Data Catalog Lineage: Core Components & Business Benefits
Share this article
Data catalog lineage refers to the documentation and visualization of the lineage of data assets within a data catalog. This helps understand the origins of data assets and their numerous transformations, lending transparency and traceability to your data estate.
This article will explore the concept, benefits, and core components of data catalog lineage.

Looking for a data catalog with an ROI you can present to your CDO? Atlan is designed for adoption and embedded with automation. It helps you save time, cut cloud costs, and make faster, better decisions that lead to revenue.
Table of contents #
- What is data catalog lineage?
- Benefits
- Core components
- Data catalog lineage: Get a rich, end-to-end view of your data estate
- Related reads
What is data catalog lineage? #
Data catalog lineage is a mapping of data assets using a data catalog, which traces the lifecycle of your data assets. It visually documents:
- How data emerges from numerous sources
- How data gets transformed by various workflows
- How data flows through your data estate — from upstream producers to downstream consumers
With data catalog lineage, you can clearly understand how data is generated, manipulated, and consumed within your data ecosystem.
What is data catalog lineage - Image by Atlan.
Also, read → 5 types of data lineage
How does data catalog lineage work? #
A data catalog like Atlan extracts lineage by reaching deep into data assets to track lineage at the granular (table and column) level.
Atlan crawls various data sources using native connectors or APIs. It also parses SQL queries to determine how data stores have created or transformed assets.
With this information, the catalog then constructs lineage by combining assets and processes into a flow of data from various resources:
- Assets represent the inputs and outputs of processes — databases, dashboards, BI tools, etc.
- Processes represent the activities that move or transform data between the assets
As a result, you get lineage for a single pane of glass.
Next, let’s look at the business benefits of data catalog lineage.
What are the benefits of data catalog lineage? #
As data catalog lineage maps your entire data estate, you can reap business benefits, such as:
- Understanding data flows across multiple tools and workflows with lineage for a single pane of glass, establishing transparency and trust in data
