Databricks Data Governance: Native Features, Atlan Integration, and Best Practices
Share this article
Databricks comes with a native data governance solution built around Unity Catalog, which is its metadata management engine. However, Databricks data governance extends beyond cataloging to data discovery, quality, lineage, security, collaboration, and more. Databricks has various out-of-the-box features to support these capabilities.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Governance – Start Product Tour
This article explores the key data governance features available in Databricks, highlights Unity Catalog’s core functionalities, and discusses how a unified control plane can help maximize these capabilities across your entire data estate.
Table of Contents
Permalink to “Table of Contents”- Databricks data governance: Native features
- Databricks data governance with Atlan + Databricks
- Summary
- Databricks data governance: Related reads
Databricks data governance: Native features
Permalink to “Databricks data governance: Native features”Unity Catalog serves as the foundation of Databricks’ data governance, offering centralized management for data and AI assets.
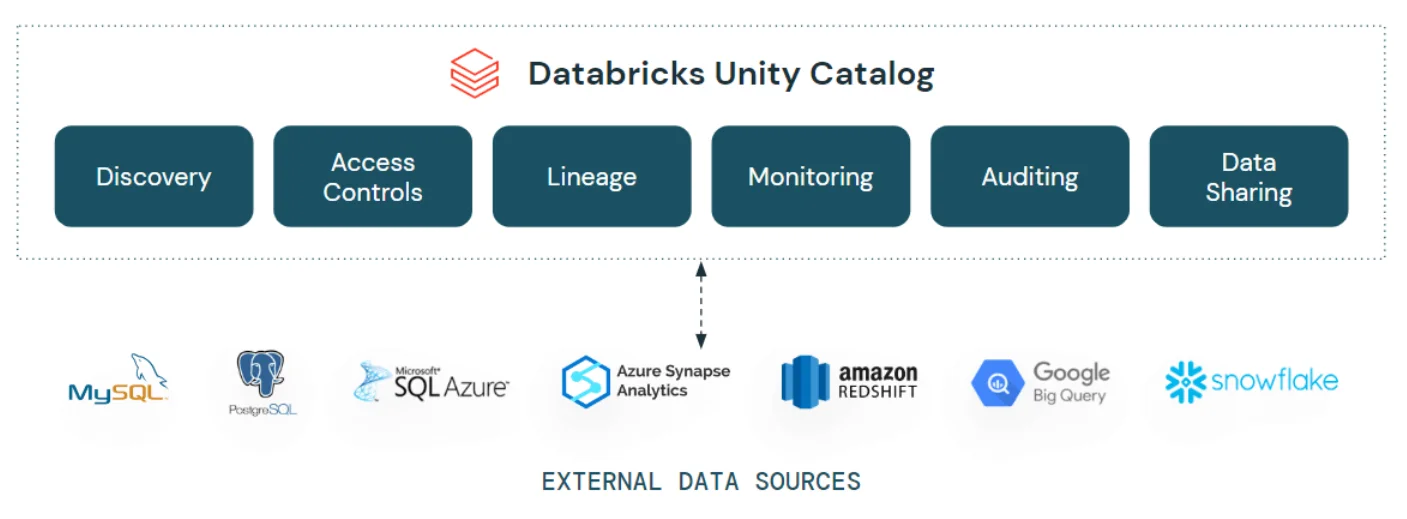
Databricks Unity Catalog - Source: Databricks blog.
Beyond cataloging, Unity Catalog supports data discovery, classification, access control, and monitoring. Additional features, such as Delta Sharing for collaboration and an Enhanced Security and Compliance Add-On, extend its functionality.
Let’s explore the essential data governance native features of Unity Catalog further:
Data cataloging
Permalink to “Data cataloging”Databricks integrates with numerous data sources, including databases, data warehouses, orchestration engines, and other data catalogs to fetch object and lineage metadata. That metadata is then exposed to a Databricks user via the Unity Catalog, which acts as the single access point for data exploration, search, and discovery.
Data discovery
Permalink to “Data discovery”You can use the Catalog Explorer to find and manage objects. It is also the primary interface you use to manage the Unity Catalog and Delta Sharing. You can also explore data in the form of Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs).
