What are the essential components of a data governance policy?
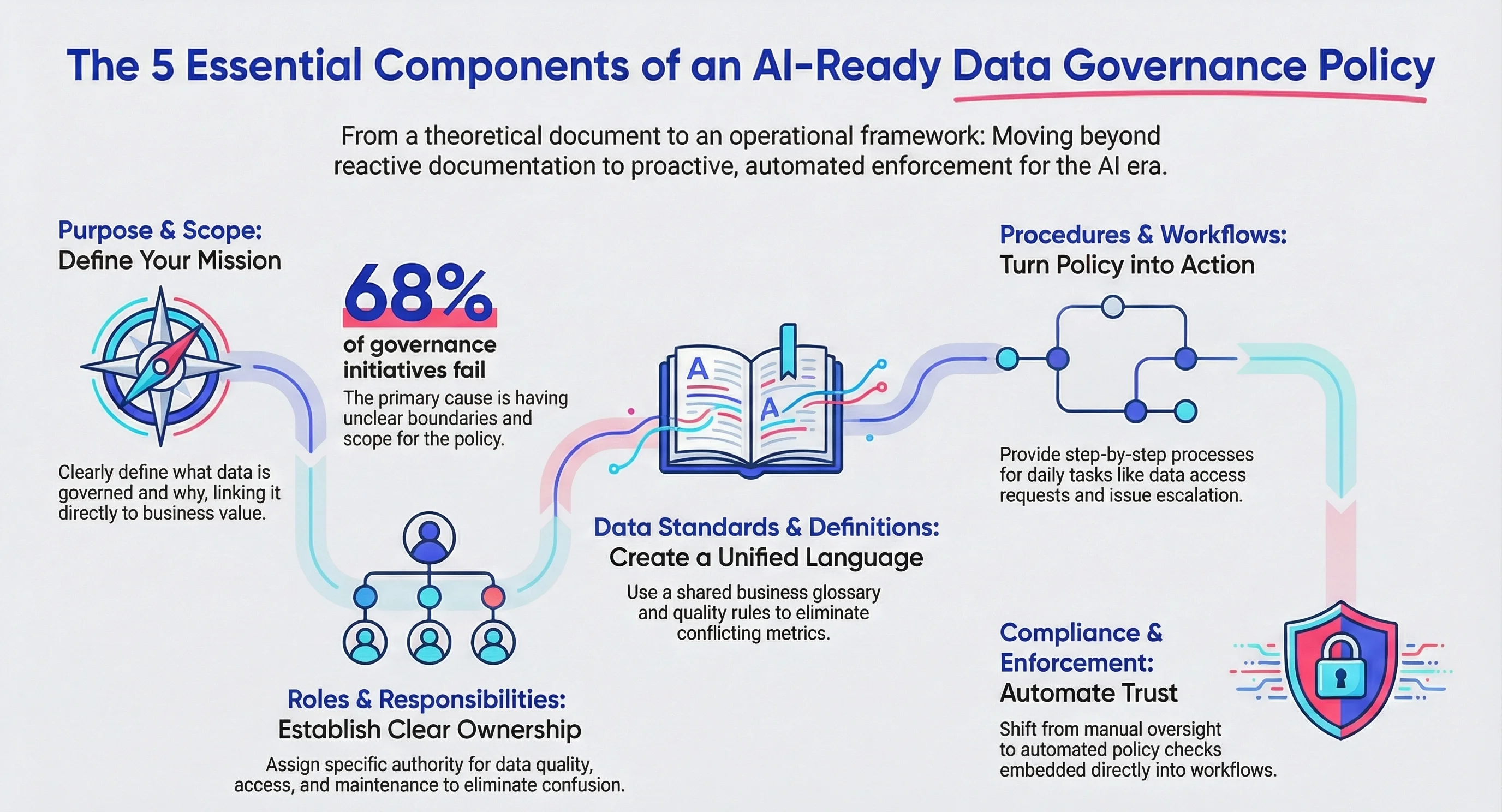
Permalink to “What are the essential components of a data governance policy?”A comprehensive data governance policy consists of five core sections that transform governance from theory into operational practice.
1. Purpose and scope
Permalink to “1. Purpose and scope”Define exactly what you’re governing and why it matters to your bottom line. This section answers the critical questions that prevent scope creep and ensure stakeholder buy-in.
