Enterprise Metadata Management and Its Importance in the Modern Data Stack

Share this article
Enterprise metadata management (EMM) has become table stakes for companies as they work to wrangle the explosive metadata growth tied to the rise of big data. What’s the best way to keep your business from drowning in metadata and instead use this information to supercharge the modern data stack?
Let’s examine what defines EMM, why it is important, and how it can be used to benefit the enterprise.
What is enterprise metadata management (EMM)? #
Enterprise Metadata Management is a set of frameworks, processes, and technologies that helps surface, search, classify and validate metadata from across your data stack. As metadata itself becomes big data, the definition of what is included as metadata is ever-expanding. Apart from the traditional technical metadata(database schemas) and business metadata(glossary), the modern data stack produces new forms of enterprise metadata like:
- Cloud computing engines and data orchestration platforms generate logs which are called performance metadata.
- As data democratization becomes a norm, more data consumers interact with each other and produces social metadata
- Logs from BI tools, notebooks, and other applications produce usage metadata
- Automatic classification of data assets as PII, GDPR, and HIPAA produces governance metadata
By providing crucial context to complex data environments, enterprise metadata management improves productivity, innovation, and collaboration for all data users. It also enables stronger data governance and helps to reduce risk.
Gartner defines EMM as “the business discipline for managing the metadata about the information assets of the organization.” The operative phrase here is “business discipline,” as it underscores the fact that EMM is of chief importance to both business and technical stakeholders.
Learn more → A Comprehensive guide on the types of enterprise metadata
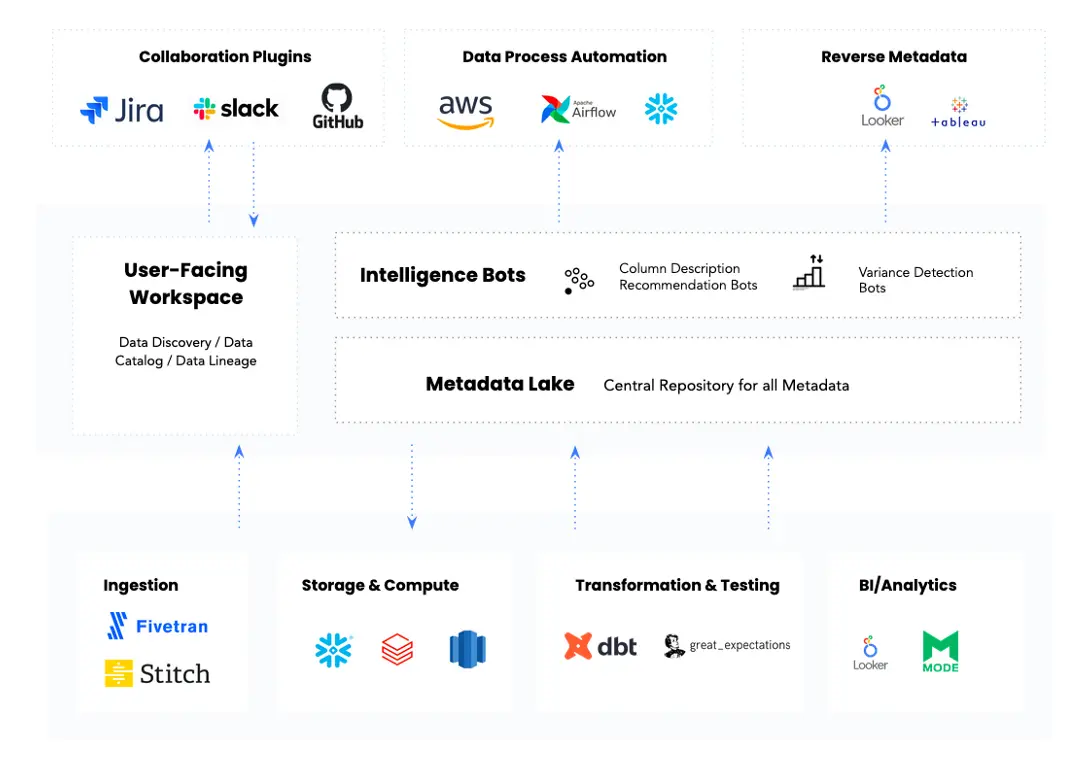
Modern enterprise metadata management stack. Source: Atlan
Importance of enterprise metadata management #
EMM is a subset of metadata management that focuses on enterprise businesses, typically large companies with 250+ employees. As the modern enterprise seeks to make better use of its vast amounts of data and accelerate transformation, data management becomes increasingly complex. This complexity has been further compounded by the shift to remote work as well as the shift to hybrid architecture.
According to the Data Innovators Guide from Hewlett-Packard, over half of enterprise organizations struggle with data management. Top data management challenges include:
- data growth (67%)
- operations management silos (67%)
- lack of visibility (60%)
These challenges largely revolve around the vast amount of data that large enterprise organizations have to manage compared to micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and small- and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). The IDG Data and Analytics Study found that the average enterprise has seven times as much data as the average SMB.
When trying to make sense of all the data at their disposal, information often ends up being tied to a certain team, function, or department and doesn’t flow naturally across the enterprise. As a result of these data silos, people in the organization are able to access specific data or its sources and others aren’t.