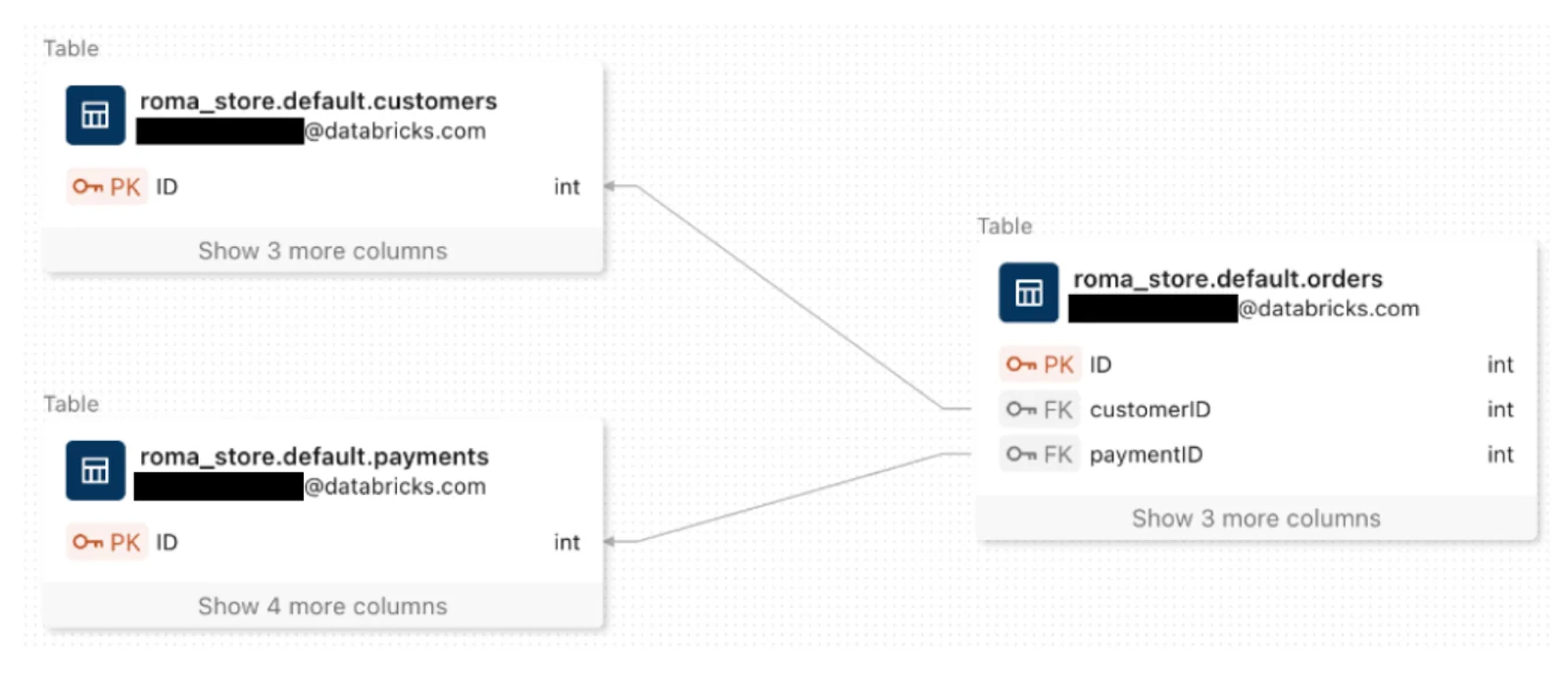
Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) in Unity Catalog - Source: Databricks Documentation.
Access management
Permalink to “Access management”Managing access to Databricks objects in a unified manner is one of the key features of Unity Catalog. You can consistently apply and audit access policies on data across the board, irrespective of the data source. Unity Catalog also lets you integrate Databricks access management with your identity provider like Okta or Microsoft Entra ID.
Data lineage
Permalink to “Data lineage”Databricks offers both table and column-level lineage to provide a detailed view of data flow and changes. This helps with data discovery, exploration, and debugging issues while consuming the data from downstream.
