Snowflake Cortex: Top Capabilities & Use Cases to Know in 2025
Share this article
Snowflake Cortex AI is a fully managed AI and ML platform built directly into your Snowflake environment. The platform provides the underlying infrastructure for model hosting, fine-tuning, inference, and lifecycle management.
With support for pre-built LLMs like Snowflake Arctic, Mistral, and Meta Llama 4, as well as Bring-Your-Own-Model (BYOM) flexibility, Cortex enables enterprises to build and operationalize generative AI at scale.
This article explores:
- Cortex AI core capabilities
- Top use cases
- Key benefits for data teams
- The need for a metadata control plane to drive secure, governed AI at scale
- Frequently asked questions about Cortex AI
Table of contents
Permalink to “Table of contents”- What is Snowflake Cortex AI?
- What are the core capabilities of Snowflake Cortex AI? An overview of Native AI and ML features
- What are the top use cases of Snowflake Cortex AI?
- What are the benefits of Snowflake Cortex AI?
- Piecing it together: The role of metadata in delivering trustworthy insights with Snowflake Cortex
- Summing up
- Snowflake Cortex FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Snowflake Cortex: Related reads
What is Snowflake Cortex AI?
Permalink to “What is Snowflake Cortex AI?”Snowflake Cortex AI is Snowflake’s in-platform engine for building and operationalizing enterprise-grade AI and ML workloads. It enables teams to run LLMs, build data agents, perform analytics, and build intelligent applications without ever moving data outside the Snowflake environment.
Watch How Atlan + Snowflake Power Trusted AI ➜
Launched in June 2023 at the Snowflake Summit, Cortex marked Snowflake’s strategic expansion into native AI. Since launch, Cortex has rapidly evolved. Early releases focused on serverless access to foundational models and text-based tasks like summarization, classification, and translation.
It became generally available in May 2024. Today, Cortex supports a growing catalog of pre-integrated LLMs (such as Snowflake Arctic, Mistral, Reka, Google, and Meta Llama 4), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), document intelligence, and more.
The platform continues to expand with innovations like Cortex Analyst, Cortex Search, and the no-code AI & ML Studio.
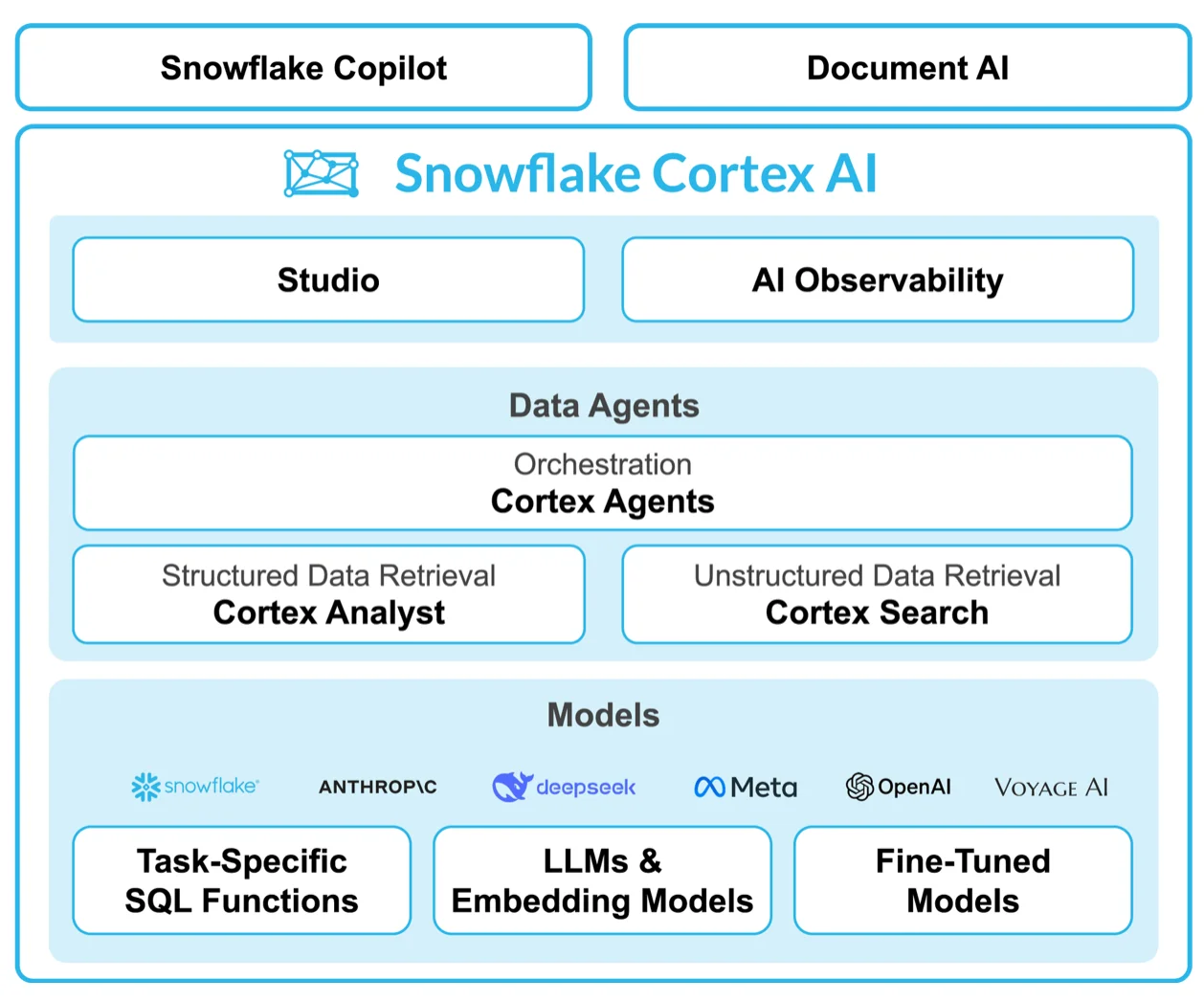
Snowflake Cortex AI - Source: Snowflake.
