What are the five core components of DataHub’s architecture?
Permalink to “What are the five core components of DataHub’s architecture?”LinkedIn DataHub is an open-source metadata platform with data discovery, observability, and governance features that provide context for AI to manage and use data safely.
DataHub’s architecture consists of the following five core components:
- DataHub GMS (Generalized Metadata Service): The backend that handles the CRUD APIs, while also sending events to a Kafka stream.
- Kafka: Kafka streams metadata change and audit events, updates the usage metrics, and also handles DataHub platform events.
- Metadata store: By default this is MySQL.
- Opensearch: An AWS open-source project that combines the functionality of Elasticsearch, Elastic KV, and Kibana to provide search, lineage, glossary, and overall context discovery in DataHub.
- Frontend: The browser-based UI that is accessible to users for managing and interacting with metadata.
DataHub can be deployed on Kubernetes-based services in AWS EKS, Azure AKS, and Google Cloud GKE. The easiest way to start exploring DataHub is using a Docker-based quickstart, which is what we’ll do next.
This quick start will take you through setting up DataHub, loading sample data, exploring the platform, and troubleshooting common errors.
What are the prerequisites for a LinkedIn DataHub quickstart demo?
Permalink to “What are the prerequisites for a LinkedIn DataHub quickstart demo?”Irrespective of what platform your machine is on, there are two key prerequisites to consider:
After installing the Docker Engine, make sure the Docker daemon is running on your system using the docker info command.
How to install key Python libraries and DataHub CLI
Permalink to “How to install key Python libraries and DataHub CLI”Open a terminal and run the following commands. If the commands are successful, you’ll be able to see the DataHub version.
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel setuptools
python3 -m pip install --upgrade acryl-datahub
datahub version
Now, you’re ready to start the installation using the DataHub CLI.
How to use DataHub’s Quickstart for installation
Permalink to “How to use DataHub’s Quickstart for installation”To begin:
- Run Docker quickstart
- Load sample data
Step 1: Running Docker quickstart
Permalink to “Step 1: Running Docker quickstart”A fair bit of complexity is abstracted away by the following command to start your DataHub installation:
datahub docker quickstart
This command uses the docker-compose.yml file that can be read using the following command:
cat .datahub/quickstart/docker-compose.yml
This file describes the containers for all key DataHub components, including their configurations, port bindings, and security rules.
For the quickstart, you don’t need to change anything in the configuration.
Make sure that the following ports are free to avoid any EADDRINUSE errors: 8080 (GMS), 3306 (MySQL), 9092 (Kafka), 9200 (OpenSearch), and 9002 (Frontend). You can clear the port by using a command like sudo lsof -i :9092, which will give you the process ID (PID), after which you can run this command to kill that process kill -9 PID. Please note that these commands are only suitable and safe for running in a sandbox or demo environment and are not suited for production environments.
Once you start the installation, you can monitor the progress on the terminal. Depending on your network connection, installation may take up to 20 minutes to complete.
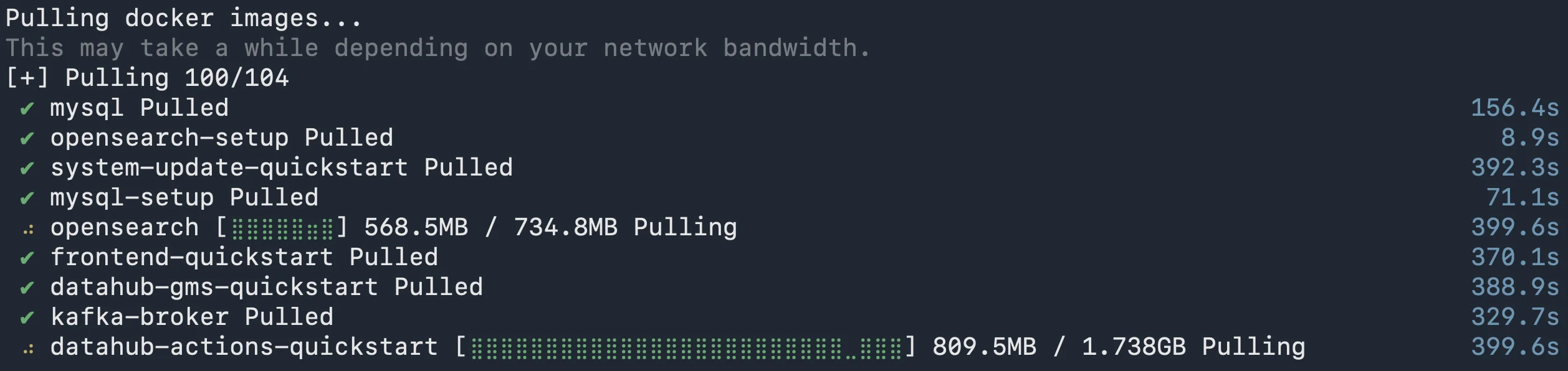
DataHub Docker images being pulled from the registry. Source: Atlan.