- Facilitating root-cause analysis of issues, improving data quality, eliminating rework, speedily resolving pipeline issues and reducing downtime
- Assessing the scope of proposed changes with impact analysis, which helps in preparing upstream and downstream users and streamlining their workflows
- Automating policy propagation via lineage mapping, thereby enabling consistency in data governance policies, definitions, and standards
Also, read → 6 benefits of data lineage
In the upcoming section, we’ll explore the core components of data catalog lineage to visualize the above benefits in action.
Data catalog lineage: 5 core components #
Data catalog lineage should be automated, actionable, intuitive, cross-system, and mapped to a column level. For this purpose, your data catalog should have the following components:
- Automated lineage discovery and mapping
- Cross-system lineage mapping
- Column-level lineage
- In-line actions (i.e., embedded collaboration)
- Intuitive visualization with interactive features
Let’s explore the specifics of each component, along with examples to help visualize the function in a data catalog.
1. Automated lineage discovery and mapping #
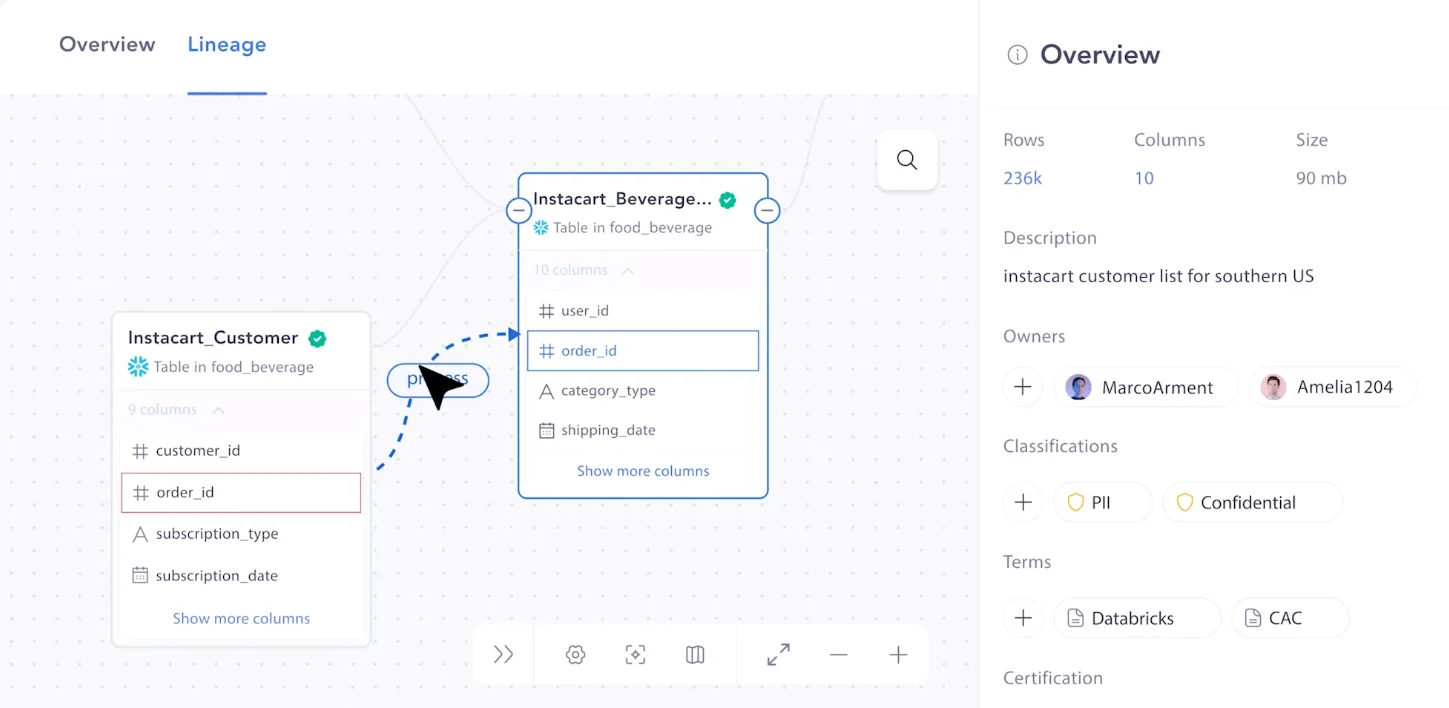
Automated lineage discovery and mapping eliminate manual efforts in recording, tracing, and visualizing data flows and dependencies. The data catalog would automatically scan data sources, metadata, and data transformation processes. This improves efficiency, accuracy, visibility, and scalability in managing data lineage.
More importantly, a data catalog with automated data lineage would offer near-instantaneous visibility into downstream and upstream dependencies, making root cause and impact analysis a breeze.
A lineage mapping in a data catalog like Atlan to perform impact analysis - Image by Atlan.
Aliaxis, a global leader in manufacturing and distributing water management solutions, reduced the effort on root cause and impact analysis by as much as 95% with automated lineage.
Aliaxis would gauge the downstream impact of table or column changes by manually analyzing code and scouring through static Word or Excel documents maintained by data product owners. With automated lineage, Aliaxis facilitates real-time understanding of dependencies and potential breakages before they occur.
Another organization whose impact analysis workflows benefited from automated lineage is Dr. Martens, a global footwear brand. Before choosing Atlan, Dr. Martens would require manual checks of downstream systems for potential impacts.