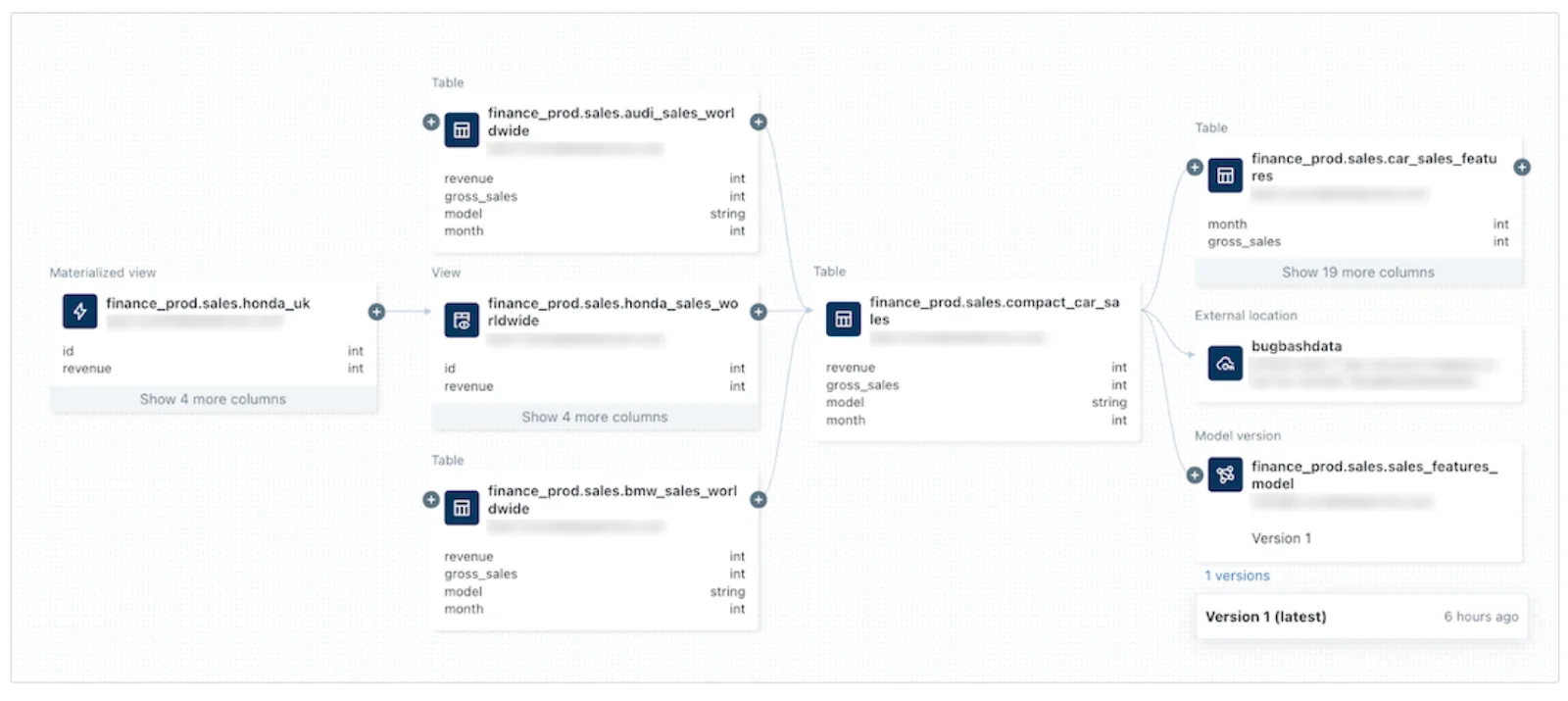
Data lineage in Unity Catalog - Source: Databricks Documentation.
AI-based classification
Permalink to “AI-based classification”There are several areas where Databricks leverages AI and ML capabilities, such as automatic classification of PII data, and root cause analysis of a pipeline issue. Databricks also uses AI to enhance its security monitoring capabilities.