Once the process finishes, you’ll see the following message saying “DataHub is now running”:
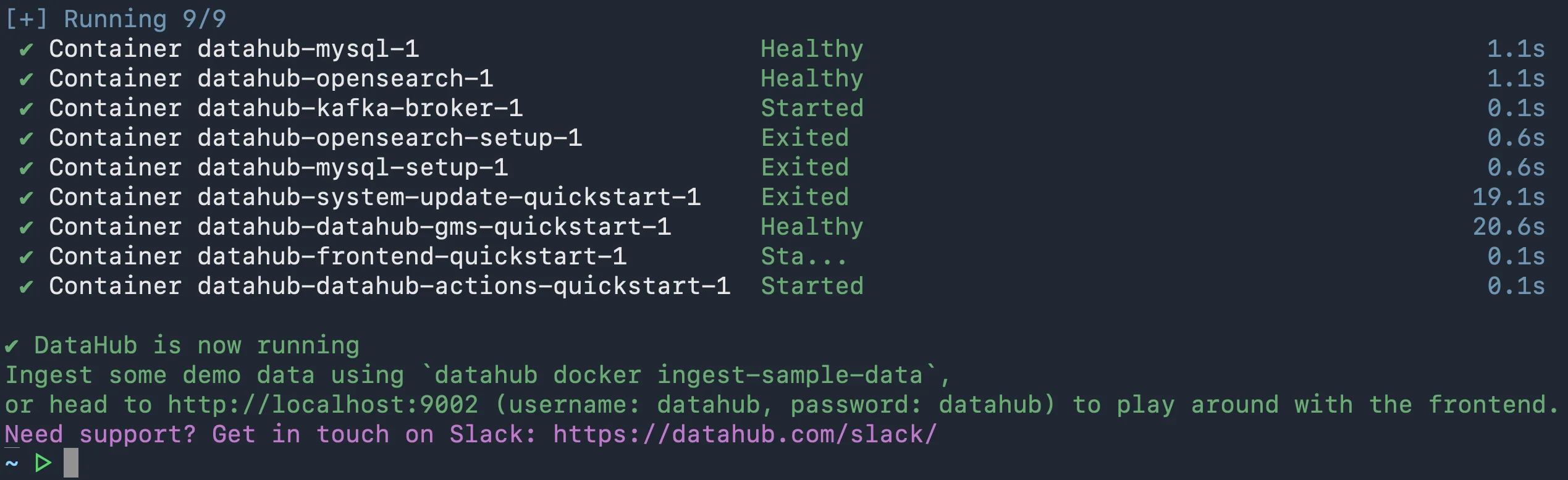
DataHub quickstart installation completed. Source: Atlan.
Step 2: Loading sample data
Permalink to “Step 2: Loading sample data”Let’s load some sample data into DataHub using the following command:
datahub docker ingest-sample-data
You’re now ready to log in to DataHub from the browser.
Exploring the DataHub UI
Permalink to “Exploring the DataHub UI”Log onto http://localhost:9002, where you should be able to see the following login screen:
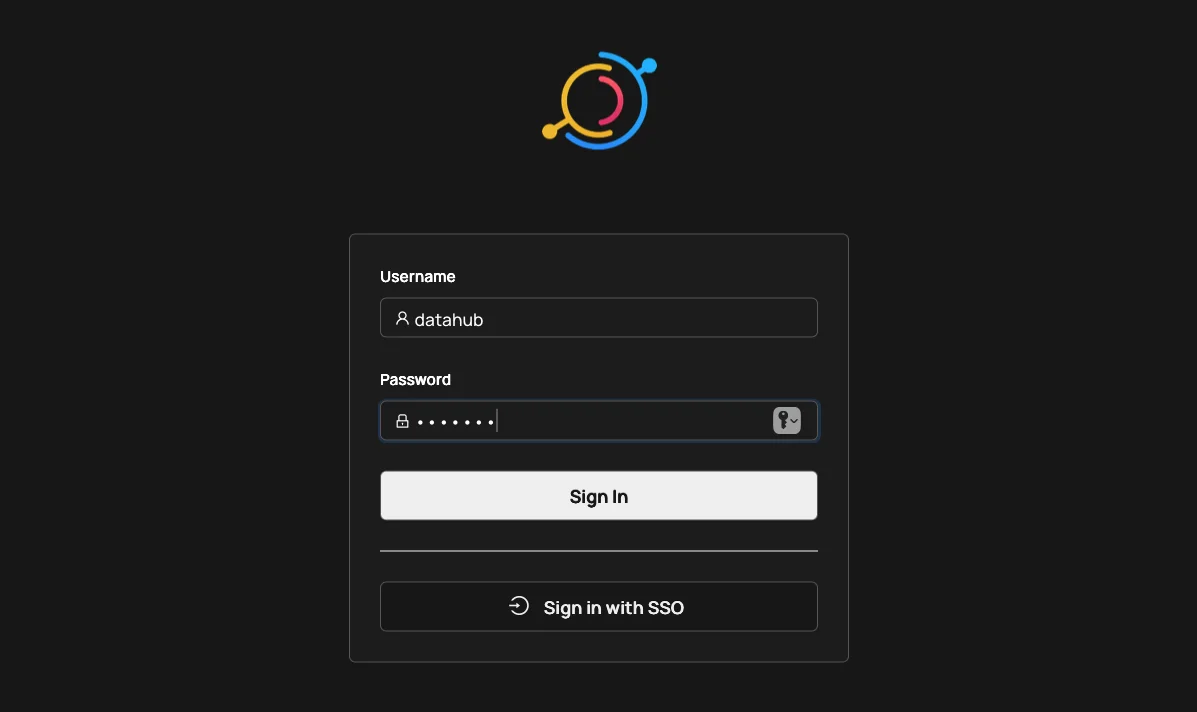
Logging into the DataHub UI. Source: Atlan.
Login credentials:
- Username: datahub
- Password: datahub
Press the Sign In button. Once you do that, you’ll land on the following landing page.
