Gartner publishes annual Magic Quadrant™(MQ) and Critical Capabilities reports to help organizations evaluate software solutions based on market trends, vendor capabilities, and emerging technologies. These reports provide independent insights that guide data and technology leaders in making strategic investments.
For the first time, Gartner has released a Magic Quadrant™ dedicated to Data & Analytics Governance Platforms, marking a major milestone for the industry.
As Generative AI reshapes the data landscape, governance has become more critical than ever. It’s central to managing enterprise AI models, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations, and building trusted, AI-ready data ecosystems.
Atlan has been recognized as a Visionary in this inaugural report, with top ratings (4.7 star rating) on Gartner Peer Insights. This recognition reflects Atlan’s commitment to helping data teams move beyond legacy governance approaches with AI-powered stewardship, proactive governance, and an open metadata lakehouse.
Below, we explore how Gartner evaluates vendors in this space, what’s driving the shift toward modern governance, and how organizations can use this report to make informed decisions for 2025 and beyond.
Attending Gartner Summit Orlando? Don't miss the sessions that matter most to you
Build Personalized AgendaGartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: An overview
Permalink to “Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: An overview”The Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms is a research report that identifies key players in the data and analytics (D&A) governance market. The report evaluates governance products that help enterprises design, implement, and monitor governance policies.
The evaluation assesses each product’s core features, functionalities, and additional criteria, grouping them into four distinct categories:
- Leaders: Demonstrate depth across a broad range of common functions and have provided core capabilities for years. Leaders have a large customer base, strong market presence, and a clear vision for the market.
- Challengers: Understand the current state of the market and have proven they can deliver. Typically, challengers have a few features that are mature and well-evolved. However, they typically lack the breadth or thought leadership of the Leaders. For the D&A governance market, Gartner notes that there are no Challengers as the overall customer base is low.
- Visionaries: Innovators with a strong understanding of trends and emerging technologies. While pushing the boundaries of their market, Visionaries often lack the market presence, brand recognition, and resources that Leaders have.
- Niche Players: Specialists in specific industries, geographical areas, or other segments. Niche Players typically serve a specific use case well and can offer pricing advantages. However, they lack the breadth, scale, and strength of their competitors. For the D&A governance market, Gartner notes that a majority of the vendors fall in this quadrant due to the emerging nature of the market.
Gartner publishes these four categories as a quadrant into which it places each company and its associated offering. The final result is an educational, visual depiction of how each offering stacks up against the other.
