Top 6 Benefits of a Data Dictionary for 2025
Share this article
Understanding the benefits of a data dictionary is crucial for any organization. A data dictionary serves as a centralized repository of information about data assets.
It helps in documenting data definitions, relationships, and usage. This clarity improves data quality and supports effective data governance.
Without a data dictionary, one has to rely on siloed, undocumented tribal knowledge or spend lots of time familiarizing with codebases, SQL queries, and logs.
This is where data dictionaries greatly help in documenting your database.
The following are the broader benefits of having a data dictionary:
Permalink to “The following are the broader benefits of having a data dictionary:”- Helps to understand the overall database design, structure, relationships, and data flow
- Facilitates building a common vocabulary and hence shared understanding amongst data users
- Helps detect errors and anomalies in data
- Enables crowdsourcing data quality and data integrity checks
- Helps save time on data discovery and enables reliable analytics and reporting
- Assists in managing data quality, consistency, and security for compliance audits
- Helps enforce database management and programming standards
- Makes it easier to onboard new analysts/data engineers into the team
Later in the post, we’ll explore 6 of these benefits of data dictionary in detail and explain how having a robust data dictionary is a crucial step toward true data democratization.
Table of content
Permalink to “Table of content”- What is a data dictionary?
- Six key benefits of a data dictionary
- How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
- Conclusion
- Related reads on data dictionary benefits
What is a data dictionary?
Permalink to “What is a data dictionary?”A data dictionary provides complete information about an organization’s data assets. This information can include:
- Column description
- Distinct values, missing values, and the frequency of each value within a column
- Data type
- Classification and glossary terms
Here’s an official data dictionary definition from the IBM Dictionary of Computing:
“A data dictionary is a centralized repository of information about data such as meaning, relationships to other data, origin, usage, and formats.”
Meanwhile, according to the DAMA Dictionary of Data Management, a data dictionary is:
“Software in which metadata is stored, manipulated and defined – a data dictionary is normally associated with a tool used to support software engineering.”
What are data dictionaries used for?
Permalink to “What are data dictionaries used for?”Traditionally, an enterprise data dictionary was an IT-owned document. It acted as a database dictionary built to store the definition or meaning of all columns in a data table. This helped catalog the structure and content of data with meaningful descriptions at the column level.
For a modern data stack, that’s not enough. We now need data dictionaries equipped to help with active metadata management — learn about the definition as well as the transformations, classifications, tags, and more. Besides technical metadata, active metadata management also covers operational, business, and social metadata.
What does an active data dictionary do? Here’s an active data dictionary definition from Gartner:
“An active data dictionary is a facility for storing dynamically accessible and modifiable information relating to midrange-system data definitions and descriptions.”
So, data dictionaries for the modern data stack should also provide information to understand everything about the data as well as everything that happened to it. This includes full context with data definitions, standards, rules, classifications, and metrics for quality assessment — mean, median, missing values, and more.
Now let’s look at the top benefits of a modern data dictionary.
Six key benefits of a data dictionary
Permalink to “Six key benefits of a data dictionary”- Spot data anomalies quickly
- Improve data quality
- Get access to trustworthy data
- Foster transparency and collaboration
- Facilitate regulatory compliance
- Enable fast and accurate data analysis
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Governance – Start Product Tour
Let’s explore each benefit in detail.
1. Spot data anomalies quickly
Permalink to “1. Spot data anomalies quickly”A modern data dictionary tracks column-level metrics such as minimum and maximum values, unique values, frequency, mean, and median.
Combined with business context and tribal knowledge, these data elements help you spot bad or missing data and anomalies at a glance.
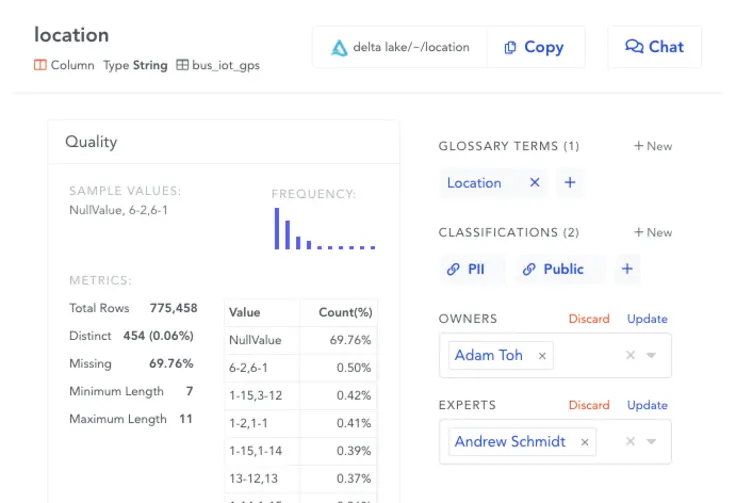
Modern data dictionaries help deploy best-in-class data profiling and quality audits without compromising on data democratization. Image by Atlan
2. Improve data quality
Permalink to “2. Improve data quality”Organizations should engage key stakeholders from various departments when building data dictionaries so that everyone agrees upon standard data definitions, rules, procedures, tags, and classifications. These standards reduce data chaos and make data easy to understand and use.