What to include:
- Specific business objectives (improve data quality for ML models, ensure GDPR compliance, reduce security risks)
- Precise data boundaries: “Customer PII in production databases” not “customer information”
- Clear exclusions to prevent mission creep
- Direct connection to revenue impact or risk mitigation
Organizations using automated metadata platforms can define scope programmatically, automatically classifying data assets based on sensitivity and applying appropriate policies without manual documentation.
Why data teams struggle here: Vague scope statements create endless debates about coverage. Research shows that 68% of data governance initiatives fail due to unclear boundaries. Be ruthlessly specific about what’s covered to prevent teams from making costly assumptions.
2. Roles and responsibilities
Permalink to “2. Roles and responsibilities”Clear ownership prevents the “not my job” syndrome that kills governance initiatives. This section eliminates confusion about decision-making authority and daily execution.
Essential role definitions:
- Data Governance Council: Strategic oversight and policy approval
- Chief Data Officer/Data Leader: Business alignment and resource allocation
- Domain Data Stewards: Day-to-day quality and access decisions
- Data Custodians: Technical implementation and maintenance
- Data Users: Consumption responsibilities and escalation procedures
Critical success factor: Map each data lifecycle stage to specific roles. Who approves new data sources? Who resolves quality issues? Who grants access permissions? Federated models work best—domain teams own quality while central teams maintain standards.
3. Data standards and definitions
Permalink to “3. Data standards and definitions”This section eliminates the chaos of conflicting metrics across teams. Without shared definitions, your organization creates parallel versions of truth that undermine decision-making.
Core components:
- Business glossary: Official definitions for key terms and metrics
- Quality thresholds: Specific accuracy, completeness, and timeliness requirements
- Naming conventions: Consistent dataset and field naming across systems
- Classification schemas: Sensitivity levels (public, internal, confidential, restricted)
- Master data hierarchies: Authoritative sources for customers, products, locations
Real-world impact: When marketing’s “active customer” definition differs from finance’s, executive dashboards show conflicting numbers. Standardized definitions prevent these trust-destroying scenarios. Modern platforms automatically propagate definitions across data assets, ensuring consistency without manual enforcement.
essential components of a data governance policy - Image by Atlan.
4. Procedures and workflows
Permalink to “4. Procedures and workflows”Transform policy statements into step-by-step processes your teams can execute without interpretation. This section bridges the gap between governance theory and daily operations.
Essential workflows:
- Data access requests: Clear approval paths with defined timeframes
- Quality issue escalation: Who to contact when data breaks
- New dataset onboarding: Security, quality, and documentation requirements
- Change management: How to modify existing data structures safely
- Exception handling: When and how to deviate from standard procedures
Implementation keys: Include specific timeframes (“48-hour approval SLA”), required documentation, and automated workflow triggers where possible. Teams need processes they can follow without constant clarification requests.
5. Compliance and enforcement
Permalink to “5. Compliance and enforcement”Without teeth, your policy becomes expensive documentation. This section defines how governance translates into measurable outcomes and behavioral change.
Enforcement mechanisms:
- Automated monitoring: Real-time policy violation detection
- Audit schedules: Regular compliance verification
- Training requirements: Role-specific governance education
- Violation consequences: Progressive responses from warnings to access removal
- Success metrics: Measurable governance effectiveness indicators
Modern approach: Shift from punitive to enabling enforcement. Build policy checks into existing workflows rather than creating separate compliance processes. Focus on making compliance easier through automation rather than relying on manual oversight.
