Data governance policy enforcement involves interpreting, monitoring, assessing, and ensuring compliance with data governance policies.
A data governance policy documents the guidelines for consistently managing your data assets. Once business leaders in your organization set these policies, data domain owners and stewards are responsible for policy enforcement.
If you’re a business steward in your business unit (or organization), this article will help you understand the crucial role you play in data governance policy enforcement. It will guide you on what data governance policy enforcement should include and how to go about it.
Data governance policy enforcement: A brief overview
Permalink to “Data governance policy enforcement: A brief overview”Data governance policy enforcement is the process of interpreting your policies, ensuring compliance with the rules, standards, and guidelines outlined by your data governance program.
Data governance policy enforcement is not just a process, it’s a key driver for data integrity, privacy, security, regulatory compliance, and trustworthiness of data assets. Your efforts in enforcing data governance policies directly contribute to these crucial aspects of your organization.
Also, read → What does a data governance policy do for your company?
Governance by exception: An essential principle for successful policy enforcement
Permalink to “Governance by exception: An essential principle for successful policy enforcement”A vital aspect of data governance policy enforcement is your approach to tackling instances of non-compliance.
Traditionally, flagging data assets as non-compliant isn’t a real-time activity, and governance professionals would only consider them once the results of manual audits are out.
In an ideal scenario, the steward should be alerted immediately when any data asset doesn’t comply with your data governance policy — due to deviations from your benchmark or human error. This proactive approach, known as governance by exception, highlights potential problems early on, mitigating risks and improving efficiency.
So, while enforcing data governance policy, incorporate governance by exception and pick tools that support real-time incident flagging, response, and remediation.
Next, let’s take a look at the roles responsible for data governance policy enforcement.
Who is responsible for data governance policy enforcement?
Permalink to “Who is responsible for data governance policy enforcement?”According to Gartner, data governance policy enforcement is the responsibility of a business information/data and analytics steward.
Ideally, the people responsible should be SMEs (subject matter experts). Their deep understanding of their domain’s data allows them to connect data governance policy enforcement with business outcomes.
It’s important to note that ‘stewardship’ isn’t a full-time job. It complements existing workflows.
For instance, a marketing SME understands sales and marketing data as they analyze it for their campaigns. As a data steward, they can add tasks, such as:
- Setting the rules of use
- Setting the standards of data quality (DQ)
- Establishing business rules to meet the DQ standards and compliance regulations
- Identifying and enforcing the decision rights framework best suited for the marketing domain
The person/people taking up this responsibility can vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and niche requirements:
- Small organizations: A centralized team or a designated data steward with extensive business knowledge (like the marketing SME) handles policy enforcement.
- Large organizations: Domain owners (like the head of marketing / a marketing expert / MarketingOps leader who understands how data must be used within the domain) play a crucial role. They collaborate with the central data governance team to ensure high-quality data use and adherence to global policies.
Summing up, domain SMEs leverage their expertise to enforce data governance policies and connect them to business goals.
Also, read → Data governance roles and responsibilities
Now, let’s look at the practical aspects of data governance policy enforcement and understand what’s involved.
What does data governance policy enforcement encapsulate?
Permalink to “What does data governance policy enforcement encapsulate?”Policy enforcement includes the following aspects:
- Monitoring data usage, access, and handling practices to ensure compliance with your organization’s established policies
- Ensuring consistency of data asset formats, semantics, and terminology with a central data policy repository
- Evaluating the business impact (operational efficiency, costs, data and analytics outcomes, and compliance efforts) of your workflows
- Quality assurance using metrics (data validity, accuracy, completeness, timeliness, integrity, and consistency) that gauge whether your data assets are fit for purpose
- Developing protocols to respond, contain, investigate, and resolve incidents
- Reviewing data assets that are in exception to set policies and resolving them, based on existing policies — if there aren’t any in place, then set new policies to fill the gap
- Spotting outliers and anomalies affecting the expected outcome of your workflows
- Educating data practitioners on maintaining compliance and the consequences of non-compliance with data governance policies
Next, let’s roll up our sleeves and dig deeper to understand the requirements and capabilities that will ensure an effective execution of your data governance policy enforcement plan.
