Most enterprises implement these in phases: Foundation (framework, roles, policies) in months 1–3, Core (quality, catalog, security) in months 4–9, and Advanced + Continuous (integration, stewardship, training, measurement) from month 10 onward. Most governance programs stall because teams try to build everything at once. A phased approach works better. Training and measurement run alongside every phase.
This gets you to operational governance in 12 to 18 months, rather than a multi-year slog. And with Gartner predicting that 60% of AI projects risk abandonment due to poor data quality, AI governance now touches every one of these components.
Here’s a quick overview of how you can prioritize implementing data governance components:
Quick Implementation Checklist
- Month 1–3: Foundation (framework, roles, policies)
- Month 4–8: Core execution (quality, catalog, security)
- Month 9–12: Advanced scaling (integration, stewardship)
- Ongoing: Training and measurement
What are the ten key components of data governance?
Permalink to “What are the ten key components of data governance?”Ten components turn raw data into something your teams can actually trust and use. Foundation components (framework, roles, policies) set up how governance works. Core components (quality, catalog, security) put controls in place. Advanced components (integration, stewardship) help you scale, and continuous components (training, measurement) keep things improving.
Here is what happens when these pieces are missing. Policies sit in documents nobody reads. Catalogs stay half-filled, and people stop trusting the data. A 2020 Accenture and Qlik study of 9,000 employees found that 48% rely on gut feeling rather than data.
When these components work together, teams spend less time troubleshooting and more time on work that matters. The key is to start with a few high-value data domains, not to roll out governance across the entire company on day one.
| Component | What it does | Key elements | How you measure it | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Framework | Sets your goals and who gets to make decisions. | Strategic objectives, scope, guiding principles, and authority structure | Adoption rate across business units, alignment with business goals | Foundation |
| 2. Roles | Makes it clear who owns what. | Data Owner, Steward, Custodian, and Consumer role definitions | % of assets with assigned owners, issue resolution time | Foundation |
| 3. Policies | Spells out the rules for handling data. | Classification standards, retention schedules, privacy protections, and access controls | Compliance rate, violation count, and employee awareness | Core |
| 4. Quality | Keeps data accurate and reliable through automated checks. | Quality metrics, validation rules, profiling, cleansing workflows, dashboards | Quality score (target >95%), issue resolution time | Core |
| 5. Catalog | Gives everyone a single place to find, understand, and trust data. | Business glossary, metadata docs, lineage tracking, search | Catalog coverage, adoption rate, time-to-discovery | Core |
| 6. Security | Protects data from unauthorized access and breaches. | Access controls, encryption, breach detection, PII masking, privacy assessments | Incident frequency, compliance audit scores | Core |
| 7. Integration | Keeps data consistent across systems. | Standardized data models, API management, cross-system connectors | Cross-system consistency, integration, and uptime | Advanced |
| 8. Stewardship | Handles day-to-day quality and change management. | Schema change management, data dictionary upkeep, and impact assessment | Change success rate, stakeholder engagement | Advanced |
| 9. Training | Teaches people how to work with data properly. | Data literacy programs, role-based training, certifications | Completion rate (target >80%), literacy scores | Continuous |
| 10. Measurement | Tracks whether governance is actually delivering value. | Business impact tracking, compliance reports, maturity assessments, and ROI | Maturity score improvement, time-to-insight reduction | Continuous |
No component works alone. Each one builds on the others and feeds the next.
How data governance components connect with each other
Permalink to “How data governance components connect with each other”Here is how they connect:
| Component | Depends on | Enables | Why the link matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Framework | Nothing (starting point) | All other components | Everything flows from strategy |
| 2. Roles | Framework | Policy enforcement, quality management | People need to know who does what |
| 3. Policies | Framework, Roles | Quality standards, security controls | Rules guide what the execution layer does |
| 4. Quality | Policies, Catalog | Reliable analytics, AI model training | Bad data in = bad decisions out |
| 5. Catalog | Framework, Roles | Discovery, self-service analytics | The central hub that everything connects to |
| 6. Security | Policies, Catalog | Risk reduction, compliance | Protects everything else you build |
| 7. Integration | Catalog, Quality | Cross-system consistency | Governance only works if it spans systems |
| 8. Stewardship | Roles, Training | Sustainable day-to-day operations | Culture change makes governance stick |
| 9. Training | Framework, Roles | User adoption | People power every component |
| 10. Measurement | All components | Continuous improvement | Proves governance is worth the effort |
Why do these components matter for enterprise leaders in 2026?