Centralized EMM is the key to unifying data management and ensuring accuracy, integrity, and consistency across large volumes of data. Because data growth goes hand in hand with metadata growth, there have been several recent developments in EMM that make agile metadata management more attainable than ever.
For example, the metadata lake presents a powerful opportunity for businesses to store all types of metadata to power a virtually unlimited number of use cases. Metadata is also one of the core pillars of data observability, a cutting-edge discipline many enterprises are adopting to improve data visibility and unite data management silos.
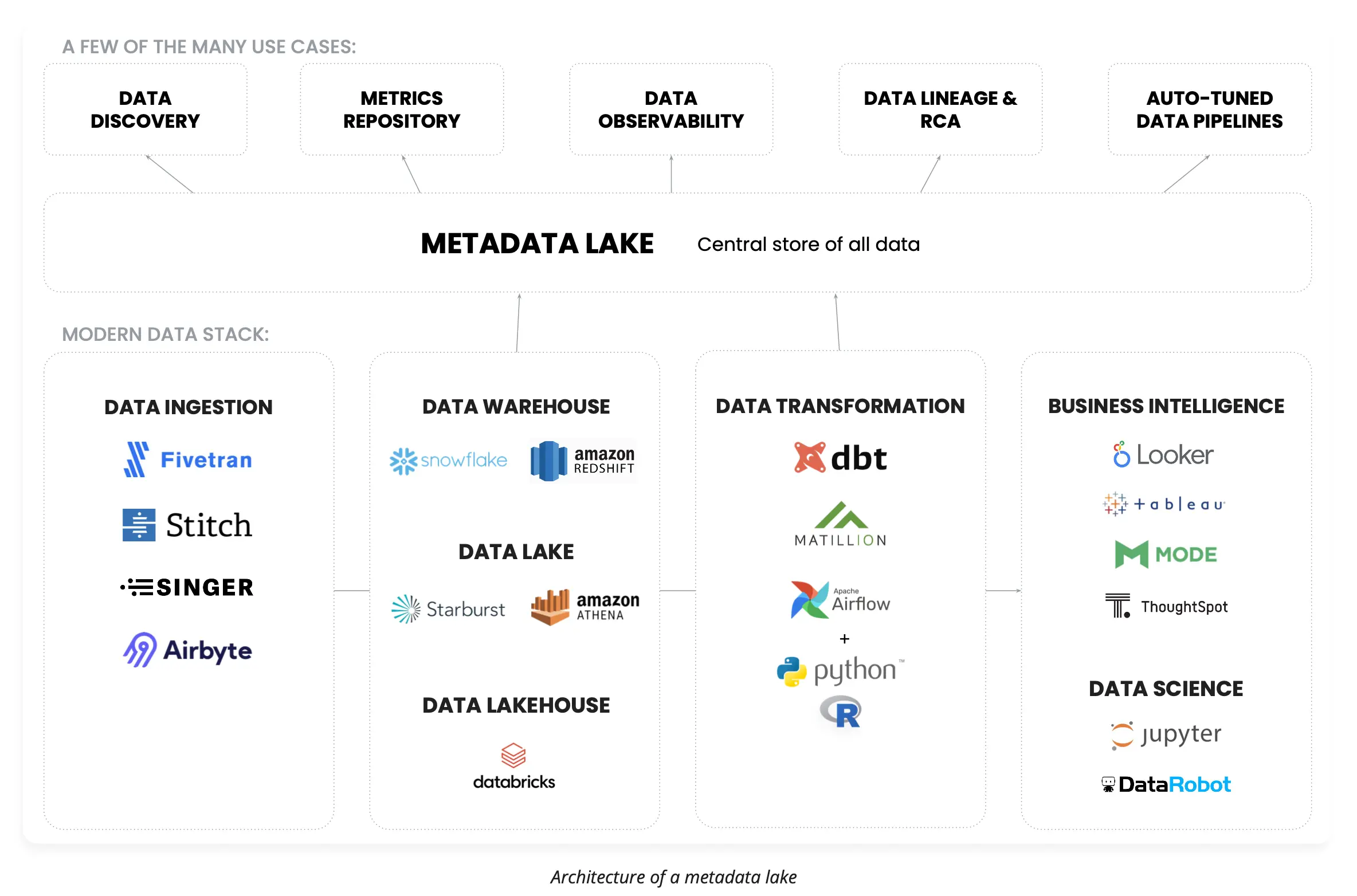
Architecture of enterprise metadata lake: A unified repository for metadata management from disperate data sources. Source: Atlan
Why is enterprise metadata management essential?
Now that you have a better understanding of how EMM enhances overall data management and collaboration, let’s consider the challenges that will occur for organizations that don’t embrace metadata management.
The challenge: limited visibility into what data is stored, copied, and protected
Enterprises operating across hybrid environments are in dire need of a way to streamline data operations. The same Hewlett-Packard study mentioned earlier found that over two-thirds (68%) of organizations believe managing data at scale is their number one data infrastructure issue. Additionally, three out of five agree that multiple tiers of storage silos create significant management complexity.
