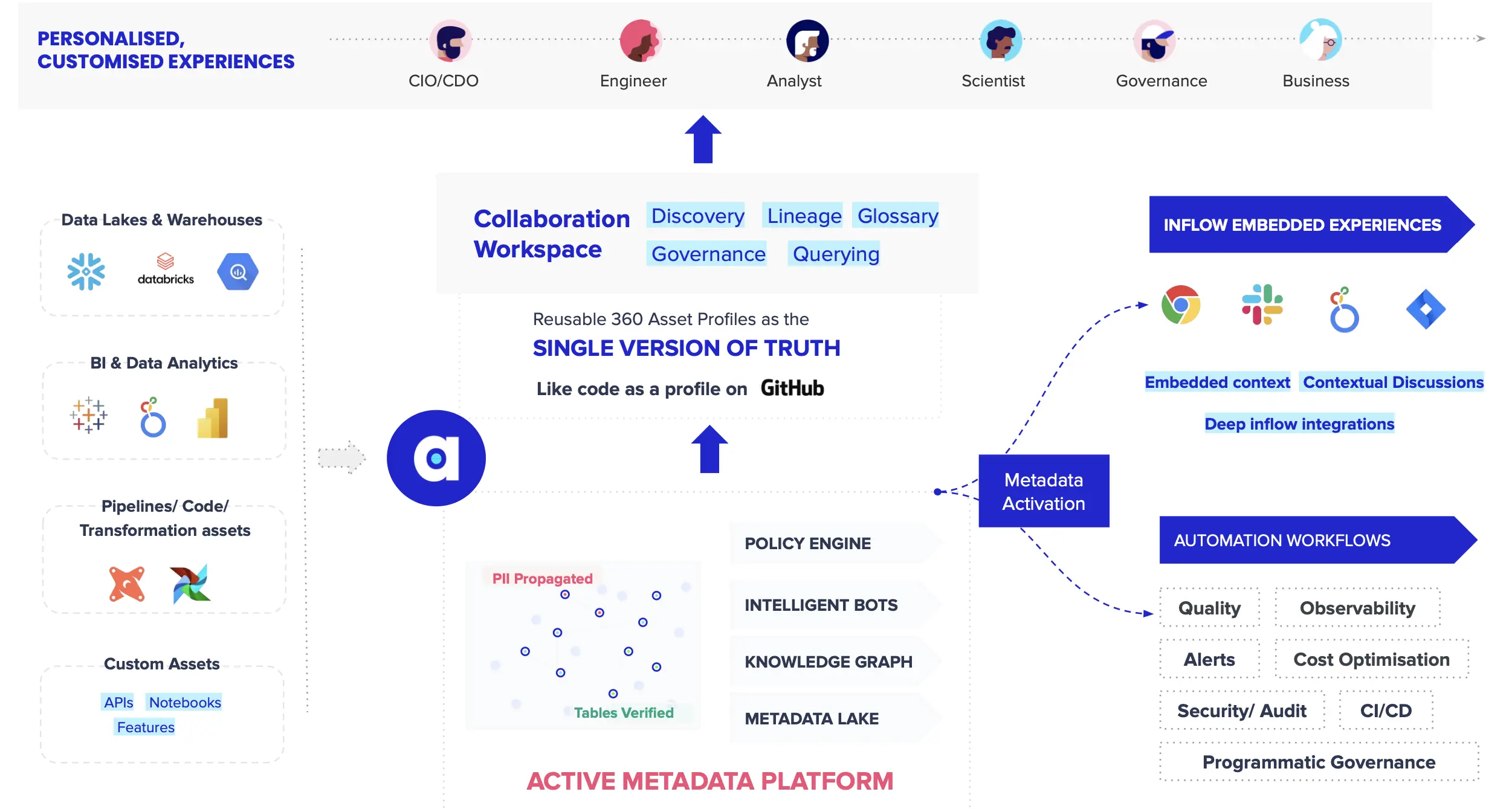
Atlan: An enterprise active metadata management platform for the modern data stack. Source: Atlan.
Data-driven organizations and institutions have been eager to embrace active metadata management as a superior way to handle metadata. Last year, Gartner replaced their Magic Quadrant for Metadata Management Solutions with the Market Guide for Active Metadata Management. “The stand-alone metadata management platform will be refocused from augmented data catalogs to a metadata ‘anywhere’ orchestration platform,” says the guide.
Metadata Management: Collection of technical, operational, business, and social metadata in one place. Source: Atlan.
A Demo of Atlan Enterprise Metadata Management Tool
Why is metadata management important?
Permalink to “Why is metadata management important?”Taking a unified approach to metadata management gives you the ability to trust that your metadata is accurate and reliable.
Metadata connects all of your organization’s data so teams can find exactly what they need, exactly when they need it. But with so much metadata existing within the modern business environment, it can be difficult to analyze data and separate the essential from the extraneous without the right context.
Without a metadata management strategy in place, data silos will emerge through the organization, and users in different departments won’t know which information is best for their needs.
What are the benefits of metadata management?
Permalink to “What are the benefits of metadata management?”Here are a few benefits of metadata management to consider:
- Improved consistency
- Better data quality
- Faster access to insights
- Reduced costs
1- Improved consistency: Creates a consistent definition of metadata across the organization so conflicting terms don’t lead to data retrieval issues.
