Which open source data governance tools lead in 2025?
Permalink to “Which open source data governance tools lead in 2025?”Here are the top 7 tools dominating the open source landscape, along with their key strengths and limitations:
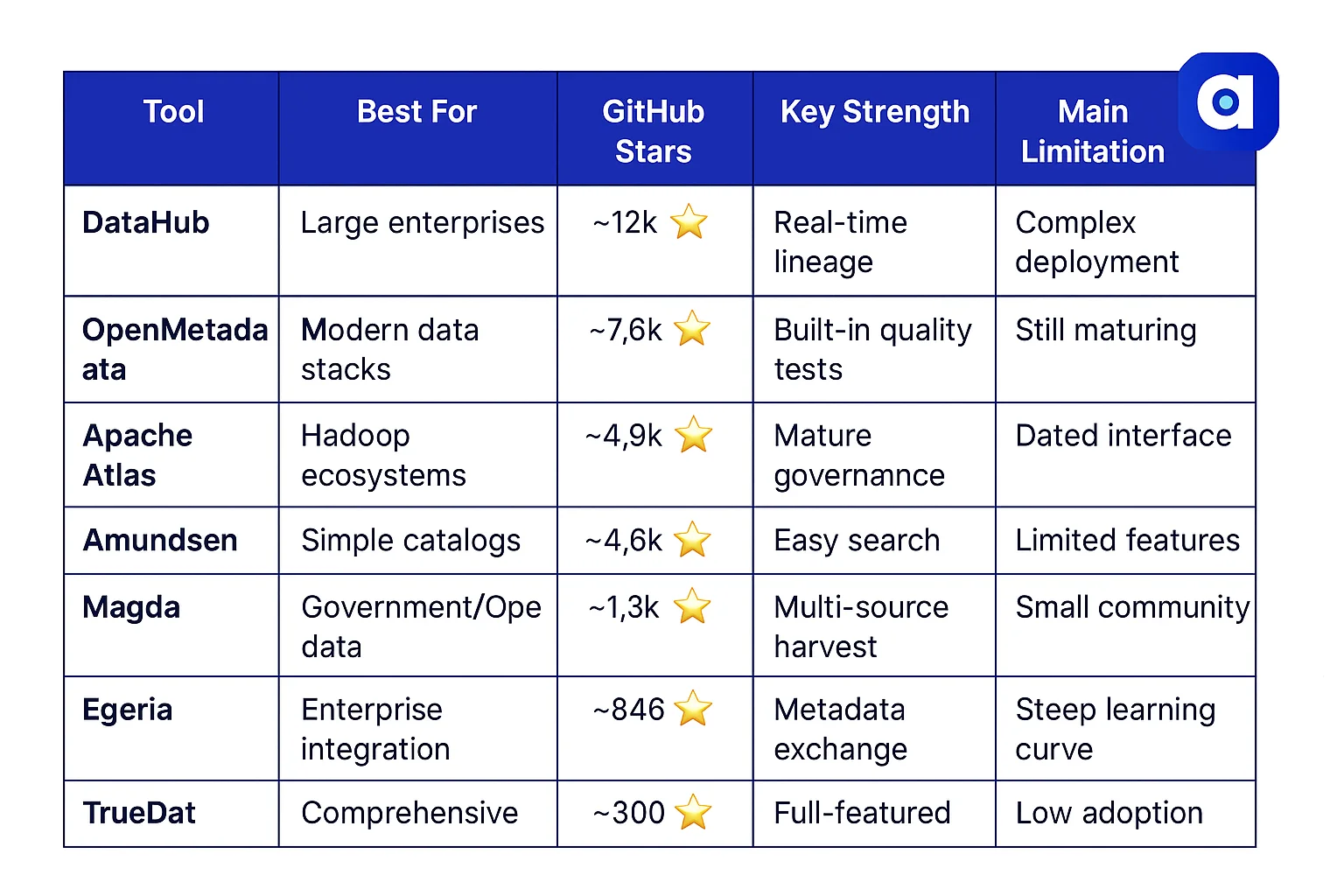
Open source data governance tools comparison in 2025. Source: Atlan.
Build Your Data-Governance Framework in 3 Minutes
Get My Governance RoadmapBest open-source data governance tools: Deep dive
Permalink to “Best open-source data governance tools: Deep dive”This section explores leading open-source data governance tools, highlighting their features and limitations.