Additionally, modern data dictionaries let you create business rules, column, and row-level permissions, and quality checks to ensure data quality and consistency.
They send real-time quality alerts and notifications and auto-generate quality reports to help you keep track of updates and ensure data quality.
3. Get access to trustworthy data
Permalink to “3. Get access to trustworthy data”A modern data dictionary maintains:
- A history of all revisions made to a data set
- Details of the person making the edits
- Data source
- Other discussions related to the data set
This centralized repository of all essential information regarding data sets helps you track data lineage and gauge whether the data quality standards are met.
Whenever you can’t verify the credibility of a data set, modern data dictionaries enable you to create discussions around that data and instantly share it with the relevant people.
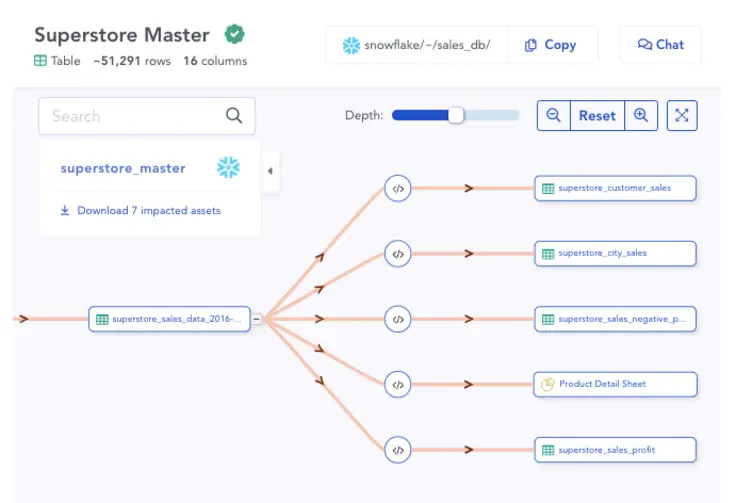
Auto-constructed visual lineage of data to give an understanding of how data has evolved through its lifecycle and how changing the data will impact downstream. Image by Atlan
4. Foster transparency and collaboration
Permalink to “4. Foster transparency and collaboration”According to data governance coach Nicola Askham, an organization can have multiple data dictionaries as it primarily contains details of the systems hosting or holding data assets. However, multiple data dictionaries can lead to siloed data, chaos, and mistrust in data uploaded by other teams.
So, if you standardize data definitions, rules, and other attributes, as mentioned earlier, you can ensure that data teams collaborate and work together to ensure complete transparency of data-related processes and preserve data integrity.
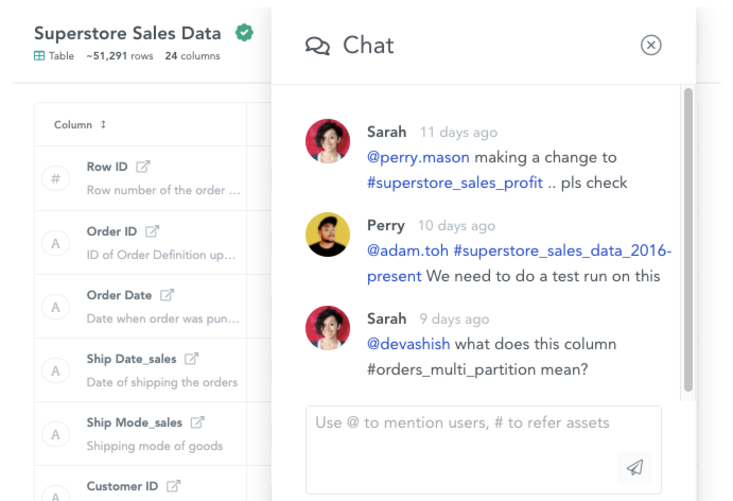
Modern data dictionaries foster collaboration and transparency. Image by Atlan
5. Facilitate regulatory compliance
Permalink to “5. Facilitate regulatory compliance”Complying with regulations such as the GDPR or CCPArequires enforcing a robust data governance program. One of the benefits of a data dictionary is that it facilitates compliance by allowing you to auto-classify PII data and set up granular access permissions and controls. As a result, only people with the right credentials can access sensitive data.