2- Better data quality: Metadata management solutions almost always leverage automation capable of identifying data issues and inconsistencies in real time.
3- Faster access to insights: Data scientists have more time to analyze data to extract real business value, and data teams can achieve faster project delivery.
4- Reduced costs: The efficiency gains and repeatable processes of metadata management decrease redundancy and reduce excess costs, such as storage costs.
Learn more: Top 6 best practices for effective enterprise metadata management.
On top of these benefits, active metadata management provides additional advantages that many businesses find appealing.
Additional benefits of active metadata management:
Permalink to “Additional benefits of active metadata management:”- Enhanced context of metadata
- Auto-classification of sensitive data
- Embedded collaboration
- Orchestration of metadata across platforms
1- Enhanced context of metadata: Business terms can be automatically correlated with any data object (such as tables, columns, saved SQL snippets, and reproducible queries).
2- Auto-classification of sensitive data: Active metadata algorithms enable businesses to automatically identify sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII), to help with compliance and designing custom access policies.
3- Embedded collaboration: All data users are able to get on the same page while still using their tools of choice with no disruption.
4- Orchestration of metadata across platforms: The modern data stack is always evolving to meet new needs — active metadata management allows disparate systems to connect, making data assets across these systems interoperable.
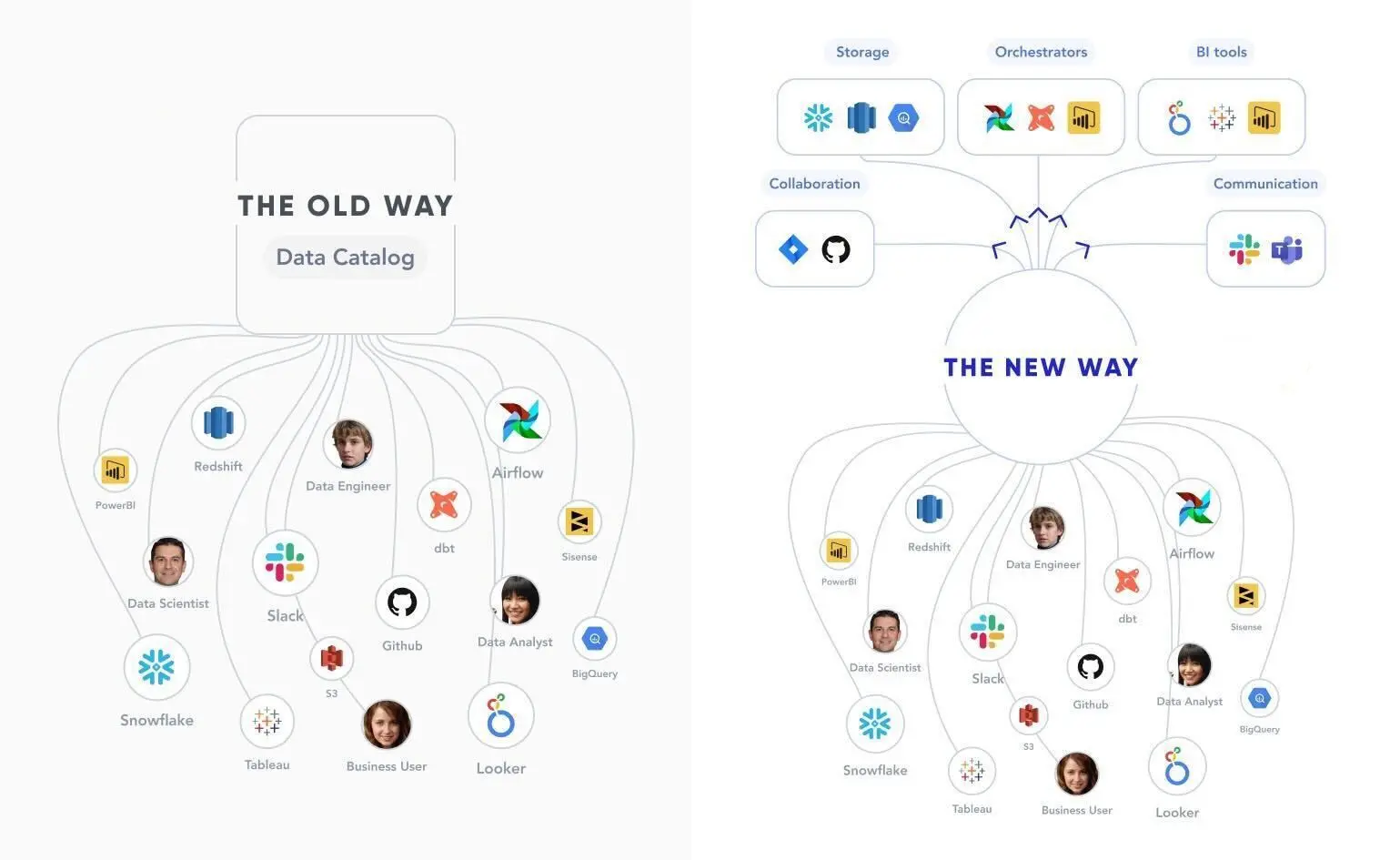
Vision for active metadata management. Image by Atlan
Data Catalog 3.0: The Modern Data Stack, Active Metadata and DataOps
Download ebook
Active Metadata: Key to metadata management automation
Permalink to “Active Metadata: Key to metadata management automation”Following are some of the examples of how active metadata help in metadata management automation at scale.