Permalink to “Why do these components matter for enterprise leaders in 2026?”Four things make governance urgent in 2026. AI needs governed data to work, breaches keep getting more expensive, teams waste too much time on bad data, and the companies that govern data well simply outperform those that do not.
Below are a few reasons why data governance components matter significantly for enterprise leaders.
AI initiative success
Permalink to “AI initiative success”AI models process language, but they do not understand your business. Governance gives them the business context they need to be useful. Without it, models hallucinate, produce biased results, and lose trust fast. Gartner predicts 60% of AI use cases will fail without governance by 2026.
At the same time, 63% of organizations still lack AI-ready data management practices. That gap is where governance comes in.
Risk mitigation
Permalink to “Risk mitigation”Breaches are expensive, and the costs keep climbing. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025 reports a global average of $4.44 million per breach. In the U.S., that number hit an all-time high of $10.22 million. Shadow AI makes things worse. IBM found that one in five breaches involved shadow AI, adding $670,000 to the average cost.
On the flip side, companies using AI and automation in their security operations saved $1.9 million per breach. Governance is not optional anymore. It is basic risk management.
Operational excellence
Permalink to “Operational excellence”McKinsey found that 30% of enterprise time is spent on non-value tasks caused by poor data. That is nearly a third of your workforce’s time wasted.
Companies that get governance right report much less time spent troubleshooting. Their data teams stop being janitors and start being architects.
Competitive advantage
Permalink to “Competitive advantage”Companies with mature data practices are far more likely to win and keep customers. The IDC Enterprise AI Maturity Study 2025 found that “AI Masters” with strong data infrastructure and governance see 24.1% revenue improvement and 25.4% cost savings.
Governance pays for itself.
How do I build each component systematically?
Permalink to “How do I build each component systematically?”Five steps get you from zero to operational governance. Start with your framework, define who owns what, write the rules, automate quality checks, and measure what matters. The “crawl, walk, run” approach works because it shows value early and builds momentum.
Here’s a quick overview of the implementation priority and its success criteria:
| Phase | Timeline | Components | What you need first | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Foundation | Months 1–3 | Framework, Roles, Policies | Nothing | Executive buy-in secured, roles assigned, policies written |
| Phase 2: Core | Months 4–9 | Quality, Catalog, Security | Foundation done | Quality scores going up, catalog adoption >40%, security controls live |
| Phase 3: Advanced | Months 10–15 | Integration, Stewardship | Core running | Cross-system integration live, stewardship processes in place |
| Ongoing | Continuous | Training, Measurement | All of the above | Quarterly maturity reviews, training completion >80% |
Step 1: Set up your framework
Permalink to “Step 1: Set up your framework”For CDOs
Tie governance goals to business outcomes that matter, like AI readiness or passing regulatory audits. Pick the data domains that are most important to your business right now. Start there, not everywhere. Your framework needs executive backing and a clear decision-rights structure. Someone has to have the final say on data standards, classification disputes, and access requests.
Without that, governance gets stuck at the first disagreement. 84.3% of Fortune 1000 companies now have a CDO, but only 47.6% say the role is working well. A clear framework makes the difference.
Example Implementation: A financial institution’s framework might prioritize regulatory compliance (Basel III, GDPR), data quality for risk modeling, and transparency for audit requirements, with clear scope boundaries covering trading, retail banking, and compliance data.
Step 2: Define who owns what
Permalink to “Step 2: Define who owns what”For Governance Leads
Accountability without authority is a recipe for failure. Data Owners need the power to make decisions, not just the blame when things go wrong.
Set up four role definitions, including:
- Data Owners are business leaders responsible for data domains. They’re accountable for data accuracy, completeness, and business value.
- Data Stewards are people managing day-to-day quality and policy compliance.
- Data Custodians are engineers who handle the technical aspects of controls, storage, and access management.
- Data Consumers are everyone using data and needs to follow the rules. Every critical data asset should have an owner. If nobody owns it, nobody fixes it.