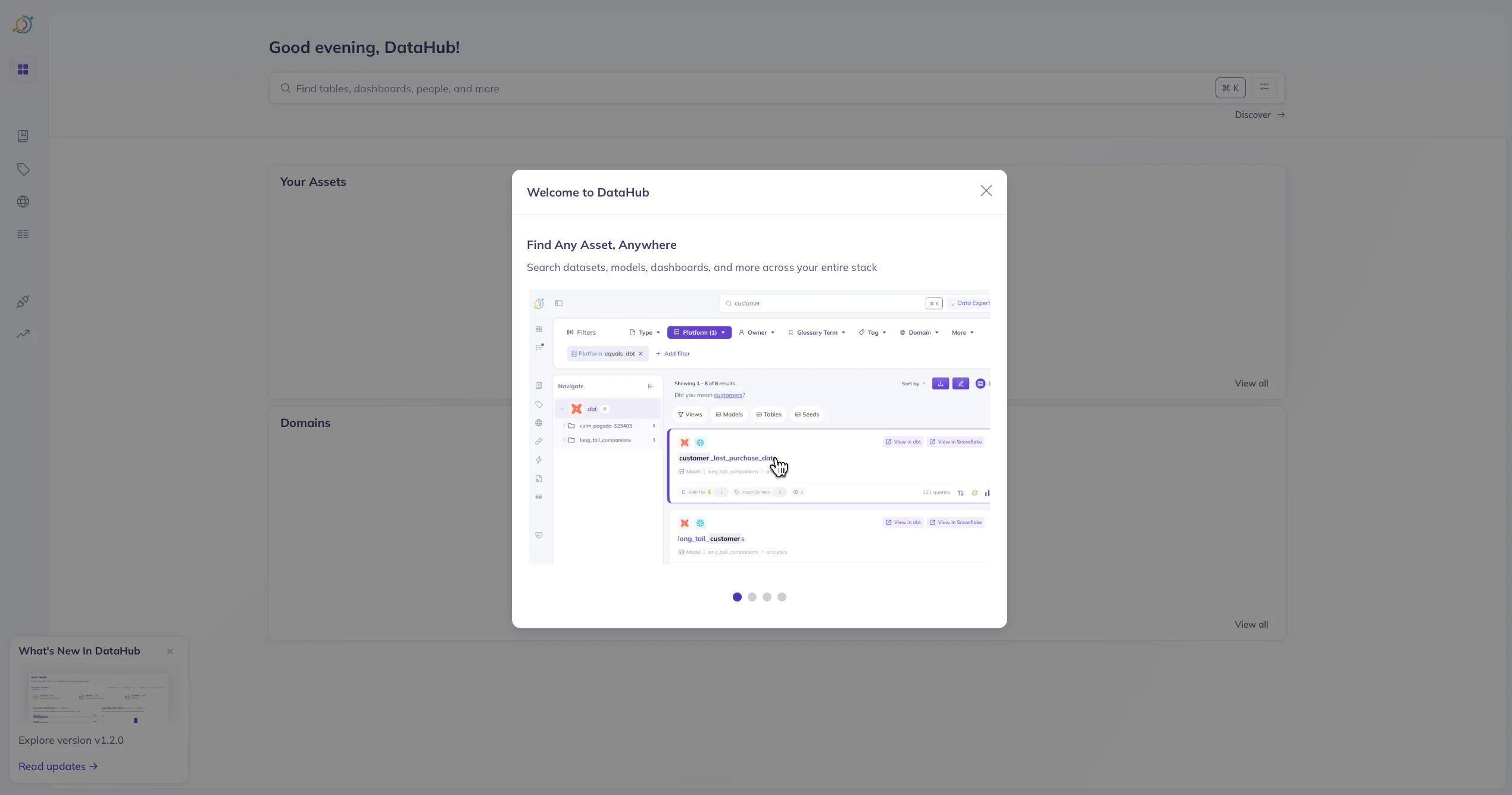
DataHub UI. Source: Atlan.
Managing data sources in DataHub
Permalink to “Managing data sources in DataHub”After loading the sample data, you’ll see a data source added. This data source is a REST endpoint that references the sample data. You can add metadata into DataHub from a range of sources.
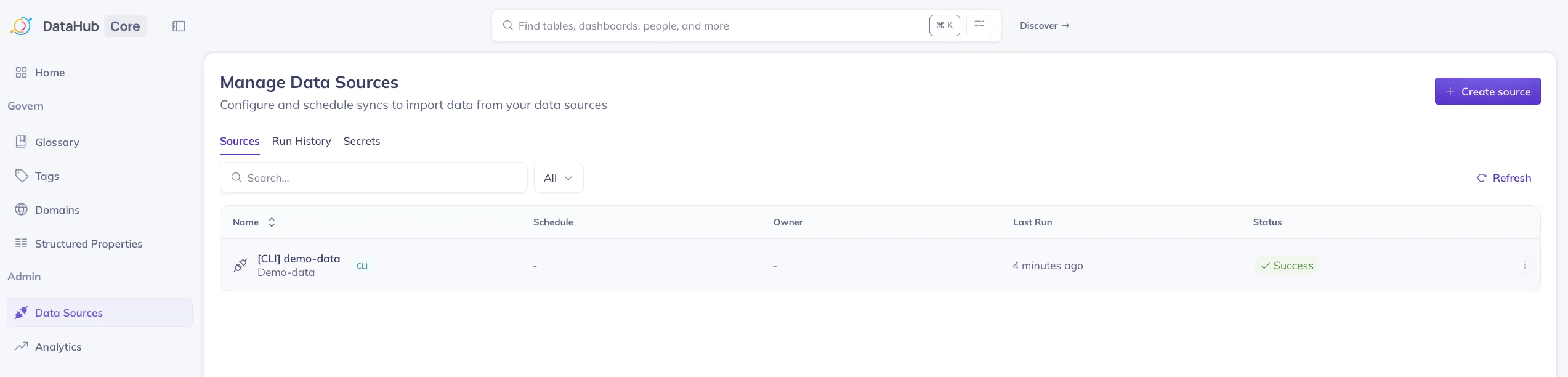
Managing data sources in DataHub. Source: Atlan.
Depending on the use case, you can either refresh the metadata for a given data source manually or you can refresh it based on a schedule, as shown in the image below.