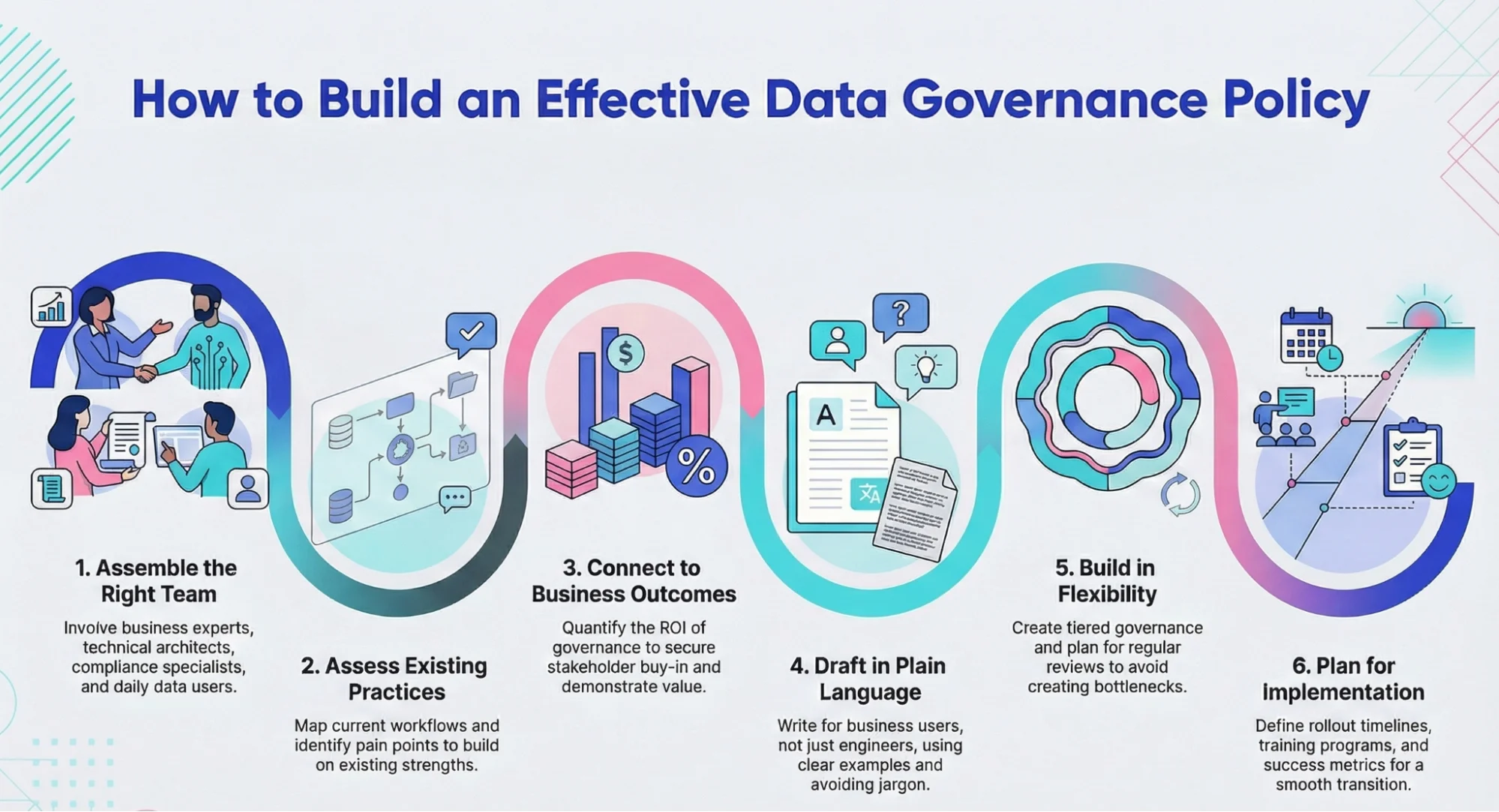
A 6 step guide to writing a data governance policy
Permalink to “A 6 step guide to writing a data governance policy”Modern data teams need policies that enable innovation, not create bottlenecks. Here’s your streamlined approach:
1. Assemble the right team
Permalink to “1. Assemble the right team”Include business domain experts, technical architects, compliance specialists, an executive sponsor, and actual end users. The biggest failures happen when governance teams write rules without input from people who use data daily.
Cross-functional collaboration ensures policies reflect real-world workflows. IT teams understand technical constraints, business users know operational needs, and compliance specialists ensure regulatory alignment.
2. Assess existing practices
Permalink to “2. Assess existing practices”Document what’s working before writing new rules. Map current workflows, identify pain points through team interviews, and review recent incidents. Build on existing strengths rather than starting from scratch.
Organizations that assess current state first reduce implementation time by 40% compared to those starting from zero. Understanding existing data handling patterns helps craft policies teams will actually follow.
How to build an effective data governance policy - Image by Atlan.
3. Connect to business outcomes
Permalink to “3. Connect to business outcomes”Quantify the ROI of governance—calculate costs of poor data quality, show how governance accelerates AI initiatives, and demonstrate competitive advantages. Example: “Accurate customer contact data improves email ROI by 23%.”
Link each policy section to tangible business value. When stakeholders understand how governance drives revenue or reduces risk, they champion rather than resist implementation.
4. Draft in plain language
Permalink to “4. Draft in plain language”Write for business users, not data engineers. Use concrete examples, maintain logical organization, and keep policies to 10-15 pages maximum. Complex documents get ignored regardless of technical merit.
Avoid jargon unless defining it. Replace “utilize metadata orchestration paradigms” with “use automated metadata management.” Clear language increases adoption and reduces clarification requests.
