Share this article
Microsoft Fabric is an end-to-end, cloud-based SaaS platform for data and analytics. It integrates a suite of tools including Data Factory, Synapse Analytics, and Power BI on a unified lakehouse architecture called OneLake.
Unlock Your Data’s Potential With Atlan – Start Product Tour
This platform supports workflows from data integration and engineering to data science and real-time analytics, enabling seamless collaboration and scalability.
By combining data storage, analytics, and visualization tools in one ecosystem, Microsoft Fabric helps organizations streamline their data processes and unlock AI-powered insights, all within a secure, scalable environment built for diverse data needs
Microsoft launched Fabric at the latest Microsoft Build on May 23, 2023, and made it generally available (GA) for purchase at its Ignite conference on November 15, 2023.
In this article, we’ll explore the architecture and components of Microsoft Fabric, followed by a quick guide to getting started with the tool.
We’ll also address the most common questions that data practitioners have been asking about Microsoft Fabric since its launch, from its pricing to its similarities with other analytics tools.
Table of contents #
- What is Microsoft Fabric?
- Microsoft Fabric architecture
- What’s new ever since Fabric’s GA announcement in November 2023?
- Microsoft Fabric in action
- How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
- Frequently asked questions about Microsoft Fabric
- Related reads
What is Microsoft Fabric? #
Microsoft Fabric is a cloud-based SaaS offering that brings together several data and analytics tools that organizations need. These include Data Factory, Data Activator, Synapse Data Warehouse, Synapse Data Engineering, Synapse Data Science, Synapse Real-Time Analytics, and Power BI.
Save Your Seat To See Atlan in Action - Live Demo Series
Fabric is built on an open, lake-centric design with a central, multi-cloud repository called OneLake.
“It’s the biggest launch of a data product from Microsoft since the launch of the SQL Server.” Satya Nadella, CEO and Chairman of Microsoft at Microsoft Build 2023
Microsoft Fabric supports open data formats (Delta-compatible formats, Trino-based platforms) across all its workloads and tiers.
It caters to technical and business data practitioners and has customers like Accenture, T-Mobile, Ferguson, Zeiss, Ernst and Young, and ABN AMRO.
Updates on Microsoft Fabric from Ignite 2023. - Source: YouTube.
The tool aims to set up a modern data architecture that leverages the principles of data mesh, data fabric, and data hub (an open and governed lakehouse platform).
Before proceeding, let’s understand two elements of Fabric — experiences and workspaces.
Experiences in Microsoft Fabric #
Each workload or capability that Microsoft Fabric offers is called an experience.
Experiences include Synapse Data Warehouse, Synapse Data Engineering, Synapse Data Science, Synapse Real-Time Analytics, Data Activator, Data Factory, and Power BI.
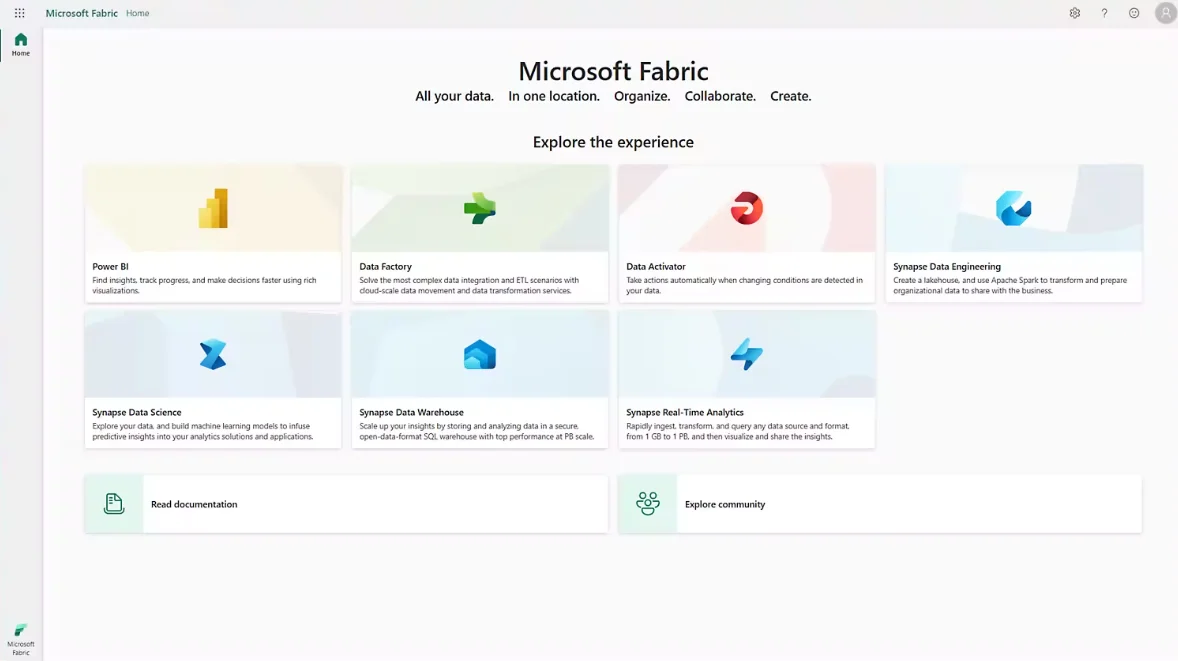
The seven experiences available in Microsoft Fabric as of November 2023. - Source: Microsoft Fabric documentation.
