Data catalogs and data lineage tools play unique yet complementary roles in data management.
A data catalog is a tool that organizes and centralizes metadata, helping users discover, access, and manage data efficiently.
Data lineage, on the other hand, tracks the origins, transformations, and destinations of data to ensure traceability and transparency.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Cataloging – Start Product Tour
While the catalog answers “what” data is available, lineage explains “where” the data comes from and “how” it evolves.
Together, they create a comprehensive framework for data governance, compliance, and enhanced decision-making, ensuring organizations can manage their data assets effectively.
According to IDG & Matillion, most businesses handle data from between 400 and 1,000 separate sources. Both data catalog and data lineage technology are indispensable for managing this complexity. Here’s how the two work synergistically together to empower employees to discover, access, and utilize the right data.
What is a data catalog?
Permalink to “What is a data catalog?”A data catalog is a workspace where users can discover and annotate data. Data catalogs contain rich metadata about an asset’s origins, purpose, and business context. They also provide fine-grained permission controls and a collaborative environment that supports editing across the company.
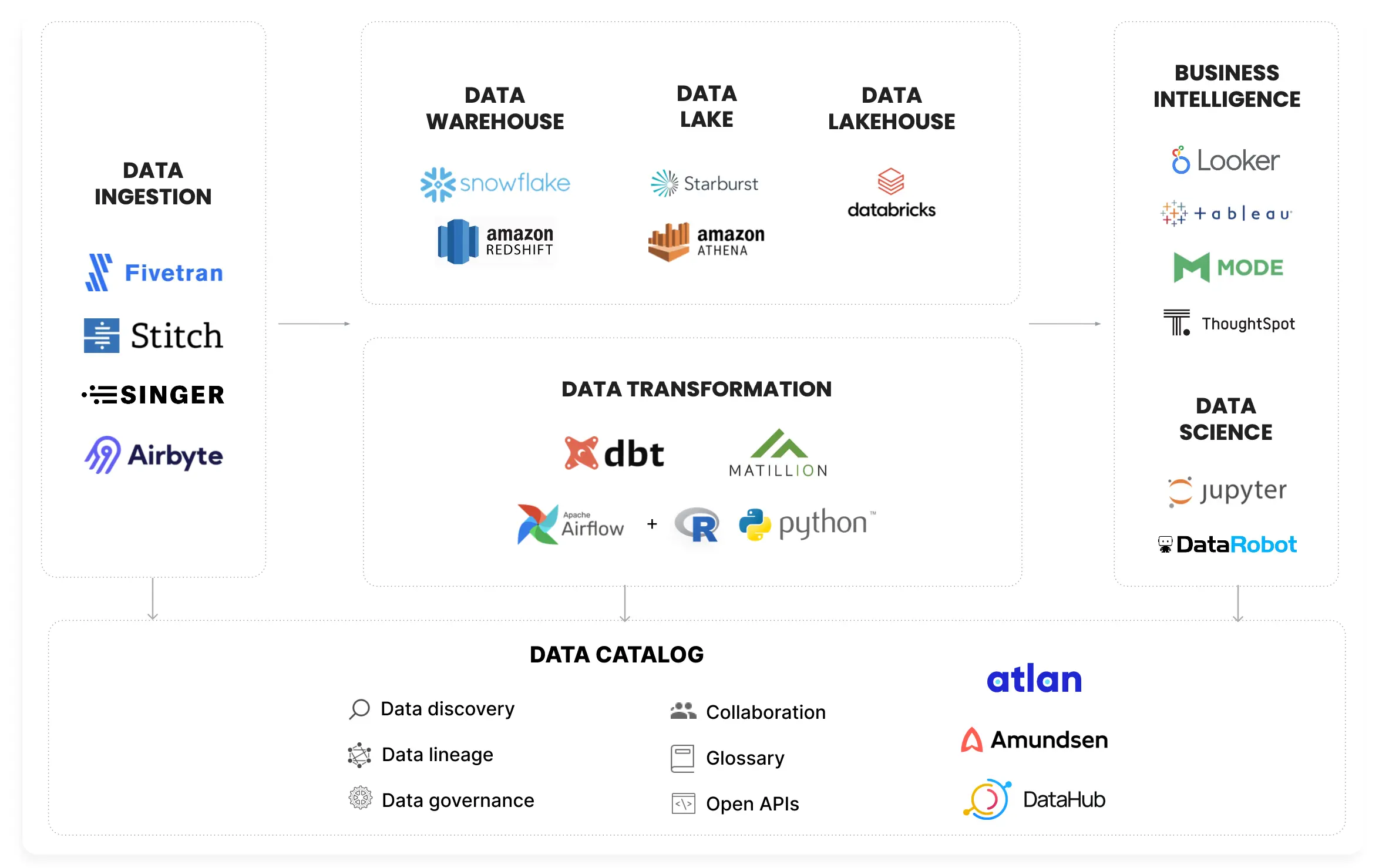
Data catalog integrating with diverse data sources and data tools. Image by Atlan.