Step 3: Write policies people can actually follow
Permalink to “Step 3: Write policies people can actually follow”For Compliance Officers
Vague policies fail. “Data must be classified” does not tell anyone what to do. “All datasets with PII must get a ‘Confidential’ tag within 48 hours of ingestion” does.
Embed policies into the tools your team already uses. A policy buried in a SharePoint folder will not change behavior. One built into GitHub, Slack, or your data catalog will.
The stakes are real: GDPR fines hit roughly €7.1 billion since 2018, with €1.2 billion in 2025 alone.
Step 4: Automate quality management
Permalink to “Step 4: Automate quality management”For Platform Engineers
Manual quality checks do not scale. Define what “good data” looks like for your organization: accuracy, completeness, timeliness, consistency. Then set up automated monitoring that catches problems before they reach anyone downstream.
The DATAVERSITY 2025 survey found 61% of organizations call data quality a top challenge. Automated dashboards turn this from a problem into a number you can track and improve.
Step 5: Measure business impact, not just compliance
Permalink to “Step 5: Measure business impact, not just compliance”For all teams
Track things leadership cares about: time saved, costs avoided, revenue opportunities unlocked. “Number of assets tagged” will not hold anyone’s attention in a board meeting.
You must show the value of the investment or the risk of losing it to gain stakeholders’ support.
How do data governance components work together?
Permalink to “How do data governance components work together?”Data governance components work as a system, organized into four layers: foundation, execution, oversight, and enablement. The foundation layer components define scope, assign ownership, and write rules for the execution layer, which in turn feeds into trust signals and compliance evidence. The oversight layer components manage risk through regulatory alignment and deliver compliance proof. Lastly, enablement layer components drive adoption through continuous optimization.
Here’s an overview of how components in each layer feed into other components:
| Layer | Components | What it does | Key activities | What it feeds into |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | 1–3 (Framework, Roles, Policies) | Sets direction | Define scope, assign ownership, and write standards | Rules for the execution layer |
| Execution | 4–7 (Quality, Catalog, Security, Integration) | Runs governance day to day | Automate controls, enforce policies, and help people find data | Trust signals and compliance evidence |
| Oversight | Spans components | Manages risk | Audit trails, regulatory alignment, risk reviews | Compliance proof |
| Enablement | 9–10 (Training, Measurement) | Drives adoption and improvement | Build data skills, track KPIs, and adjust the approach | Feedback for continuous optimization |
Foundation layer
Permalink to “Foundation layer”Foundation layer components answer three questions: What data matters most? Who owns it? What rules apply? If those answers are unclear, everything downstream struggles.
Your strategy and scope determine which data needs governance and why. The operating model assigns accountability while policies and standards define the rules.
Execution layer
Permalink to “Execution layer”The Execution layer puts policies into practice through automation. Quality monitoring, catalog discovery, column-level lineage, and security controls all live here.
Think of data lineage as your company’s map. Data often takes five or six hops from a source system like Salesforce to a final BI dashboard. When something breaks, lineage lets you trace the problem in minutes instead of hours.
Technical components in the execution layer implement policies at scale:
- Quality management ensures data meets standards
- Metadata catalogs enable discovery and understanding
- Lineage tracks dependencies and impacts
- Security protects sensitive information
- Master data ensures cross-domain consistency
- Lifecycle management handles temporal aspects
Oversight and enablement layers
Permalink to “Oversight and enablement layers”In the oversight layer, components provide audit support and regulatory alignment necessary to deliver compliance proof. They manage risk using audit trails and risk reviews.
Enablement layer components include tooling to automate execution and measurement, which drives continuous improvement.
Start with one or two high-value domains and prove that governance works. Then expand. The Precisely and Drexel University 2025 Outlook shows 71% of organizations now have some form of governance, up from 60% in 2023. But only 15% call theirs mature.
The difference between having a program and running a good one usually comes down to how well these layers connect.
Which enterprise frameworks align with these data governance elements?