Workspaces in Microsoft Fabric #
Microsoft Fabric lets you set up workspaces depending on your workflows and use cases. A workspace is where you can collaborate with others to create reports, notebooks, lakehouses, etc.
Here’s an image that shows what the workspace of a data engineer would look like in Microsoft Fabric.
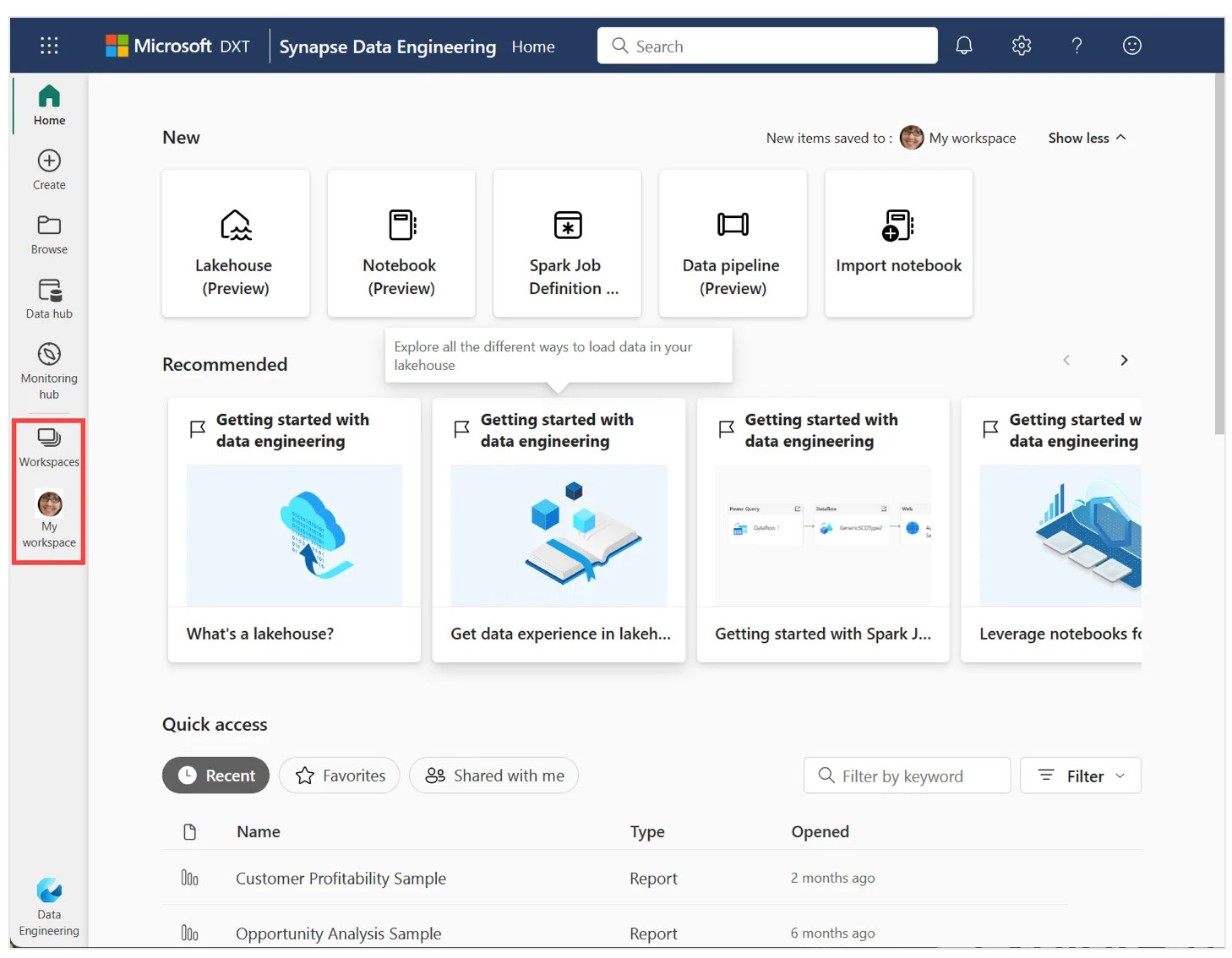
The Microsoft Fabric workspace for the data engineering persona - Source: Microsoft Fabric documentation.