Snowflake Cortex supports a wide range of use cases, including text processing and summarization, AI-augmented business intelligence, and document chatbots. Before exploring use cases, let’s look at its core capabilities.
What are the core capabilities of Snowflake Cortex AI? An overview of Native AI and ML features
Permalink to “What are the core capabilities of Snowflake Cortex AI? An overview of Native AI and ML features”The Snowflake Cortex suite of AI features include:
- Snowflake Cortex LLM Functions (generally available): Understand, query, translate, summarize, and generate text with SQL or Python functions and the LLM of your choice
- Snowflake Copilot (generally available): Use an LLM assistant to understand your data with natural language queries, generate and refine SQL queries, and understand Snowflake’s features
- Document AI (generally available): Intelligent data processing (IDP) to extract content from a large volume of documents at scale
- Cortex Fine-Tuning (generally available): Customize LLMs to increase their accuracy and performance for use-case specific tasks
- Cortex Search (generally available): A text search service that provides LLMs with context from your latest proprietary data
- Cortex Analyst (generally available): A natural language interface for asking business questions
- Cortex Agents (public preview): Orchestrate across both structured and unstructured data sources to deliver insights
- AI Observability (public preview): Helps evaluate, debug, and optimize generative AI applications with systematic performance metrics, traceability, and more
- ML Functions (generally available): Perform predictive analysis to get insights from your Snowflake data assets using SQL functions
Let’s explore some of the most prominent Snowflake Cortex capabilities further.
Snowflake Cortex LLM Functions
Permalink to “Snowflake Cortex LLM Functions”Cortex LLM Functions can be grouped under:
-
COMPLETE function: This is a general purpose function to perform several tasks, from aspect-based sentiment classification and synthetic data generation to customized summaries.
The syntax for COMPLETE functions is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.COMPLETE( <model>, <prompt_or_history> [ , <options> ] ) -
Task-specific functions: These are pre-built, managed functions that automate routine tasks, such as generating summaries or performing quick translations, without requiring customization.
Task-specific functions include:
-
CLASSIFY_TEXT: Categorizes a given text into predefined categories.