Permalink to “Which enterprise frameworks align with these data governance elements?”Three well-known frameworks map to these 10 components. They give you a head start, so you do not have to figure out everything from scratch.
| Framework | Covers components | Focus area | Maturity benchmark | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAMA-DMBOK | 1–3, 4–5, 6-7 | Data governance, metadata management, and security and integration disciplines. | 11 knowledge areas | Broad governance programs |
| ISO 8000 | 4, 10 | Quality and measurement | International certification | Quality-focused programs, global teams |
| NIST Privacy Framework | 6 | Security and privacy | Risk-based (Identify, Govern, Control, Communicate, Protect) | Regulated industries (healthcare, finance, government) |
DAMA-DMBOK framework integration
Permalink to “DAMA-DMBOK framework integration”DAMA-DMBOK covers 11 knowledge areas and provides a solid blueprint for program design.
- Components 1-3 (Framework, Roles, Policies) align with DAMA’s Data Governance and Data Architecture disciplines
- Components 4-5 (Quality, Catalog) correspond to Data Quality Management and Metadata Management functions
- Components 6-7 (Security, Integration) map to Data Security and Data Integration disciplines
ISO 8000 standards compliance:
ISO 8000 provides international benchmarks for data quality that apply across regions and teams.
- Provides international standards for data quality management that directly support Component 4
- Offers structured approaches for metadata management supporting Component 5
- Establishes quality measurement frameworks essential for Component 10
Modern platforms like Atlan automate these standards into daily workflows, reducing the manual effort required to stay compliant.
NIST privacy framework application
Permalink to “NIST privacy framework application”For healthcare, finance, and government teams, NIST provides the compliance foundation.
- Governs Component 6 implementation with structured privacy risk management
- Provides assessment methodologies supporting Component 10’s measurement requirements
- Offers incident response frameworks complementing data security policies
Aligning your security component with NIST standards makes audit preparation faster and strengthens regulatory readiness.
Modern data governance platforms like Atlan integrate these established frameworks into automated workflows, reducing manual implementation overhead while maintaining compliance with international standards.
Related reading: Data Governance Framework
How does AI governance extend these components?
Permalink to “How does AI governance extend these components?”AI governance does not replace the 10 components. It adds new requirements to each one. Your framework remains the same, but AI introduces new needs for bias detection, model transparency, and algorithmic accountability.
78% of organizations used AI in 2024, up from 55% in 2023. But only one in five companies has mature governance for autonomous AI agents, according to Deloitte’s 2026 State of AI report. Governance is not keeping up. This is why AI governance needs to live inside your existing components, not as a separate program.
| Component | What it covers today | What AI adds | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Framework | Goals and scope | AI ethics principles, risk classification | EU AI Act compliance mapping, model risk tiers |
| 2. Roles | Owner, Steward, Custodian | Model Owner, ML Engineer accountability | Cross-functional AI governance councils |
| 4. Quality | Accuracy and completeness checks | Bias detection, model drift, and fairness metrics | Demographic parity testing, ongoing model validation |
| 5. Catalog | Data asset discovery and lineage | AI model registry, feature stores, training data lineage | Model-to-data lineage, experiment tracking |
| 6. Security | Access controls, encryption | Algorithmic audit trails, explainability | SHAP values, model decision logging |
| 8. Stewardship | Data quality ownership | Model performance monitoring | MLOps and data stewardship working together |
| 9. Training | Data literacy programs | AI governance literacy, model risk awareness | Responsible AI training for business users |
| 10. Measurement | Data quality KPIs | Model performance, fairness KPIs | Bias audits, model ROI tracking |
Context is the big challenge here. On the open internet, “TAM” could mean a hundred things. In your company, it means “Total Addressable Market.” Governance gives AI models that context.
Without it, AI agents work without guardrails, and data leaks become a matter of time. IBM found that 97% of AI-related breaches happened where access controls were missing.
Related reading: AI-Ready Data
What are common pitfalls when rolling out data governance aspects?
Permalink to “What are common pitfalls when rolling out data governance aspects?”When rolling out data governance, common pitfalls arise when data owners hold accountability without decision-making authority, policies are built outside people’s workflows, over-engineering occurs before understanding the problem, and technical metrics do not align with business impact.
These mistakes kill governance programs, and none of them are about technology.
Q: What’s the biggest mistake organizations make with governance roles?
Permalink to “Q: What’s the biggest mistake organizations make with governance roles?”Assigning accountability without authority. Data Owners need decision-making power, not just responsibility for outcomes they can’t control.