The meticulous, real-time logs ensure that you’re aware of all the changes happening to data and the details of the person making those changes.
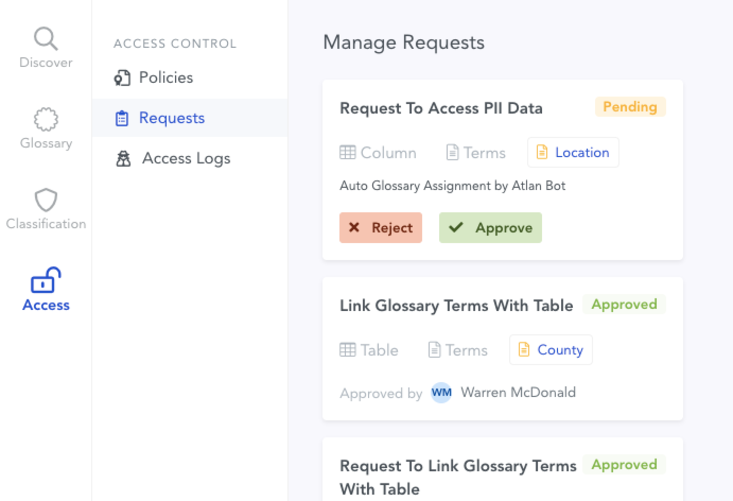
Data access control to protect the privacy and security of PIIs and sensitive data. Image by Atlan
6. Enable fast and accurate data analysis
Permalink to “6. Enable fast and accurate data analysis”Another key benefit of a data dictionary is faster analytics and BI. Both technical and business teams are involved in setting up and managing a modern enterprise data dictionary.
The data dictionaries auto-classify sensitive data, auto-generate row-level metrics, standardize format and definitions, and offer context that goes beyond technical metadata. They’re also built to empower business users to perform advanced analytics without any support from IT.
This simplifies the process of finding relevant data sets to work with to solve a business problem.
How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan
Permalink to “How organizations making the most out of their data using Atlan”The recently published Forrester Wave report compared all the major enterprise data catalogs and positioned Atlan as the market leader ahead of all others. The comparison was based on 24 different aspects of cataloging, broadly across the following three criteria:
- Automatic cataloging of the entire technology, data, and AI ecosystem
- Enabling the data ecosystem AI and automation first
- Prioritizing data democratization and self-service
These criteria made Atlan the ideal choice for a major audio content platform, where the data ecosystem was centered around Snowflake. The platform sought a “one-stop shop for governance and discovery,” and Atlan played a crucial role in ensuring their data was “understandable, reliable, high-quality, and discoverable.”
For another organization, Aliaxis, which also uses Snowflake as their core data platform, Atlan served as “a bridge” between various tools and technologies across the data ecosystem. With its organization-wide business glossary, Atlan became the go-to platform for finding, accessing, and using data. It also significantly reduced the time spent by data engineers and analysts on pipeline debugging and troubleshooting.
A key goal of Atlan is to help organizations maximize the use of their data for AI use cases. As generative AI capabilities have advanced in recent years, organizations can now do more with both structured and unstructured data—provided it is discoverable and trustworthy, or in other words, AI-ready.
Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes
Permalink to “Tide’s Story of GDPR Compliance: Embedding Privacy into Automated Processes”- Tide, a UK-based digital bank with nearly 500,000 small business customers, sought to improve their compliance with GDPR’s Right to Erasure, commonly known as the “Right to be forgotten”.
- After adopting Atlan as their metadata platform, Tide’s data and legal teams collaborated to define personally identifiable information in order to propagate those definitions and tags across their data estate.
- Tide used Atlan Playbooks (rule-based bulk automations) to automatically identify, tag, and secure personal data, turning a 50-day manual process into mere hours of work.
Book your personalized demo today to find out how Atlan can help your organization in establishing and scaling data governance programs.
Conclusion
Permalink to “Conclusion”To summarize, the benefits of a data dictionary include faster detection of data anomalies, improved data quality, availability of trustworthy data, greater transparency within data teams, better regulatory compliance, and faster analytics.
To know more about setting up an enterprise data dictionary for your organization, check out Atlan’s data catalog, which goes beyond the traditional dictionary and provides a complete profile of the data.
FAQs about Benefits of a Data Dictionary
Permalink to “FAQs about Benefits of a Data Dictionary”1. What are the benefits of a data dictionary?