Next, let’s look at the various components that make up Microsoft Fabric.
Microsoft Fabric architecture: The core components of the Microsoft Fabric #
Microsoft Fabric architecture has seven workloads that run on top of OneLake — the storage layer that can pull data from Microsoft’s platforms, Amazon S3, and eventually from Google Cloud Platform.
These workloads include:
- Data Factory: The data integration service
- Microsoft Synapse Analytics offerings: Microsoft Synapse Analytics tools have been integrated into Microsoft Fabric. These are:
- Synapse Data Warehousing: Lake-centric warehousing that scales compute and storage independently
- Synapse Data Engineering: A Spark service for designing, building, and maintaining your data estate to support data analysis
- Synapse Data Science: A service to create and deploy end-to-end data science workflows at scale
- Synapse Real-Time Analytics: Cloud-based analysis of data from apps, websites, and device
- Power BI: Microsoft’s flagship business intelligence service
- Data Activator: A no-code experience for data observability and monitoring
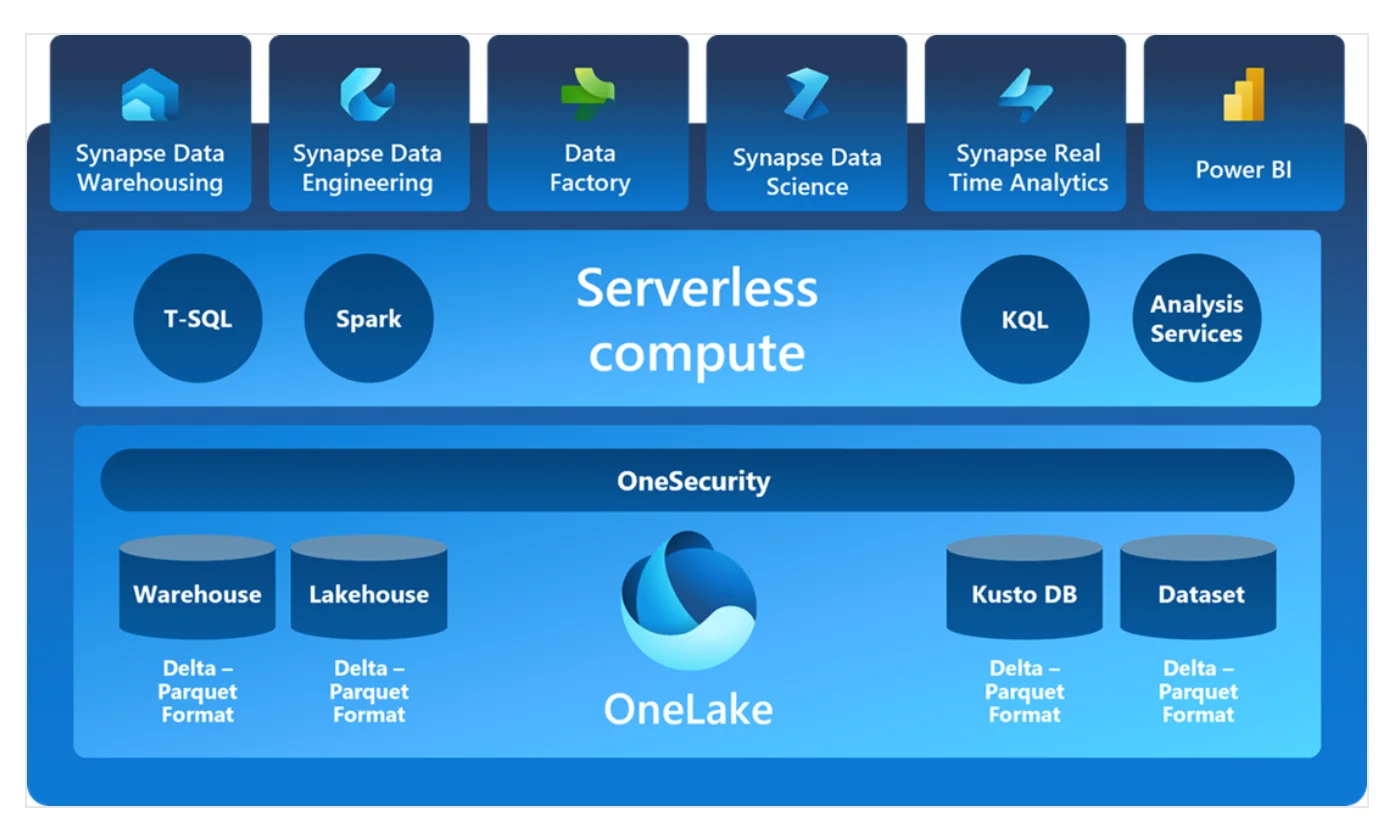
Microsoft Fabric architecture and its components - Source: Microsoft Fabric documentation.
OneLake as the storage layer #
OneLake is the central repository for Microsoft Fabric and is a lakehouse architecture. All data is stored in the delta lake format, abandoning relational storage.
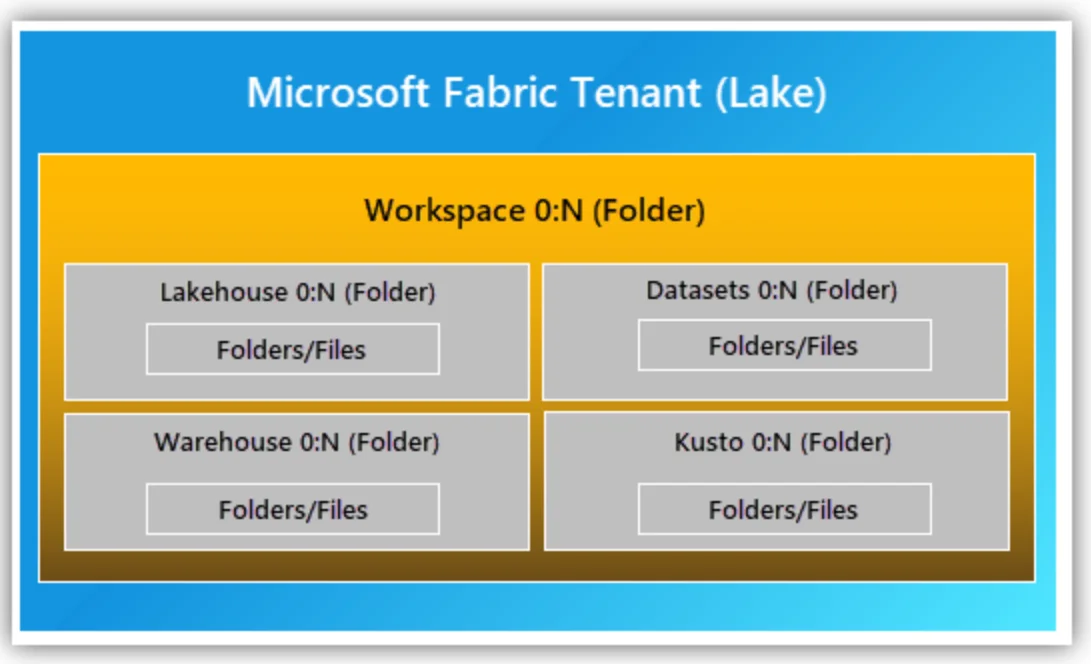
Data storage options in Microsoft Fabric and how they all come together in OneLake - Source: Microsoft Fabric documentation.
Since delta lake is open-source, the Fabric architecture is also open. So, you can integrate any product that can read from a delta lake.
OneLake’s data hub is the central unit for finding, exploring, and using the various data assets within Fabric.
A handy feature of OneLake is that you can create shortcuts that point to other data locations, such as ADLS Gen2 or AWS S3. As a result, you don’t have to make multiple copies of your assets.