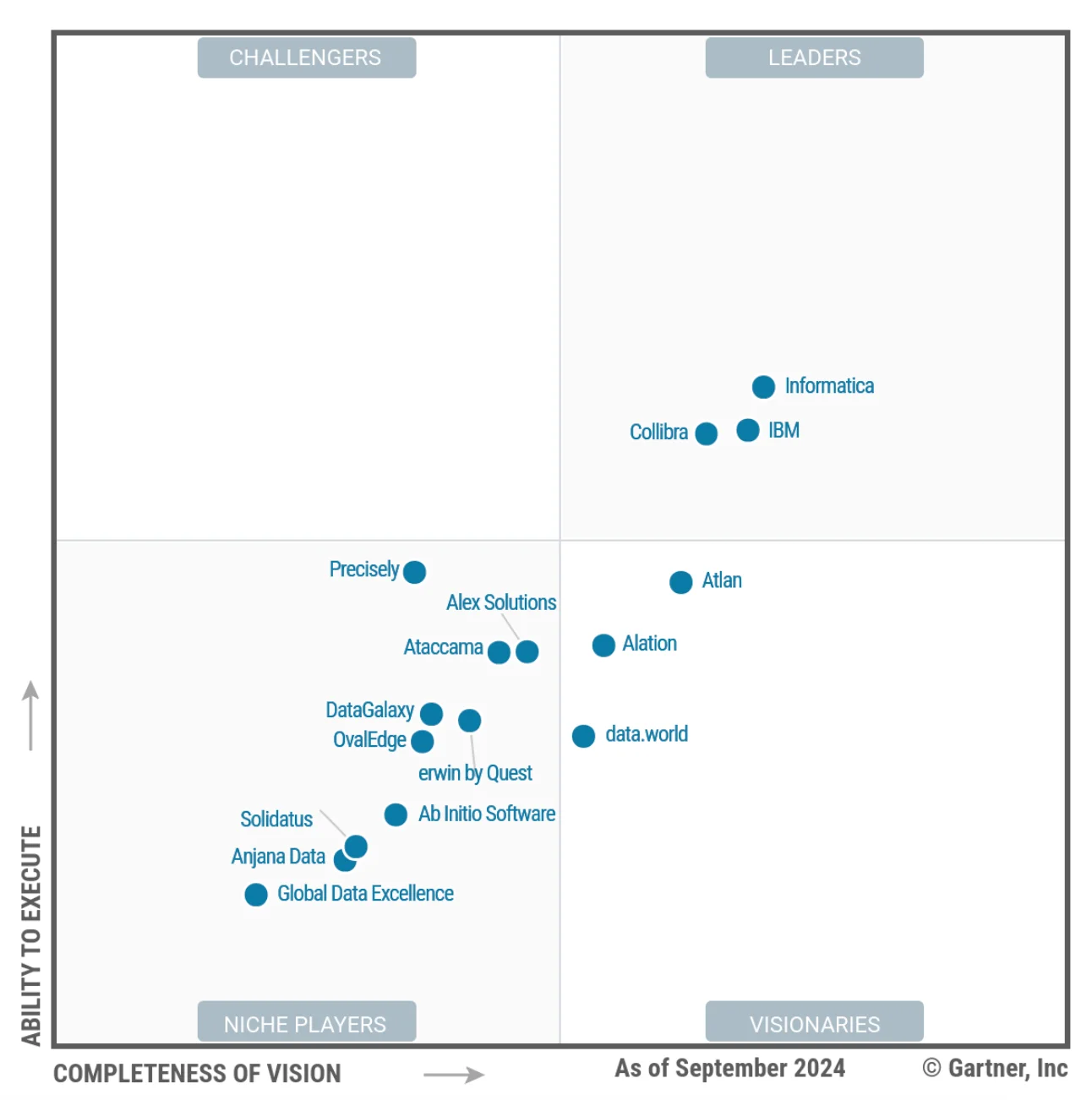
Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms - Source: Gartner.
Next, let’s take a sneak peek at the essential capabilities and criteria for inclusion and ranking specified by Gartner for its Magic QuadrantTM for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms.
Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Essential capabilities
Permalink to “Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Essential capabilities”According to Gartner, D&A governance platforms should have capabilities that enable data governance policy setting and enforcement, as well as functionalities such as:
- Active metadata management
- Business glossary development and maintenance
- Data cataloging
- Data lineage and impact analysis
- Data classification and tag management
- UI supporting diverse user personas
- Automation for various data governance tasks (data quality checks, integration, etc.)
Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Inclusion criteria
Permalink to “Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Inclusion criteria”To qualify for inclusion, Gartner specifies several criteria, such as:
- General availability from June 1, 2024
- Support large-scale deployments with many concurrent users and high data volumes
- Ensure seamless integration with third-party tools for metadata management, MDM, data quality, security, etc.
- Demonstrate operationalization and automation of policy-setting, enforcement, and execution in at least three scenarios
- Provide administration, management, and end-user-facing functionality for diverse user roles, such as data steward, data quality analyst, data engineer, BI analyst, and citizen user
- Maintain an installed base of at least 25 paying production customers for their flagship data governance initiative
- Global presence–direct or partner-provided sales and support operations in at least two regions (North America, South America, EMEA, or Asia/Pacific)
- Rank among the top organizations based on Gartner’s Customer Interest Indicator (CII) – a metric calculated using a weighted mix of internal and external inputs reflecting Gartner client interest, vendor customer engagement, and vendor customer sentiment in the last 18 months
Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Ranking criteria
Permalink to “Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Ranking criteria”The ranking criteria for Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms include:
- Ability to execute
- Completeness of vision
Since the data and analytics governance market is still evolving, Gartner has focused on “characteristics related to vision (marketing understanding, marketing, strategy, product strategy, and innovation) rather than execution (market responsiveness and track record).”
Attending Gartner Summit Orlando? Don't miss the sessions that matter most to you
Build Personalized AgendaGartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Market overview and Atlan’s perspective
Permalink to “Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Market overview and Atlan’s perspective”The data and analytics governance platform market is a rapidly evolving market with a marked shift towards a unified platform for D&A governance and metadata management.