Amundsen
Permalink to “Amundsen”Origin: Amundsen, Lyft’s data discovery platform
Best for: Teams prioritizing simple, effective data discovery
Standout Features:
- Google-like search experience for intuitive discovery
- User popularity rankings surface most-used datasets
- Lightweight deployment with minimal infrastructure needs
- Strong integration with common analytics tools
Key Limitations:
- Limited built-in data lineage capabilities
- Fewer governance features than comprehensive platforms
- Development activity has decreased recently
- No native data quality monitoring
Latest release – v0.13.0 – Apr 2025 (GitHub)
DataHub
Permalink to “DataHub”Origin: LinkedIn’s DataHub replaced WhereHows to meet growing metadata search and discovery demands.
Best for: Large organizations needing robust real-time capabilities
Standout Features:
- Real-time schema change alerts catch breaking changes instantly
- Column-level lineage graphs show precise data relationships
- Strong community support with active development
- Comprehensive API for custom integrations
Key Limitations:
- No built-in data quality testing framework
- Resource-intensive deployment requirements
- Complex configuration for enterprise features
- Limited out-of-box user interface customization
Latest release – v0.13.0 – Mar 2025 (GitHub)
Apache Atlas
Permalink to “Apache Atlas”Origin: Apache Foundation project for big data governance, pioneer in open-source data catalogs with governance features
Best for: Organizations heavily invested in Hadoop ecosystems
Standout Features:
- Mature governance framework with years of production use
- Fine-grained lineage tracking across Hadoop components
- Tag-based policy management for flexible access control
- Strong integration with Hive, HBase, and other Apache tools
Key Limitations:
- UI feels outdated compared to modern alternatives
- Limited cloud-native integrations
- Slower development pace than newer projects
- Complex setup for non-Hadoop environments
Latest release – v2.4 – Feb 2025 (GitHub)
Magda
Permalink to “Magda”Overview: Developed by CSIRO’s Data61 (Australia), Magda (“Making Australian Government Data Available”) created an open data portal for government datasets.
Core focus – Federated data catalog geared to government/open-data portals.
Stand-out features – Multi-source harvesters, CKAN bridge, fine-grained ACLs.
GitHub stats – ≈ 1.3 k ⭐
Latest release – v2.5 – Jan 2025 (GitHub)
Primary gap – Smaller dev community; limited column-level lineage.
OpenMetadata
Permalink to “OpenMetadata”Overview: Launched in August 2021, OpenMetadata is an open-source project standardizing metadata with a schema-first approach, featuring a centralized store and ingestion framework.
Core focus – Unified platform for discovery, lineage, quality and observability.
Stand-out features – Built-in great-expectations tests, REST+Kafka ingestion, modern React UI.
GitHub stats – ≈ 7.6 k ⭐
Latest release – v1.4.0 – May 2025 (GitHub)
Primary gap – Relatively young; enterprise RBAC and SSO still maturing.
Egeria
Permalink to “Egeria”Overview: Launched in 2019 by the Linux Foundation’s AI & Data arm, Egeria focuses on vendor-agnostic metadata exchange, built on principles of platform independence, scalability, and data accessibility.
Core focus – Federated metadata exchange across heterogeneous tools.
Stand-out features – Type system, bi-directional lineage, governance actions framework, metadata archival, and metadata provenance.
GitHub stats – 846 ⭐
Latest release – 5.3, 21 May 2025 (GitHub)
Primary gap – Steeper learning curve; Java-heavy stack.
TrueDat
Permalink to “TrueDat”Overview: Developed by BlueTab (now IBM), TrueDat is arguably the most comprehensive open-source data governance tool available, filling a market gap.
Core focus – Data dictionary, data catalog, and governance portal born inside Santander.
Stand-out features – Business glossary, dataset certification workflow, RBAC.
GitHub stats – ≈ 0.3 k ⭐
Latest release – v4.9 – Feb 2025 (GitHub)
Primary gap – Low star count; niche community and slower issue turn-around.
How to pick and deploy an open-source data-governance tool? (5-step guide)
Permalink to “How to pick and deploy an open-source data-governance tool? (5-step guide)”-
Step 1: Define must-have capabilities
List the non-negotiables for your stack—lineage depth, glossary, RBAC model, connector coverage, container support, security posture. -
Step 2: Score short-list options
Build a quick matrix: feature fit, GitHub stars/commits, release cadence, licence, community activity, and ease of integration with your lake/warehouse. Rank; pick the top two. -
Step 3: Pilot in one high-value domain
Stand up the chosen tool in a sandbox, ingest a single data-domain (e.g., customer tables), and loop in the business steward. Validate search, lineage, and policy tagging. -
Step 4: Automate ingestion & access policies
Wire the tool to CI/CD or orchestration (Airflow, dbt, GitHub Actions). Automate metadata ingestion and apply tag-based RBAC so governance happens in-flow, not by ticket. -
Step 5: Measure & expand
Track adoption (daily active users), query speed, incident MTTR. If KPIs improve, roll out domain by domain; if not, iterate connectors or re-score the runner-up tool.