Microsoft Fabric’s Dataflow Gen2 conducted on an F2 capacity, has the following observations:
- Data Ingestion: Processing 750 million rows into a data warehouse took approximately 47 minutes and 18 seconds, achieving a throughput of 258,888 records per second.
- Lakehouse Processing: Ingesting 120 million rows into a Lakehouse was completed in 2 minutes and 28 seconds, resulting in a throughput of 810,810 records per second.
Also, read → Databricks Lakehouse Platform built on top of the open-source Delta Lake | Real-World Benefits of Microsoft Fabric | Microsoft Fabric For Healthcare
What’s new ever since Fabric’s GA announcement in November 2023? #
Since the launch during Build 2023, Microsoft has introduced several capabilities, such as:
- Shortcuts: Virtualize data in OneLake without moving or duplicating it; Shortcuts are available for OneLake, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, Amazon S3, and Microsoft Dataverse.
- Mirroring (a data replication capability): Access and manage any database or warehouse from Fabric without switching database clients; Mirroring will be available for Azure Cosmos DB, Azure SQL DB, Snowflake, and Mongo DB.
- Integration with Microsoft Purview: Use Purview’s data security and compliance capabilities to manage sensitive data on Fabric; Use the Microsoft Purview Data Catalog to browse and search through your Fabric assets.
Data security and governance for your Fabric data with Microsoft Purview. - Source: Microsoft Blog
- Data Activator in public preview: Since October 2023, Data Activator is available to all Fabric users, without having to sign up to be a preview user.
- Copilot in Fabric (public preview): Copilot will be available within the Power BI, Data Factory, Data Engineering, and Data Science experiences. You can use Copilot to build reports, summarize insights, build pipelines, and develop ML models. This preview will roll out in stages. According to Arun Ulagaratchagan, Corporate VP, Azure Data-Microsoft, "customers with Fabric capacity (F64 or higher) or Power BI Premium capacity (P1 or higher) will have access to the Copilot preview by the end of March 2024.”
What’s new with Microsoft Fabric as of November 2023. - Source: Microsoft Blog.
Microsoft Fabric and AI #
Microsoft is infusing Fabric with Azure OpenAI Service at every layer so that data practitioners can leverage generative AI to support their daily workflows.
According to Arun Ulagaratchagan, here’s how you can use Copilot within the various Fabric experiences:
- In Power BI, create reports and summarize your insights into narrative summaries.
- In Data Factory, describe how you want to ingest and transform the data using natural language and Copilot handles the rest.
- When working in a notebook in Data Engineering or Data Science, quickly enrich, model, analyze, and explore your data with Copilot.
Satya Nadella delves into the capabilities of Copilot at Ignite 2023. - Source: YouTube.
Microsoft Fabric in action: Data science and real-time analytics #
Microsoft Fabric is being used to solve data warehousing, integration, real-time analytics, data science and machine learning, and other such requirements.
According to Arun Ulagaratchagan, Corporate Vice President, Azure Data–Microsoft “25,000 organizations around the world are already using Fabric today, including 67% of the Fortune 500. 84% of these companies are using three or more workloads.”
To get started, choose the relevant experience when you set up Fabric — Power BI, Data Factory, Microsoft Purview, Synapse Data Engineering, Synapse Data Science, Synapse Data Warehouse, or Synapse Real-Time Analytics.
Depending on the persona you choose, the Fabric workspace will be customized. For example, if you choose Data Engineering, here’s what you’ll see right on top — set up for the Lakehouse, Notebook, or a Spark Job.
A Forrester Consulting study commissioned by Microsoft reported a 379% return on investment over three years for enterprises deploying Fabric. As of November 2024, Microsoft Fabric has been adopted by numerous organizations seeking a unified data platform.
Read more → Microsoft Fabric use cases
How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan #
The recently published Forrester Wave report compared all the major enterprise data catalogs and positioned Atlan as the market leader ahead of all others. The comparison was based on 24 different aspects of cataloging, broadly across the following three criteria:
- Automatic cataloging of the entire technology, data, and AI ecosystem
- Enabling the data ecosystem AI and automation first
- Prioritizing data democratization and self-service
These criteria made Atlan the ideal choice for a major audio content platform, where the data ecosystem was centered around Snowflake. The platform sought a “one-stop shop for governance and discovery,” and Atlan played a crucial role in ensuring their data was “understandable, reliable, high-quality, and discoverable.”