The syntax for CLASSIFY_TEXT is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.CLASSIFY_TEXT( <input> , <list_of_categories>, [ <options> ] ) -
EXTRACT_ANSWER: Finds answers to a question within unstructured data
The syntax for EXTRACT_ANSWER is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.EXTRACT_ANSWER( <source_document>, <question>) -
PARSE_DOCUMENT: Extracts text (OCR mode) or text with layout elements (LAYOUT mode) from documents in specific stages, returning a JSON object
The syntax for PARSE_DOCUMENT is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.PARSE_DOCUMENT( '@<stage>', '<path>', [ { 'mode': '<mode>' }, ] ) -
SENTIMENT: Analyzes text sentiment, scoring from -1 (negative) to 1 (positive)
The syntax for SENTIMENT is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.SENTIMENT(<text>) -
SUMMARIZE: Produces a summary of the input text
The syntax for SUMMARIZE is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.SUMMARIZE(<text>) -
TRANSLATE: Translates text between supported languages
The syntax for TRANSLATE is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.TRANSLATE( <text>, <source_language>, <target_language>) -
EMBED_TEXT_768: Generates a 768-dimension vector embedding for the input text
The syntax for EMBED_TEXT_768 is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.EMBED_TEXT_768( <model>, <text> ) -
EMBED_TEXT_1024: Generates a 1024-dimension vector embedding for the input text
The syntax for EMBED_TEXT_1024 is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.EMBED_TEXT_1024( <model>, <text> )
-
-
Helper functions: These are pre-built, managed functions that minimize failures in LLM operations, such as counting tokens in an input prompt to prevent exceeding model limits.
Helper functions include:
-
COUNT_TOKENS: Returns the token count for the given input text, based on the specified model or Cortex function.
The syntax for COUNT_TOKENS is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.COUNT_TOKENS( <model_name> , <input_text> ) SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.COUNT_TOKENS( <function_name> , <input_text> ) -
TRY_COMPLETE: Operates like the COMPLETE function but returns NULL instead of an error code if execution fails.
The syntax for TRY_COMPLETE is as follows:
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.TRY_COMPLETE( <model>, <prompt_or_history> [ , <options> ] )
-
Snowflake Copilot
Permalink to “Snowflake Copilot”Snowflake Copilot is an LLM-powered assistant that simplifies data analysis with natural language queries while ensuring robust data governance. Running securely within Snowflake Cortex, it respects RBAC and accesses only datasets you are authorized to use.
You can interact with Copilot in SQL Worksheets and Snowflake Notebooks in Snowsight. Copilot assists with:
- Exploring datasets
- Generating and refining SQL queries
- Optimizing performance
- Answering questions about Snowflake features
Read more → Snowflake Copilot: Uses, Benefits, Best Practices, and FAQs
Document AI
Permalink to “Document AI”Document AI is a Snowflake AI feature that uses Arctic-TILT (Text Image Layout Transformer)–a proprietary LLM–to extract data (text, table values, handwritten content) from PDFs and other unstructured documents into a structured output.
Document AI supports both zero-shot extraction and fine-tuning. You can extract structured data from new document types out of the box, or fine-tune the model on your own documents for higher accuracy, ensuring the results and training data stay private to your organization.
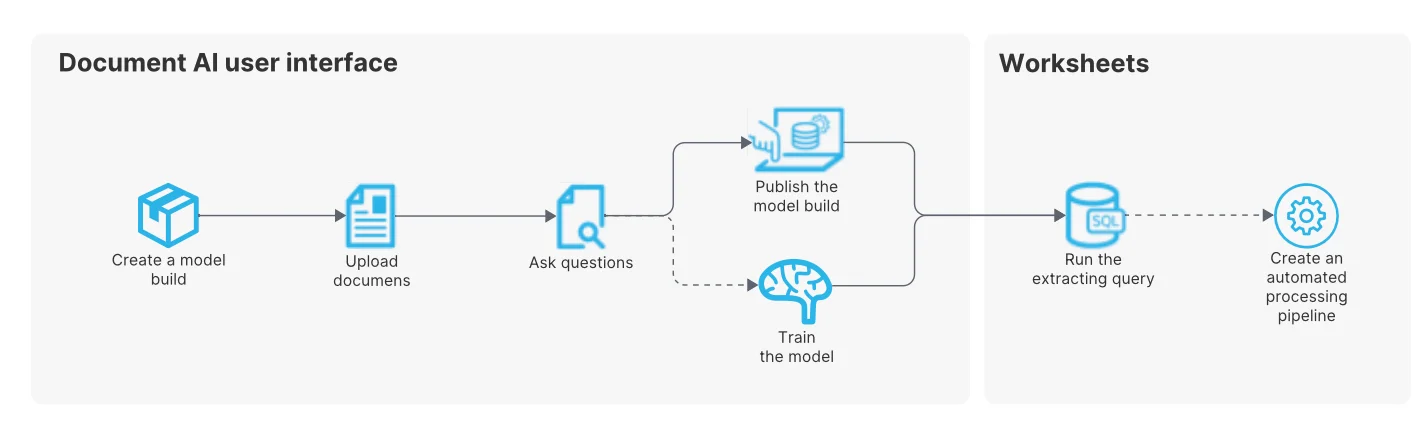
How Document AI processes documents - Source: Snowflake Documentation.