Give them real decision-making power over their domains. It includes the authority to block data assets that do not meet quality thresholds.
Q: Why do governance policies often fail to stick?
Permalink to “Q: Why do governance policies often fail to stick?”A governance policy in a document nobody opens is just words. Build policies into the tools your team uses every day: GitHub for developers, Slack for communication, BI tools for analysts. If following governance means leaving your workflow, most people will not bother.
Q: How do technical implementations go wrong?
Permalink to “Q: How do technical implementations go wrong?”Buying a complex platform before you know what you need wastes money and time. Start with one high-value use case that shows quick ROI.
A single well-governed data domain opens the door. An 18-month platform build that launches to low adoption does not.
Q: What causes governance programs to lose momentum?
Permalink to “Q: What causes governance programs to lose momentum?”If you only track technical metrics like “number of assets tagged,” executives will tune out. Measure and communicate business impact: time saved, costs avoided, revenue unlocked. Trust comes from transparency.
When a pipeline breaks, tell people right away. “The pipeline failed today, do not use the dashboard,” builds more trust than silence.
Should you choose open-source or enterprise platforms?
Permalink to “Should you choose open-source or enterprise platforms?”When choosing tools for data quality, catalog, security, and integration, teams must decide between open-source and enterprise platforms. Open-source tools cost less up front and offer more flexibility, but they require significant engineering effort to maintain and integrate. Enterprise platforms cost more upfront, but they offer built-in compliance reporting, a unified user experience, and vendor support. At scale, they often reduce the total cost of ownership.
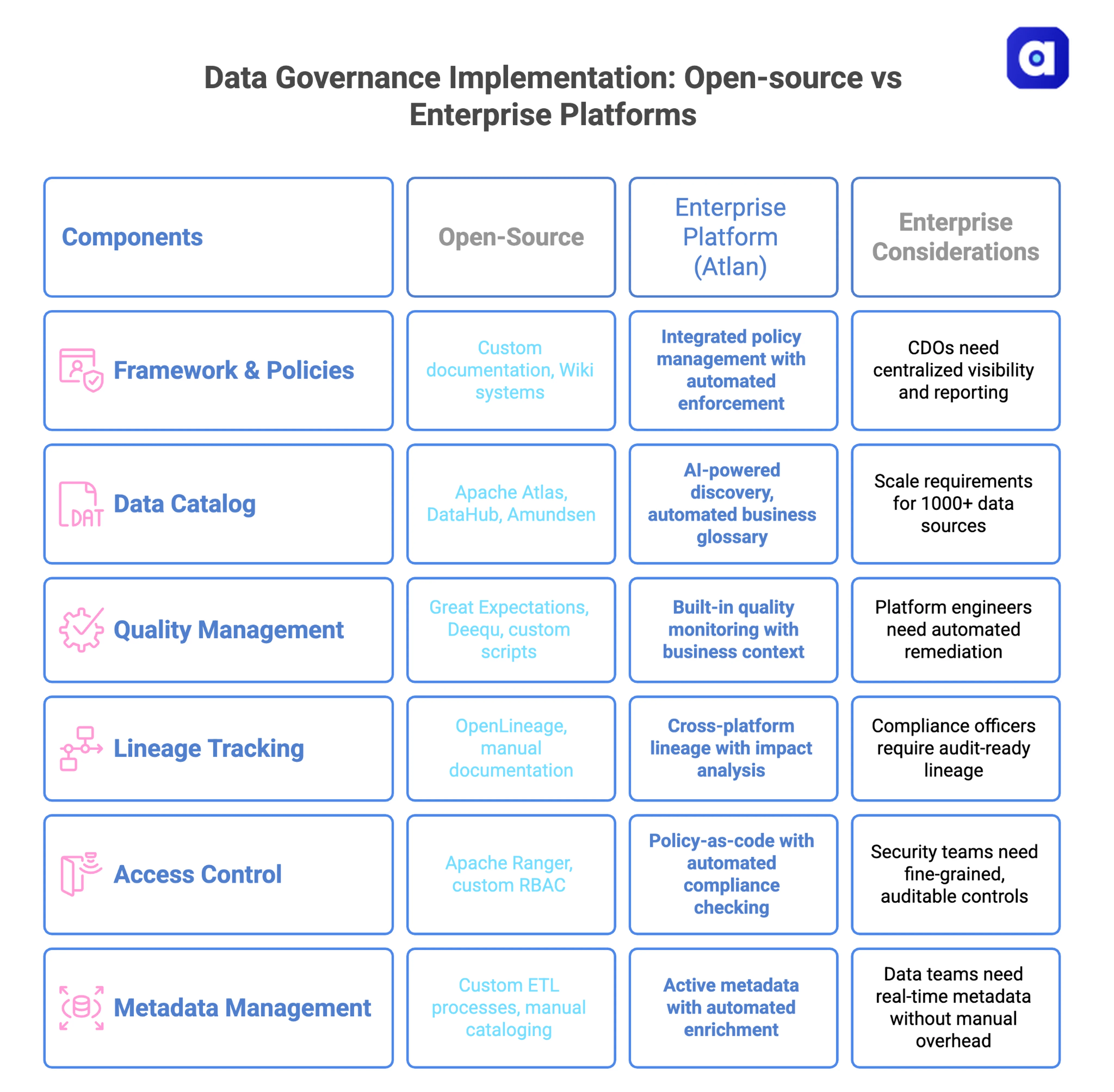
Open-source works well for teams with strong engineering and simpler governance needs. Enterprise platforms make more sense when you need automated compliance, broad integration, and high adoption. For large-scale rollouts, total cost of ownership often favors managed platforms because they cut engineering overhead and automate compliance reporting.
Adoption comes down to one thing: meeting people where they work. If 40% of users drop off at the login screen of a separate tool, the program has failed. The platform needs to appear within the tools your team already uses.
Related reading: What is a Data Catalog?
How Atlan approaches data governance key components
Permalink to “How Atlan approaches data governance key components”Most governance programs struggle because traditional tools treat each component as its own system. The catalog lives in one tool. Quality monitoring sits in another. Security runs in a third.
Stewards end up jumping between interfaces, and policies are not enforced consistently. Measuring anything requires manually pulling data from multiple sources.
Atlan brings all 10 components into a single active metadata platform:
- Framework & Policies (Components 1, 3) become automated classification and tagging rules instead of static PDFs.
- Roles & Access (Component 2) are enforced directly inside discovery and access workflows.