The solution: full data visibility at scale
Didi Chuxing, a mobile transportation company committed to advanced EMM, relies on advanced analytics to offer their customers an optimal ride-hailing experience. By utilizing rich metadata about the company’s data assets, employees gain full visibility into all data so they can easily explore, discover, and make use that information to improve their product. Metadata ensures that crucial data context — what it means, where it came from, it’s quality — is not lost among the teams working to analyze it.
Not only does has EMM improved their internal operations and customer satisfaction, it has allowed the company to monetize anonymized data through a partnership with traffic management authorities to facilitate smarter road planning. Talk about maximizing the value of data!
The challenge: lack of trust and accessibility
It’s common for business users to have trust issues if they’re operating in an unreliable system where data quality problems are commonplace. Imagine the sales rep who has to send weekly emails to the engineering team asking, “Is this dashboard accurate?” Such points of friction are major productivity killers and an annoyance for everyone involved.
“Every year, poor data quality costs organizations an average $12.9 million. Apart from the immediate impact on revenue, over the long term, poor quality data increases the complexity of data ecosystems and leads to poor decision making.” - Gartner
Data reliability issues are sure to abound in the absence of EMM. But sometimes users are unable to retrieve the data they need at all, in which case it becomes an issue of not just quality but overall accessibility. Metadata management is the key to connecting the dots between large quantities of data and providing the necessary understanding surrounding its context, meaning, and lineage.
The solution: empowering business users to self-serve dependable data
Huntington Bank, a full-service banking provider, realized several years ago that in order to provide customers with five-star personalized service, their staff would need self-service access to high-quality data. However, their systems and processes for managing data were insufficient — even technical users found it hard to understand where data was coming from, where it was going, and who was using it.
To solve this challenge and empower their teams to make more customer-centric decisions, Huntington Bank leveraged an “outside in” approach to metadata management. They knew it would be too difficult to train all 12,000+ employees on the intricacies of metadata curation, so they looked at existing processes (e.g., what people were searching for) and found ways to organize their data for more effective data discovery and democratization.
The challenge: compliance with laws and regulations
Many organizations find it difficult to achieve the level of data governance required to meet increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. According to Deloitte’s compliance guidance, “Managing your metadata is a prerequisite for providing insight into data flows and related controls in your organization.”
The solution: taking a bottom-up approach to data governance
In modern data governance systems, it is ideal for data users to have a flexible and highly automated system for managing the processes surrounding the structured creation, usage, and deletion of data. That’s exactly what one Fortune 500 company did when they adopted Atlan’s metadata management solution to create a practitioner-led data foundation with governance controls fitting for a public enterprise in the cloud era.
The company’s use of EMM technology helped them unify elaborate data relationships across many sources, which significantly improved their data governance for more accurate reporting and compliance.
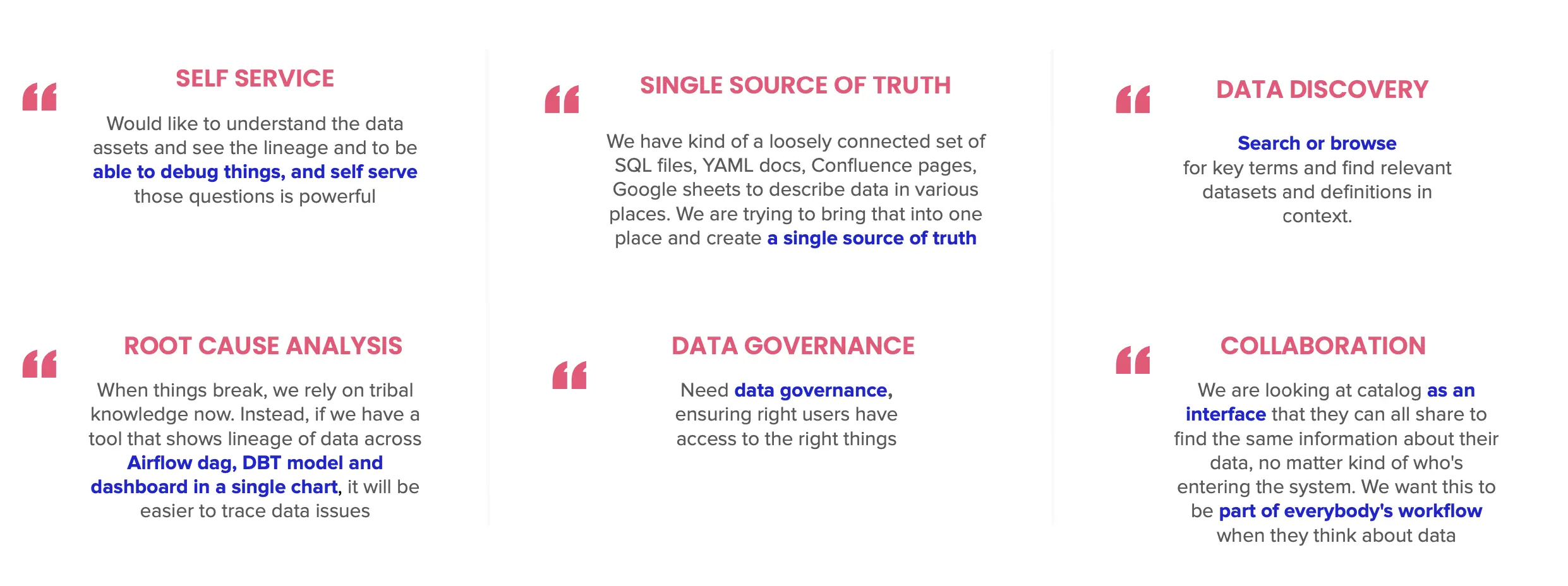
Enterprise metadata management use cases. Source: Atlan
Enterprise metadata management: Use cases
There are several ways metadata management can be used to provide value throughout the enterprise, including:
- data classification
- data discovery
- data lineage
- data governance
- data democratization
Here are a few practical examples of how EMM can benefit the modern enterprise.
