OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Compare Architecture, Capabilities, Integration & More
OpenMetadata and DataHub explained
Permalink to “OpenMetadata and DataHub explained”Summarize and analyze this article with 👉 🔮 Google AI Mode or 💬 ChatGPT or 🔍 Perplexity or 🤖 Claude or 🐦 Grok (X) .
What is OpenMetadata?
Permalink to “What is OpenMetadata?”OpenMetadata is an open-source platform built to unify metadata across tools, enabling discovery, observability, and governance.
Born from the team behind Databook at Uber, it offers metadata flexibility and extensibility. Its latest update (Nov 2023) added support for:
- Domains
- Data products
- Modern data mesh architectures
GitHub stats – ≈ 7.2 k ⭐ | Latest release – v1.8.8 – July 2025 (GitHub)
What is DataHub?
Permalink to “What is DataHub?”DataHub is LinkedIn’s second open-source metadata platform, built after WhereHows, to unify metadata across diverse systems.
It uses a generalized metadata service for discovery and governance. DataHub’s October 2023 release added capabilities, such as:
- Column-level lineage for tools like dbt, Redshift, Power BI, and Airflow
- Improvements around cross-platform lineage with Kafka and Snowflake
- Support for Data Contracts (only in CLI)
GitHub stars – ≈ 10.9 k ⭐ | Latest release – v1.2.0 – July 2025 (GitHub)
What are the six key differences between OpenMetadata and DataHub?
Permalink to “What are the six key differences between OpenMetadata and DataHub?”Let’s compare OpenMetadata vs- DataHub based on 6 critical factors driving business use cases for your organization:
- Architecture and technology stack:
- OpenMetadata offers a simpler architecture with a unified metadata model.
- DataHub provides a more complex, streaming-first setup with broader API and graph capabilities.
- Metadata modeling and ingestion:
- OpenMetadata relies on Airflow for pull-based extraction.
- DataHub uses Kafka for pull/push flexibility.
- Data governance capabilities:
- OpenMetadata enriches governance with contextual metadata like Importance for better discovery.
- DataHub emphasizes automation with its event-based Actions Framework.
- Table and column-level lineage: Both platforms support column-level lineage with support for various modern data tools.
- Data quality and data profiling:
- OpenMetadata offers built-in data quality profiling and a native framework.
- DataHub provides native assertions, contract support, and integrations for external data quality checks.
- Upstream and downstream integrations: Both platforms have a plugin-based architecture for metadata ingestion.
Let’s consider each of these factors in detail and clarify our understanding of how they fare.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: How do their architecture and technology stacks compare?
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: How do their architecture and technology stacks compare?”OpenMetadata
Permalink to “OpenMetadata”OpenMetadata opts for a simpler, schema-first architecture focused on extensibility and flexibility with a unified metadata model.
MySQL stores all the metadata, which is thoroughly searchable – powered by Elasticsearch. Systems and people using OpenMetadata interact with the REST API either calling it directly or via the UI.