For another organization, Aliaxis, which also uses Snowflake as their core data platform, Atlan served as “a bridge” between various tools and technologies across the data ecosystem. With its organization-wide business glossary, Atlan became the go-to platform for finding, accessing, and using data. It also significantly reduced the time spent by data engineers and analysts on pipeline debugging and troubleshooting.
A key goal of Atlan is to help organizations maximize the use of their data for AI use cases. As generative AI capabilities have advanced in recent years, organizations can now do more with both structured and unstructured data—provided it is discoverable and trustworthy, or in other words, AI-ready.
Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes #
- Tide, a UK-based digital bank with nearly 500,000 small business customers, sought to improve their compliance with GDPR’s Right to Erasure, commonly known as the “Right to be forgotten”.
- After adopting Atlan as their metadata platform, Tide’s data and legal teams collaborated to define personally identifiable information in order to propagate those definitions and tags across their data estate.
- Tide used Atlan Playbooks (rule-based bulk automations) to automatically identify, tag, and secure personal data, turning a 50-day manual process into mere hours of work.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization in establishing and scaling data governance programs.
Frequently asked questions about Microsoft Fabric #
Let’s look at some of the most common questions people have about Microsoft Fabric.
1. Is Microsoft Fabric a PaaS or a SaaS? What’s the difference? #
Microsoft Fabric is a Software as a Service (SaaS). It combines existing PaaS services that Microsoft offers (i.e., Synapse, Data Factory, Power BI, etc.) to offer an integrated, end-to-end environment for all types of data users.
2. How is Microsoft Fabric different from Azure Synapse Analytics? #
Microsoft Fabric is seen as a successor to Azure Synapse Analytics.
Unlike Synapse, which is a PaaS, Fabric is a SaaS. This primarily affects the Fabric architecture and pricing.
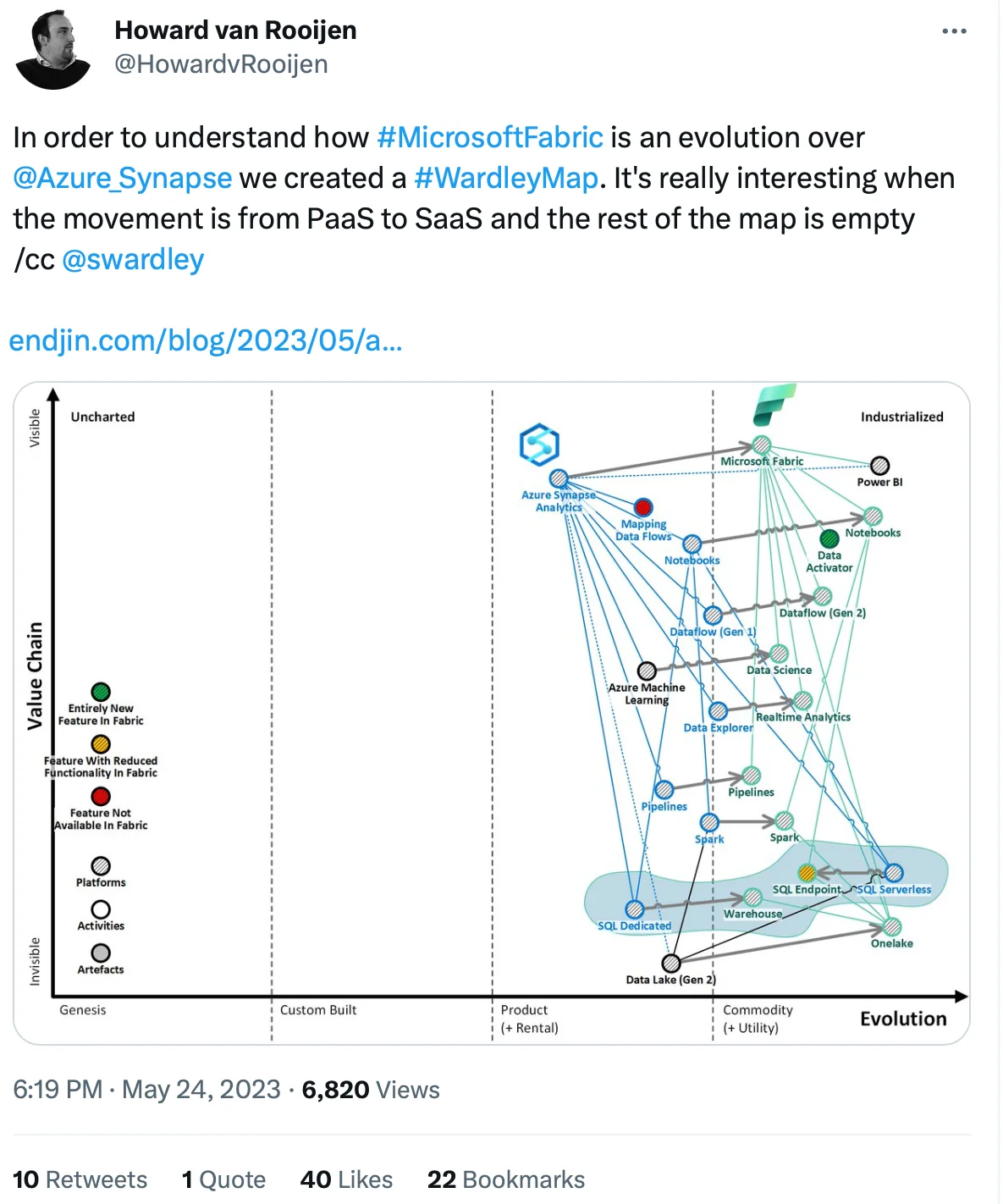
How is Microsoft Fabric an evolution over Azure Synapse - Source: Twitter.