Permalink to “1. What are the benefits of a data dictionary?”A data dictionary provides several benefits, including improved data quality, enhanced understanding of data relationships, and streamlined data management processes. It serves as a centralized repository for data definitions, which helps teams collaborate effectively.
2. What specific benefits does a data dictionary offer for content creators?
Permalink to “2. What specific benefits does a data dictionary offer for content creators?”For content creators, a data dictionary provides clear definitions and guidelines for data usage. This ensures consistency in content creation, reduces ambiguity, and enhances collaboration among team members.
3. What are the key components of an effective data dictionary?
Permalink to “3. What are the key components of an effective data dictionary?”An effective data dictionary includes data definitions, data types, relationships between data elements, and usage guidelines. It should also provide information on data sources and any relevant metadata.
Related reads on data dictionary benefits
Permalink to “Related reads on data dictionary benefits”- Data Dictionary — Examples, Templates, Best Practices, How To Create One, and Available Tools
- Top 6 Benefits of a Data Dictionary
- Snowflake Data Dictionary — Documentation for Your Database
- Data Dictionary vs. Business Glossary: Definitions, Examples & Why Do They Matter?
- Data Catalog vs. Data Dictionary — Differences, Benefits & Use Cases
- Data Catalog: What It Is & How It Drives Business Value
- What Is a Metadata Catalog? - Basics & Use Cases
- Modern Data Catalog: What They Are, How They’ve Changed, Where They’re Going
- Open Source Data Catalog - List of 6 Popular Tools to Consider in 2025
- 5 Main Benefits of Data Catalog & Why Do You Need It?
- Enterprise Data Catalogs: Attributes, Capabilities, Use Cases & Business Value
- The Top 11 Data Catalog Use Cases with Examples
- 15 Essential Features of Data Catalogs To Look For in 2025
- Data Catalog vs. Data Warehouse: Differences, and How They Work Together?
- Snowflake Data Catalog: Importance, Benefits, Native Capabilities & Evaluation Guide
- Data Catalog vs. Data Lineage: Differences, Use Cases, and Evolution of Available Solutions
- Data Catalogs in 2025: Features, Business Value, Use Cases
- AI Data Catalog: Exploring the Possibilities That Artificial Intelligence Brings to Your Metadata Applications & Data Interactions
- Amundsen Data Catalog: Understanding Architecture, Features, Ways to Install & More
- Machine Learning Data Catalog: Evolution, Benefits, Business Impacts and Use Cases in 2025
- 7 Data Catalog Capabilities That Can Unlock Business Value for Modern Enterprises
- Data Catalog Architecture: Insights into Key Components, Integrations, and Open Source Examples
- Data Catalog Market: Current State and Top Trends in 2025
- Build vs. Buy Data Catalog: What Should Factor Into Your Decision Making?
- How to Set Up a Data Catalog for Snowflake? (2025 Guide)
- Data Catalog Pricing: Understanding What You’re Paying For
- Data Catalog Comparison: 6 Fundamental Factors to Consider
- Alation Data Catalog: Is it Right for Your Modern Business Needs?
- Collibra Data Catalog: Is It a Viable Option for Businesses Navigating the Evolving Data Landscape?
- Informatica Data Catalog Pricing: Estimate the Total Cost of Ownership
- Informatica Data Catalog Alternatives? 6 Reasons Why Top Data Teams Prefer Atlan
- Data Catalog Implementation Plan: 10 Steps to Follow, Common Roadblocks & Solutions
- Data Catalog Demo 101: What to Expect, Questions to Ask, and More
- Data Mesh Catalog: Manage Federated Domains, Curate Data Products, and Unlock Your Data Mesh
- Best Data Catalog: How to Find a Tool That Grows With Your Business
- How to Build a Data Catalog: An 8-Step Guide to Get You Started
- The Forrester Wave™: Enterprise Data Catalogs, Q3 2024 | Available Now
- How to Pick the Best Enterprise Data Catalog? Experts Recommend These 11 Key Criteria for Your Evaluation Checklist
- Collibra Pricing: Will It Deliver a Return on Investment?
- Data Lineage Tools: Critical Features, Use Cases & Innovations
- OpenMetadata vs. DataHub: Compare Architecture, Capabilities, Integrations & More
- Automated Data Catalog: What Is It and How Does It Simplify Metadata Management, Data Lineage, Governance, and More
- Data Mesh Setup and Implementation - An Ultimate Guide
- What is Active Metadata? Your 101 Guide
Photo by Pixabay
Share this article


