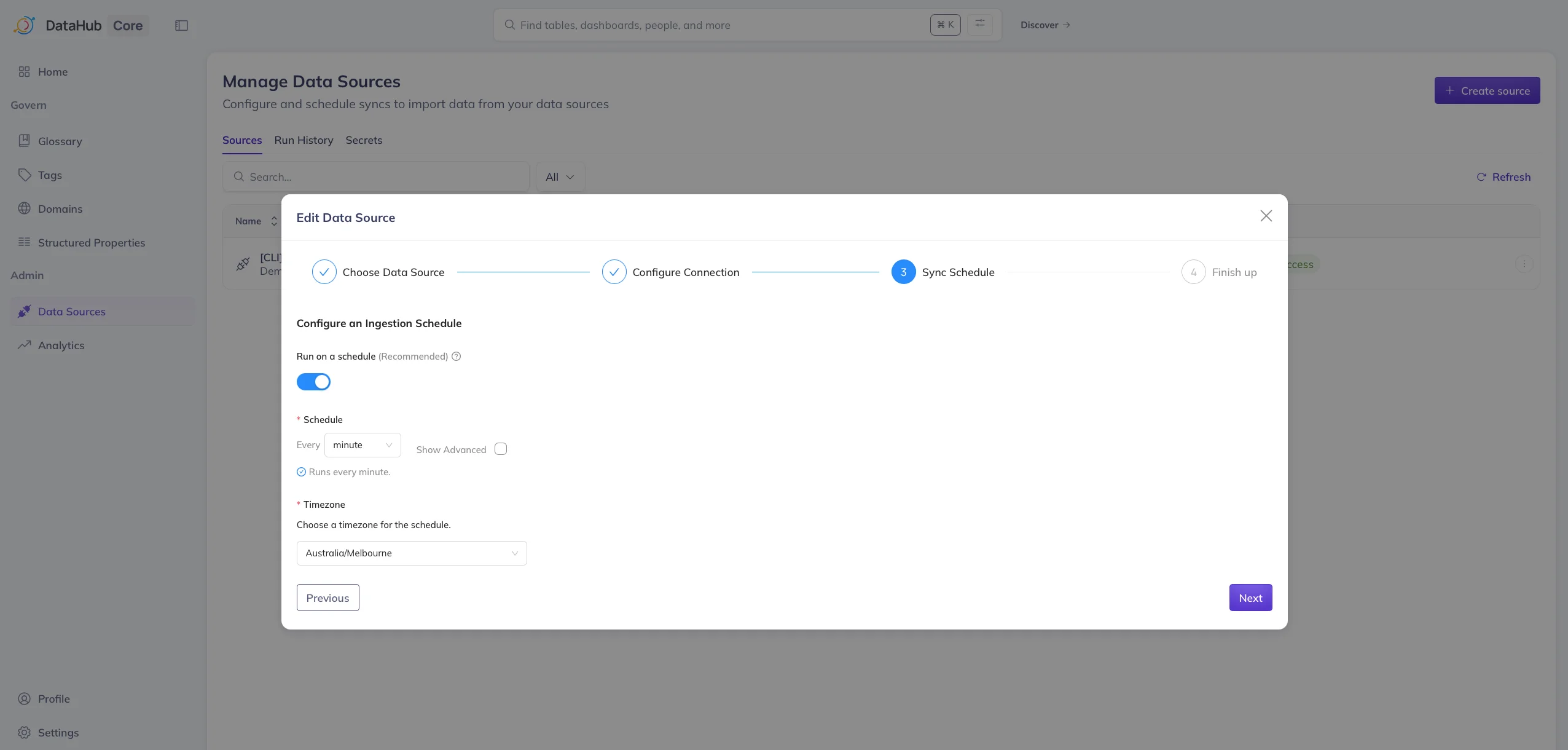
Updating data sources in DataHub. Source: Atlan.
Common issue: Tags not loading or OpenSearch delays
Permalink to “Common issue: Tags not loading or OpenSearch delays”A quick sidenote before we move on to the next section – after loading a bunch of metadata for testing purposes, you might see a lar and even see errors like the following in the JS console:
Failed to load tags: java.lang.RuntimeException: Failed to execute search: entity types [TAG], query , filters: null, start: 0, count: 10
Or you might see errors that pop up on the page, similar to the one illustrated below.
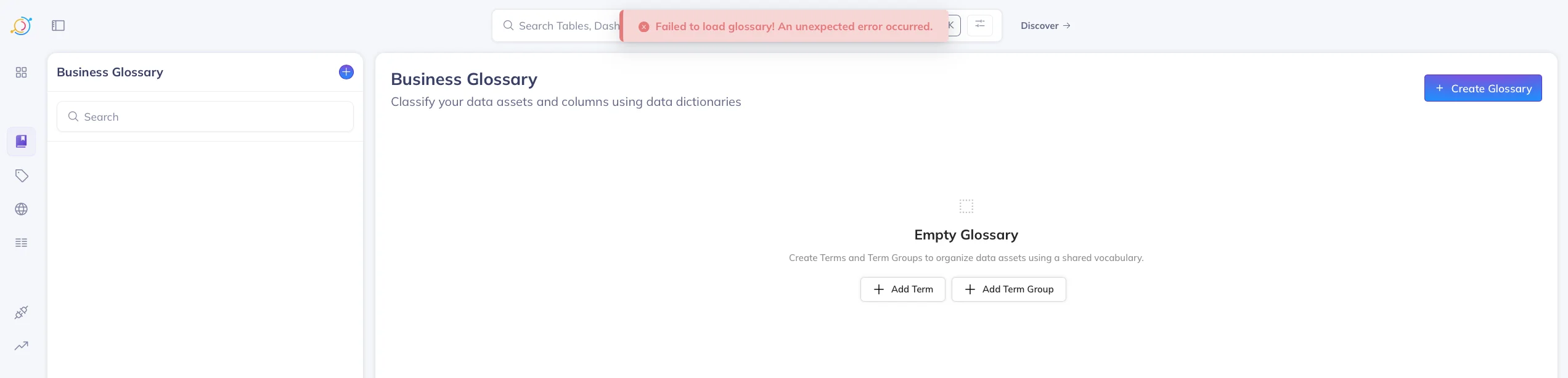
Error messages in DataHub. Source: Atlan.
One explanation for DataHub’s failure to update OpenSearch indexes in a timely manner: If the page is stuck, restart the quickstart using the DataHub CLI. You can just run the datahub docker quickstart command to do that.
Discovering data assets in DataHub
Permalink to “Discovering data assets in DataHub”Use the top search bar to find:
- Tables
- Dashboards
- Reports
- Pipelines
- Glossary terms
Below this search bar is a list of recently accessed assets.