5. Build in flexibility
Permalink to “5. Build in flexibility”Create tiered governance based on data sensitivity, establish clear exception processes, and plan quarterly reviews. Rigid policies become bottlenecks that teams circumvent through shadow IT.
Different data types require different controls. Customer PII needs stricter governance than internal analytics data. Flexible frameworks adapt to evolving business needs without complete policy rewrites.
6. Plan for implementation
Permalink to “6. Plan for implementation”Include phased rollout timelines, role-specific training programs, required tools, and success metrics. The best policies create direct paths from documentation to daily practice.
How to implement your data governance policy
Permalink to “How to implement your data governance policy”1. Define clear approval authority
Permalink to “1. Define clear approval authority”Data governance policies typically follow a hierarchical approval path:
- Data Governance Committee: Reviews and recommends
- Executive sponsor (often CDO or CIO): Validates business alignment
- Board of Directors/Executive Leadership: Gives final approval for enterprise-wide policies
For domain-specific policies, approval might stop at the department head level, while enterprise policies affecting multiple departments require C-suite sign-off.
2. Establish enforcement responsibility
Permalink to “2. Establish enforcement responsibility”The enforcement model typically includes:
- Data stewards: Monitor adherence in their domains
- Data governance office: Coordinates enforcement activities
- Automated systems: Flag policy violations in real-time
- Audit teams: Periodically verify compliance
- IT security: Enforce access-related policies
The most successful enforcement models implement what Gartner calls “just-in-time governance”—embedding policy checks directly into workflows where data is created or accessed rather than as separate processes.
3. Roll out in phases
Permalink to “3. Roll out in phases”Start with high-impact, low-complexity policies affecting critical data assets. Prove value quickly, then expand scope. Attempting enterprise-wide implementation simultaneously overwhelms teams and guarantees resistance.
Regulatory compliance in your data governance policy
Permalink to “Regulatory compliance in your data governance policy”Effective policies must harmonize with regulatory frameworks:
- GDPR alignment requires addressing data subject rights, lawful processing basis, impact assessments, breach notifications, and data minimization principles. Organizations handling EU citizen data need explicit consent mechanisms and data portability features built into policy workflows.
- CCPA/CPRA alignment needs consumer access and deletion rights, opt-out mechanisms, service provider requirements, and data inventory maintenance. California regulations require organizations to respond to consumer requests within 45 days, necessitating automated request handling.
- SOC 2 alignment covers access controls, change management, risk assessments, monitoring requirements, and incident response protocols. Service organizations must demonstrate continuous compliance through audit trails and policy enforcement logs.
Create policy frameworks that accommodate the strictest requirements while enabling region-specific variations. Map policies to specific regulatory requirements for clear compliance traceability.
Common pitfalls that cause governance policy failures
Permalink to “Common pitfalls that cause governance policy failures”- Overly complex documentation: Policies exceeding 20 pages get ignored. Studies show that policy adoption drops 60% when documents exceed 15 pages. Keep it concise and actionable.
- Lack of executive sponsorship: Without visible C-suite support, governance becomes seen as IT’s problem. Policies need champions who demonstrate commitment through resource allocation and enforcement.
- Ignoring existing workflows: Policies that disrupt daily operations face resistance. Successful governance integrates with how teams already work rather than requiring complete process overhauls.
- Insufficient training: Teams can’t follow policies they don’t understand. Role-specific training increases compliance from 40% to 85% in the first year.
- No measurement framework: What gets measured gets managed. Without clear metrics, organizations can’t demonstrate governance value or identify improvement areas.
- Manual enforcement at scale: Human oversight can’t keep pace with modern data volumes. Manual processes create bottlenecks that slow business initiatives and reduce compliance effectiveness.
Data governance policy templates and examples
Permalink to “Data governance policy templates and examples”If your organization is in the early stages of establishing best practices and standards around data, knowing where to start with your data governance policy can be challenging. Here are publicly-available data governance policies you can use as models:
- Oklahoma Office of Management & Enterprise Services offers comprehensive policy coverage with specific focus on governance roles and responsibilities.
- New Hampshire Department of Education provides detailed job duties for key individuals and outlines intended policy outcomes for measuring success.
- University of New South Wales Sydney demonstrates the multi-policy approach, separating standard data governance from research data governance for distinct requirements.
- East Carolina University showcases concise yet comprehensive coverage—scope, roles, and accountability in a short, precise document.