There is a lot of overlap between both solutions, in terms of warehousing, data engineering, data science, and real-time analytics capabilities.
This can lead to users trying to understand the differences in functionalities.
However, it’s important to note that while Synapse focused on warehousing, Fabric aims to be a single platform for all data users and their daily workflows.
Read more → Microsoft Fabric vs. Azure Synapse Analytics
So, in addition to almost everything Synapse offers, Fabric streamlines the user experience further with single storage for all data types (with a lakehouse) and Power BI for its user interface.
3. Can I integrate my existing workloads from Synapse to Microsoft Fabric? #
According to Bogdan Crivat, Partner Director of Engineering at Microsoft, the company is "investing significant development efforts in migration processes and tooling. And our migration efforts are prioritizing current PaaS Synapse Analytics customers.”
Microsoft is working on developing tools to help you migrate code, reuse notebooks and pipelines, etc. However, there’s no automatic upgrade path for your existing Synapse workloads. You’ll have to manually migrate them by adjusting the notebooks, SQL scripts, pipelines, etc.
It’s also important to note that Microsoft Fabric doesn’t support several T-SQL commands. This can affect some of the warehouse-related migrations. Here’s a complete list of commands that Fabric doesn’t support yet.
4. Will Microsoft discontinue Azure Synapse Analytics? #
As of November 2023, Microsoft has no plans to retire Azure Synapse Analytics.
5. How is Microsoft Fabric different from Databricks and Snowflake? #
Databricks is offering a unified data analytics platform that combines the best aspects of a data warehouse and a data lake. The platform components include Delta Lake (storage), Runtime (processing), Workspace (the collaboration layer), Machine Learning, and SQL Analytics (BI).
Snowflake is a cloud-native data warehouse that supports different types of workloads via its Data Cloud.
Microsoft Fabric aims to bring everything for the various data practitioners under one roof — data integration, data engineering, data warehousing, real-time processing, analytics, and BI.
For instance, its OneLake is like your “OneDrive for data”. And the UI is built using Power BI, rather than Synapse Studio, to focus on delivering better user experiences.
6. Can Microsoft Fabric be used on-premise? #
As of now, Microsoft Fabric is a SaaS cloud-based offering.
7. How much does Microsoft Fabric cost? Is it free? #
Microsoft Fabric’s pay-as-you-go pricing starts at $0.36/hour for 2 Capacity Units (CU). You can also reserve capacity, starting at $0.215/hour for 2 CUs.
Meanwhile, the pricing for OneLake storage starts at $0.023 per GB per month. The Networking billing details aren’t out yet.
8. What is a Capacity Unit (CU)? #
A capacity is the ability of a resource to either perform an activity or to produce output. Capacity Units (CUs) will define this ability, representing a set of resources that you can use at any given time.