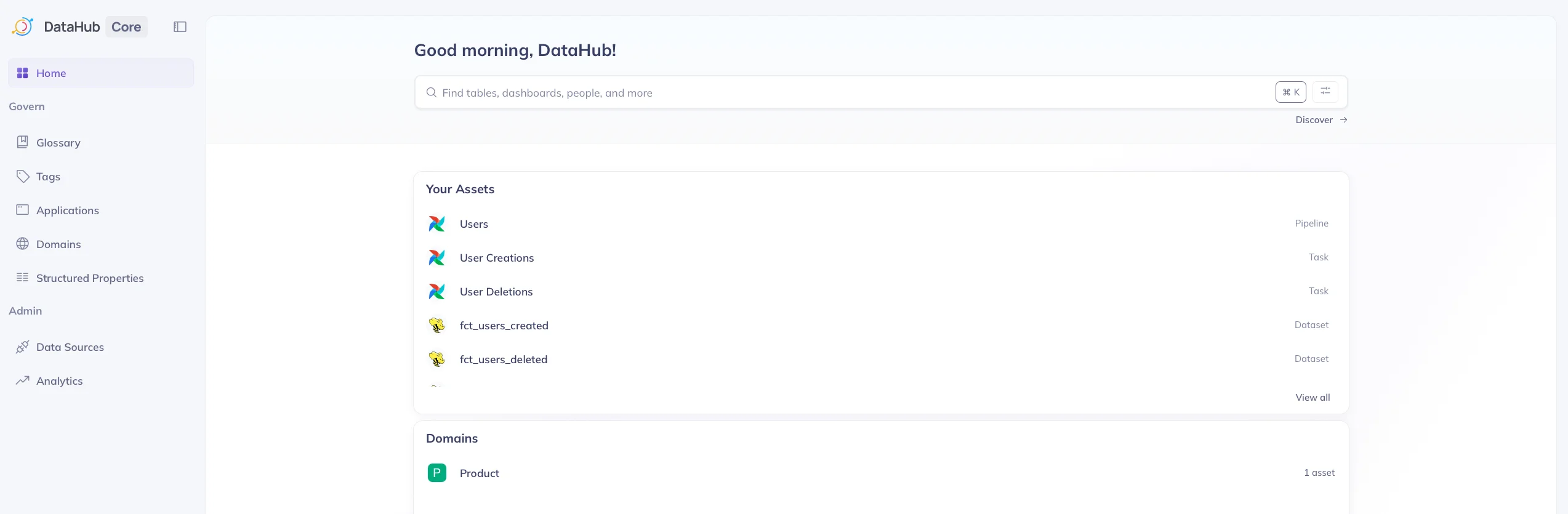
Recently accessed assets listed on DataHub UI. Source: Atlan.
Pressing the Discover button leads you to the following page, which allows you to manage all the data assets registered within DataHub. The following image shows metadata from multiple sources, such as Hive, Spark, MySQL, Redshift, Airflow, etc., loaded into DataHub.
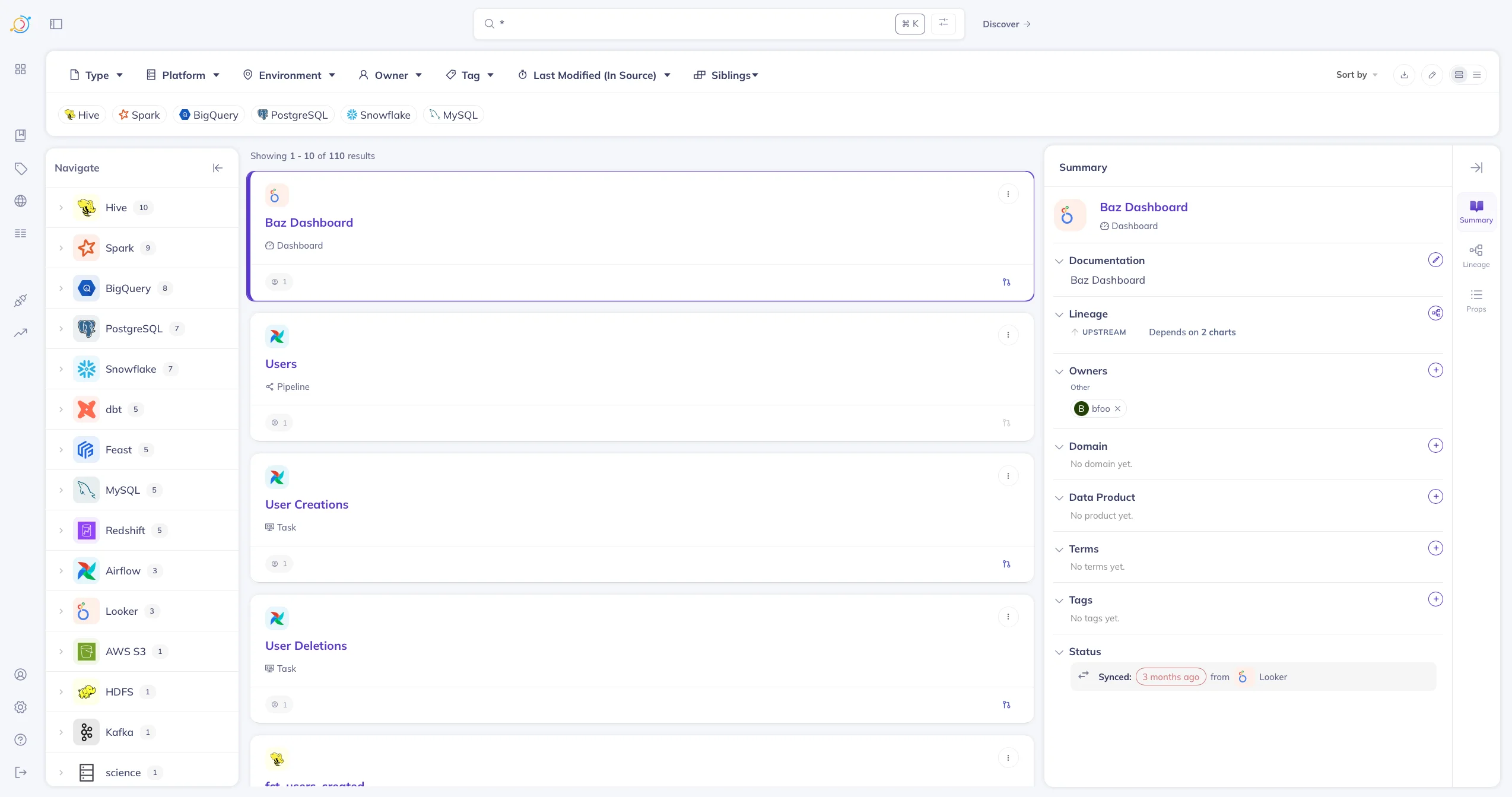
Discovering data assets in DataHub. Source: Atlan.