Also, read → Automated data lineage
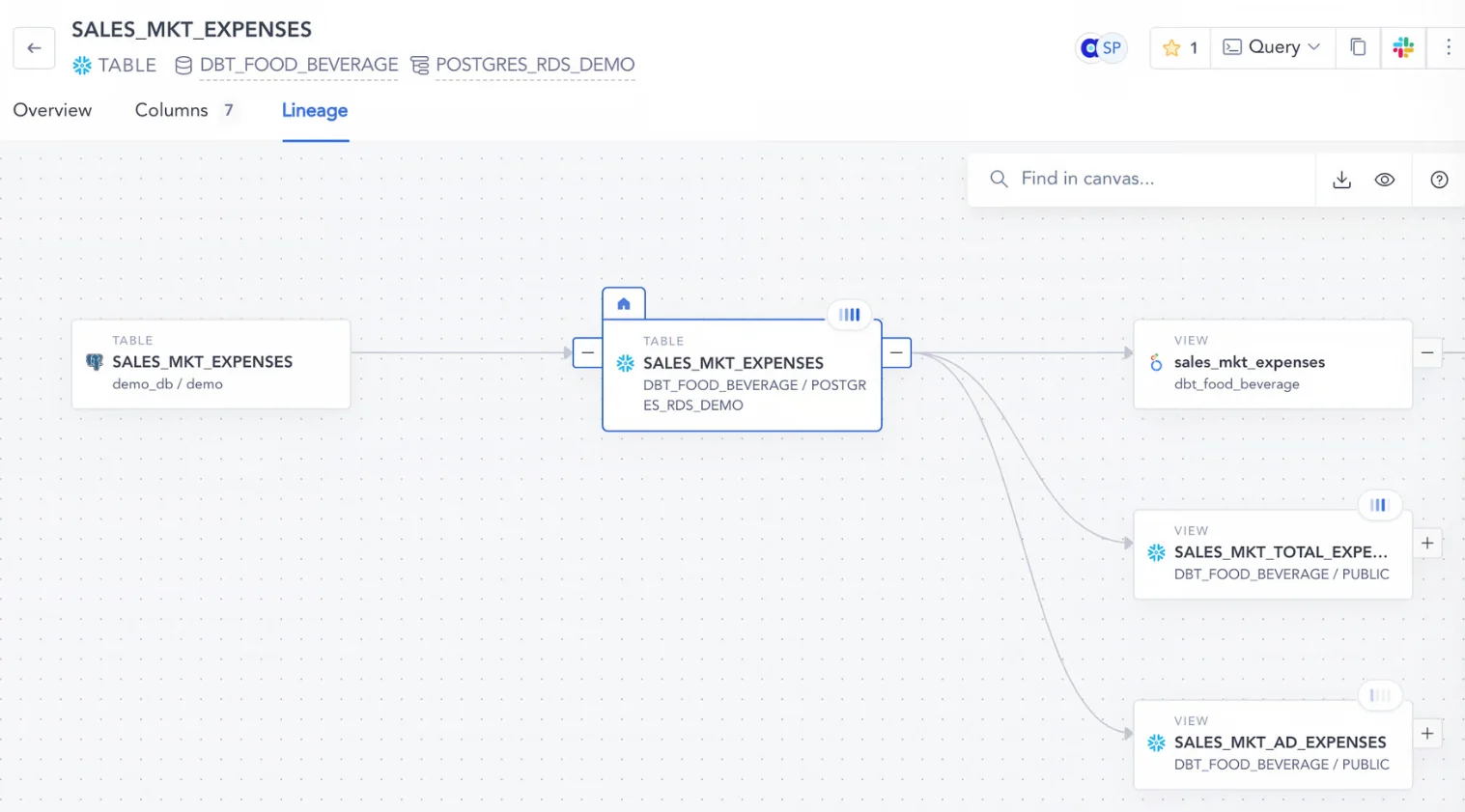
2. Cross-system lineage mapping #
Cross-system lineage mapping involves tracing data lineage across different systems, applications, and platforms — data sources like Redshift, ETL tools like Fivetran, BI tools like Looker, etc.
For instance, you can observe how transactional data, from customer interactions in the CRM system through billing calculations and validations, affects financial reporting in the accounting system.
Cross-system lineage mapping would help link these data flows to specific business processes, such as invoicing or payment processing.
Also, read → Data lineage 101
3. Granularity of lineage mapping down to a column level #
Column-level lineage captures lineage at a granular level, down to individual data columns or attributes.
As a result, you can tell exactly how a field in a table was created and when, in the process of data transformation, it was changed. For instance, you can evaluate the impact of a column-level data type change on a downstream report.
Similarly, you can tag columns with appropriate sensitivity levels and propagate access controls accordingly. For example, if the column Customer Name is tagged as PII, then all the columns created using Customer Name will automatically have PII tagged to it.