Audit logging and monitoring
Permalink to “Audit logging and monitoring”Unity Catalog also captures essential information with its audit logs and system tables, which can be used to comprehensively audit the Databricks ecosystem for all system and user activity. This includes access logs, network logs, grants, permissions, among other things.
Also, read → Databricks Unity Catalog: Native capabilities
These features lay a solid foundation for data governance within Databricks, but a modern data platform is seldom built on a single data storage or processing tool.
Besides dealing with multiple data sources and targets, you have to manage several data processing tools in your data ecosystem. Managing these diverse systems requires a unified control plane that can oversee data across the entire ecosystem. Atlan addresses this need by complementing Databricks and enabling governance across various tools.
Let’s see how the Atlan + Databricks integration can help you better govern your data across your organization.
Enhancing Databricks data governance with Atlan
Permalink to “Enhancing Databricks data governance with Atlan”Atlan uses an adaptive data governance framework rather than a one-size-fits-all for greater flexibility and ecosystem support. Atlan has close integrations with a wide variety of tools, from which it can bring data assets. It also works closely with metadata and governance engines to offer a seamless translation layer for managing discovery, governance, lineage, and quality activities.
Integrating Atlan with Databricks and other tools results in Atlan being the control plane of data, which is built around the principle of diversity in data assets, personas, data tools, and use cases. Atlan’s integration with Databricks is easy to set up and lets you work with the following features:
- Data access management: Atlan crawls metadata from the Unity Catalog and provides a consistent layer of asset management on top of it with Atlan-specific constructs for ownership, governance, and privilege management, such as Personas, Purposes, and more.
- Extract lineage metadata: Atlan’s lineage extraction gives you three options. You can:
- Hit the Databricks REST API for extracting lineage
- Manually extract lineage and export it to an object store like S3 (more suitable for on-prem deployments of Databricks)
- Query the lineage system tables directly
- Extract usage metadata: Similar to lineage metadata, you can also extract usage metadata for usage and popularity metrics in Atlan. Atlan will get the data from the query history and other system tables for this.