Historically, organizations relied on siloed, standalone tools for governance initiatives, including data security, privacy management, records retention, and risk management.
These fragmented solutions led to overlapping capabilities, integration challenges, and higher costs without additional business benefits.
As a result, there’s a preference for a unified platform supporting multiple policy dimensions.
At Atlan, we believe that the convergence of platforms will see the emergence of a metadata control plane as the unified platform for D&A governance. Some of the other trends shaping the D&A governance market are as follows:
- There’s a need for D&A governance platforms catering to diverse personas, teams, and use cases.
- Active metadata is becoming a key part of D&A governance, connecting data silos with semantic models.
- AI, metadata, knowledge-graph and GenAI will continue getting used for augmenting data governance tasks. GenAI, in particular, is expected to reduce the technical know-how barrier required for governance work.
- There’s a growing demand for capabilities to govern AI models, leading to functionalities that establish:
- A fully automated, no-code way with connectors for unstructured data and AI apps and automated model lineage and explainability
- AI stewardship helping humans of data work with AI to create iterative trust loops
- A collaboration hub for AI policymaking
- A unified trust engine based on metadata control plane to power AI applications
Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Atlan is a Visionary
Permalink to “Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms: Atlan is a Visionary”Atlan is a Visionary in the Magic QuadrantTM for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, seen as an emerging trusted advisor in the governance community because of:
- A platform that enables “humans of data” to manage AI-ready data, metadata and stewardship efforts
- A proven track record, with a good win rate in competitive evaluations.
- A focus on long-term leadership in data governance
- A customer-centric approach along with opportunities for continuous learning and improvement (courses, certifications, templates, and more)
- A focus on AI-driven solutions and open metadata lakehouse infrastructure to address data scale and diversity
- An offering that includes automation, AI recommendations and tools to enrich and govern data at source
Using Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms report for data-driven decision making
Permalink to “Using Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms report for data-driven decision making”Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms report thoroughly evaluates the data governance market, identifying leaders, challengers, visionaries and niche players.
Used intelligently, Gartner’s insights can help you make informed data governance tooling investments that will continue to provide business value for years to come.
FAQs about Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms
Permalink to “FAQs about Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms”1. What is the Gartner Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms?
Permalink to “1. What is the Gartner Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms?”Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platform is a research report that evaluates and positions data governance tools based on their completeness of vision and ability to execute.
2. Who is the Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platform report for?
Permalink to “2. Who is the Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platform report for?”Gartner’s Magic Quadrant™ for Data and Analytics Governance Platform report is for data and analytics leaders who are investing in operationalizing and automating the work of data and analytics governance.
3. What is a Data and Analytics Governance Platform (D&AGP)?
Permalink to “3. What is a Data and Analytics Governance Platform (D&AGP)?”As defined by Gartner, Data and Analytics Governance Platforms (D&AGP):
- Develop and deploy a diverse set of governance policies
- Monitor and enforce those policies across their organization
4. How does Gartner evaluate data governance tools?
Permalink to “4. How does Gartner evaluate data governance tools?”Gartner evaluates data governance tools by using two main criteria: completeness of vision and ability to execute.
Completeness of vision assesses a vendor’s market understanding, business model, and innovation. Meanwhile, ability to execute focuses on product performance, pricing, operations, customer experience, and overall business viability.
5. What are the benefits of using a Magic Quadrant evaluation?
Permalink to “5. What are the benefits of using a Magic Quadrant evaluation?”Using a Magic Quadrant evaluation helps organizations objectively compare vendors, understand market dynamics, and identify solutions that align with their business goals. It simplifies the decision-making process by providing a clear visual representation of vendor strengths and weaknesses.
6. How can I choose the right D&A governance tool based on the Magic Quadrant?
Permalink to “6. How can I choose the right D&A governance tool based on the Magic Quadrant?”To choose the right tool, consider your organization’s specific needs and priorities, then compare vendors within the relevant quadrant.
7. What trends are influencing the D&A governance market in 2025?
Permalink to “7. What trends are influencing the D&A governance market in 2025?”According to Gartner, the data and analytics governance market is observing a convergence of platforms, platforms catering to diverse personas, and capabilities to support AI governance, among others.
Share this article



