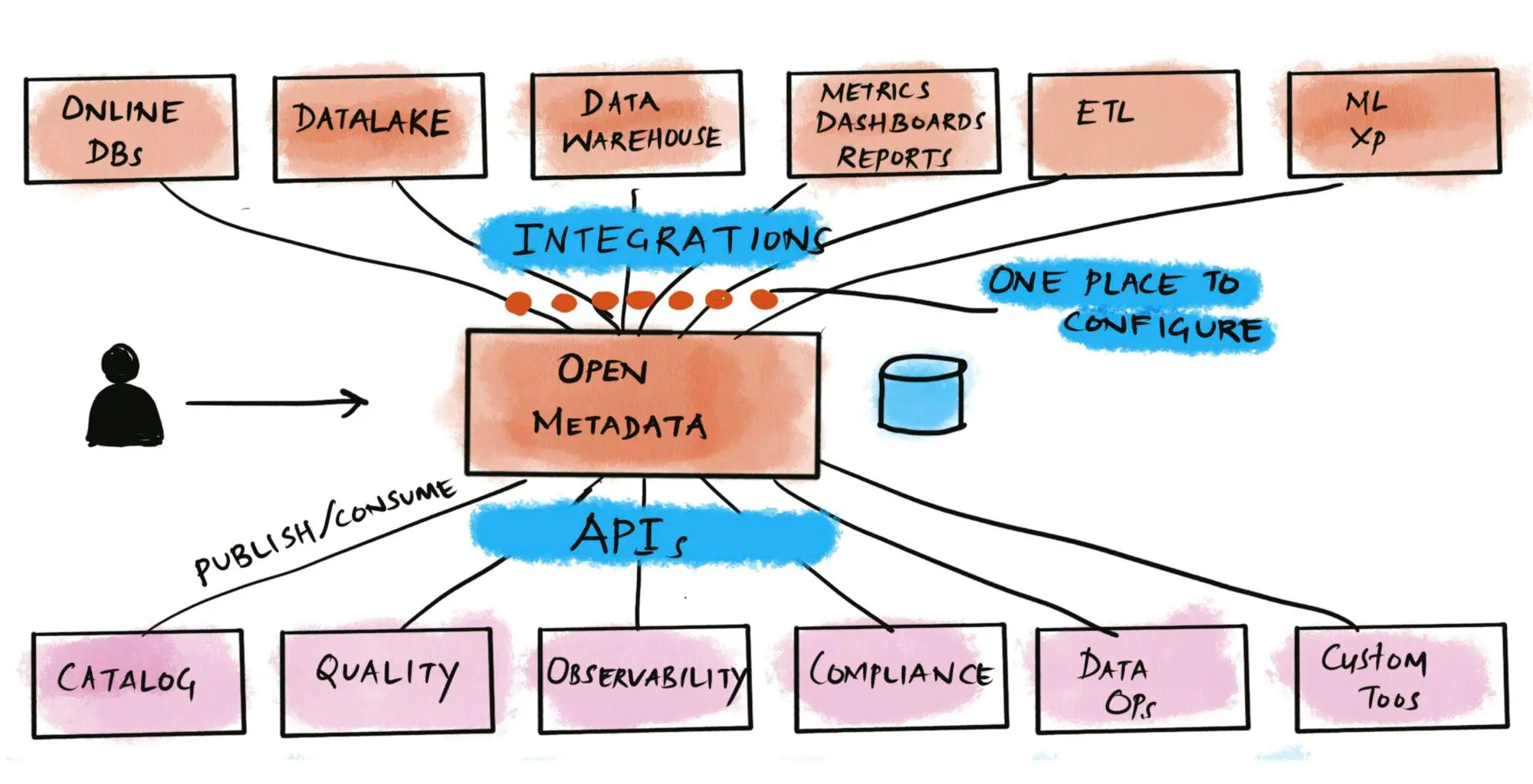
From fragmented, duplicated, and inconsistent metadata to a unified metadata system. Source: OpenMetadata
DataHub
Permalink to “DataHub”On the other hand, DataHub uses a more distributed, real-time ingestion design with Kafka to store the data in three separate layers:
The data in these layers is served via an API service layer.
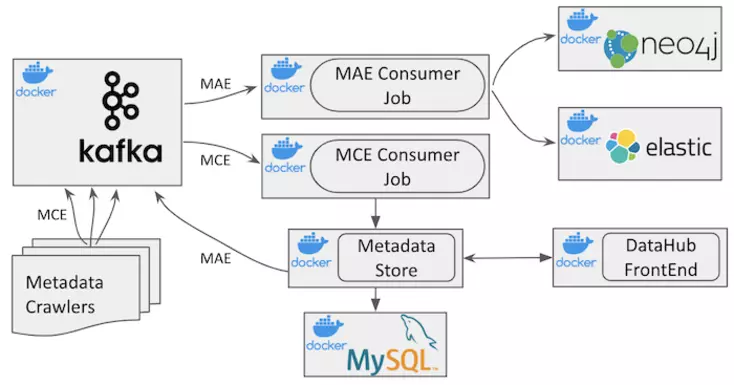
High level understanding of DataHub architecture. Image source: LinkedIn Engineering
In addition to the standard REST API, DataHub also supports Kafka and GraphQL for downstream consumption.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Architecture & tech stack comparison summary
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Architecture & tech stack comparison summary”Feature | OpenMetadata | DataHub |
|---|---|---|
Architecture | MySQL + Elasticsearch; no dedicated graph DB | MySQL + Elasticsearch + Neo4j; Kafka-mediated ingestion engine |
APIs & ingestion | REST API; batch ingestion | REST, GraphQL, and Kafka; supports real-time metadata streaming |
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: What are the differences in metadata modeling and ingestion?