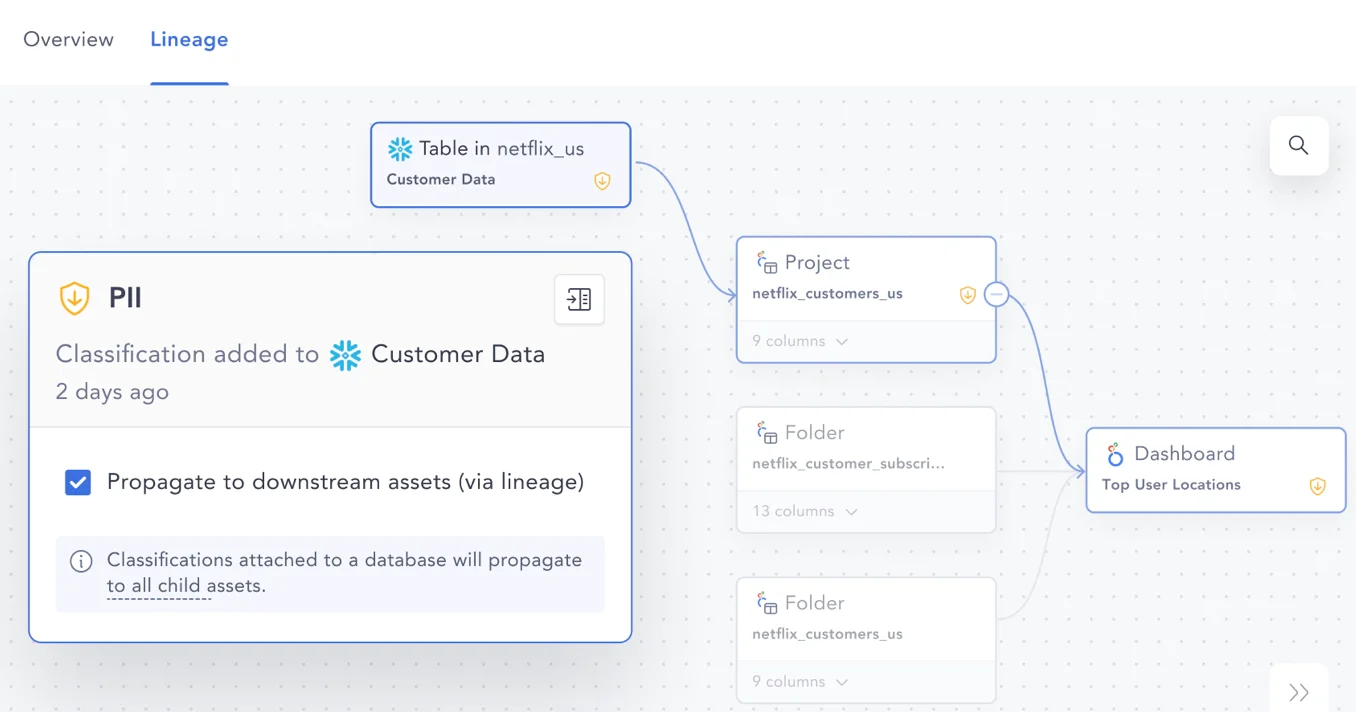
Granularity of lineage mapping down to a column level - Image by Atlan.
Tide, a UK-based digital bank, combined column-level data lineage with automation to identify, tag, and secure personal data within five hours — a task that would have taken at least 50 days.
Also, read → Column-level lineage explained
4. In-line actions #
In-line actions enable embedded collaboration, where you work within the data lineage visualization, without switching apps. You can:
- Start discussions and ask questions (via Slack)
- Report issues like broken dashboards (using Jira)
- Notify downstream consumers of upstream changes (via announcements within the data catalog)
If you’re using an active data catalog with embedded collaboration like Atlan, you can import data assets to Google Sheets using the Atlan Chrome extension. This helps you assess the downstream impact of any changes made to an upstream asset.