- Programmable bots help automatically identify and tag sensitive columns based on regulatory compliance requirements — HIPAA, GDPR, BCBS 239, etc.
- Bots help with auto-classification and auto-tagging based on specific naming conventions of data assets.
- Active metadata management platforms parse SQL queries and automatically create column-level lineage and also auto-classify PII data.
- Active metadata intelligently suggests recommendations and alerts and thereby making it easier for people to make the right decisions — surfacing commonly used data assets, stopping pipeline workflows when data quality issues are detected.
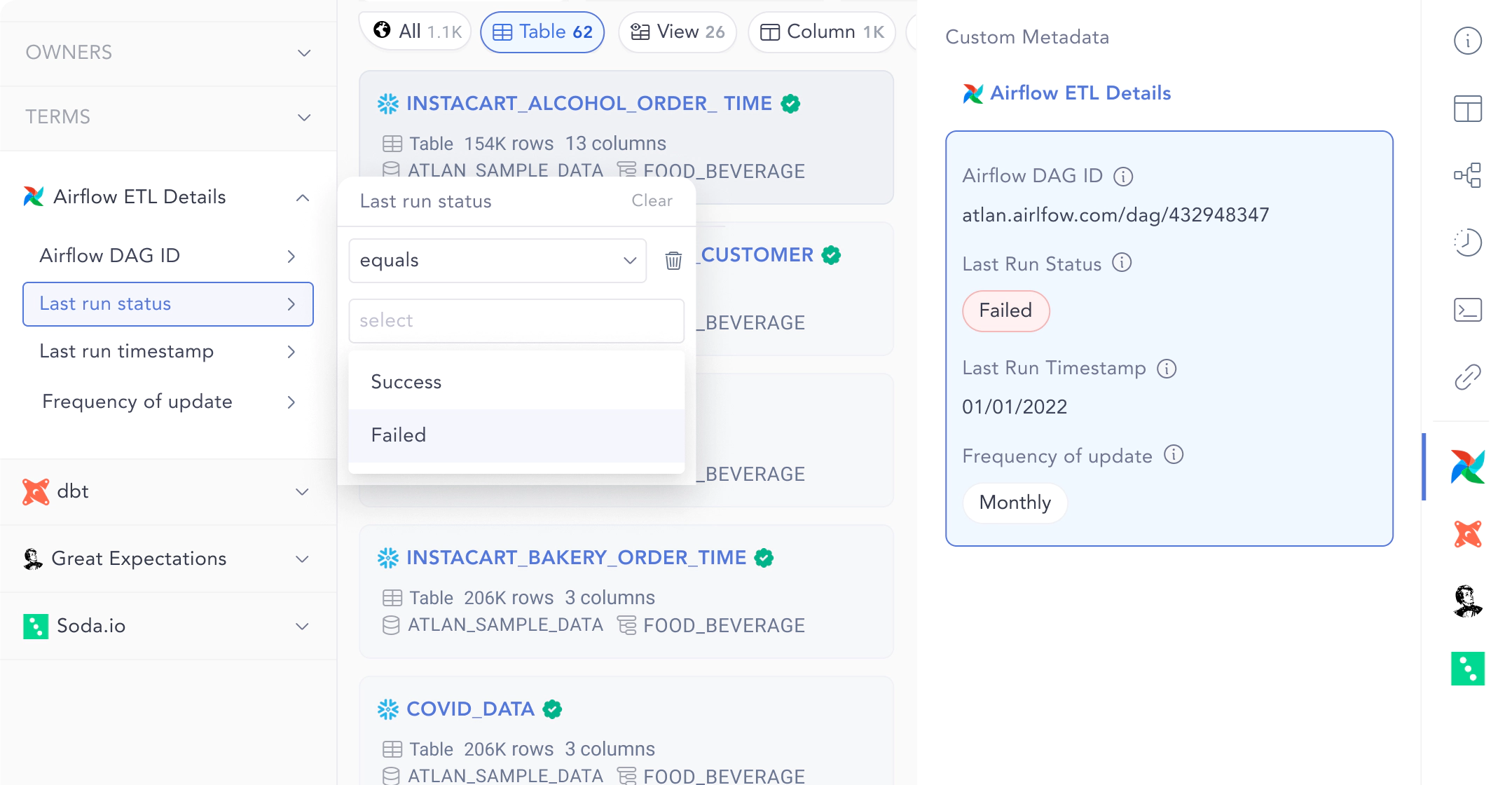
Custom metadata like pipeline errors, ETL status and orchestration DAG logs gives context about the health of the data asset. Source: Atlan.
What are metadata management tools?
Permalink to “What are metadata management tools?”Metadata management tools are solutions that help extract value from the metadata that is stored by a business. Because the number of data users within a business is often increasing and their level of data expertise may vary, metadata management tools are useful because they make discovering, organizing, and interacting with metadata simple for anyone, regardless of technical proficiency.