- Brandeis University ties every data source to a specific “data trustee,” ensuring complete ownership coverage across the data estate.
- University of Nevada Las Vegas includes comprehensive sections on data access, usage, and integrity standards.
Choose the template that best matches your organizational communication style and goals, or combine strengths from multiple examples.
How modern data governance platforms automate policy enforcement
Permalink to “How modern data governance platforms automate policy enforcement”Manual governance can’t keep pace with the speed and scale of modern data. Traditional methods like reviews, spreadsheets, and periodic audits create delays, inconsistencies, and blind spots. Issues are often discovered only after damage is done.
Modern catalogs like Atlan automate policy enforcement by tying governance rules directly to data assets. Policies activate instantly based on sensitivity, lineage, and usage, so access controls and masking kick in the moment sensitive data appears.
Atlan’s active metadata monitors data access continuously, flagging violations in real time rather than weeks later. Automated lineage mapping makes downstream impact clear whenever policies change.
With automated controls, teams report 53% reduction in engineering workload and 20% higher data user satisfaction compared to manual governance approaches. Teams shift from firefighting compliance issues to strategic data initiatives.
Book a demo to see how Atlan automates policy enforcement across your entire data ecosystem.
Real stories from real customers: Transforming policy into practice
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: Transforming policy into practice”
Modernized data stack and launched new products faster while safeguarding sensitive data
"Austin Capital Bank has embraced Atlan as their Active Metadata Management solution to modernize their data stack and enhance data governance. Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics, highlighted, 'We needed a tool for data governance… an interface built on top of Snowflake to easily see who has access to what.' With Atlan, they launched new products with unprecedented speed while ensuring sensitive data is protected through advanced masking policies."

Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics
Austin Capital Bank
🎧 Listen to the podcast: Austin Capital Bank From Data Chaos to Data Confidence

53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
"Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. 'Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,' Kiwi.com shared. Atlan's intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams."
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to the podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan
Moving forward with data governance policy
Permalink to “Moving forward with data governance policy”Effective data governance balances control with enablement. Define clear objectives tied to business outcomes, then map decision rights to each stage of the data lifecycle. The strongest policies rely on automation, embedding compliance checks into everyday workflows instead of adding extra oversight. Modern platforms enforce rules at the point of data creation and use, shifting governance from reactive documentation to proactive risk management.
See how Atlan helps organizations implement automated policy controls at scale.
Frequently asked questions about data governance policy
Permalink to “Frequently asked questions about data governance policy”1. What are the key components of a data governance policy?
Permalink to “1. What are the key components of a data governance policy?”A data governance policy typically includes purpose and scope, roles and responsibilities, data standards and definitions, procedures and workflows, and compliance enforcement mechanisms. These components ensure clarity and accountability in data management practices across the organization.
2. How can I implement a data governance policy in my organization?
Permalink to “2. How can I implement a data governance policy in my organization?”Start by assessing existing policies, identifying key stakeholders, and drafting a collaborative document. Ensure the policy aligns with business objectives and establish a framework for monitoring compliance. Phased rollout with executive sponsorship increases adoption success rates from 40% to over 80%.
3. What is the difference between data governance and data policy?
Permalink to “3. What is the difference between data governance and data policy?”Data governance refers to the overall management of data availability, usability, integrity, and security. In contrast, a data policy is a specific guideline or rule that governs how data should be handled within the organization. Policies are the documented rules; governance is the operating system that enforces them.
4. How does a data governance policy support data privacy regulations like GDPR?
Permalink to “4. How does a data governance policy support data privacy regulations like GDPR?”A data governance policy helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations by establishing clear guidelines for data handling, access control, and accountability. It ensures data is managed in ways that protect individual privacy rights through automated consent management, data subject request workflows, and breach notification procedures.
5. What are the benefits of having a data governance policy?
Permalink to “5. What are the benefits of having a data governance policy?”Having a data governance policy enhances data quality, ensures compliance with regulations, improves decision-making, and fosters trust in data. It clarifies roles and responsibilities, leading to more effective data management. Organizations report 40% reduction in data quality issues and 60% faster compliance verification after implementing formal policies.
6. How does Atlan help with data governance policy implementation?
Permalink to “6. How does Atlan help with data governance policy implementation?”Atlan provides centralized policy management, automated enforcement through active metadata, and real-time monitoring of policy violations. The platform integrates governance policies directly with data assets, enabling automatic policy application based on sensitivity, lineage, or usage patterns without manual intervention.
Share this article



