The modern “third-generation” data catalog enables everyone from product managers to data scientists to track and collaboratively maintain an organization’s diverse data assets at scale. Data lineage tools then use techniques such as SQL parsing, API crawling, and custom API ingestion to track and visualize the history of these assets as they flow through the company.
Companies can select from a wide variety of open-source and commercial data catalog solutions to implement a solution that meets their needs.
What is data lineage?
Permalink to “What is data lineage?”Data lineage tracks the lifecycle of your data. A good data lineage implementation tells you the origin of your data and how it’s changed over time. It tracks table-level lineage and column-level lineage, showing how your organization’s data structures change over time.
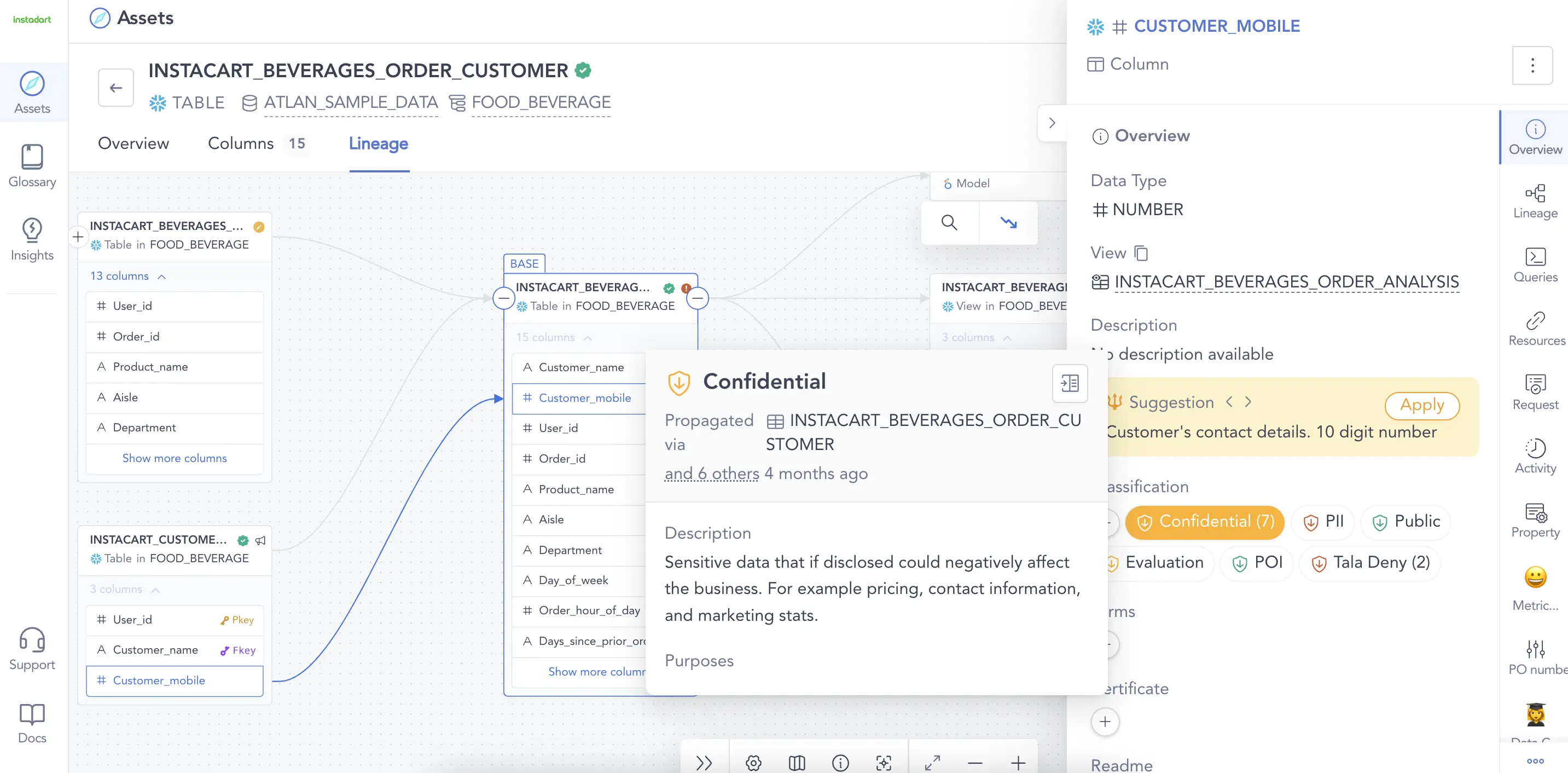
Automated data lineage: Understand how data flows from the source to the dashboards. Image by Atlan.
Data catalogs and data lineage together solve the problem of metadata management. A data catalog centralizes critical business information in a single source of truth. Lineage provides confidence that data is current and enables tracing the impact of any changes across the company.
Data catalog vs. data lineage: enabling efficient use of data
Permalink to “Data catalog vs. data lineage: enabling efficient use of data”Every company produces tons of data. And every company needs a way to account for it. The difference between a data catalog vs. data lineage lies in how both contribute to solving this problem at scale.
As per Data Catalog Statistics 2024 by Scoop, The global data catalog market has experienced significant growth, with revenues increasing from USD 718.1 million in 2022 to an anticipated USD 5,235.2 million by 2032, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22.6%.
The data catalog provides the foundation for describing and securing access to data. Enterprise data catalogs are used by a diverse range of business users - data scientists, engineers, product managers, and executives - to discover data and generate insights essential to running the business.