While there is no shortage of tools to choose from to facilitate metadata management, there are a handful of capabilities that you should focus on when evaluating your options:
- Metadata discovery/harvesting
- Metadata repository (a catalog, inventory, or dictionary)
- Metadata lineage and governance
- Metadata automation and intelligence
- Metadata collaboration and connectivity
Ideally, your metadata management toolset will feature all of the above functionality — considering the challenges you will face if any of these features are missing from your data stack. This may have you wondering, “Is there a comprehensive solution that fulfills all of these needs?”
According to the article Metadata Management Tools Market Size, Forecast Report 2032 by Global Market Insights, the global metadata management tools market was valued at approximately USD 9.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 19.6%, reaching around USD 44.7 billion by 2032.
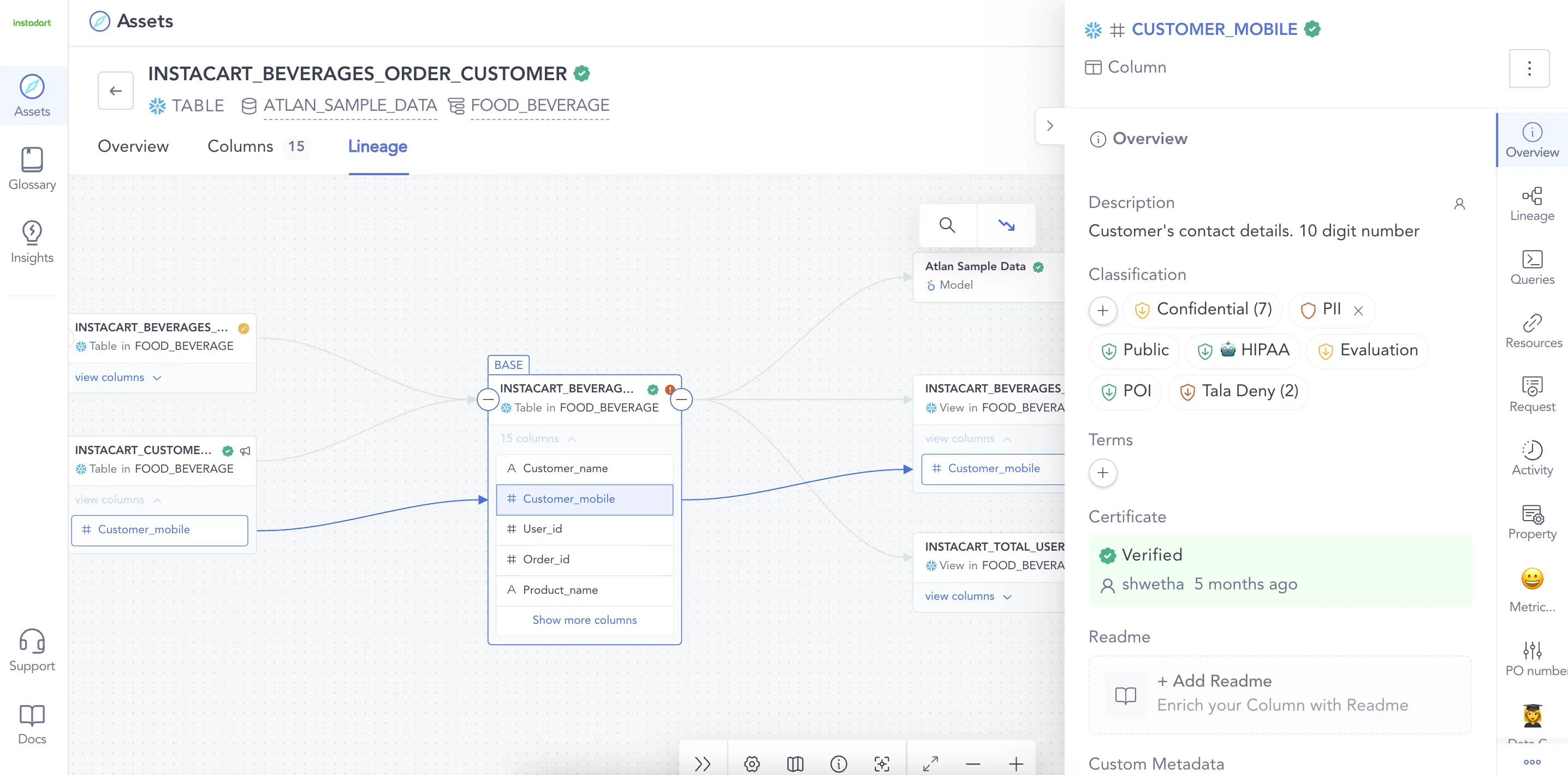
Metadata Management: Automated data lineage and governance. Source: Atlan.
Active metadata management platform
Permalink to “Active metadata management platform”Metadata management has come a long way and continues to evolve at a rapid pace. As a result, Gartner notes that “metadata management has shifted from focusing on reports, inventories and static impact analysis, toward intelligent optimization, data discovery and use-case analysis.”
Let’s take a look at how the active metadata management platform ticks all of these boxes and satisfies both the current and future needs of the modern business.
What are the elements of an active metadata platform?