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: What are the differences in metadata modeling and ingestion?”One of the major differences between the two tools is that DataHub focuses on both pull and push-based data extraction, while OpenMetadata is clearly designed for a pull-based data extraction mechanism.
Both DataHub and OpenMetadata, by default, primarily use push-based extraction, although the difference is that DataHub uses Kafka and OpenMetadata uses Airflow to extract the data.
Different services in DataHub can filter the data from Kafka and extract what they need, while OpenMetadata’s Airflow pushes the data to the API server, DropWizard, for downstream applications.
Both tools also differ in how they store the metadata.
DataHub uses the Pegasus Definition Language (PDL) with custom annotations to store the model metadata. Meanwhile, OpenMetadata uses annotated JSON schema-based documents to store entity relationships.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Metadata modeling & ingestion comparison summary
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Metadata modeling & ingestion comparison summary”Feature | OpenMetadata | DataHub |
|---|---|---|
Extraction mechanism | Primarily pull-based via Airflow | Pull and push-based via Kafka |
Ingestion flow | Airflow pushes data to DropWizard API server | Services extract filtered data from Kafka |
Metadata storage format | Annotated JSON schema-based documents | Annotated Pegasus Definition Language (PDL) |
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: What are the differences in data governance capabilities?
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: What are the differences in data governance capabilities?”Both OpenMetadata and DataHub offer built-in role-based access control for managing access and ownership.
To improve your search and discovery experience:
- OpenMetadata introduces concepts like Importance, to provide additional context
- DataHub uses a construct called Domains as a high-level tag on top of the usual tags and glossary terms
In 2022, DataHub released their Actions Framework to power up the data governance engine. The Actions framework is an event-based system that allows you to trigger external workflows for observability purposes. The data governance engine automatically annotates new and changed entities.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Data governance capabilities comparison summary
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Data governance capabilities comparison summary”Feature | OpenMetadata | DataHub |
|---|---|---|
Governance automation | Automatically annotates new and updated entities | Event-driven Actions Framework to trigger external workflows |
Access and ownership | Role-based access control | Role-based access control |
Context for discovery | Importance scores add relevance and context to search and discovery | Domains layered over tags and glossary for enhanced search |
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: What are the differences in data lineage capabilities?
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: What are the differences in data lineage capabilities?”OpenMetadata
Permalink to “OpenMetadata”Both table-level and column-level lineages were already available in OpenMetadata. Support for column-level lineage using the API has also been around since the 0.11 release in July 2022.
OpenMetadata’s Python SDK for Lineage allows you to fetch custom lineage data from your data source entities using the entityLineage schema specification for storing lineage data.
DataHub
Permalink to “DataHub”Since the November 2022 release, DataHub has been able to support column-level data lineage. More improvements were made over the course of the last year.
With DataHub, you can extract column-level lineage in three different ways now:
- Automatic extraction
- DataHub API
- File-based lineage
Column-level lineage is supported for BigQuery, Snowflake, dbt, Looker, PowerBI, and 20+ modern data tools.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Data lineage capabilities comparison summary
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Data lineage capabilities comparison summary”| Feature | OpenMetadata | DataHub |
|---|---|---|
| Column-level lineage | Available since v0.11 (July 2022) | Available since November 2022 |
| Extraction methods | Python SDK using entityLineage schema to fetch custom lineage | Three methods: • Automatic extraction • API • File-based ingestion |
| Tool support | SDK-based, customizable per data source | Built-in support for BigQuery, Snowflake, dbt, Looker, Power BI, and 20+ modern tools |
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: How do they compare on data quality monitoring and profiling?
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: How do they compare on data quality monitoring and profiling?”OpenMetadata
Permalink to “OpenMetadata”OpenMetadata has integrated data quality and profiling and allows data quality tests for supported database connectors. Using OpenMetadata’s Data Quality workflows, you can:
- Run assertions using out-of-the-box tests (for business and data engineering
- Send test failure notifications
- Track real-time test failure
- Inform data consumers on data quality test resolutions
You can also write custom tests using the API and OpenMetadata’s SDK.