Let’s dive one level deeper and take a look at how you can manage data assets in DataHub.
Managing a data asset in DataHub
Permalink to “Managing a data asset in DataHub”Each asset page includes:
- Data structure and profile: Technical metadata along with descriptive statistics.
- Business context and documentation: Description and notes for the data asset.
- Data quality: Automated tests for checking data quality.
- Data governance: Tags, domains, owners, lineage, and glossary terms.
The following image shows a Snowflake data asset, invoices_18 in the reporting schema selected on the page.
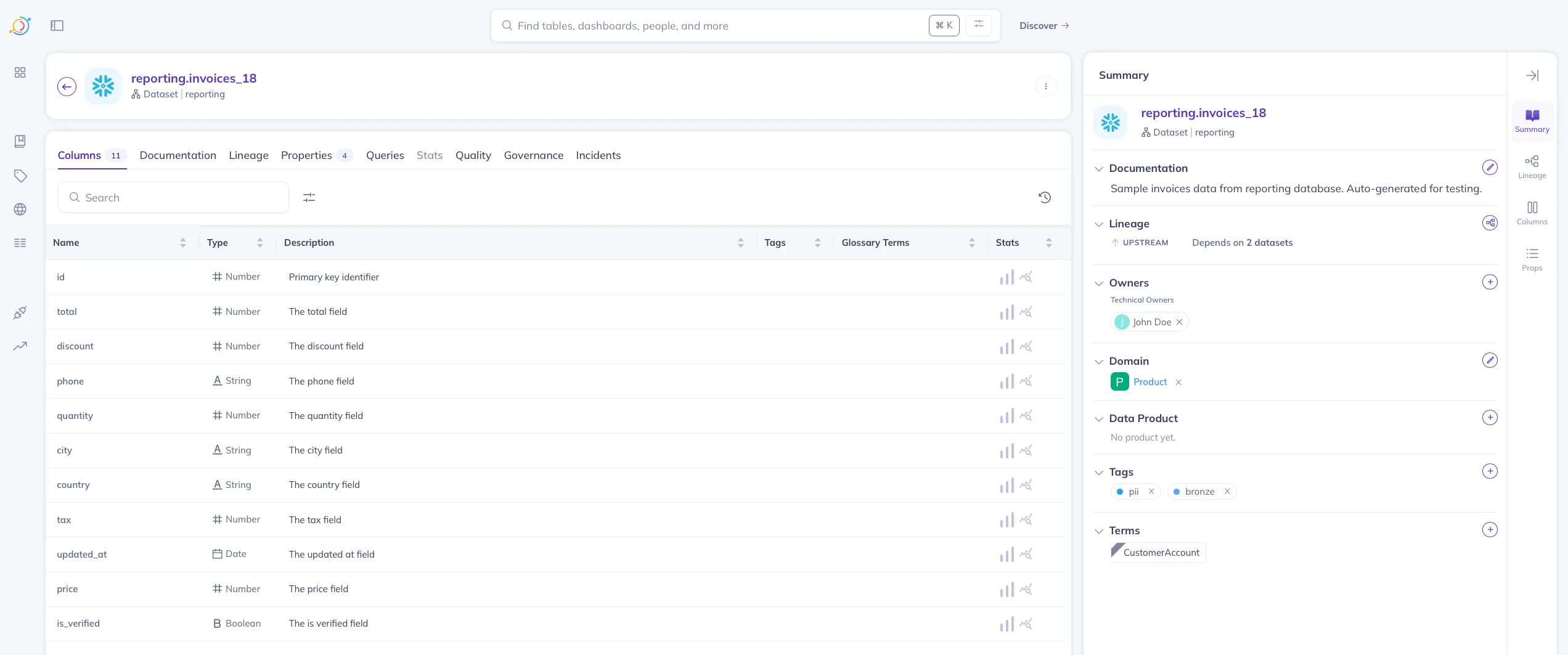
A sample Snowflake data asset on the DataHub UI. Source: Atlan.
Column-level lineage in DataHub
Permalink to “Column-level lineage in DataHub”Here’s a quick look at the column-level lineage interface of DataHub.