Permalink to “What are the elements of an active metadata platform?”An active metadata platform features five key elements:
- The metadata lake
- Programmable-intelligence bots
- Embedded collaboration plugins
- Data process automation (DPA)
- Reverse metadata

Atlan: An enterprise active metadata management tool for the modern data stack. Source: Atlan.
The Ultimate Guide to Evaluating an Enterprise Data Catalog
Download free ebook
The metadata lake: A unified repository to store all kinds of metadata, in raw and processed forms, built on open APIs and powered by a knowledge graph. The metadata lake provides much-needed flexibility for limitless use cases such as data discovery, lineage, observability.
Programmable-intelligence bots: A framework that allows teams to create customizable ML or data science algorithms to drive intelligence. AI-driven metadata intelligence increases efficiency across areas such as data organization, quality assurance, and compliance.
Embedded collaboration plugins: A set of integrations, unified by the common metadata layer, that seamlessly integrates data tools with each data team’s daily workflow. Embedded collaboration ensures equitable access and data democratization across the diverse members that make up data teams
Data process automation (DPA): An easy way to build, deploy, and manage workflow automation bots that will emulate human decision-making processes to manage a data ecosystem. DPA is another essential way to increase metadata management efficiency; for example, it could recommend parameters for scaling up a cloud warehouse and assist with resource allocation.
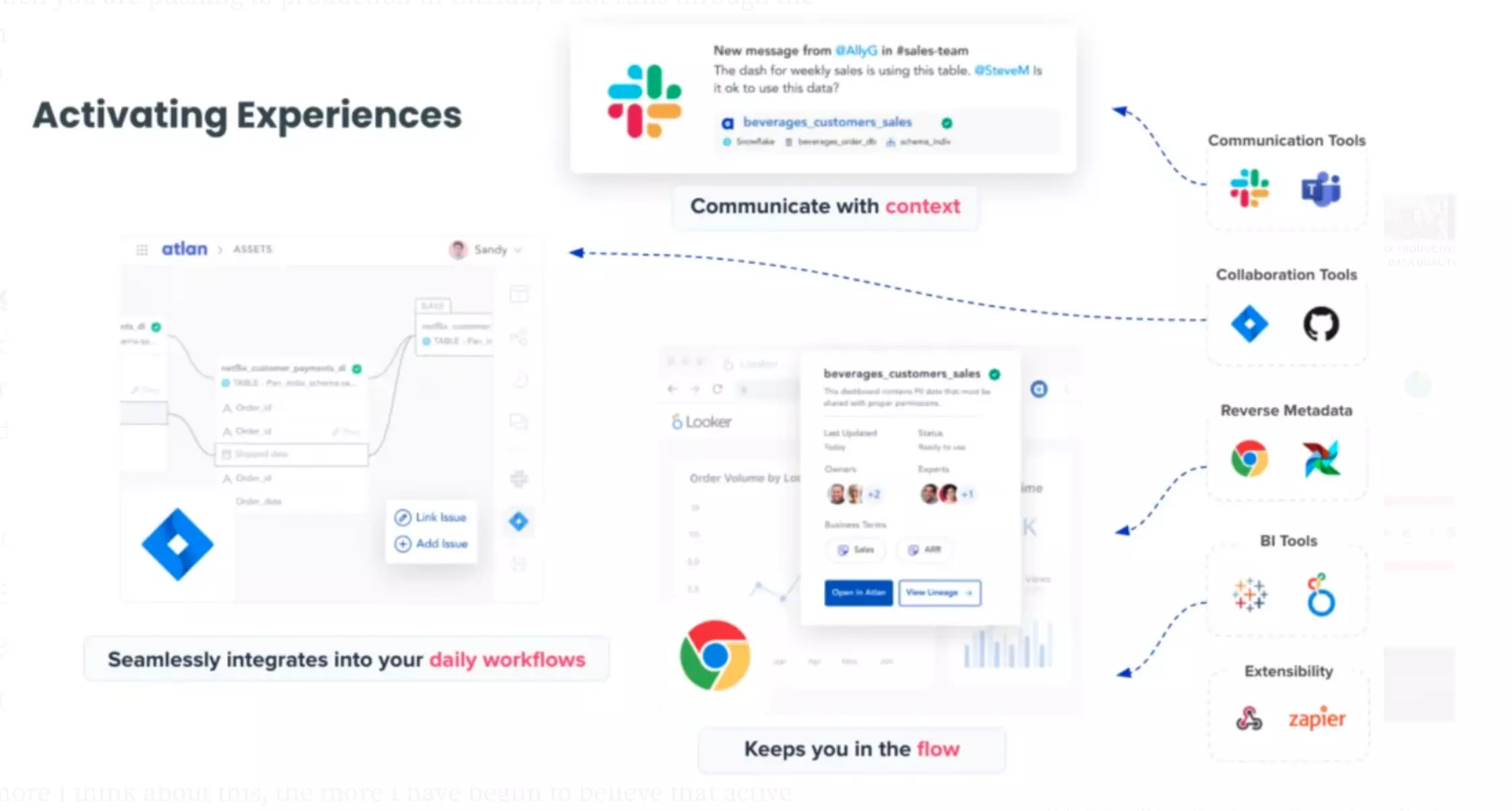
Reverse metadata: Orchestration to make relevant metadata available to the end-user, wherever and whenever they need it, rather than in a standalone catalog. Reverse metadata ensures that data users always get the full context, no matter what tools they are working in.