Enterprise metadata management for data classification
Let’s say that analysts at the Atlanta, Chicago, and Los Angeles offices of an insurance company need to collaborate on an annual report without exposing sensitive data to breach. In most organizations this would require setting up sophisticated staging areas, ETL pipelines, and manually written SQL queries.
However, a more strategic approach following EMM best practice would empower all members of the business to access, explore, and understand data assets with ease. As a result, more data users would be able to surface critical business insights to drive effective decision-making (rather than having to rely on those with a high level of technical proficiency).
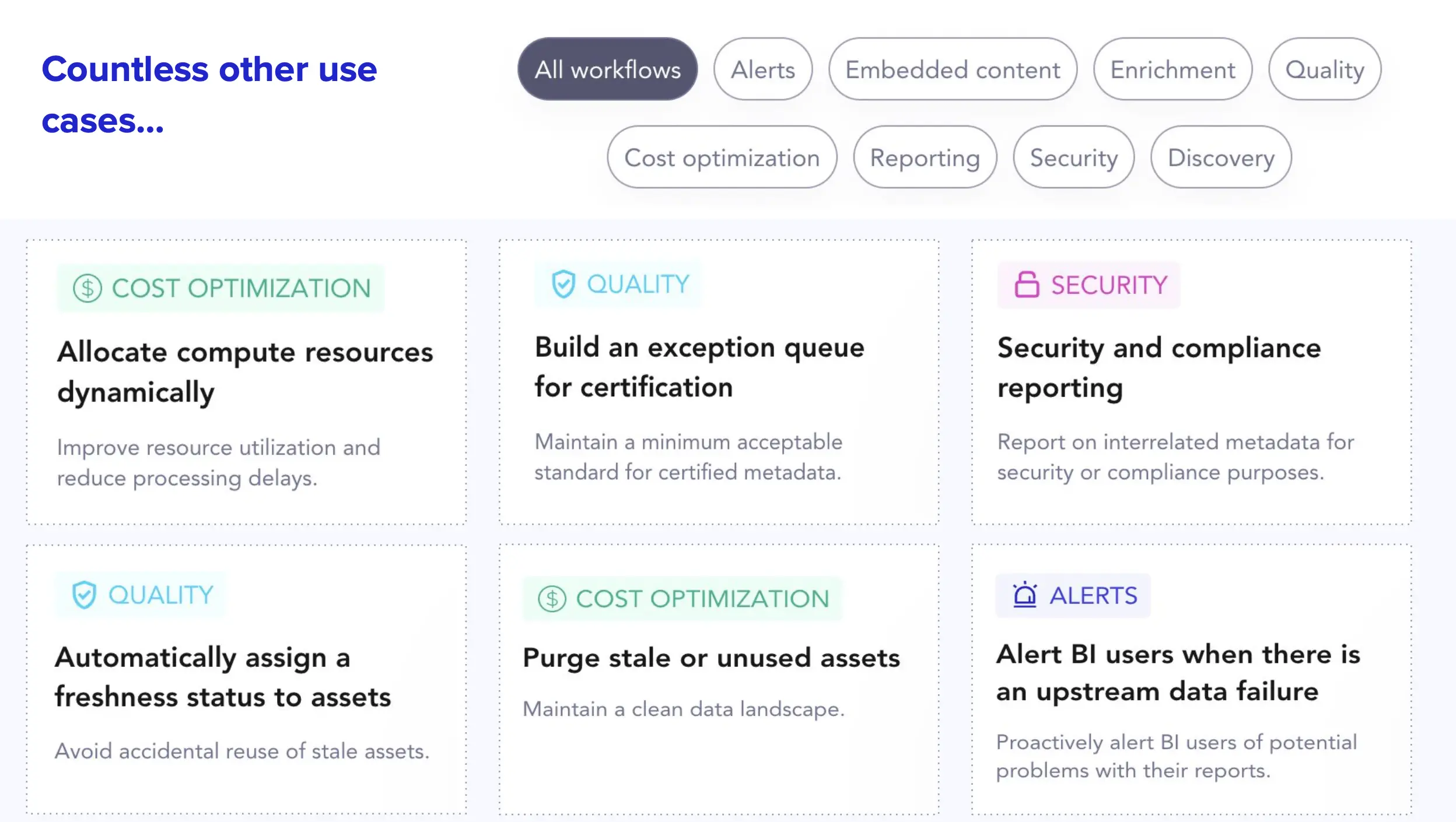
Limitless possibilities to leverage enterprise metadata to solve new data management use cases. Source: Atlan
Enterprise metadata management for data discovery
Metadata is one of the most valuable strategic assets that an enterprise possesses. The troves of data video streaming giant Netflix has at their disposal are spread across multiple platforms such as Amazon S3, Redshift, and MySql. To unite these disparate data sources through EMM, the company built their own metadata management platform, Metacat, to provide a unified API that allows them to discover and access metadata from wherever they please. They use Metacat as a single source of truth and metadata access layer to power everything from content recommendations to the thumbnails that change based on each user's taste.