Cortex Fine-Tuning
Permalink to “Cortex Fine-Tuning”Cortex Fine-Tuning is a fully managed service to fine-tune popular LLMs using your data. This helps you customize your LLMs and deliver more relevant and accurate results.
The fine-tuning features are provided as the FINETUNE function, supporting the following:
- CREATE: Creates a fine-tuning job with the given training data
- SHOW: Lists all the fine-tuning jobs (that you can access)
- DESCRIBE: Describes the progress and status of a specific fine-tuning job
- CANCEL: Cancels a fine-tuning job
Cortex Search
Permalink to “Cortex Search”Cortex Search is a search engine to help you find the information you need from enterprise documents and other unstructured data using hybrid retrieval (combining keyword retrieval and vector retrieval):
- RAG engine for LLM chatbots: Provides contextual responses for LLM chat applications using semantic search
- Enterprise search: Powers a high-quality search bar that can be embedded in your application
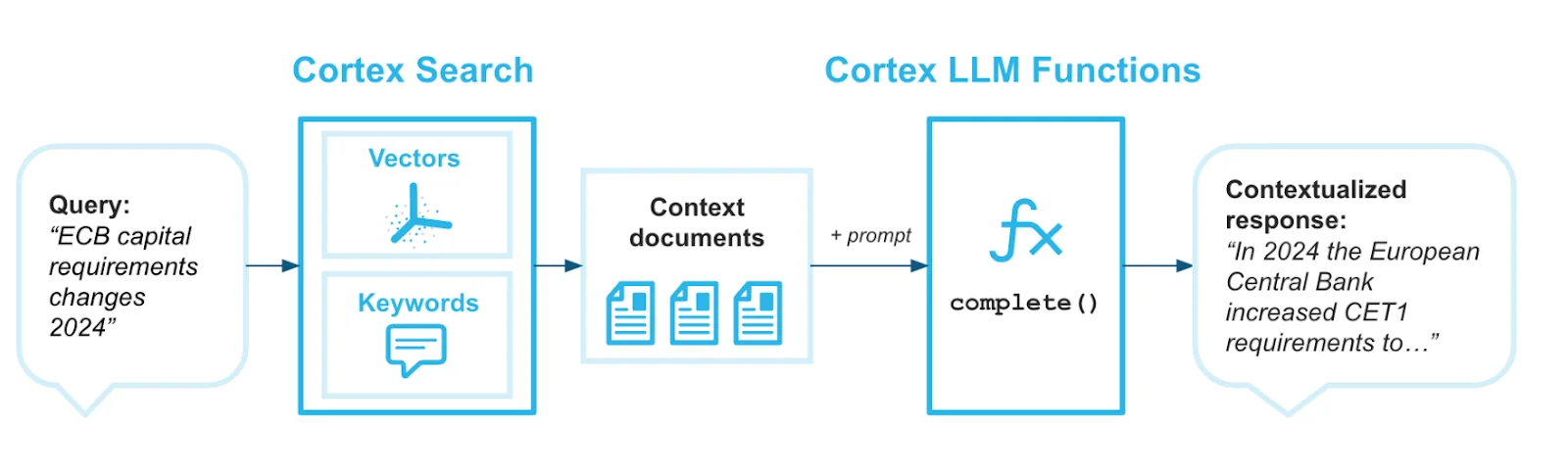
Cortex Search in Snowflake Cortex AI - Source: Snowflake Documentation.
Cortex Analyst
Permalink to “Cortex Analyst”Cortex Analyst is a fully managed service offering a conversational interface to interact with structured data in Snowflake. So, data practitioners can ask business questions in natural language, without writing SQL, and get direct answers quickly.