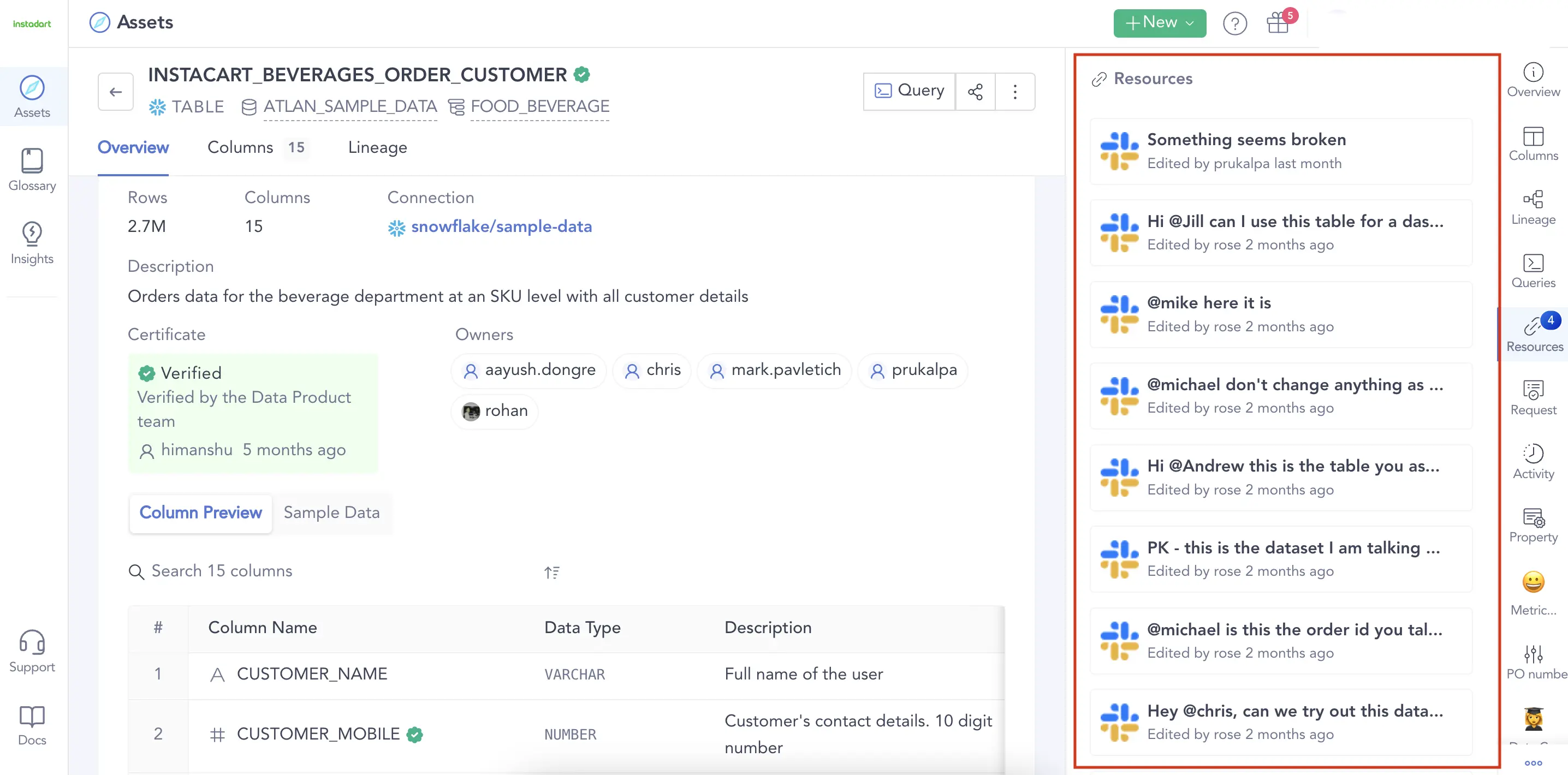
Modern Metadata Management tools enables collaboration between teams. Source: Atlan.
Also, read → Metadata management in data lakes
Now that you understand the key features to look for in a metadata management tool, let’s take a look at some best practices.
Metadata management best practices
Permalink to “Metadata management best practices”In addition to the technology and processes behind effective metadata management, there are a few high-level principles you should keep in mind whenever planning, executing or measuring metadata management activities:
- Design a metadata strategy: The foundation of successful metadata management is to develop a strategy that supports business objectives and can be shared with key stakeholders. It should answer the following questions:
- What is the data asset about?
- Descriptions (tables, columns)
- Keywords or tags
- Themes or categories
- Why does the data asset exist?
- Data source
- Lineage
- Impact analysis
- Where is the data asset from?
- Spatial coverage
- Language
- Business domains
- Who is responsible for the data asset?
- Creator or owner
- Contributors or experts
- Point of contact
- When was the data asset created and updated?
- Creation date
- Last updated or modified date
- Update frequency
- How can the data asset be used?
- License
- Classification
- Use cases
- What is the data asset about?