- Automated governance workflows: Atlan lets you create no-code governance workflows for the creation of new data assets, handling of data access requests, and more.
- Automated policy compliance: Atlan helps you define six types of policies for quality, privacy, security, lifecycle, ethics, and data models. You can create and manage these policies using the Policy Center, which you can enable with the help of the admin user.
- Import and update (push) tags : Atlan also helps you enable automatic PII tag propagation and tag-based access policies for better tag-based controls. The Atlan + Databricks connection allows you to both import and push tags, enabling a two-way communication of tags across both systems using Atlan’s reverse sync option.
By integrating with Databricks, Atlan acts as a unified control plane that enhances governance activities while supporting the features of Databricks and other tools in your ecosystem.
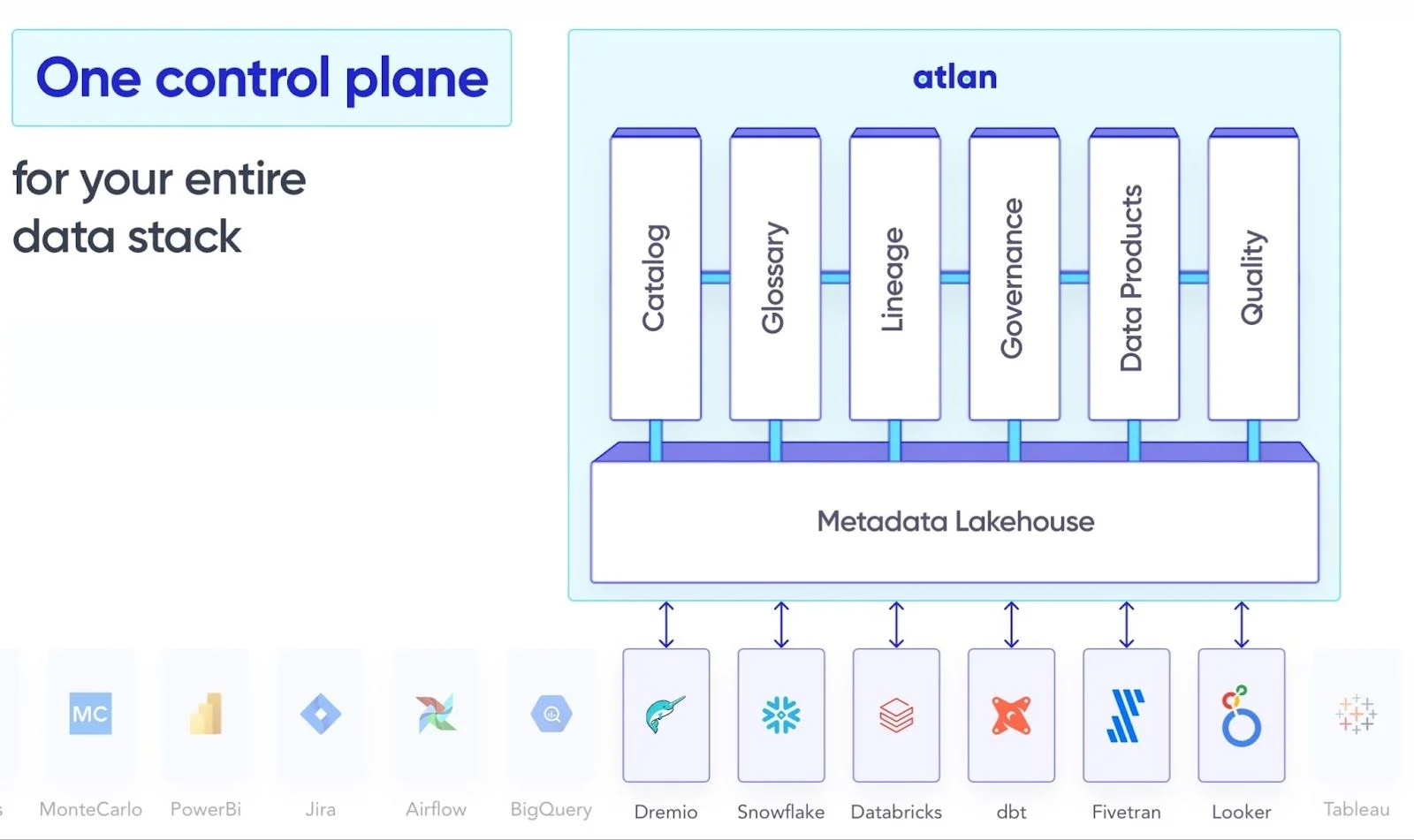
A unified control plane for Databricks data governance - Source: Atlan.
Many businesses, including Contentsquare, REA Group, and Global Excel Management have successfully used Atlan to improve data governance. These companies report greater efficiency and collaboration, demonstrating the value of integrating Atlan with Databricks and other tools.
Summary
Permalink to “Summary”Databricks’ native governance features, built around Unity Catalog, provide a solid foundation for managing data and AI assets. From cataloging and lineage tracking to access control and audit logging, Databricks supports effective data governance within its platform.
However, modern data architectures require governance across diverse tools and systems. By integrating Atlan with Databricks, organizations can create a unified control plane that extends governance capabilities across their entire data ecosystem.
Databricks data governance: Related reads
Permalink to “Databricks data governance: Related reads”- Databricks Summit 2025: What to Expect at the Data + AI Summit
- Data Governance and Compliance: An Act of Checks and Balances
- Data Compliance Management: Concept, Components, Steps (2025)
- Databricks Unity Catalog: A Comprehensive Guide to Features, Capabilities, Architecture
- Data Catalog for Databricks: How To Setup Guide
- Databricks Lineage: Why is it Important & How to Set it Up?
- Databricks Metadata Management: FAQs, Tools, Getting Started
- Databricks Cost Optimization: Top Challenges & Strategies
- Databricks Data Mesh: Native Capabilities, Benefits of Integration with Atlan, and More
- Data Catalog: What It Is & How It Drives Business Value
- Databricks Data Compliance: A Complete 2025 Guide
Share this article


