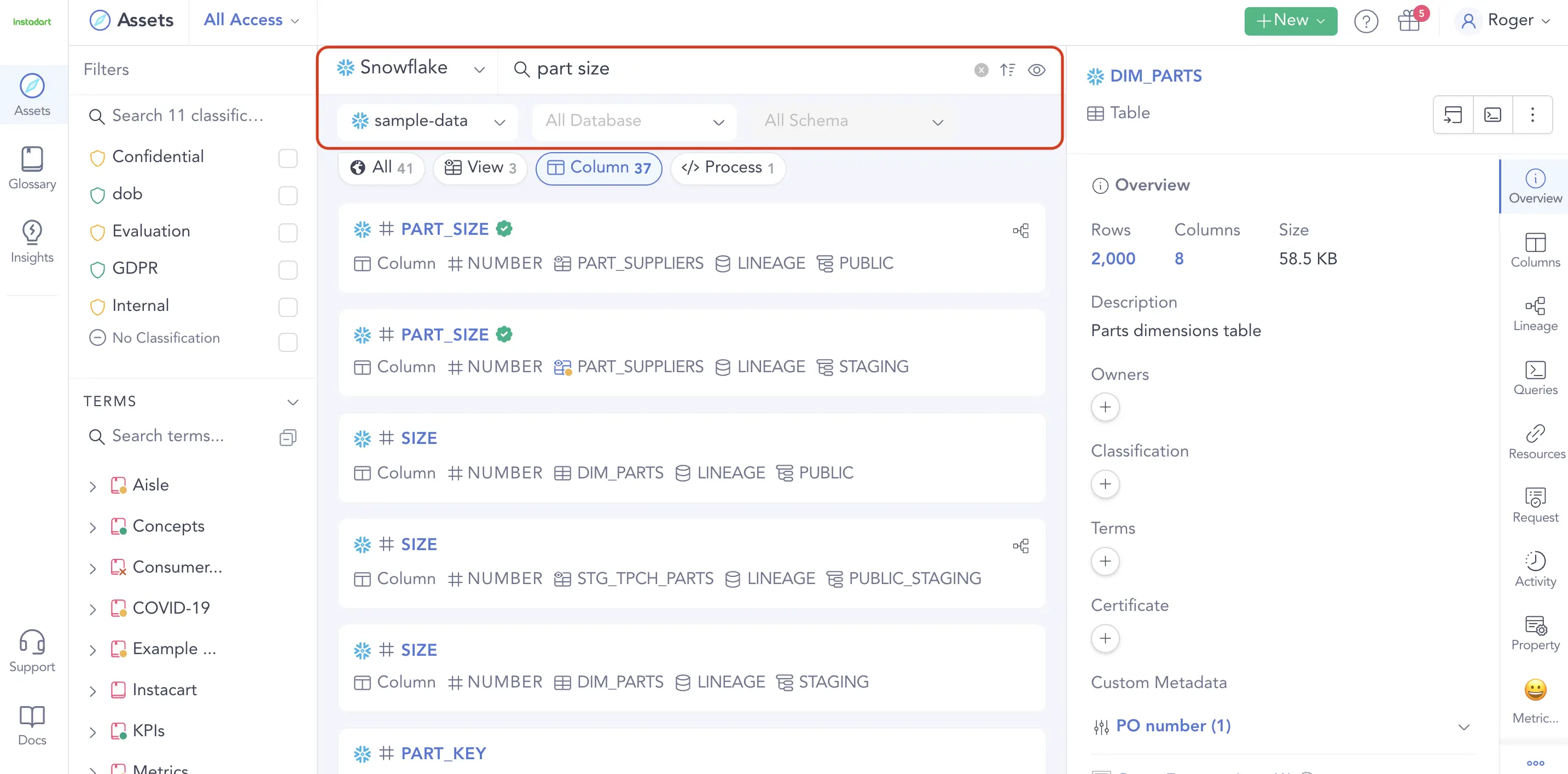
Enterprise metadata management enables data discovery and search across multiple data sources. Source: Atlan
Enterprise metadata management for data lineage and governance
Data lineage uncovers where data comes from and how it has evolved throughout its lifecycle. As such, it is an essential part of effective data governance. If an organization were to adopt an active metadata management solution, data lineage activities could be carried out automatically based on existing metadata such as column descriptions and SQL codes. This would remove the need for users to have to input information over and over again to fill in contextual information in lineage diagrams. Automated data lineage can capture the full context of data (sources, how data sets are built/aggregated, quality factors, transformation details) to ensure reliable data is being used to make business decisions.