How do you ensure enforcement is accurate and effective?
Permalink to “How do you ensure enforcement is accurate and effective?”Since policy enforcement involves monitoring whether the policies set are being followed, you must have tools in place that document data asset definitions, policies, and guidelines.
Gartner recommends capabilities such as metadata management, monitoring, enforcement analytics, and audit trails for such tools.
An active data governance platform would be equipped with a centralized metadata repository, asset profiles, data quality and security dashboards, and more. So, make sure the active data governance platform you choose allows you to:
- Establish a centralized policy repository for metadata management
- Set up a transparency center for real-time monitoring
- Track how well policies are followed with enforcement analytics
- Maintain clear records of policy enforcement with advanced audit trails
Let’s see how the above elements help with your policy enforcement plan.
1. Establish a centralized policy repository for metadata management
Permalink to “1. Establish a centralized policy repository for metadata management”Metadata provides essential context and information about data assets, such as their definitions, relationships, and ownership. For data governance policies, metadata can be policy type, owner, enforcement date, validity, review period, and purpose.
An active data governance platform like Atlan offers a central repository for data governance policies encompassing the above details. The in-built AI copilot can help you document the data governance policy purpose, scope, etc., and auto-suggest associated terms, metrics, workflows, and more at scale.
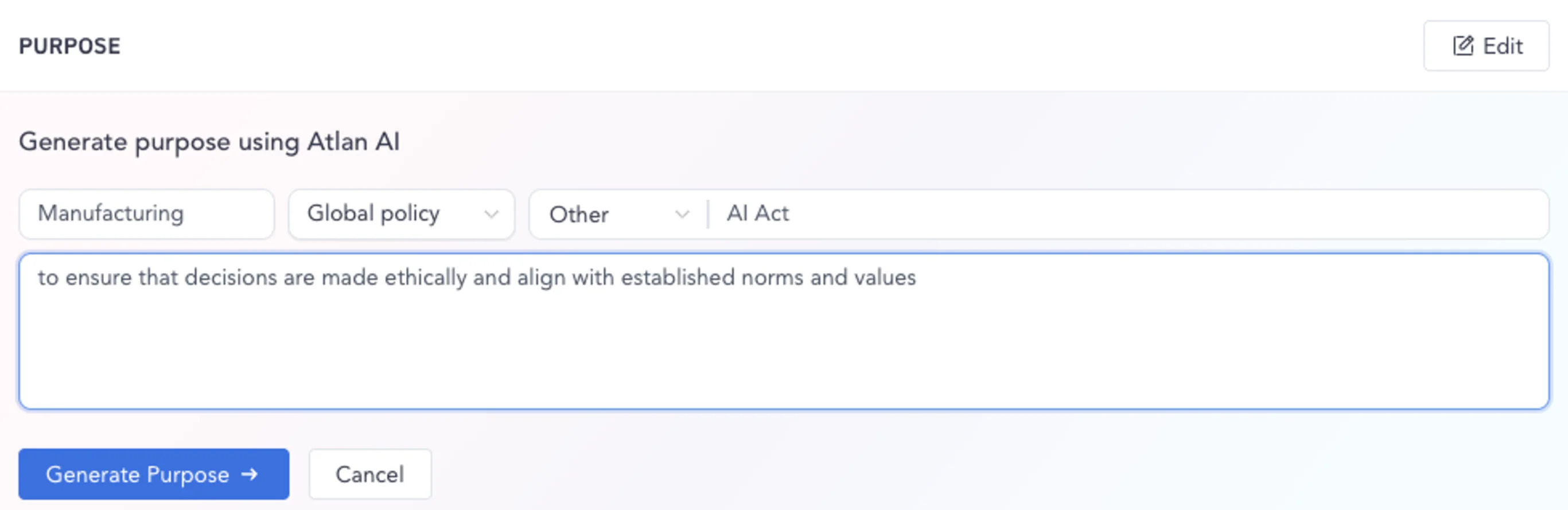
Auto-documenting data governance policies using Atlan AI - Image by Atlan.