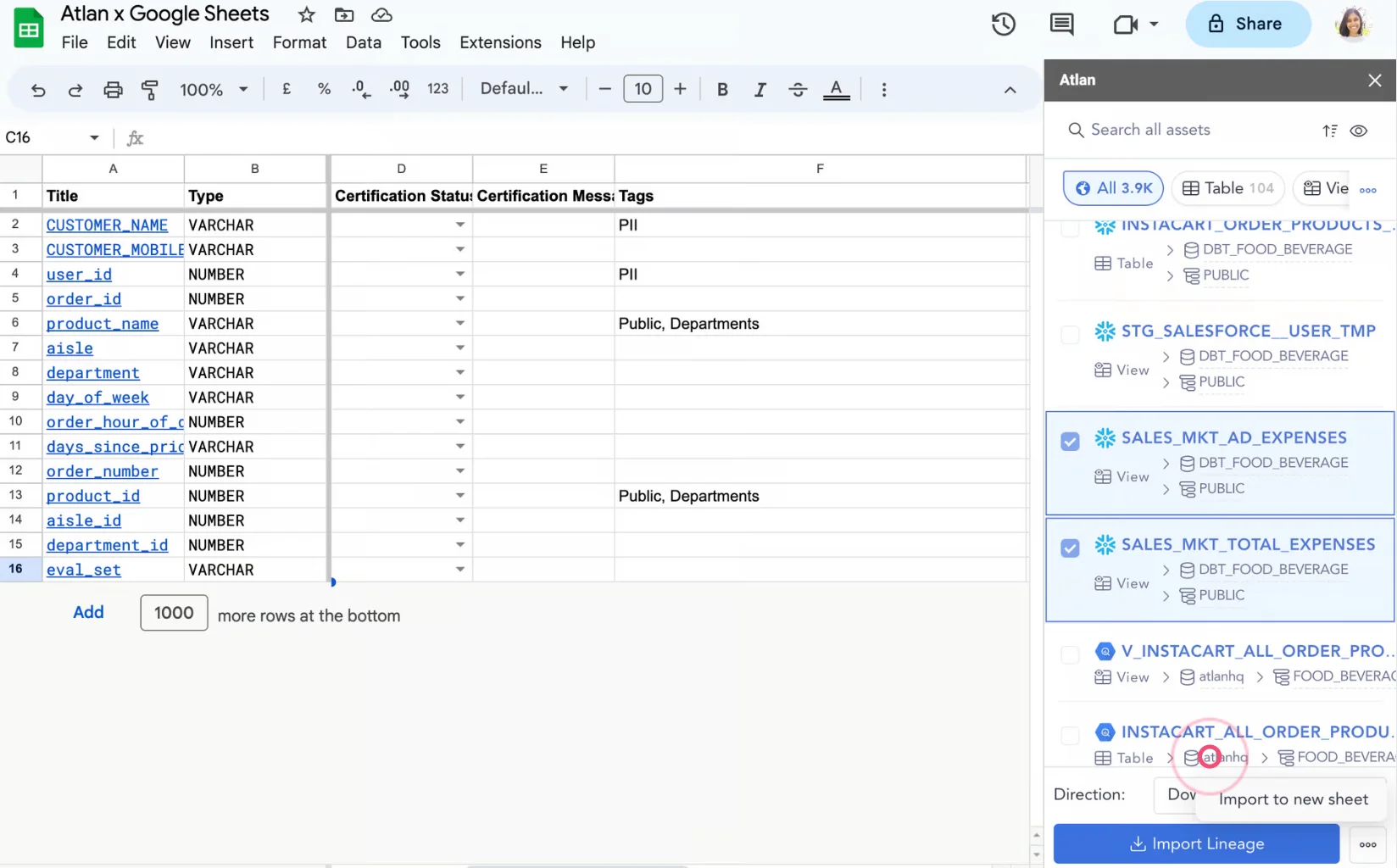
Importing data assets to Google Sheets using Atlan’s Chrome extension - Image by Atlan.
You can then make changes to column metadata — description, owner, tags, certification status — and push them back to the data catalog.