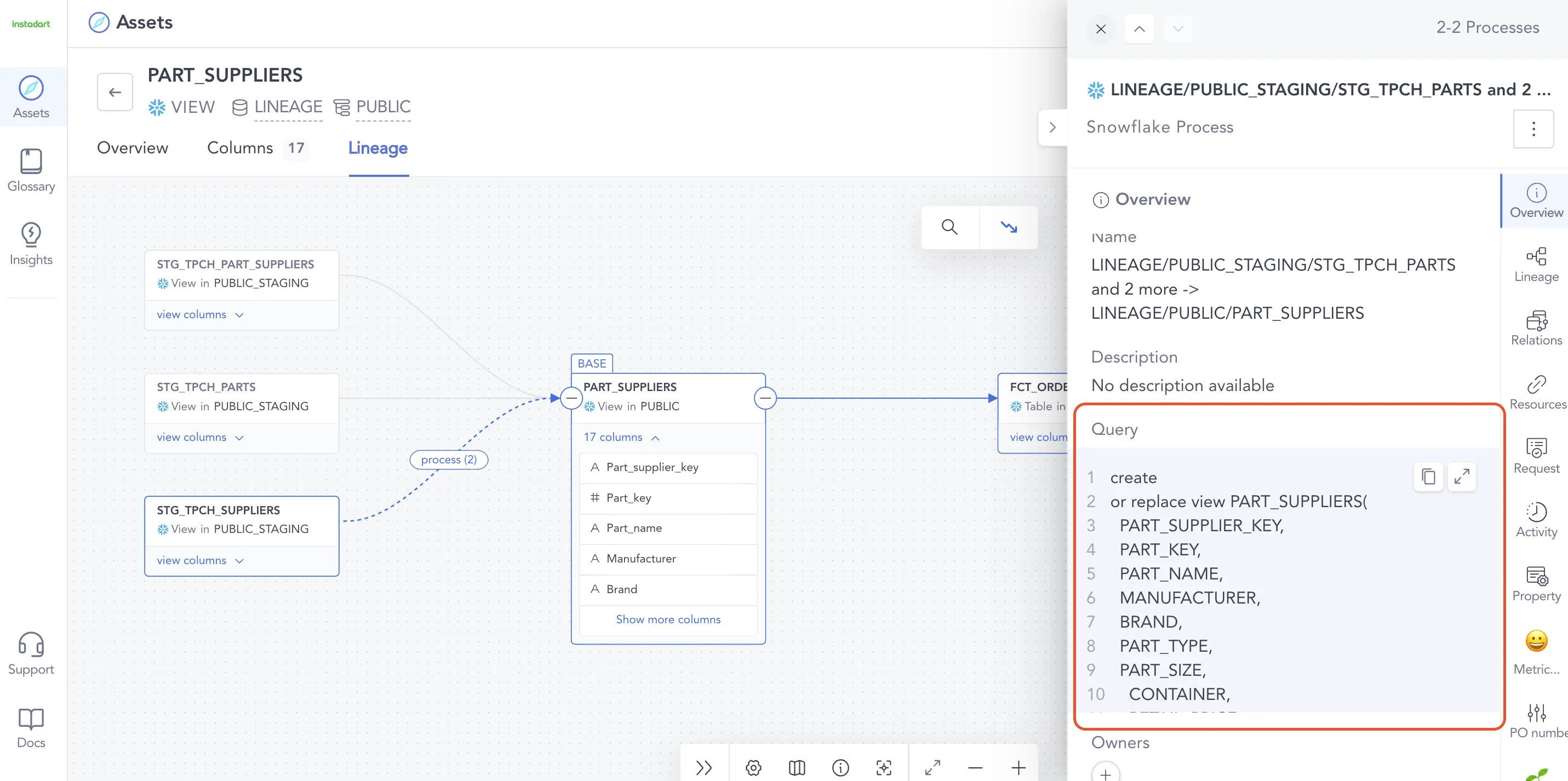
SQL queries are now a valuable enterprise metadata which helps track data trasformations. Source: Atlan
Enterprise metadata management for data democratization
True data democratization is only possible when teams have visibility of all data throughout the business and are able to use that data in their daily workflows. For delivery and e-commerce logistics company Delhivery, they saw their average time to onboard a new team member go from one to two months to a whopping three to four months as the business and its data kept growing.
They didn’t have a clear way to make important business context available and usable for frontline teams until they adopted an active metadata platform, Atlan, to provide the seamless user experience they desired. One of the key components that makes this possible is reverse metadata — orchestration that makes relevant metadata available to the end user inside the tools they are already using.