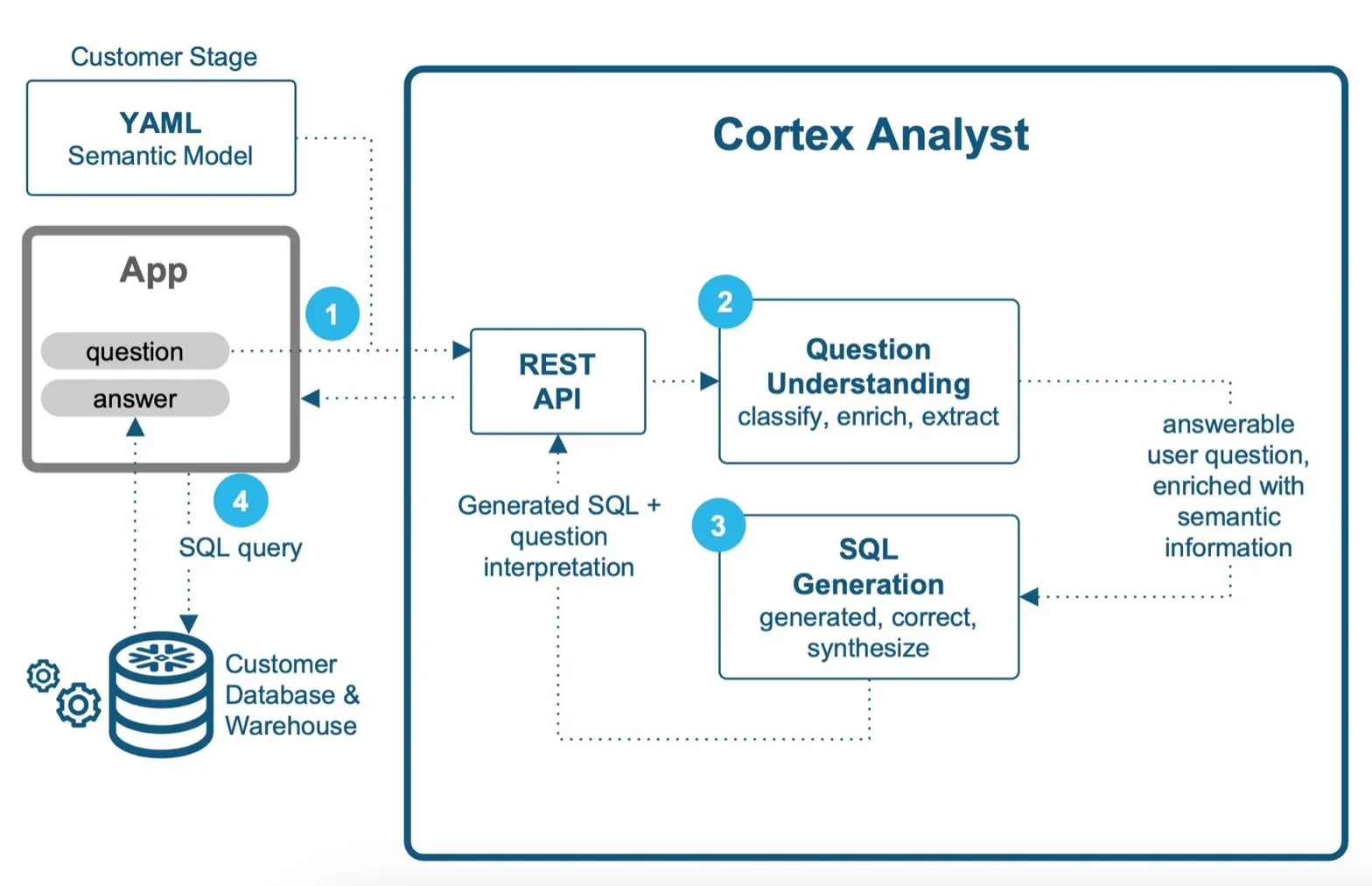
Snowflake Cortex Analyst - Source: Snowflake Blog.
It’s important to note that Cortex Analyst only answers SQL-based questions and doesn’t address broader business-related queries like identifying trends.
Cortex Analyst is powered by the latest Meta Llama and Mistral models. It integrates with business tools and platforms, such as Streamlit apps, Slack, Teams, custom chat interfaces, etc. via REST API.
Cortex Analyst doesn’t use customer data to train or fine-tune models, and no data (metadata and prompts) leaves Snowflake’s governance boundary. It leverages semantic model metadata (table names, column names, value types) for SQL query generation during inference.
Cortex Agents
Permalink to “Cortex Agents”Cortex Agents act as AI-powered orchestrators that break down complex user queries, plan multi-step tasks, and route them through the right tools—Cortex Analyst for structured data and Cortex Search for unstructured content.