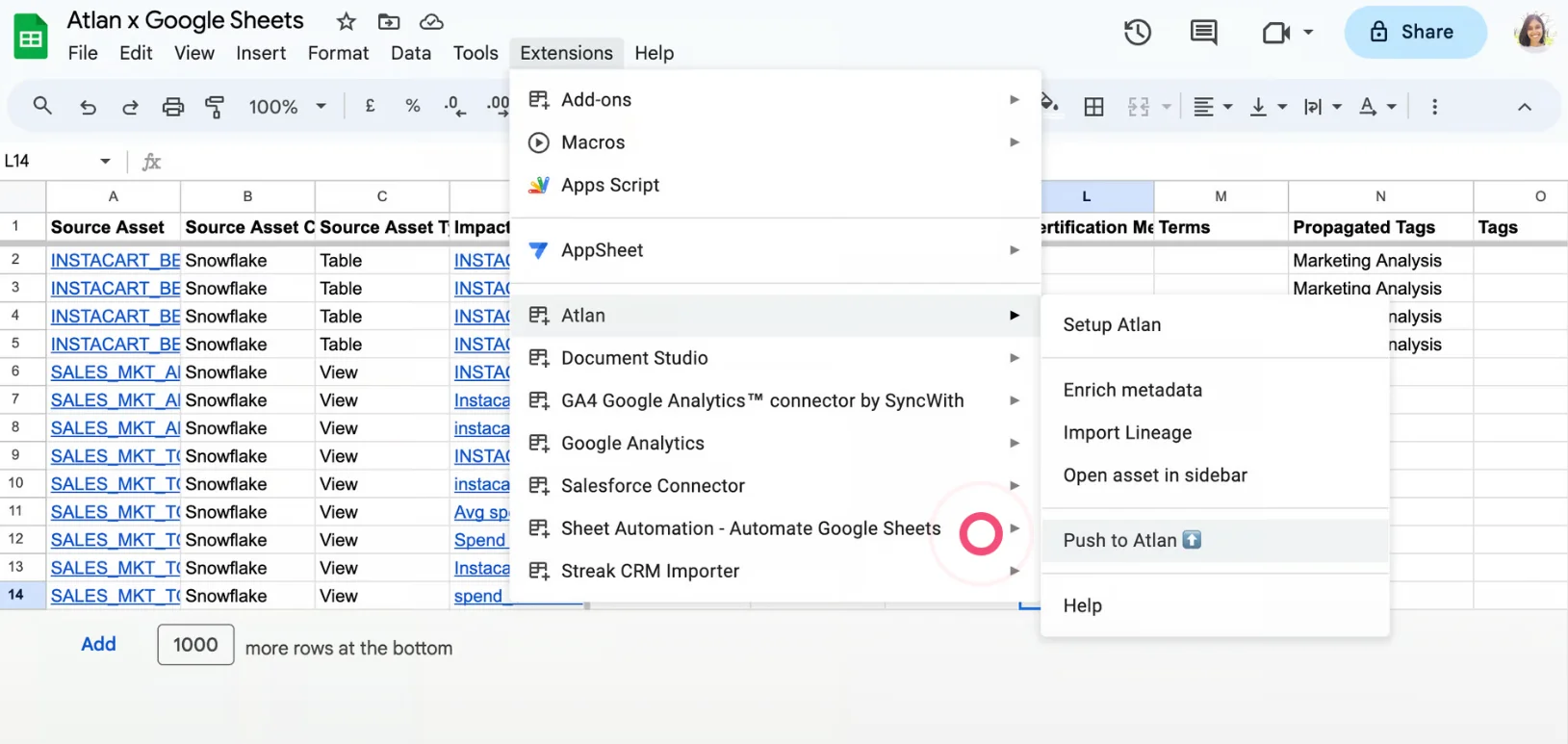
Syncing data assets in a Google sheet with the data catalog - Image by Atlan.
5. Intuitive visualization with interactive features #
[Intuitive and interactive data catalog lineage] enhances user experience by making it easier to grasp relationships, dependencies, and data flows.
For instance, the lineage graph allows you to explore and analyze data assets effectively by using features like zooming, filtering, highlighting, and drill-down capabilities. This helps you focus on specific aspects of the lineage, improving your understanding of data transformations and workflows.
You could expand the lineage upstream for root cause analysis, explore downstream assets to gauge impact, and drill down to see lineage depth, hierarchy, process nodes, etc. This would facilitate analysis and support informed decision-making.