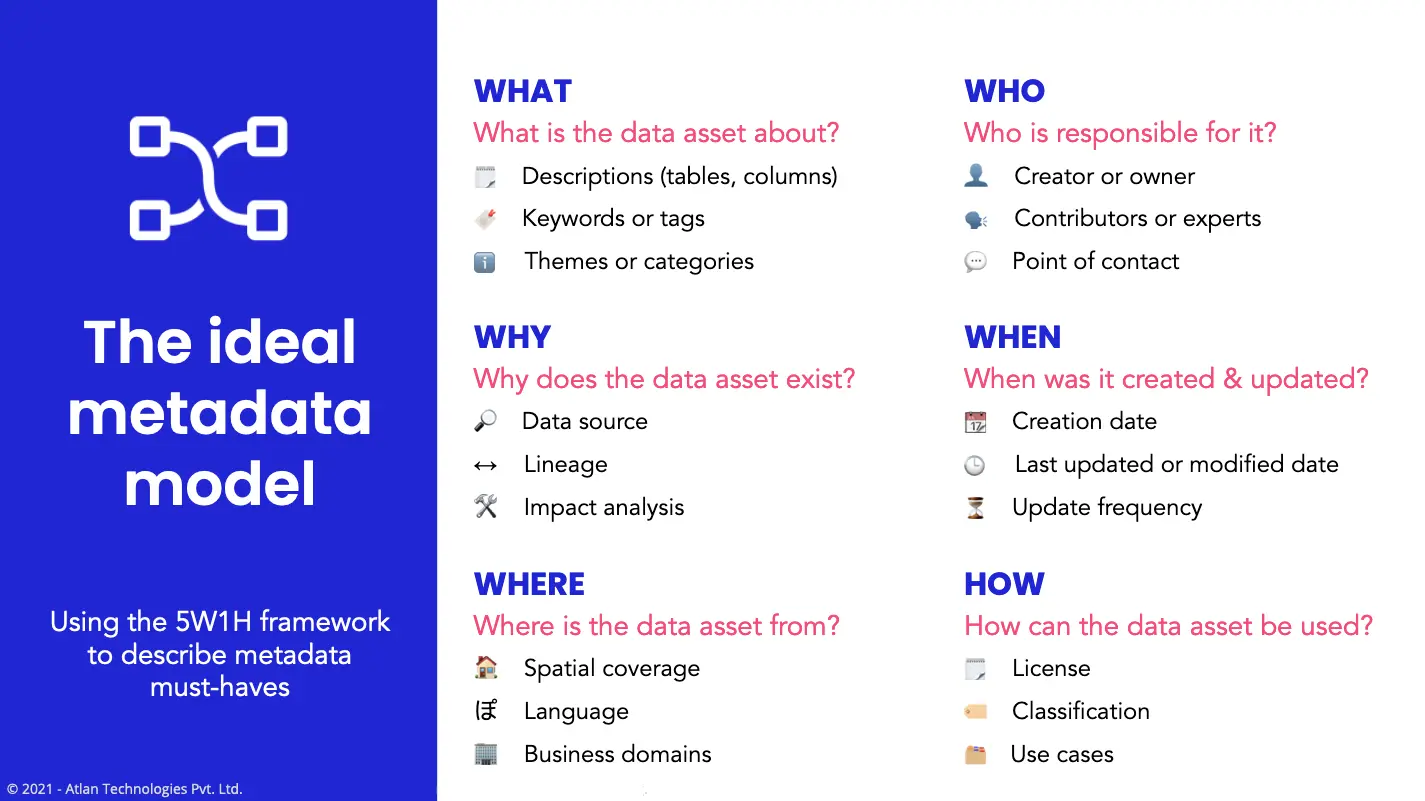
5W1H: A framework for a robust metadata management model. Image by Atlan
Leverage all types of metadata: To capture the full value of your data through metadata-driven intelligence, you must use all four categories of metadata outlined above.
Democratize metadata: Maximize visibility and usability for all users across the business so they can discover, digest, and trust the information they need.
Practice continuous metadata improvement: Metadata management is an organization-wide process — use feedback from diverse data users to refine your metadata strategy on an ongoing basis.
Learn more: 6 Metadata Management Best Practices for 2025
Also, read → Toward Holistic Metadata Management | Metadata Management for Enterprises | Demystifying Metadata Management
The future of metadata management and data catalogs
Permalink to “The future of metadata management and data catalogs”As metadata itself becomes big data, rapid advances in cloud platforms, such as Snowflake, allow businesses to extract intelligence that would not have been possible just a few years ago. With the ability to store all types of metadata in both raw and processed forms, the metadata lake will drive the next wave of innovation in active metadata management and power use cases that haven’t even been imagined yet.
Active metadata is the driving force behind a number of new and exciting developments in the world of data: autonomous DataOps, augmented data catalogs, data fabric, and the data mesh, among others.
The rapid adoption of active metadata management comes in tandem with the advent of “Data Catalog 3.0.” This new generation of data catalogs is built around diverse data assets, end-to-end data visibility, and embedded collaboration. Currently, most enterprises are managing metadata in a way that just won’t work in the business world of tomorrow. Here’s how a third-generation active metadata platform solves these major roadblocks:
| Second-generation data catalogs | Third-generation data catalogs |
|---|---|
| Siloed context | Embedded context |
| Generic experience | Personalized experiences |
| Minimum automation | Autonomous |
| Top-down governance | Federated governance |
While the rest of the modern data stack has evolved over the past few years, metadata management tools are still lagging behind. Data Catalog 3.0 is a much-needed evolution in metadata management, allowing metadata to be searched, analyzed, and maintained the same way as all other types of data.