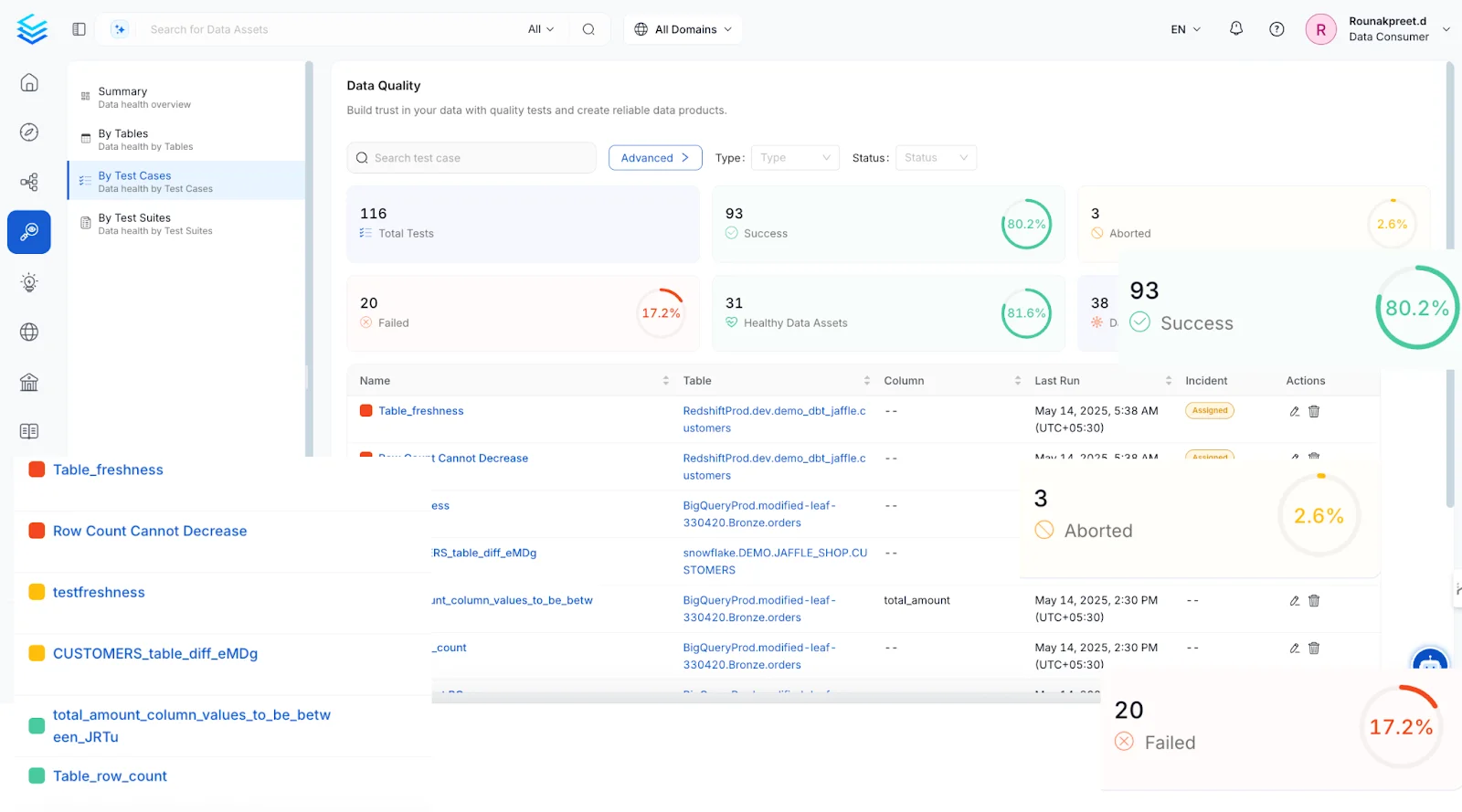
Data quality in OpenMetadata. Image source: OpenMetadata
Meanwhile, OpenMetadata’s Profiler tab helps you understand the shape of your data and to quickly validate assumptions.