Tip: Document time spent on self-hosting, upgrades, and custom scripts—this gives you a baseline to compare against managed governance platforms later.
Pros & limitations of open-source data governance tooling
Permalink to “Pros & limitations of open-source data governance tooling”While open-source data governance tools offer compelling advantages, it’s crucial to understand their trade-offs.
Pros
- No vendor lock-in or licence fees
- Full code transparency for security audits
- Vibrant communities driving innovation
Cons
- Self-hosting and upgrades require DevOps time
- Feature gaps (quality tests, AI governance) often need custom code
- Enterprise support, SLAs and advanced automation typically absent
Open-source projects are flexible and cost-effective, but teams often outgrow DIY scripts when they need real-time policy automation, drift alerts, and SLA-backed support.
Open source vs. Atlan: side-by-side snapshot
Permalink to “Open source vs. Atlan: side-by-side snapshot”The decision between an open-source stack and a commercial, managed platform like Atlan depends heavily on an organization’s specific needs, resources, and maturity in data governance.
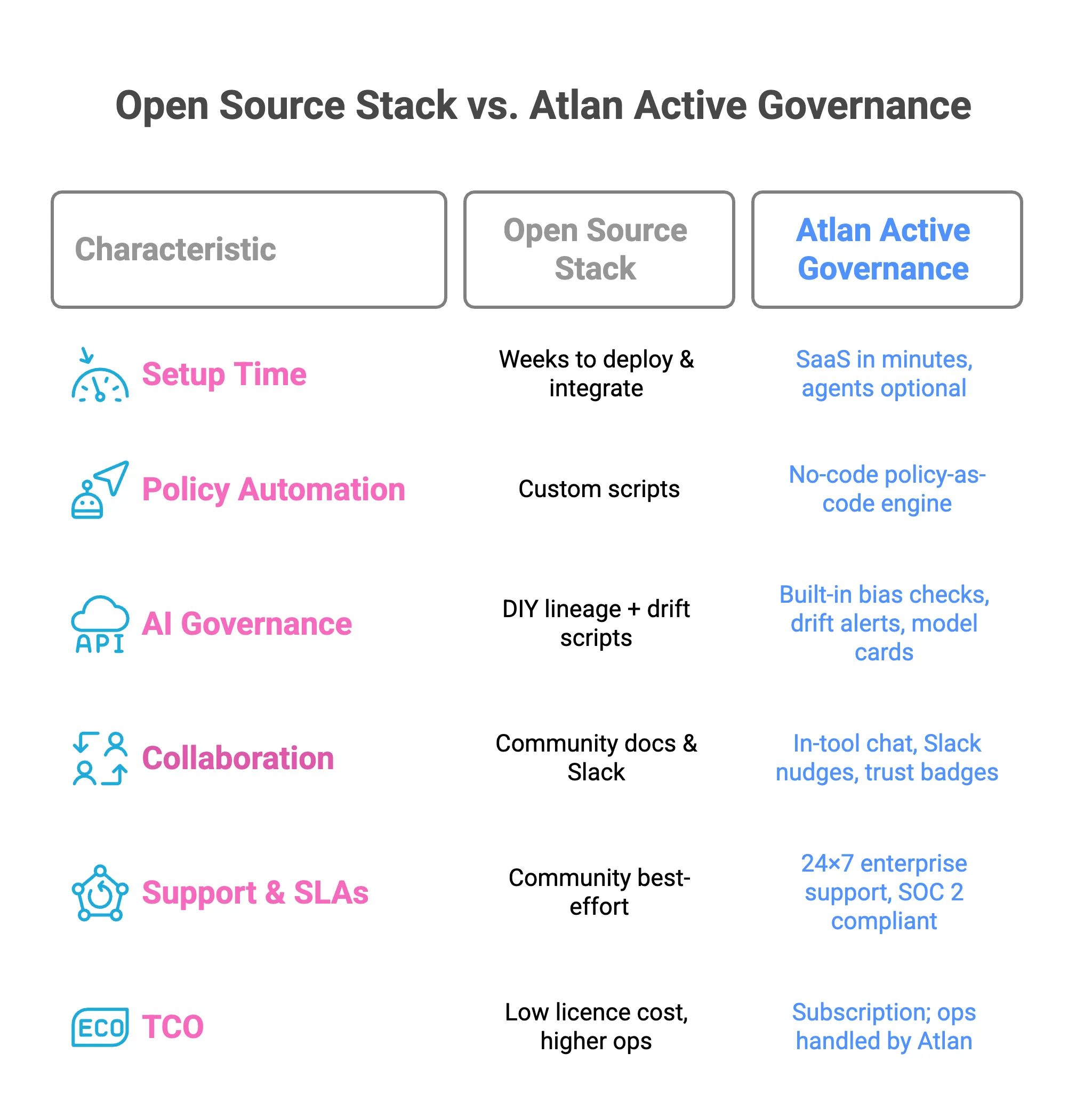
Open source vs. Atlan: side-by-side snapshot in 2025. Source: Atlan.