They handle ambiguity, split tasks into subtasks, and reflect on results to improve accuracy.
With built-in compliance and governance, Cortex Agents help enterprises build sophisticated conversational apps and scale data experiences.
Currently, Cortex Agents is in public preview and not available across all regions.
AI Observability
Permalink to “AI Observability”AI Observability enables teams to monitor and improve the reliability of generative AI applications built with Snowflake Cortex. It offers systematic evaluations using techniques like LLM-as-a-judge, allowing you to benchmark accuracy, latency, and cost.
AI Observability can be used to evaluate a variety of task types, such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and summarization. With tracing features that capture every step of the AI workflow—from input prompts to tool usage and final responses—teams can debug issues, compare configurations, and reduce hallucinations.
Snowflake Cortex ML Functions
Permalink to “Snowflake Cortex ML Functions”ML functions in Snowflake Cortex provide automated predictions and insights through machine learning, simplifying data analysis. Snowflake selects the appropriate model for each feature, allowing you to leverage machine learning without technical expertise—just provide your data.
“These (i.e., ML functions) powerful out-of-the-box analysis tools help time-strapped analysts, data engineers, and data scientists understand, predict, and classify data, without any programming.” - Snowflake Documentation
Cortex ML Functions can be grouped under:
- Time-series functions: Use machine learning to analyze time-series data, identifying how a specified metric changes over time and in relation to other data features. The model delivers insights and predictions based on detected trends. The available functions include:
- Forecasting: Forecasting predicts future metric values based on past trends in the data.
- Anomaly detection: Anomaly detection identifies metric values that deviate from expected patterns.
- Other analysis functions: These are ML functions that don’t use time-series data:
- Classification: Classification categorizes rows into two or more classes based on their most predictive features.
- Top insights: Top Insights identifies dimensions and values that have an unexpected impact on the metric.
What are the top use cases of Snowflake Cortex AI?
Permalink to “What are the top use cases of Snowflake Cortex AI?”From enabling natural language analytics to running custom models at scale, Snowflake Cortex AI supports several generative AI use cases. The top use cases include (but aren’t limited to):
-
Natural-language data exploration and processing to improve self-service analytics
Business users ask questions in plain English, and Cortex Analyst translates them into SQL—reducing dependency on BI teams.
-
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and semantic search to democratize knowledge
Cortex Search enables LLMs to retrieve relevant context from proprietary data before generating responses.
-
Intelligent document processing to automate data extraction at scale
Document AI extracts structured data from PDFs and scanned documents, enabling automated workflows for finance, HR, and legal.
-
AI-powered business intelligence to accelerate analytics workflows
Use Copilot (SQL development assistant) and Cortex Analyst (a full-fledged agentic AI system) to generate insights, create dashboards, and optimize reporting pipelines faster.
-
Built-in ML functions for predictive analytics without MLOps overhead
Run forecasting, anomaly detection, and classification directly within ELT pipelines using SQL UDFs. For instance, a subscription-based company can detect churn risk in near real-time and trigger targeted retention campaigns automatically.
-
Custom model hosting and inference to operationalize private AI models securely
Bring your own fine-tuned model and serve it via SQL or REST—all within Snowflake’s perimeter using Snowpark Container Services. For example, a healthcare company can train a custom LLM on de-identified patient records to improve internal diagnostics or documentation summarization workflows.
-
Conversational data apps and AI agents to reduce reporting complexity
Use Cortex Agents to build enterprise copilots that can handle structured queries, unstructured document lookups, and user disambiguation, embedded in tools like Slack or Teams.
“Agents use Cortex Analyst (structured) and Cortex Search (unstructured) as tools, along with LLMs, to analyze data. Cortex Search extracts insights from unstructured sources, while Cortex Analyst generates SQL to process structured data.” - Snowflake documentation
What are the benefits of Snowflake Cortex AI?