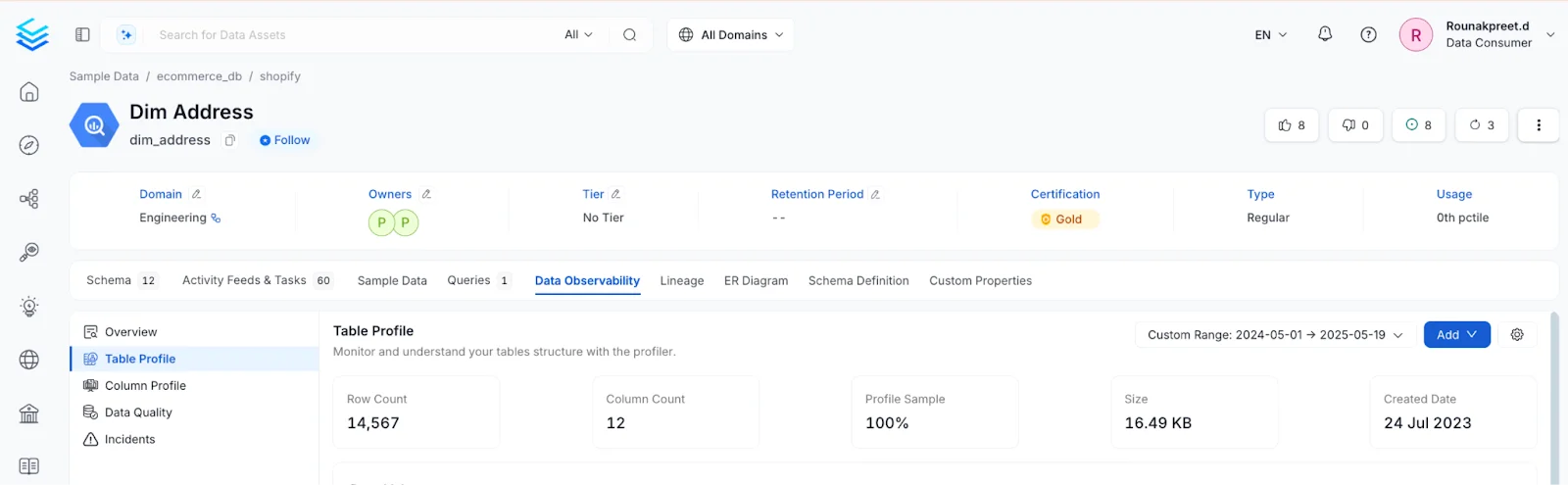
Data profiling in OpenMetadata. Image source: OpenMetadata
As of June 2025, OpenMetadata 1.8 has introduced data contracts–machine‑readable schemas, SLAs, and quality guarantees that can be enforced automatically.
DataHub
Permalink to “DataHub”By default, it doesn’t provide any data quality information for ingested assets. For that information, you must use tools like Great Expectations and dbt tests, with which DataHub integrates seamlessly. So, you can use these tools to fetch the metadata and their testing and validation results.
Like in OpenMetadata, you can create custom data quality assets in DataHub using API and SDKs.
DataHub also supports assertions–to define and run native data quality tests–and data contracts to enforce data quality at the source and target layers.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Data quality and monitoring comparison summary
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Data quality and monitoring comparison summary”Feature | OpenMetadata | DataHub |
|---|---|---|
Native data quality framework | Yes — OpenMetadata Data Quality Framework with ~30 built-in tests | To an extent. It supports assertions to define and run native data quality tests and data contracts. |
Custom test development | Yes | Yes |
Data profiling | Built-in profiling during metadata ingestion | Not available natively |
Data contracts | Introduced in June 2025 with OpenMetadata 1.8 | Yes — supports schema, freshness, and semantic validations via contracts |
Alerts | Yes — observability alerts for schema changes, test failures, pipeline statuses | No — quality alerts only via external tools or data contracts |
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Which upstream and downstream integrations are supported?
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Which upstream and downstream integrations are supported?”Both DataHub and OpenMetadata have a plugin-based architecture for metadata ingestion. This enables them both to have smooth integrations with a range of tools from your data stack.