Modern data problems require modern solutions - Try Atlan, the data catalog of choice for forward-looking data teams! 👉 Book your demo today
Once that’s in place, a company can track where that data came from and - just as importantly - who’s using it, both upstream and downstream. A good data lineage tool will record your data’s journey across the company over time. It enables users to identify the root causes of problems, assess the impact of changes, and implement end-to-end data governance.
Both of these pieces - data catalog and data lineage - are essential for meeting many business compliance requirements. Take the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Under GDPR, you need to know what data is Personally Identifiable Information (PII) that belongs to a customer. You also need to know all the locations where data lives - databases, support tickets, report caches, cold storage, etc. - so you can purge it upon request.
A data catalog answers the first question. Data lineage answers the second.
Data catalog use cases
Permalink to “Data catalog use cases”To clarify this, let’s look at the different ways you would use both a data catalog and data lineage.
The common uses for a data catalog include:
- Context plane for data
- Data discovery
- Metadata management
- Data governance
Context plane for data
Permalink to “Context plane for data”Without a data catalog, it can be hard - if not impossible - to know what data you have. This complicates every data-related task in your company from delivering data-driven apps to ensuring regulatory compliance.
Data that sits dormant or undiscovered is called “dark data.” Veritas estimates that over half of a company’s data is dark. It sits unused or underutilized, its value untapped.
A data catalog eliminates the dark data problem by accounting for all data sources in a central repository. This basic capability enables all other data catalog use cases, such as discovery and metadata management.
Data discovery
Permalink to “Data discovery”Data discovery becomes much easier once all data sources are unified in a data catalog. Users can create natural language queries using a data catalog’s search interface to find the data they need within minutes instead of days.