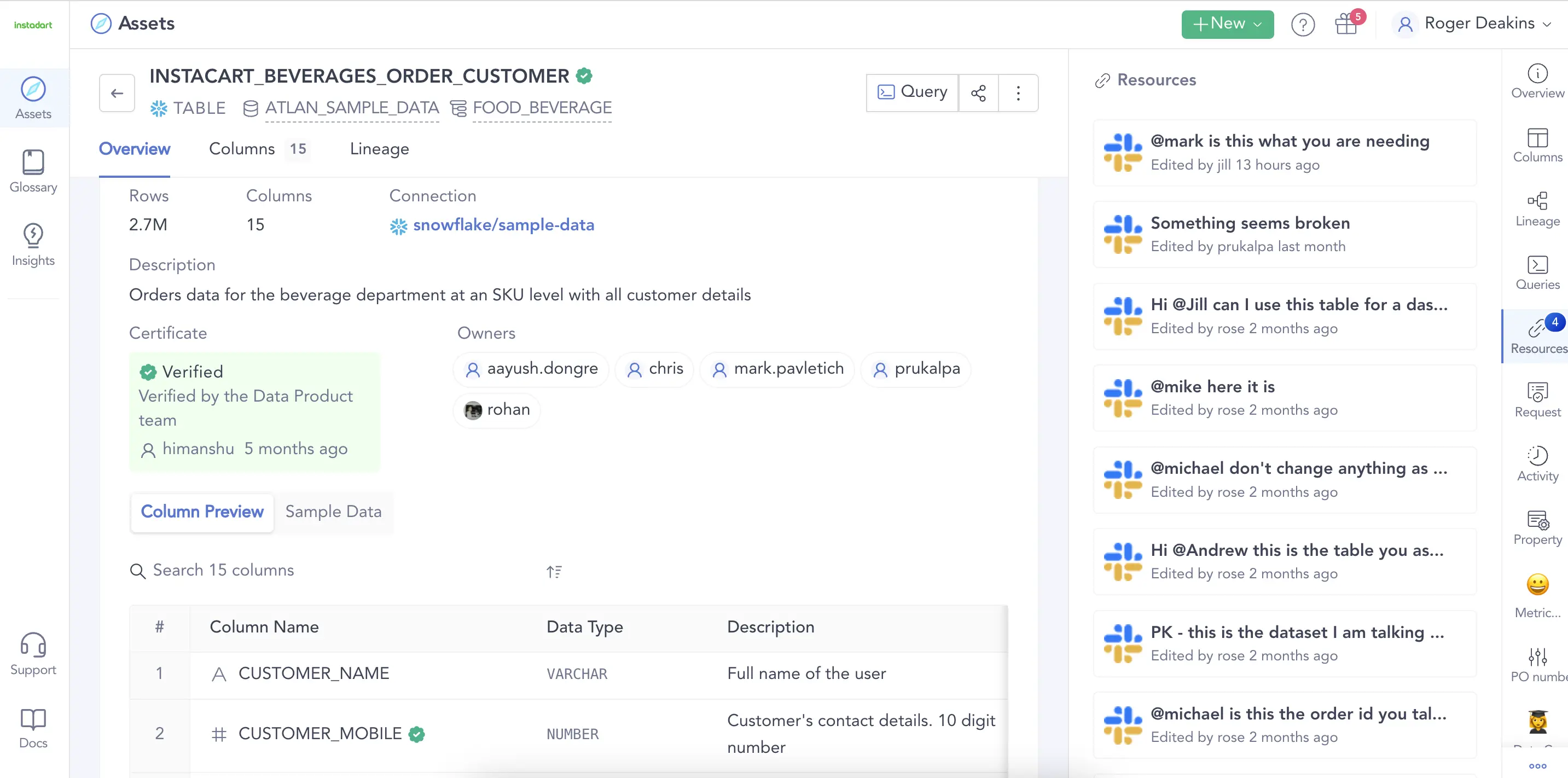
Social metadata like comments, notes, votes, and chat logs helps improve trust in data. Source: Atlan
What is an enterprise metadata management tool?
An enterprise metadata management tool is a technology that makes it easier to extract value from the metadata that is stored by a business. While some EMM tools focus on a single use case, a new generation of metadata management platforms cover a range of crucial functionality including metadata storage, harvesting, and intelligence.
What types of enterprise metadata management tools are there?
Here are a few examples of the different categories of EMM tools:
- Platform-specific tools, such as Oracle Enterprise Metadata Management (meant to integrate with other tools in the brand’s technology suite)
- Industry-specific tools, such Anaplan for business consulting firms
- Open source data catalog software, such as Apache Atlas
- Enterprise data catalogs, such as Atlan, that allow data to be managed in a centralized, collaborative, and user-friendly manner
Active metadata management is the future of EMM
Active metadata is the key to future-proofing the enterprise organization’s data stack: It enables a data ecosystem that is always on, intelligent, and is action-oriented. Instead of only storing and organizing data like a traditional metadata management platform, an active metadata platform automates finding, inventorying, and activating all different types of metadata across multiple capabilities and domains.
The movement toward active metadata management has also been embraced by Gartner. In 2021, the company did away with their Quadrant for Metadata Management Solutions, replacing it with the Market Guide for Active Metadata Management.
Here are the key characteristics to look for in a true active metadata management platform:
- Has a unified repository for storing raw and processed metadata and is capable of continuously collecting new metadata without human intervention.
- Automatically creates business intelligence by connecting the dots between disparate pieces of metadata.
- Allows technical users to customize machine learning or data science algorithms.
- Contains embedded collaboration plugins to seamlessly integrate various data tools.
- Features data process automation for building, deploying, and managing workflow automation bots.