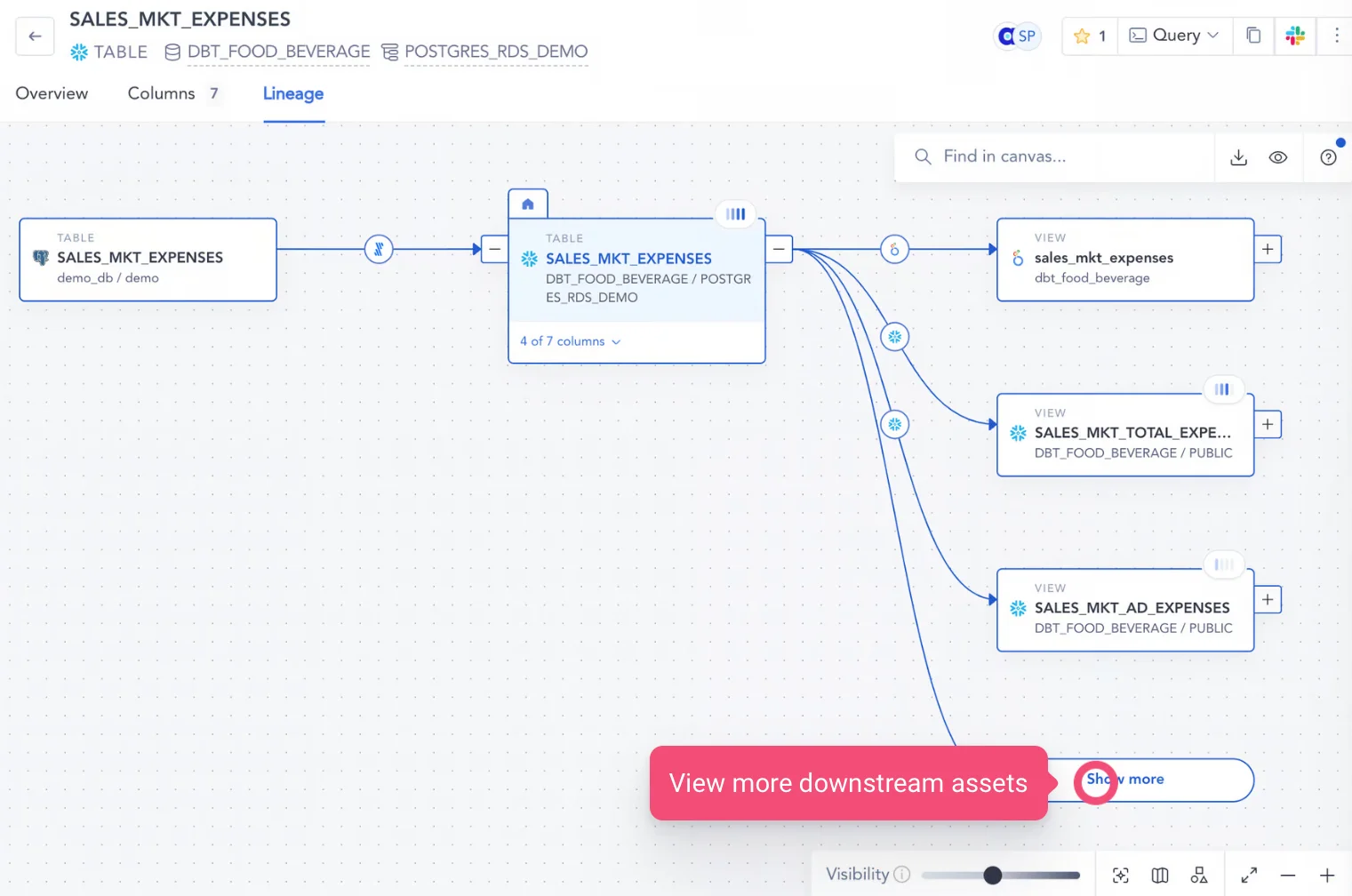
Exploring upstream and downstream assets with interactive controls - Image by Atlan.
You could also personalize your views to see additional metadata, check data flows, and use filters to further customize and enrich the viewing experience.