Atlan: The next generation of metadata management
Permalink to “Atlan: The next generation of metadata management”Atlan is a third-generation, active metadata platform that unifies metadata from every tool and data domain, creates personalized discovery experiences for every data user, and drives automation across every part of the modern data stack through orchestration.
Atlan leverages these four core principles of modern metadata management:
Permalink to “Atlan leverages these four core principles of modern metadata management:”- Programmable bots
- Embedded collaboration
- End-to-end visibility
- Open by default.
If you’re striving to unlock the full potential of your business’s metadata, you must check out all possibilities that Atlan promises to unlock.
How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
Permalink to “How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan”The recently published Forrester Wave report compared all the major enterprise data catalogs and positioned Atlan as the market leader ahead of all others. The comparison was based on 24 different aspects of cataloging, broadly across the following three criteria:
- Automatic cataloging of the entire technology, data, and AI ecosystem
- Enabling the data ecosystem AI and automation first
- Prioritizing data democratization and self-service
These criteria made Atlan the ideal choice for a major audio content platform, where the data ecosystem was centered around Snowflake. The platform sought a “one-stop shop for governance and discovery,” and Atlan played a crucial role in ensuring their data was “understandable, reliable, high-quality, and discoverable.”
For another organization, Aliaxis, which also uses Snowflake as their core data platform, Atlan served as “a bridge” between various tools and technologies across the data ecosystem. With its organization-wide business glossary, Atlan became the go-to platform for finding, accessing, and using data. It also significantly reduced the time spent by data engineers and analysts on pipeline debugging and troubleshooting.
A key goal of Atlan is to help organizations maximize the use of their data for AI use cases. As generative AI capabilities have advanced in recent years, organizations can now do more with both structured and unstructured data—provided it is discoverable and trustworthy, or in other words, AI-ready.
Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes
Permalink to “Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes”- Tide, a UK-based digital bank with nearly 500,000 small business customers, sought to improve their compliance with GDPR’s Right to Erasure, commonly known as the “Right to be forgotten”.
- After adopting Atlan as their metadata platform, Tide’s data and legal teams collaborated to define personally identifiable information in order to propagate those definitions and tags across their data estate.
- Tide used Atlan Playbooks (rule-based bulk automations) to automatically identify, tag, and secure personal data, turning a 50-day manual process into mere hours of work.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization in establishing and scaling data governance programs.
FAQs about Metadata Management
Permalink to “FAQs about Metadata Management”1. What is metadata management?
Permalink to “1. What is metadata management?”Metadata management is a framework of processes, policies, and technologies used to catalog and manage data assets throughout their lifecycle. It involves cleaning, classifying, and organizing data to ensure accuracy, consistency, and usability, forming the foundation for data discovery, governance, and collaboration.
2. Why is metadata management important for my organization?
Permalink to “2. Why is metadata management important for my organization?”Effective metadata management helps organizations maximize the value of their data. It improves data discovery, enhances data quality, and supports governance and compliance. By ensuring data integrity and accessibility, metadata management enables better decision-making and operational efficiency.
3. How can I implement an effective metadata management system?
Permalink to “3. How can I implement an effective metadata management system?”To implement a robust metadata management system: Define clear policies and processes for metadata usage, invest in tools like data catalogs to automate metadata collection and management, ensure stakeholder collaboration to maintain metadata accuracy, and continuously monitor and update the metadata framework to adapt to changing business needs.
4. How does metadata management improve data governance?
Permalink to “4. How does metadata management improve data governance?”Metadata management enhances data governance by providing a structured approach to managing data assets. It ensures consistent data definitions, tracks data lineage, and enforces policies for data usage. This leads to improved compliance and accountability across the organization.
5. How can metadata management enhance data security and compliance?
Permalink to “5. How can metadata management enhance data security and compliance?”By cataloging and organizing data, metadata management ensures that sensitive information is properly classified and protected. It enables organizations to enforce security policies, track data access, and comply with regulatory requirements, reducing risks of data breaches and non-compliance penalties.
Metadata Management: Related reads
Permalink to “Metadata Management: Related reads”- Metadata Management: Benefits, Automation, Best Practices, and Tools
- What is metadata management and why is it so important?
- Data Catalog: Does Your Business Really Need One?
- Top 6 Metadata Management Best Practices for 2025
- Active Metadata: Definition, Characteristics, Use Cases & More
- Enterprise Metadata Management and Its Importance in the Modern Data Stack
- Snowflake Metadata Management: Importance, Challenges, and Identifying The Right Platform
- Databricks Metadata Management— FAQs, Tools, Getting Started
- DataHub: LinkedIn’s Open-Source Tool for Data Discovery, Catalog, and Metadata Management
- Data Catalog Vs. Metadata Management: Differences, and How They Work Together?
- Difference between Master Data Management(MDM) and Metadata Management
Photo by Vitaly Vlasov from Pexels.
Share this article


