Permalink to “What are the benefits of Snowflake Cortex AI?”With Cortex, you can run AI workloads natively in Snowflake. It “enables organizations to expedite delivery of generative AI applications with LLMs while keeping their data in the Snowflake security and governance perimeter.“
Key benefits include:
- No data movement: Run AI directly where your data lives
- Develop full-stack RAG applications: Build document chatbots within Snowflake and without data movement, setup delays, or deep ML expertise
- Faster experimentation to production: Go from prototype to deployment without managing infrastructure – self-service sentiment analysis, summarization, and translation tasks
- Support diverse use cases: SQL, REST, and no-code interfaces enable analysts, engineers, and business users to build and interact with AI applications as well as generate insights (like demand for resources, potential incidents)
- Governance by design: Models, data, and prompts remain within Snowflake’s secure environment
- Multi-interface access: Use SQL, REST, Python (Snowpark), or no-code tools
- Pre-integrated LLMs + BYOM: Use best-in-class models or bring your own, all within a unified control plane
- Lower operational burden: Built-in observability, error handling, and compliance tracking
Piecing it together: The role of metadata in delivering trustworthy insights with Snowflake Cortex
Permalink to “Piecing it together: The role of metadata in delivering trustworthy insights with Snowflake Cortex”Snowflake Cortex represents a significant step forward in democratizing AI and ML capabilities for businesses of all sizes.
By eliminating the need for complex infrastructure setup and providing a user-friendly interface, Snowflake Cortex empowers Snowflake users to leverage AI for text analytics, predictive modeling, and custom application development.
However, AI-powered results are only as good as the underlying data and metadata.
The problem with enterprise AI tools is a lack of trust in the results they deliver. While AI-powered tools like Snowflake Cortex hold immense potential, the accuracy and reliability of their outputs are fundamentally tied to the quality of the data and metadata they process.
Metadata provides context on data asset relationships, structures, and meanings across your data estate.
“Metadata itself is evolving into big data, becoming the foundation for the future of AI and LLM applications. Metadata will need to live in a metadata lake or lakehouse to power trust and context at scale.” - Prukalpa Sankar on the role of metadata in modern enterprise data stacks
Also, read → The role of metadata management in enterprise AI
To unlock the full value of Cortex, enterprises need a metadata control layer that connects insights to the underlying data fabric, and that’s where Atlan comes in.
Atlan acts as the metadata-driven control plane that makes Snowflake Cortex insights accurate, traceable, and compliant. It connects deeply with your data stack, enriching every Cortex workflow with lineage, ownership, sensitivity tags, and business context. This transforms Cortex from a powerful inference engine into a fully governed AI layer.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Cataloging – Start Product Tour ➜
With Atlan, teams can:
- Understand where Cortex-generated insights came from: View complete lineage across datasets, models, prompts, and outputs to trace how AI decisions were made.
- Audit which data assets were used and how: Track asset usage across Snowflake and Cortex to maintain transparency and simplify compliance reporting.
- Enable two-way tag sync: Classify sensitive data (e.g., PII, PCI, or domain-specific tags) in Atlan and push those classifications back into Snowflake.
- Use no-code Policy Center for policy coverage monitoring across your data estate: Define rules, such as “No model may train on raw customer PII unless certified,” or “Block inference on untagged columns,” and let Atlan translate these into Snowflake masking policies and pre-execution checks.
- Capture version history and get drift alerts: Automatically capture every retrain, parameter update, or schema change. Get alerts when new columns appear or model drift could impact insight reliability.
- Collaborate across roles with shared context around every dataset and model: Add ownership, documentation, and business definitions around every dataset and model, helping data, AI, and business teams stay aligned.
Experience Atlan on Snowflake – Book a Demo ➜
Summing up
Permalink to “Summing up”Snowflake Cortex simplifies data workflows and allows organizations to take advantage of AI to build, deploy, and scale AI-driven applications within Snowflake.
From natural language analytics and document processing to custom model hosting and AI agents, Cortex supports a wide range of use cases—all with enterprise-grade security, performance, and flexibility.This means faster experimentation, streamlined production workflows, and the ability to operationalize AI with full visibility and control.
As data and AI continue to converge, platforms like Cortex—especially when paired with a metadata layer like Atlan—will be critical for delivering intelligent, trustworthy, and context-aware systems at scale.
Snowflake Cortex FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Permalink to “Snowflake Cortex FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)”1. What is Cortex AI in Snowflake?
Permalink to “1. What is Cortex AI in Snowflake?”Snowflake Cortex AI is a fully managed AI and ML platform built directly into the Snowflake Data Cloud. It enables teams to run LLMs, build AI-powered applications, perform document processing, and analyze unstructured data without moving data out of Snowflake’s governed environment.