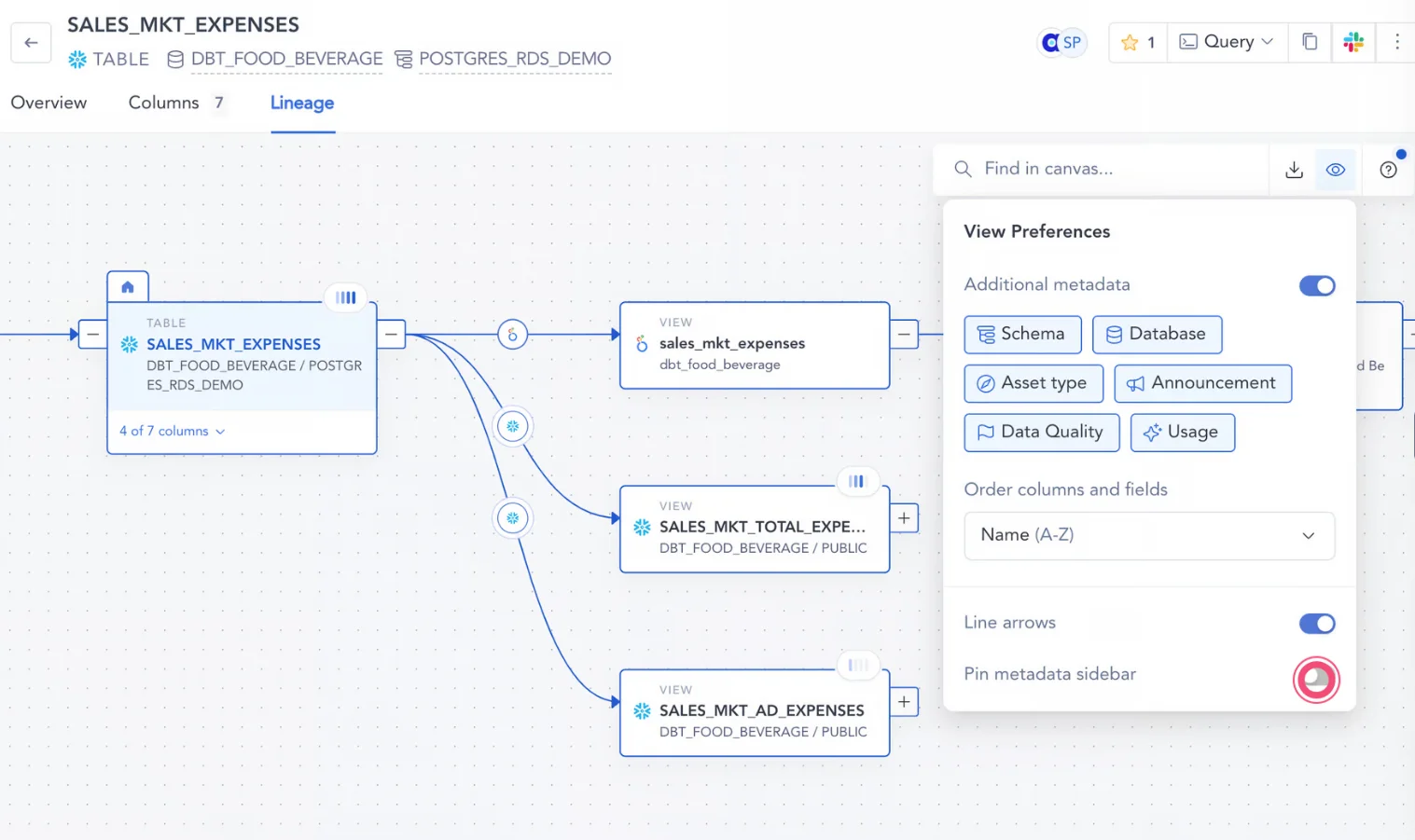
Personalizing the data lineage view with metadata and additional filters - Image by Atlan.
Data catalog lineage: Get a rich, end-to-end view of your data estate #
Data catalog lineage can provide a rich visualization of your data estate, while automating tasks such as policy propagation, upstream and downstream dependency mapping, and more. This helps ensure compliance, data quality, transparency, traceability, and trustworthiness, thereby optimizing your data governance efforts.
So, when you evaluate data catalog lineage tools, consider the components covered in this article and ask for demos that explore these capabilities.
Data catalog lineage: Related reads #
- What is Data Lineage? Tracking the Journey of Your Data
- 6 Benefits of Data Lineage with Insights Into How Businesses Are Leveraging It
- Data Lineage Tools: The Critical Features That Many Tools Lack
- Column-Level Lineage: What It Is and How To Use It
- Automated Data Lineage: Key Benefits, Tools Evaluation Guide
- Data Trust Value Chain 101: From Creation to Analysis
- Unlocking Data Governance with Data Lineage
- 5 Main Benefits of Data Catalogs
- 15 Essential Features of Data Catalogs to Look for in 2024
Share this article