As a result, you can enforce data governance policies within minutes, with adequate context.
2. Set up a transparency center for real-time monitoring
Permalink to “2. Set up a transparency center for real-time monitoring”Real-time monitoring of data usage, access patterns, and compliance with data governance policies support your data governance enforcement efforts.
An active data governance platform will provide automated alerts and notifications to inform you about policy violations, unusual activities, workflow interruptions, and more from a single, unified dashboard.
This dashboard provides real-time context on everything related to data governance policy enforcement.
In Atlan, that central location is called Policy Center, using which you can:
- Observe all data governance policies at a glance and see how your data assets have been governed over time
- Look at various policy types and filter them by their scope size
- Explore and investigate overlapping policies
- Review actions requiring your approval
- Incorporate governance by exception — you’re immediately notified of incidents of non-compliance
- Review assets that are ungoverned or non-compliant
- Decide further course of action for policies that are expiring
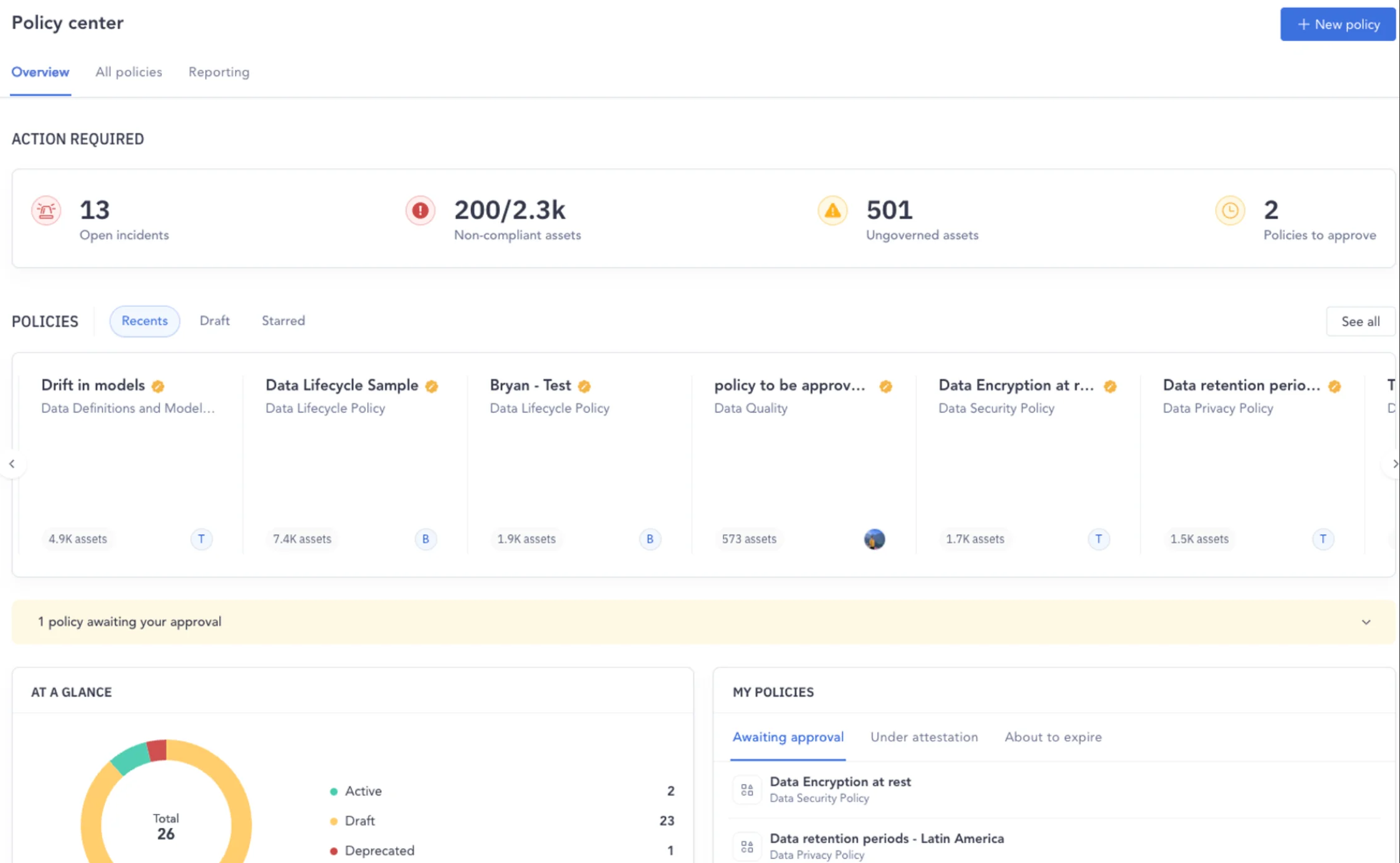
Policy center offers all the context you need on policy enforcement in real-time - Image by Atlan.