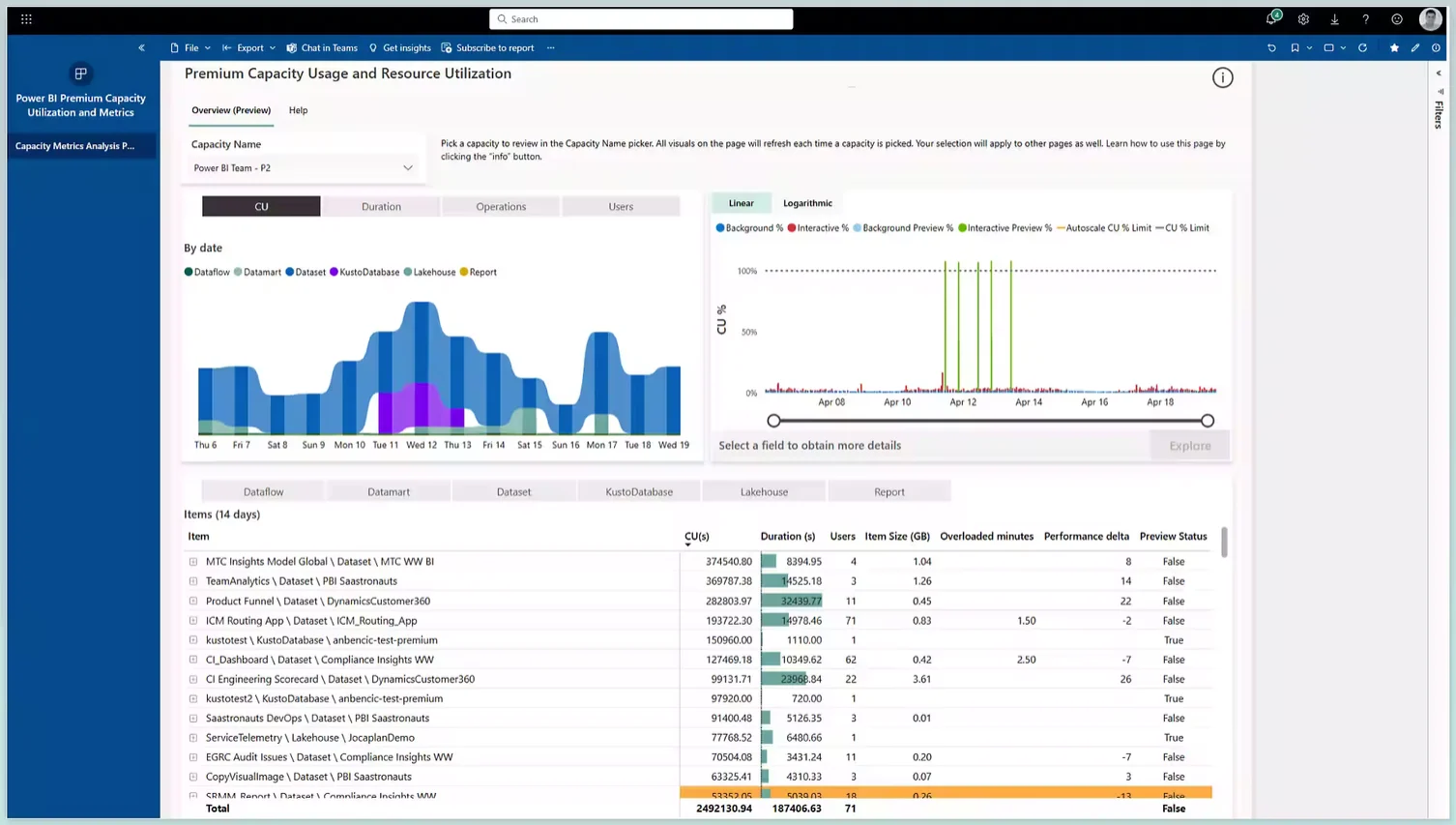
How pricing with work in terms of Capacity Units (CU) - Source: Microsoft.
Microsoft Fabric: Related reads #
- Microsoft Fabric: A Comprehensive Overview of Microsoft’s New Data Platform
- Microsoft Fabric Copilot: Capabilities, Benefits, Applications
- 7 Microsoft Fabric Use Cases in Data and Analytics
- Data Fabric Architecture: Components, Tooling, and Deployment
- Data Fabric: Can it Future-Proof Your Architecture, Unify Your Data, and Save Costs?
- Implementing a Data Fabric: A Scalable and Secure Solution for Maximizing the Value of Your Data
- Data Mesh vs. Data Fabric: How do you choose the best approach for your business needs?
- Data Fabric Use Cases: Understanding its Suitability & Applicability for Your Business
Share this article