DataHub’s lineage view includes:
- Upstream sources
- Downstream dashboards/reports
- Transformation-level relationships
- Impact analysis
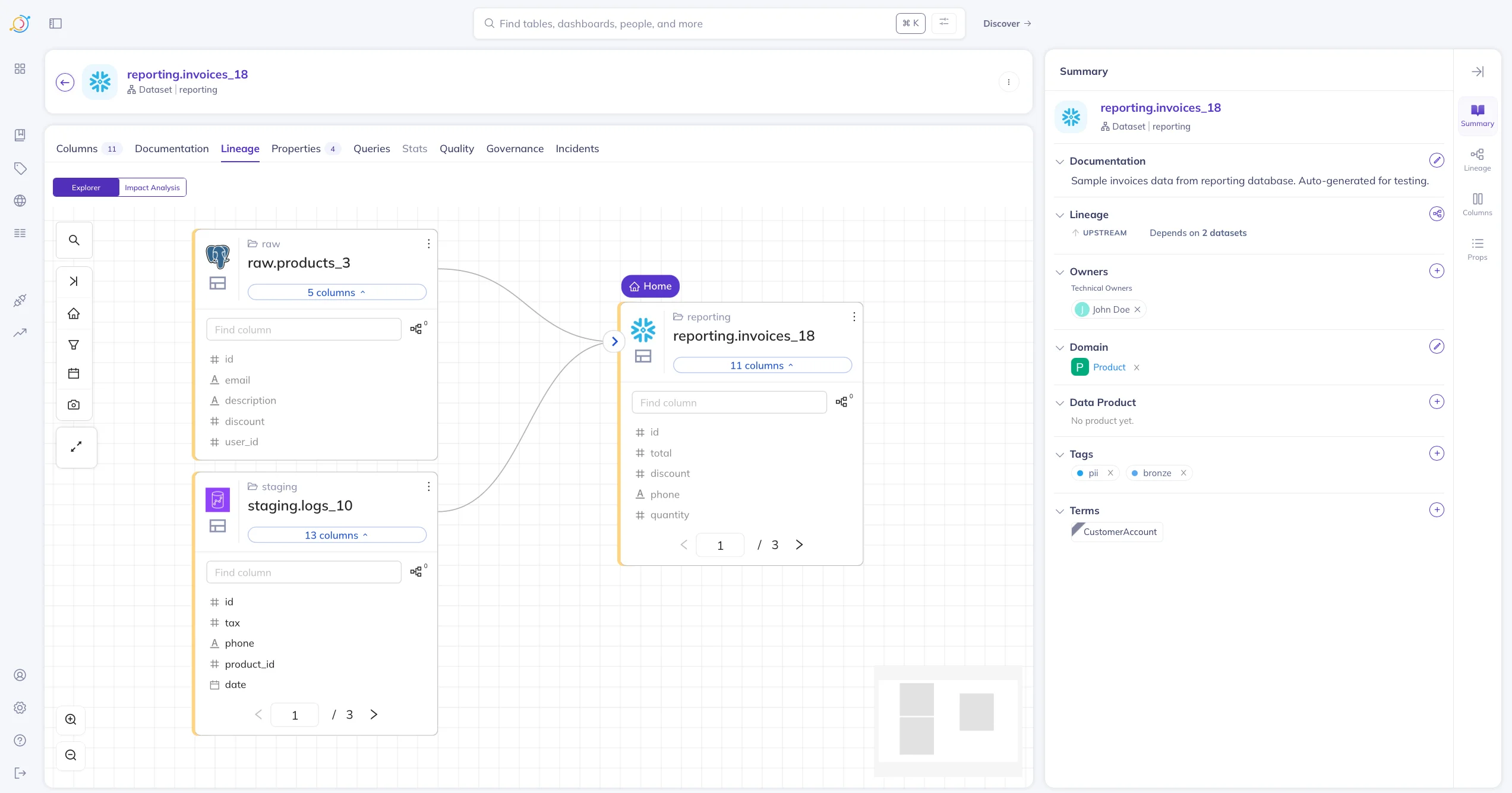
Column-level lineage in DataHub. Source: Atlan.
DataHub asset summary
Permalink to “DataHub asset summary”The Summary page highlights:
- Asset counts by category
- Domain distribution
- Glossary coverage
- Platform-level usage metrics
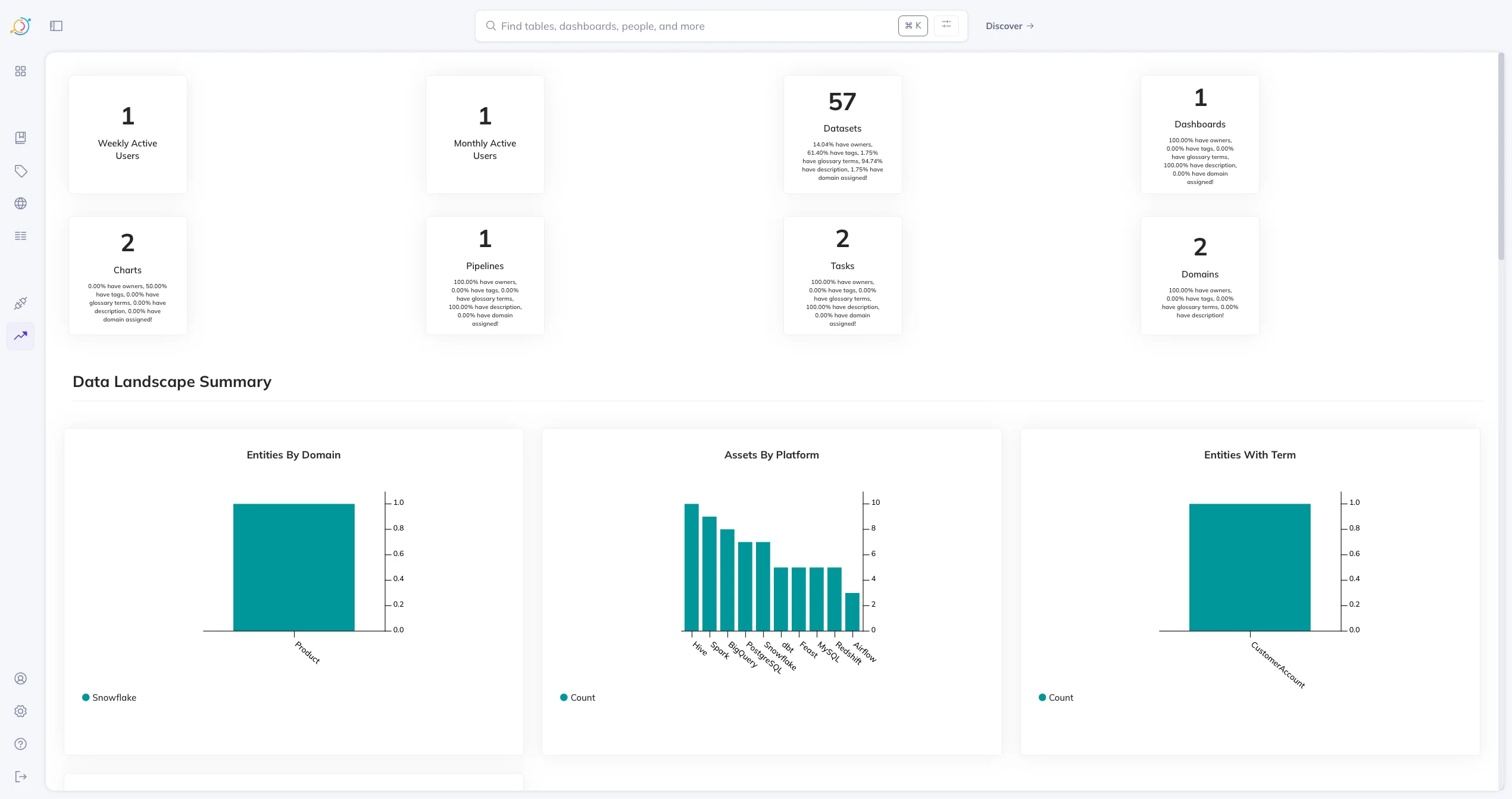
DataHub asset summary page. Source: Atlan.