OpenMetadata supports over fifty connectors for ingesting metadata, such as:
- Databases
- BI tools
- Message queues
- Data pipelines
- Other metadata cataloging tools like Apache Atlas and Amundsen
Meanwhile, DataHub offers a GraphQL API, an Open API, and a couple of SDKs for your application or tool to develop and interact with DataHub.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Comparison summary
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Comparison summary”Both DataHub and OpenMetadata try to address the same problems around data cataloging, search, discovery, governance, and quality. Both tools were born out of the need to solve these problems for big organizations with lots of data sources, teams, and use cases to support.
Although these tools are a bit apart in terms of their release history and maturity, there’s a significant overlap in their features. Here’s a quick summary of some of the most important features.
Feature | OpenMetadata | DataHub |
|---|---|---|
Search & discovery | Elasticsearch | Elasticsearch |
Metadata backend | MySQL | MySQL |
Metadata model specification | JSON Schema | Pegasus Definition Language (PDL) |
Metadata extraction | Pull and push | Pull |
Metadata ingestion | Pull | Pull |
Data governance | RBAC, glossary, tags, importance, owners, and the capability to extend entity metadata | RBAC, tags, glossary terms, domains, and the Actions Framework |
Data lineage | Table-level and column-level | Table-level and column-level |
Data profiling | Built-in with the possibility of using external tools | Via third-party integrations, such as dbt and Great Expectations |
Data quality | In-house OpenMetadata Data Quality Framework, along with the possibility of using external tools like Great Expectations | Native data contract enforcement, DQ via third-party integrations, such as dbt and Great Expectations |
APIs & ingestion | REST API; batch ingestion | REST, GraphQL, and Kafka; supports real-time metadata streaming |
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: How to choose
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: How to choose”OpenMetadata and DataHub are both powerful, open-source metadata platforms, however, you can:
- Choose OpenMetadata if you need a simpler architecture, built-in data quality profiling and tests, and native support for data contracts
- Choose DataHub if you need real-time metadata streaming, advanced API integrations, and flexibility (via assertions and actions)
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your stack, use cases, and preferred governance approach—whether you want metadata to be:
- More active and embedded in workflows (OpenMetadata) OR
- Mediated through external triggers and integrations (DataHub)
What are the pros and cons of open-source metadata management tools?
Permalink to “What are the pros and cons of open-source metadata management tools?”Open-source tools offer flexibility and transparency, but come with trade-offs.
Pros
- No license costs or vendor lock-in
- Transparent code for reviews and audits
- Strong community-driven development
Cons
- DevOps effort needed for setup and maintenance–lengthier setup times and higher operational costs
- May lack enterprise features like AI governance or built-in quality checks
- Custom scripts for policy setting and enforcement
- No guaranteed support or SLAs
While open-source platforms are adaptable, scaling often demands custom scripts, automation, and built-in support.
Open source vs. Atlan: When to choose an active metadata control plane like Atlan
Permalink to “Open source vs. Atlan: When to choose an active metadata control plane like Atlan”Choosing between an open-source stack and a managed platform like Atlan depends on your organization’s metadata management maturity, priorities, and available resources.
Open-source tools provide essential building blocks for metadata management, but a platform like Atlan’s active metadata control plane brings them together into a unified, managed solution.
This allows data teams to maintain agility and velocity without the need to stitch together disparate scripts and custom code.
FAQs about Open Metadata vs. DataHub
Permalink to “FAQs about Open Metadata vs. DataHub”1. What is OpenMetadata and how does it differ from DataHub?
Permalink to “1. What is OpenMetadata and how does it differ from DataHub?”OpenMetadata is an open-source metadata management tool designed to provide a unified metadata model. DataHub is also open-source, but focuses on a generalized metadata service. Both tools offer features for data cataloging, governance, and lineage tracking, but their architectures and approaches to metadata management vary.
2. What are the key features of OpenMetadata?
Permalink to “2. What are the key features of OpenMetadata?”OpenMetadata offers several key features, including:
- Unified metadata model
- Flexible metadata ingestion
- Robust data governance capabilities like role-based access control, column-level data lineage tracking, etc.