Build Your Data-Governance Framework in 3 Minutes
Get My Governance RoadmapWhile open-source projects provide the foundational building blocks for data governance, a platform like Atlan’s active governance packages them into a unified, managed solution. This allows teams to maintain agility and velocity without the need to stitch together disparate scripts and custom code.
Let us help you build your active governance → Book a personalized demo.
Real wins by real companies: Modern governance in action
Permalink to “Real wins by real companies: Modern governance in action”
Modernized data stack and launched new products faster while safeguarding sensitive data
"Austin Capital Bank has embraced Atlan as their Active Metadata Management solution to modernize their data stack and enhance data governance. Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics, highlighted, 'We needed a tool for data governance… an interface built on top of Snowflake to easily see who has access to what.' With Atlan, they launched new products with unprecedented speed while ensuring sensitive data is protected through advanced masking policies."

Ian Bass, Head of Data & Analytics
Austin Capital Bank
🎧 Listen to podcast: Austin Capital Bank From Data Chaos to Data Confidence

53 % less engineering workload and 20 % higher data-user satisfaction
"Kiwi.com has transformed its data governance by consolidating thousands of data assets into 58 discoverable data products using Atlan. 'Atlan reduced our central engineering workload by 53 % and improved data user satisfaction by 20 %,' Kiwi.com shared. Atlan's intuitive interface streamlines access to essential information like ownership, contracts, and data quality issues, driving efficient governance across teams."
Data Team
Kiwi.com
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Kiwi.com Unified Its Stack with Atlan

One trusted home for every KPI and dashboard
"Contentsquare relies on Atlan to power its data governance and support Business Intelligence efforts. Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead, explained, 'Atlan is the home for every KPI and dashboard, making data simple and trustworthy.' With Atlan's integration with Monte Carlo, Contentsquare has improved data quality communication across stakeholders, ensuring effective governance across their entire data estate."

Otavio Leite Bastos, Global Data Governance Lead
Contentsquare
🎧 Listen to podcast: Contentsquare's Data Renaissance with Atlan
Ready to move from DIY scripts to automated, AI-ready governance?
Permalink to “Ready to move from DIY scripts to automated, AI-ready governance?”Let us help you build your active governance
Book a Personalized DemoFAQs about open source data governance tools
Permalink to “FAQs about open source data governance tools”What is Open source data governance?
Permalink to “What is Open source data governance?”Open source data governance refers to the management of data assets using community-driven tools and practices. It emphasizes transparency, collaboration, and flexibility, allowing organizations to adapt to changing data needs while ensuring compliance and security.
Are open-source governance tools really free?
Permalink to “Are open-source governance tools really free?”Yes, the source code is free to use, modify, and deploy, which makes it cost-effective from a licensing standpoint. However, there are additional costs involved in hosting, infrastructure, maintenance, custom development, and integrations that organizations need to plan for.
Which open-source tool is best for lineage?
Permalink to “Which open-source tool is best for lineage?”DataHub and Apache Atlas are among the most robust when it comes to lineage capabilities. Both offer APIs and native UI support to capture, visualize, and query column- and table-level lineage across various data sources.
Do open source data governance tools handle quality tests?
Permalink to “Do open source data governance tools handle quality tests?”OpenMetadata is currently the only tool in this group that offers built-in support for data quality tests. For other tools like DataHub, Atlas, or Amundsen, users typically need to rely on external integrations or plugins to manage data quality checks.
Can I integrate open-source data governance tools with Snowflake?
Permalink to “Can I integrate open-source data governance tools with Snowflake?”Yes, most open-source data governance tools support Snowflake integration either directly or through connectors. This is typically done using ingestion jobs powered by Kafka, Airflow, or other orchestrators that connect Snowflake metadata with the governance platform.
When should I switch from open source to a managed data governance platform?
Permalink to “When should I switch from open source to a managed data governance platform?”If you require enterprise-grade SLAs, enhanced scalability, AI-powered monitoring, and faster implementation timelines, a managed platform becomes a better fit. It reduces operational overhead and ensures that updates, support, and security are handled by the provider.
Share this article



