Metadata management
Permalink to “Metadata management”Data catalogs don’t just track data, but also metadata - i.e., data about data. Metadata includes everything from ownership and description information to data classifications used in regulatory compliance. Rich metadata increases data’s value and quality by certifying its timeliness, accuracy, and business purpose.
Data catalogs enable crowdsourcing metadata management across the company. With all data tracked in one single source of truth, more employees can not only discover data but also help enrich it.
Data governance
Permalink to “Data governance”Regulations such as GDPR require securing customer’s Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and deleting it when you no longer have a business use requiring retention. With a data catalog, you can classify data, measure how much data is appropriately tagged, and issue alerts when you detect potential anomalies (e.g., an untagged field holding what appears to be a credit card number).
Data lineage use cases
Permalink to “Data lineage use cases”Now let’s look at the most common use cases for data lineage:
- Root cause analysis
- Impact analysis
- Automating data maintenance tasks
Root cause analysis
Permalink to “Root cause analysis”What happens if a data transformation process changes the format of a field in a database? Or a data engineer deletes a column that she thought “no one was using”?
In most companies, this results in reports and data pipelines that are downstream consumers of the data source breaking. As a result, multiple people spend hours figuring out what went wrong and deploying fixes.
Data lineage enables tracking such problems down to their root cause. Because you can see how data flows from data sources to data consumers, you can easily pinpoint which process made the change and fix it at its source.
Impact analysis
Permalink to “Impact analysis”Root cause analysis is good. But preventing breaking changes in the first place is even better. With data lineage, data engineers can see exactly which tables and columns are being used by downstream consumers. The data team can then work with these stakeholders closely whenever it needs to deploy a breaking change.
Automating data maintenance tasks
Permalink to “Automating data maintenance tasks”Companies can leverage data lineage to automate tasks that would otherwise take days, weeks, or months to complete. For example, they can utilize the auditing trails created by data lineage to help certify that they handle data according to regulatory requirements and their own data governance standards.
How data catalogs and data lineage work together
Permalink to “How data catalogs and data lineage work together”This case of Postman, makers of the popular API development and testing tool, shows how a data catalog and data lineage evolve together in practice.
The company originally struggled with duplicated metrics and daily Slack user inquiries about data provenance. Data duplication and user confusion sowed distrust in the company’s data.
As Postman’s Prudhvi Vasa puts it, “building trust is hard, but losing it is easy—it just takes one mistake.”
To solve this, it first tried cataloging data in a Confluence document, and then Google Sheets. It quickly outgrew both solutions. They eventually moved to Atlan as their dedicated data cataloging solution.
Once the company had its data in a data catalog, it built its lineage system over it. This involved gathering information on their data’s origins (a process you can perform manually but that’s accomplished much more efficiently via automation.
Postman could finally ask - and answer - questions about their data’s origins and its interconnections. Users could now discover data easily. They could also see how a proposed change to a data asset would affect other assets and users across the company.
Netflix faced and solved a similar set of challenges. In their case, they worked backward from the goal of developing a comprehensive data lineage network. That first entailed creating a flexible data catalog representing the company’s diverse assets. They then developed a separate data lineage model that users can navigate via a graph database.
Future of data catalogs and data lineage
Permalink to “Future of data catalogs and data lineage”Creating a data catalog is only the first step. No one will use a data catalog unless it’s usable. And that means moving away from the notion of a data catalog as a standalone entity.
Data catalogs will continue to evolve to bring metadata to users where they work - e.g., in Slack or their favorite BI tool. Data catalogs will become repositories of active metadata that cut across all of a company’s data infrastructure and business productivity tools.
Similarly, data lineage networks are indispensable - but only if users can easily visualize the journey their data takes. A simple flow visualization is a good start. But in the future, we’ll see more data lineage systems take Netflix’s lead, representing lineage flows as searchable, navigable graphs.
How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
Permalink to “How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan”The recently published Forrester Wave report compared all the major enterprise data catalogs and positioned Atlan as the market leader ahead of all others. The comparison was based on 24 different aspects of cataloging, broadly across the following three criteria:
- Automatic cataloging of the entire technology, data, and AI ecosystem
- Enabling the data ecosystem AI and automation first
- Prioritizing data democratization and self-service
These criteria made Atlan the ideal choice for a major audio content platform, where the data ecosystem was centered around Snowflake. The platform sought a “one-stop shop for governance and discovery,” and Atlan played a crucial role in ensuring their data was “understandable, reliable, high-quality, and discoverable.”