2. What are the benefits of Snowflake Cortex?
Permalink to “2. What are the benefits of Snowflake Cortex?”Benefits include access to high-performing LLMs, native support for text and document processing, seamless model deployment (including BYOM), built-in observability for monitoring, and flexible interfaces for both technical and business users. It accelerates time to value while maintaining enterprise-grade governance and control.
3. What models are available in Cortex?
Permalink to “3. What models are available in Cortex?”Cortex includes pre-integrated access to leading LLMs such as Snowflake Arctic, Mistral, Meta Llama 4, and Claude. It also supports Bring Your Own Model (BYOM), allowing you to deploy and fine-tune open-source or proprietary models securely within Snowflake.
4. What types of workloads can Cortex AI support?
Permalink to “4. What types of workloads can Cortex AI support?”Cortex supports a broad range of generative AI and ML workloads, including natural language querying, RAG-based search, document intelligence, SQL generation, anomaly detection, forecasting, classification, and custom AI agent orchestration.
5. What interfaces are available for interacting with Cortex?
Permalink to “5. What interfaces are available for interacting with Cortex?”Cortex supports SQL UDFs, REST APIs, Snowpark (Python), and no-code interfaces such as the AI & ML Studio. Tools like Snowflake Copilot and Cortex Analyst provide natural language interfaces for querying and exploring data.
6. How do I choose an LLM model in Snowflake Cortex?
Permalink to “6. How do I choose an LLM model in Snowflake Cortex?”To achieve the best performance per credit, choose a model that’s a good match for the content size and complexity of your task.
If you’re not sure where to start, try the most capable models first to establish a baseline. According to Snowflake, “reka-core and mistral-large2 are the most capable models offered by Snowflake Cortex, and will give you a good idea what a state-of-the-art model can do.”
Depending on your use case, you can switch to medium models (which can handle a low to moderate amount of reasoning) or small models (suitable for simple tasks like code or text completion).
7. Do I need ML or AI expertise to use Snowflake Cortex?
Permalink to “7. Do I need ML or AI expertise to use Snowflake Cortex?”No. Cortex is designed to support users across skill levels. Analysts can use natural language interfaces, engineers can invoke models using SQL or Python, and data scientists can deploy fine-tuned models—all without managing infrastructure.
8. How can you calculate the cost of using Snowflake Cortex?
Permalink to “8. How can you calculate the cost of using Snowflake Cortex?”Snowflake Cortex LLM functions incur a compute cost based on the number of tokens processed. A token is roughly four text characters.
The cost varies depending on the model and Cortex function being used. For detailed information on pricing, we recommend referring to this Snowflake credit consumption table or contacting account representatives directly.
9. Are there any limitations to using Snowflake Cortex?
Permalink to “9. Are there any limitations to using Snowflake Cortex?”There are no usage quotas applied at the account level. However, to provide LLM capabilities to all Snowflake customers, Cortex LLM functions may experience throttling during high usage periods.
Throttled requests will return an error and can be retried later.
10. How does Cortex handle governance and security?
Permalink to “10. How does Cortex handle governance and security?”All models, prompts, and responses are executed within Snowflake’s secure perimeter. Cortex enforces access controls through Snowflake’s native RBAC and integrates with enterprise governance policies to ensure compliance and data protection.
11. How does Cortex handle AI safety?
Permalink to “11. How does Cortex handle AI safety?”Cortex supports fine-grained RBAC, does not use customer data to train shared models, and offers AI Observability tools to detect hallucinations, measure groundedness, and trace model behavior, helping teams build trustworthy, auditable AI applications.
Snowflake Cortex: Related reads
Permalink to “Snowflake Cortex: Related reads”- 6 Snowflake Cortex Use Cases to Consider in 2025
- Snowflake Horizon for Data Governance: Here’s Everything We Know So Far
- How to Set Up Data Governance for Snowflake: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Snowflake Copilot: Here’s Everything We Know So Far About This AI-Powered Assistant
- Snowflake Data Cloud Summit 2025: Keynotes, AI Tracks, and How to Make the Most of It
- Snowflake Data Lineage: A Step-by-Step How to Guide
- How to Set Up a Data Catalog for Snowflake: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Snowflake Data Catalog: What, Why & How to Evaluate
- Snowflake Data Mesh: Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Glossary for Snowflake: Shared Understanding Across Teams
- Personalized Data Discovery for Snowflake Data Assets
- Snowflake Data Dictionary
Share this article


