- Quality, Catalog, and Lineage (Components 4–5) live in one interface so teams can see trust signals, definitions, and dependencies in context.
- Security & Privacy (Component 6) use policy‑driven masking and access controls that follow data across tools.
- Integration (Component 7) connects to 100+ data sources, reducing manual stitching between systems.
- Stewardship (Component 8) is supported by playbooks and workflows that route reviews, approvals, and impact assessments to the right people.
- Training & Measurement (Components 9–10) are powered by dashboards that track adoption, data quality, and governance KPIs in real time.
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business’s disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security. It benefits users in many ways, including:

Modernized data stack and launched new products faster while safeguarding sensitive data
"Austin Capital Bank has embraced Atlan as their Active Metadata Management solution to modernize their data stack and enhance data governance. Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics, highlighted, 'We needed a tool for data governance… an interface built on top of Snowflake to easily see who has access to what.' With Atlan, they launched new products with unprecedented speed while ensuring sensitive data is protected through advanced masking policies."

Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics
Austin Capital Bank
🎧 Listen to podcast: Austin Capital Bank From Data Chaos to Data Confidence
Curious which components could unlock the same speed for your team?
Book a Personalized Demo
53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
"Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. 'Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,' Kiwi.com shared. Atlan's intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams."
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
"Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, 'Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.' With Atlan's integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate."

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare's Data Renaissance with Atlan
Which components should you prioritize in your governance roadmap?
Permalink to “Which components should you prioritize in your governance roadmap?”If you are building a governance program from scratch, start with the Foundation tier. Get executive buy-in, assign owners for your most important data domains, and write the policies that matter most for your regulatory and business context. Do not try to do everything at once. Proving value in one domain builds the credibility you need to expand.
| Goal | Components | Timeline | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI readiness | Framework + Quality + Catalog | 3-4 months | Context + clean data + discovery |
| Regulatory compliance | Policies + Security + Measurement | 4-6 months | Rules + controls + proof |
| Data quality improvement | Quality + Stewardship + Training | 2-3 months | Checks + owners + adoption |
| Scale data products | Catalog + Integration + Roles | 4-5 months | Discovery + automation + ownership |
The teams that succeed treat governance as something that grows over time, not a one-and-done project. Focus on sustainable processes, not perfect rollouts.