- Integration with several other data tools
3. How can OpenMetadata improve data governance in an organization?
Permalink to “3. How can OpenMetadata improve data governance in an organization?”OpenMetadata enhances data governance by providing a centralized metadata repository that supports role-based access control and data lineage tracking. This allows organizations to manage data ownership, ensure compliance, and improve data quality through better visibility and control over their metadata assets.
4. What are the advantages of using DataHub for data management?
Permalink to “4. What are the advantages of using DataHub for data management?”DataHub offers advantages, such as:
- A flexible architecture that supports various data systems
- Column-level data lineage tracking
- Integration capabilities with tools like dbt and Great Expectations
- An event-based governance framework that allows organizations to automate workflows and improve data observability
5. How does DataHub facilitate data discovery and collaboration?
Permalink to “5. How does DataHub facilitate data discovery and collaboration?”DataHub facilitates data discovery through its search capabilities and user-friendly interface. It allows users to explore data assets, understand their relationships, and collaborate effectively by providing insights into data lineage and quality. This enhances data accessibility and promotes a collaborative data culture.
Share this article
Atlan is the next-generation platform for data and AI governance. It is a control plane that stitches together a business's disparate data infrastructure, cataloging and enriching data with business context and security.
OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Related reads
Permalink to “OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Related reads”- Enterprise Metadata Management Solutions: Emerging Trends & Must-Have Product Capabilities in 2025
- Data Governance in Action: Community-Centered and Personalized
- AI and Data Governance Manifesto
- Snowflake Data Governance — Features, Frameworks & Best practices
- Open Source Data Governance Tools - 7 Best to Consider in 2025
- Compliance Metadata Management: The Key to Meeting AI & Data Regulations at Scale in 2025
- A Guide to Gartner Data Governance Research — Market Guides, Hype Cycles, and Peer Reviews
- 5 Popular Data Governance Certification & Training in 2025
- 8 Best Data Governance Books Every Data Practitioner Should Read in 2025
- Automated Data Governance: How Does It Help You Manage Access, Security & More at Scale?
- Data Governance and Compliance: Act of Checks & Balances
- Data Governance vs. Data Management: What’s the Difference?
- Enterprise Data Governance — Basics, Strategy, Key Challenges, Benefits & Best Practices.
- Data Governance Tools: Importance, Key Capabilities, Trends, and Deployment Options
- Data Governance Tools Comparison: How to Select the Best
- Data Governance Tools Cost: What’s The Actual Price?
- Data Governance Process: Why Your Business Can’t Succeed Without It
- Data Governance and Compliance: Act of Checks & Balances
- Data Compliance Management: Concept, Components, Getting Started
- Data Governance for AI: Challenges & Best Practices
- Regulatory Data Lineage Tracking for Audit Success in 2025
- A Guide to Gartner Data Governance Research: Market Guides, Hype Cycles, and Peer Reviews
- Gartner Data Governance Maturity Model: What It Is, How It Works
- Data Governance Maturity Model: A Roadmap to Optimizing Your Data Initiatives and Driving Business Value
- Data Governance vs Data Compliance: Nah, They Aren’t The Same!
- Data Governance in Banking: Benefits, Implementation, Challenges, and Best Practices
- Open Source Data Governance - 7 Best Tools to Consider in 2025
- Federated Data Governance: Principles, Benefits, Setup
- Data Governance Committee 101: When Do You Need One?
- Data Governance for Healthcare: Challenges, Benefits, Core Capabilities, and Implementation
- Data Governance in Hospitality: Challenges, Benefits, Core Capabilities, and Implementation
- 10 Steps to Achieve HIPAA Compliance With Data Governance
- Snowflake Data Governance — Features, Frameworks & Best practices
- Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities: A Round-Up
- Data Governance Policy: Examples, Templates & How to Write One
- Data Governance Framework: Examples, Templates & How to Create one?
- 7 Best Practices for Data Governance to Follow in 2025
- Benefits of Data Governance: 4 Ways It Helps Build Great Data Teams
- Key Objectives of Data Governance: How Should You Think About Them?
- The 3 Principles of Data Governance: Pillars of a Modern Data Culture




