- Utilizes reverse metadata orchestration to make relevant metadata available to the end user, wherever and whenever they need it.
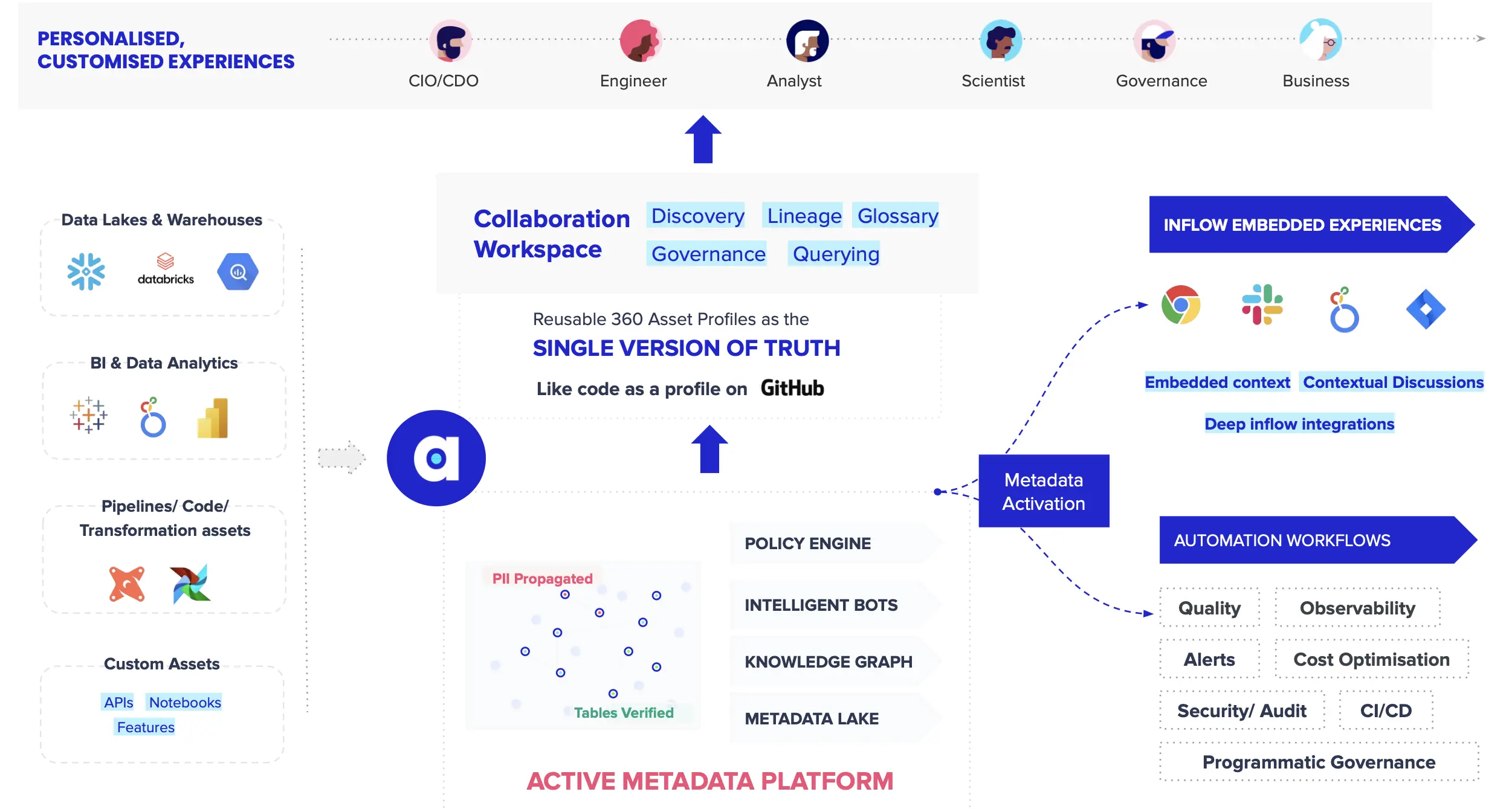
Atlan: An enterprise active metadata management tool for the modern data stack. Source: Atlan
A Demo of Atlan Enterprise Metadata Management Tool
Enterprise metadata management: What's next?
EMM is vital for the enterprises of today to ensure both technical and business users can locate, access, understand, and use data that exists within the enterprise ecosystem. It helps minimize friction and establish strong data teams and a company-wide data culture in which everyone has seamless access to the information they need to do their best work.
If you are evaluating an enterprise metadata solution for you organization, do take Atlan for a spin. Atlan is a third-generation data catalog and metadata management tool built on the premise of embedded collaboration that is key in today’s modern workplace, borrowing principles from GitHub, Figma, Slack, Notion, Superhuman, and other modern tools that are commonplace today.
Enterprise metadata management: Related reads
- What is metadata: Definition, examples, and types
- What is metadata management and why is it so important?
- 6 Metadata Management Best Practices to Follow in 2023
- What is the difference between data catalog and metadata management?
- Data Catalog: Does Your Business Really Need One?
- Enterprise data catalog: Definition, importance & benefits
Share this article