98.4% of Fortune 1000 organizations are increasing their data and AI investments. Governance programs that show real value will receive the largest share of that spending.
Build your data governance with expert help. Atlan’s active metadata platform brings all 10 components into one place, getting you from framework to working governance in weeks, not months.
Implement your data governance with expert help
Book a Personalized DemoFAQ about data governance key components
Permalink to “FAQ about data governance key components”1. What are the key components of data governance?
Permalink to “1. What are the key components of data governance?”Data governance has 10 components: governance framework, roles and responsibilities, policies and procedures, data quality management, catalog and metadata management, data security and privacy, data integration and interoperability, data stewardship and change management, training and education, and performance measurement. They work as a connected system. Most teams start with the Foundation layer (framework, roles, policies) and build out from there.
2. How does data governance impact data quality and compliance?
Permalink to “2. How does data governance impact data quality and compliance?”Governance improves data quality by establishing clear owners, automated checks, and standards to ensure accuracy, completeness, and timeliness. On the compliance side, it enforces rules through policies, access controls, and audit trails.
3. What roles and responsibilities are involved in data governance?
Permalink to “3. What roles and responsibilities are involved in data governance?”Four roles drive governance. Data Owners (business leaders) are accountable for data domains. Data Stewards (often business analysts) handle day-to-day quality and documentation. Data Custodians (engineers) manage the technical side, security, and access. Data Consumers (everyone else) follow access policies and usage rules. In 2026, AI governance adds Model Owners and ML Engineers to the mix.
4. What are the challenges of maintaining data governance in a decentralized environment?
Permalink to “4. What are the challenges of maintaining data governance in a decentralized environment?”Decentralized setups struggle with consistency. Different teams classify data differently, apply conflicting quality standards, or run separate catalogs. The answer is federated governance: a central framework with domain-level execution. The central team sets the standards. Domain teams enforce them in their own context. Data catalogs with automated policy enforcement help bridge the gap.
5. How can data governance enhance data security and privacy?
Permalink to “5. How can data governance enhance data security and privacy?”Governance connects classification to access controls. When you classify data at ingestion (flagging PII, financial records, or health data), security controls kick in automatically. Access reviews become routine instead of one-off scrambles. Audit trails show who accessed what and when.
6. Does AI change which data governance components I need?
Permalink to “6. Does AI change which data governance components I need?”The same 10 components still apply. AI just adds new needs to each one. Component 4 (quality) grows to include bias detection and model drift monitoring. Component 5 (catalog) adds AI model registries and feature stores. Component 6 (security) picks up algorithmic audit trails and explainability. The ones doing it well layer AI controls onto existing components instead of starting from scratch.
7. Which components should you prioritize in your governance roadmap?
Permalink to “7. Which components should you prioritize in your governance roadmap?”Start with the Foundation: framework, roles, and policies. These three cost the least, take the least time, and unlock everything else. Once they are solid, add Core components one domain at a time. Show value before you expand. AI governance is not a separate project in 2026. It is part of what you are already building. Every framework, quality check, and catalog entry you set up today becomes the foundation your AI efforts need tomorrow. Your roadmap does not need to be complicated. It needs to be intentional.
8. What metrics prove governance is working?
Permalink to “8. What metrics prove governance is working?”Track business-facing outcomes, not just technical activity. Examples include: Reduction in data incidents, time saved in analysis, faster audit preparation, increased AI model accuracy, and improved data-user satisfaction.
If governance does not reduce risk, save time, or unlock revenue, it is not delivering value.
9. Should governance start centrally or within business domains?
Permalink to “9. Should governance start centrally or within business domains?”Start centrally for standards and decision rights. Execute within domains for speed and ownership. A federated model works best. The central team defines policies and quality thresholds. Domain teams apply them to their own datasets. This balances consistency with agility.
Share this article



