As a result, data governance policy enforcement becomes seamless, precise, and less time-consuming.
3. Track how well policies are followed with enforcement analytics
Permalink to “3. Track how well policies are followed with enforcement analytics”Gauging the effectiveness of data governance policy enforcement requires observing various aspects, such as user access, data quality, and data lineage. This also helps you measure the impact of policy enforcement on business operations and data and analytics workflows.
An active data governance platform will help you:
- Track who has query access
- Check data governance policies in place
- Review data assets tagged automatically by propagation (via lineage)
- Assess data asset enrichment completion (for example, assets without descriptions, certificates, tags, owners, etc.)
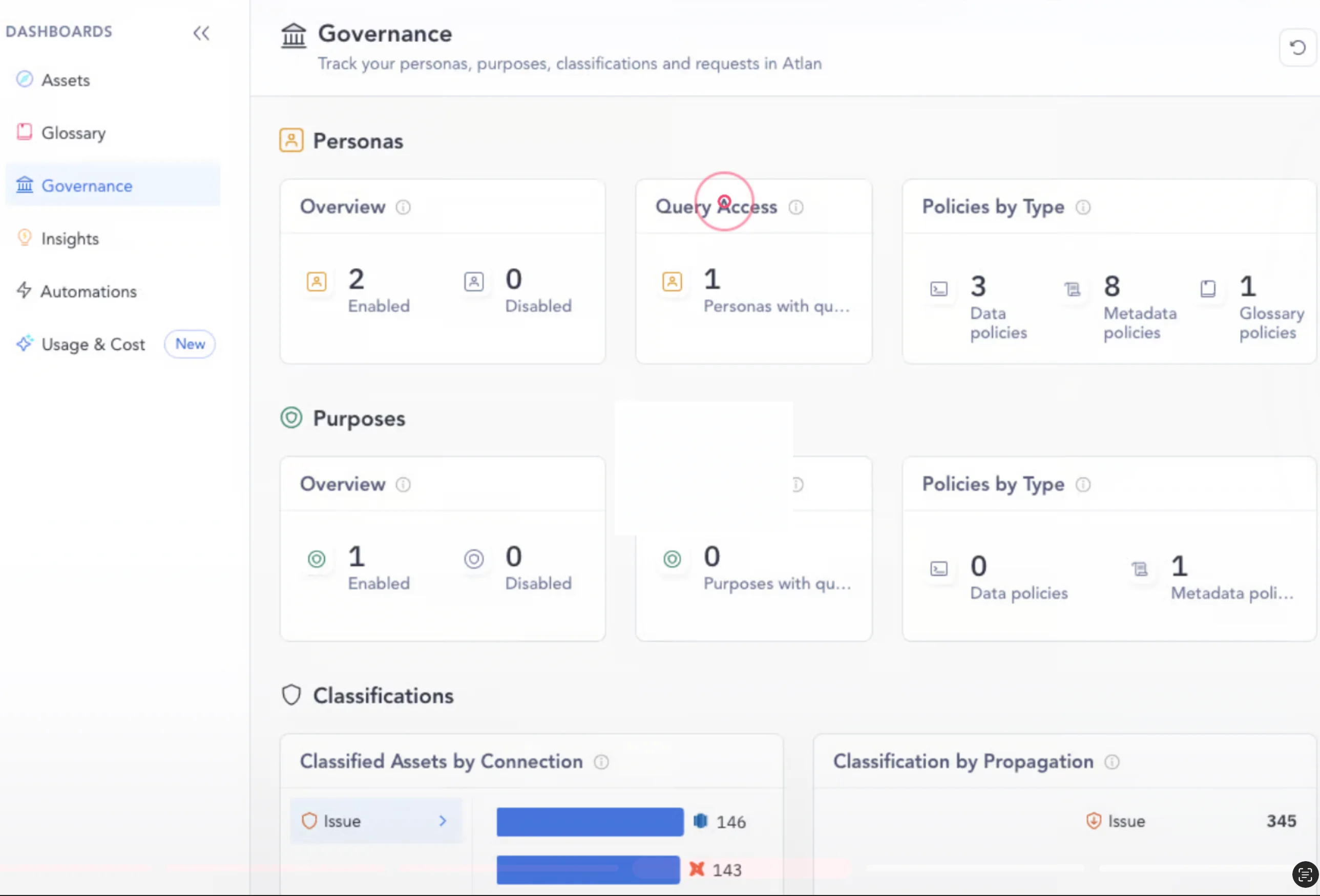
Policy enforcement analytics at a glance in an active data governance platform like Atlan - Image by Atlan.
As a result, you can get insights into the effectiveness of policy enforcement measures, address potential bottlenecks, and optimize your data governance efforts.
4. Maintain clear records of policy enforcement with advanced audit trails
Permalink to “4. Maintain clear records of policy enforcement with advanced audit trails”Audit trails record everything from policy changes and access requests to data asset modifications. This enables traceability, transparency, and accountability, making your data governance program more effective.