For another organization, Aliaxis, which also uses Snowflake as their core data platform, Atlan served as “a bridge” between various tools and technologies across the data ecosystem. With its organization-wide business glossary, Atlan became the go-to platform for finding, accessing, and using data. It also significantly reduced the time spent by data engineers and analysts on pipeline debugging and troubleshooting.
A key goal of Atlan is to help organizations maximize the use of their data for AI use cases. As generative AI capabilities have advanced in recent years, organizations can now do more with both structured and unstructured data—provided it is discoverable and trustworthy, or in other words, AI-ready.
Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes
Permalink to “Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes”- Tide, a UK-based digital bank with nearly 500,000 small business customers, sought to improve their compliance with GDPR’s Right to Erasure, commonly known as the “Right to be forgotten”.
- After adopting Atlan as their metadata platform, Tide’s data and legal teams collaborated to define personally identifiable information in order to propagate those definitions and tags across their data estate.
- Tide used Atlan Playbooks (rule-based bulk automations) to automatically identify, tag, and secure personal data, turning a 50-day manual process into mere hours of work.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization in establishing and scaling data governance programs.
Conclusion: data catalog vs. data lineage
Permalink to “Conclusion: data catalog vs. data lineage”In today’s businesses, data is repeatedly imported, exported, transformed, stored, and displayed in multiple, redundant ways. Without a way to catalog and trace this movement, finding accurate data can become a nightmare - and compliance becomes nearly impossible.
Understanding data catalog vs. data lineage means understanding the two different but essential roles each plays in solving this problem. A data catalog tells you what you have. Data lineage tells you where everything is and how it all relates. Using both solutions, your company can ensure data accuracy, implement data governance, and manage business change.
Want to go deeper? Learn more about the modern data stack and its components - and how data catalog and data lineage fit within the larger picture.
FAQs about Data Catalog vs Data Lineage
Permalink to “FAQs about Data Catalog vs Data Lineage”1. What is a data catalog, and how does it work?
Permalink to “1. What is a data catalog, and how does it work?”A data catalog organizes and classifies metadata, making it easier for users to discover and access data. It acts as a central repository that indexes data assets, providing context through descriptions, tags, and ownership details. Data catalogs improve data discovery and governance by ensuring transparency and accessibility.
2. How does data lineage help in tracking data flow?
Permalink to “2. How does data lineage help in tracking data flow?”Data lineage tracks the flow of data from its origin to its final destination, mapping every transformation along the way. This helps organizations understand data dependencies, ensure accuracy, and maintain compliance by providing a clear audit trail for data movement.
3. What are the key differences between data catalog and data lineage?
Permalink to “3. What are the key differences between data catalog and data lineage?”A data catalog focuses on metadata management and data discovery, offering context and accessibility. Data lineage, on the other hand, maps data flow and transformations, ensuring traceability and compliance. Together, they provide a comprehensive view of data governance.
4. Why is data lineage important for data governance and compliance?
Permalink to “4. Why is data lineage important for data governance and compliance?”Data lineage ensures compliance by providing a transparent view of data origins, transformations, and usage. It supports governance frameworks by offering insights necessary for auditing, impact analysis, and root cause investigations, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements.
5. How do data catalog and data lineage improve data quality?
Permalink to “5. How do data catalog and data lineage improve data quality?”Data catalogs enhance data quality by providing detailed metadata, enabling better data understanding and usage. Data lineage ensures data accuracy by tracing its journey, identifying inconsistencies, and validating data integrity across systems.
6. What challenges might arise when implementing data catalog or lineage tools?
Permalink to “6. What challenges might arise when implementing data catalog or lineage tools?”Common challenges include integration complexity, data quality management, user adoption, and scalability. Organizations often face difficulties in aligning these tools with existing systems and processes, which can hinder their effective implementation.
Share this article




