This page is driven by platform-level events, which can update these metrics and distributions in real-time.
DataHub has a lot of other features, such as Compliance Forms, Data Usage & Query History, Incidents, Applications, etc., the full list of which you can find here in the official documentation.
Next, let’s look at the limitations of and best practices for running DataHub.
What are the limitations of LinkedIn DataHub?
Permalink to “What are the limitations of LinkedIn DataHub?”Many of the key limitations of DataHub center on the management, governance, and security of its components. Here are some examples:
- Metadata testing and data quality monitoring aren’t fully automated in the open-source version of DataHub.
- Metadata discovery can be slow at times, especially when you have a large number of data assets in your data ecosystem.
- Built-in logging and observability are limited; third-party tooling may be required to integrate with DataHub.
- Reliability and scalability of the platform will need additional maintenance work.
- Many key features, especially those related to automation, are not available in the open-source version of DataHub.
Most limitations require ongoing engineering or DevOps resources to manage. Let’s now look at some general best practices for running DataHub.
What are the best practices for running a LinkedIn DataHub demo?
Permalink to “What are the best practices for running a LinkedIn DataHub demo?”To ensure reliable, scalable deployments on DataHub , you should ensure the following:
- Use Docker only for demos: The Docker quickstart is just for you to test the waters. Use Helm for production deployments, whether on-premises or in the cloud with AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Scale OpenSearch: The Docker quickstart only has a minimal number of nodes for every service that makes DataHub work. Deploy multi-node clusters to handle indexing load.
- Integrate with your IdP: To ensure secure access to DataHub, integrate it with your organization’s IdP using one of the identity integration methods DataHub supports.
- Rebuild OpenSearch indexes periodically: For data discovery to work( in real-time) and for recent metadata updates to be searchable from the UI, you must ensure that the OpenSearch indexes are rebuilt periodically.
- Set up observability: To ensure the reliable working of DataHub, you need to configure DataHub’s logging, monitoring, and observability the right way. If required, you can integrate with log aggregation and monitoring tools.
- Backups: Another key thing that’s needed for your production DataHub deployment is a comprehensive backup strategy. Backing up the core backend database is the most important. You can also backup other metadata storage components too.
- Apply enterprise security & governance policies: Implement the usual security, networking, and governance guardrails and controls, especially when using open-source software in production.
Ready to explore this LinkedIn DataHub demo for your use case?
Permalink to “Ready to explore this LinkedIn DataHub demo for your use case?”DataHub’s quickstart demo gives you a fast, hands-on way to understand how its metadata, lineage, and search capabilities work in practice. Whether you’re evaluating open-source metadata platforms, building a proof of concept, or testing fit for AI-era governance, the Docker quickstart offers the simplest path to get started.
However, if you’re looking for deeper deployment options, extensible APIs, and rich metadata management, then consider an enterprise alternative like Atlan.
FAQs about LinkedIn DataHub demo
Permalink to “FAQs about LinkedIn DataHub demo”1. Is LinkedIn DataHub free?
Permalink to “1. Is LinkedIn DataHub free?”Yes. DataHub is fully open-source under the Apache 2.0 license. You can self-host it at no cost, but enterprise-grade reliability requires engineering time for deployment, scaling, monitoring, and maintenance.
2. How long does it take to set up a DataHub demo?
Permalink to “2. How long does it take to set up a DataHub demo?”The Docker quickstart usually takes 15–20 minutes (for a technical user), depending on your system and network speed.
A full production deployment takes significantly longer because it requires Kubernetes configuration, multi-node OpenSearch clusters, authentication setup, and monitoring.
3. What are the biggest limitations of open-source DataHub?
Permalink to “3. What are the biggest limitations of open-source DataHub?”Key limitations include:
- Limited automation for data quality and metadata testing
- Slow search/index updates at scale
- Lightweight logging and observability
- Manual operational overhead for upgrades, monitoring, and performance tuning
- Many advanced enterprise features available only in the commercial SaaS offering
4. When should I consider an out-of-the-box, commercial alternative to LinkedIn DataHub?
Permalink to “4. When should I consider an out-of-the-box, commercial alternative to LinkedIn DataHub?”Choose an out-of-the-box metadata control plane as an alternative to LinkedIn DataHub when you need:
- Zero-maintenance hosting
- SSO/identity integration
- Enterprise SLAs
- Built-in monitoring, scaling, and secure deployment
- Advanced governance and automation features
- Column-level, cross-system, automated and actionable data lineage
- AI governance, app framework, MCP support
Share this article



