In an active data governance platform like Atlan, audit trails are embedded within data asset profiles. You can see all activities related to a specific data asset, from updates to workflows using that asset, in real-time — similar to version history logs tracked by apps like Google Docs or Notion.
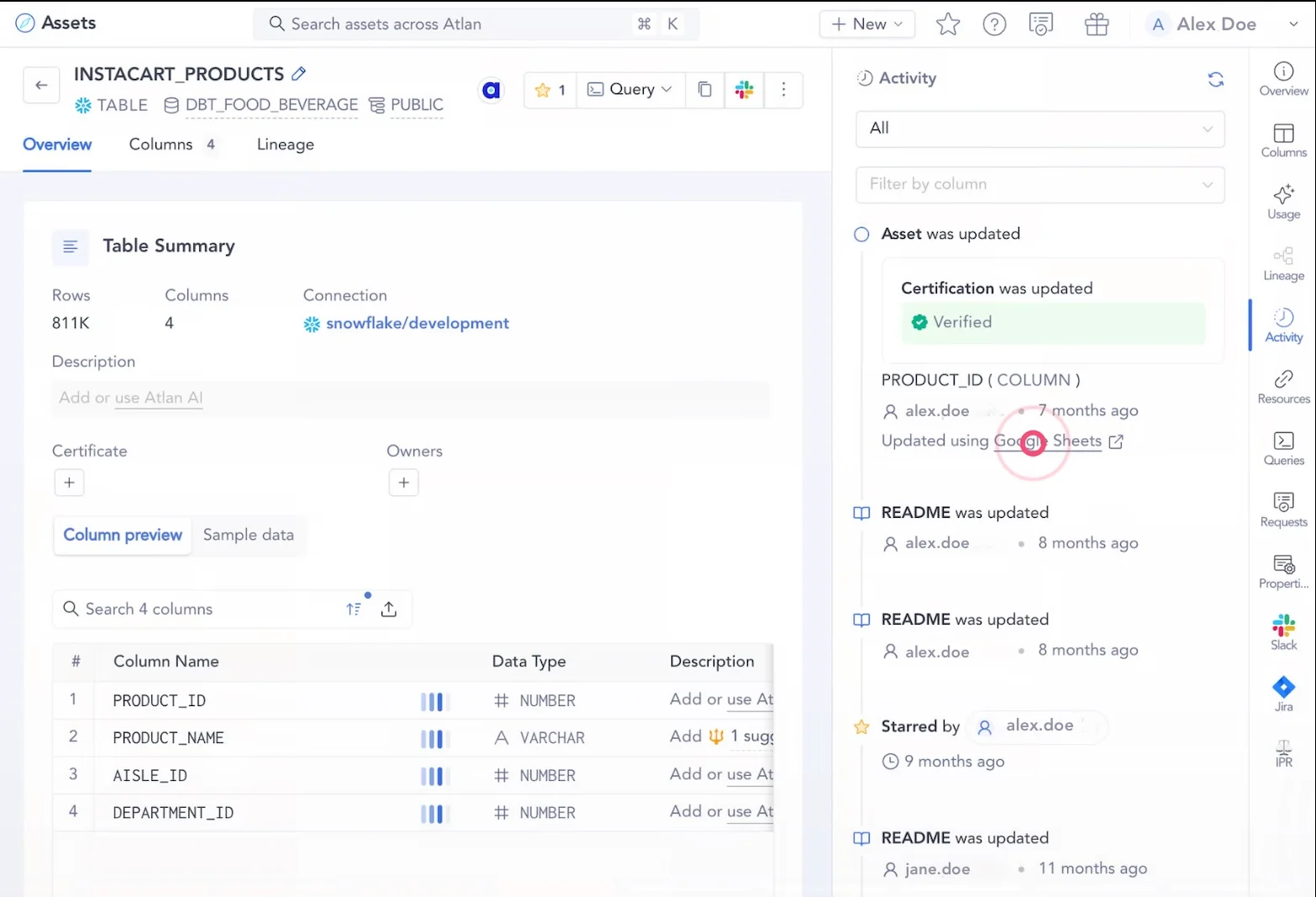
Ensuring comprehensive audit trails using activity logs for data assets in Atlan - Image by Atlan.
As a result, you get a complete snapshot of everything an asset has undergone by visiting its profile.
How do you go about data governance policy enforcement? The following section provides a step-by-step guide that can serve as a blueprint and help you get started.
How to enforce data governance policy: Getting started in 9 steps
Permalink to “How to enforce data governance policy: Getting started in 9 steps”Enforcing data governance policy requires careful, step-by-step planning that involves all the relevant stakeholders. Here’s how you can go about data governance policy enforcement in nine steps:
- Identify business SMEs, such as data and analytics stewards within each domain, department, or team
- Document and communicate data governance policies with all relevant stakeholders — employees, contractors, and partners
- Set up an active data governance platform with a centralized policy repository, transparency center, enforcement analytics, and advanced audit trails in real-time
- Identify data quality metrics to spot anomalies, outliers, or deviations from the benchmark
- Establish data policy enforcement metrics, such as:
- Policy adherence and violation rates
- Incident response rates
- Regulatory compliance adherence
- Training completion rate
- Catalog adoption rate
- Practice governance by exception by establishing tolerance limits and tracking performance to identify, report, and resolve all cases of policy non-compliance immediately
- Conduct regular training sessions and awareness programs about your data governance policies
- Perform periodic audits and assessments to identify instances of non-compliance with data governance policies and fix them
- Communicate regularly with business leaders, data domain owners, and other senior management roles to share your findings, review data governance policies, and offer feedback on policy enforcement
Summing up
Permalink to “Summing up”Effective data governance policy enforcement involves several activities, such as monitoring policies, developing incident response protocols, and conducting regular real-time audits.
Successful policy enforcement requires a collaborative effort between business leaders, domain owners, data stewards, and data practitioners.
An active data governance platform can help with capabilities such as a centralized policy repository, policy enforcement monitoring and analytics, and advanced audits.
This ensures compliance, data quality, and effective data governance while fostering a culture of accountability and data-driven decision-making.
Book your personalized demo today.
Share this article



















