What does Snowflake’s catalog architecture look like?
Permalink to “What does Snowflake’s catalog architecture look like?”Snowflake’s catalog architecture consists of a native governance layer (Horizon) built on top of the Snowflake AI Data Cloud.
It integrates with an open Iceberg metadata layer (Open Catalog) and leverages system metadata services that support discovery, lineage, governance, and interoperability.
Snowflake Horizon: The internal governance and policy layer for Snowflake AI Data Cloud
Permalink to “Snowflake Horizon: The internal governance and policy layer for Snowflake AI Data Cloud”Horizon acts as Snowflake’s internal metadata and governance plane. It unifies:
- Object metadata (databases, schemas, tables, columns)
- Tagging, classification, and access policies
- Lineage
- Discovery and search
- Governance for Snowflake-managed Iceberg tables
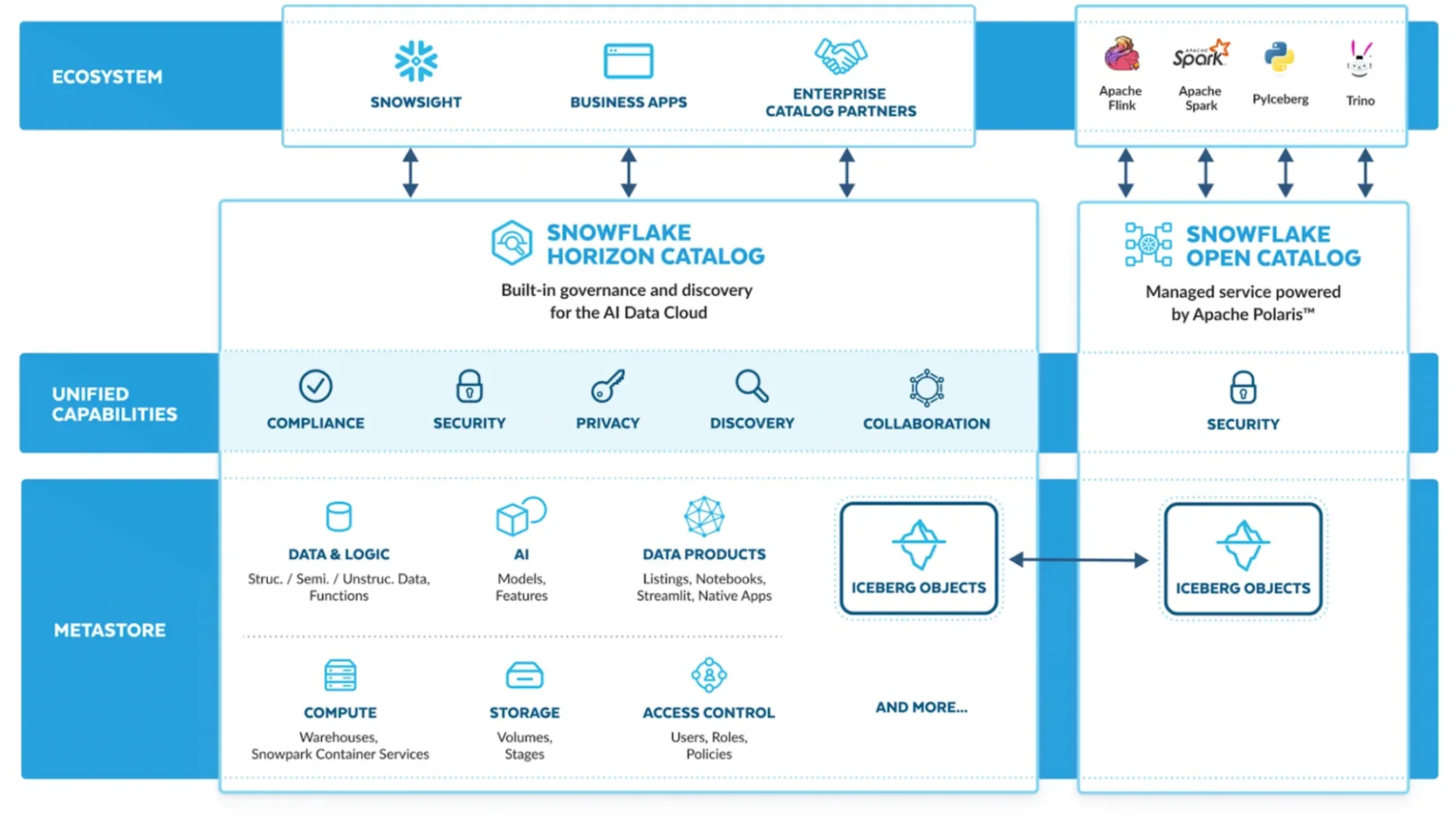
Snowflake data catalog architecture. Source: Snowflake Blog.
At the heart of Snowflake Horizon is the global repository for the Snowflake AI Data Cloud, which includes:
- Structured, semi-structured and unstructured data and models
- Snowflake Notebooks
- Streamlit
- Snowflake Native Apps and Listings
Snowflake data dictionary: The technical metadata foundation
Permalink to “Snowflake data dictionary: The technical metadata foundation”Snowflake’s metadata backbone is formed by the following metadata services:
- INFORMATION_SCHEMA provides real-time metadata about database objects in your account, including tables, views, columns, and constraints. Querying requires SQL knowledge.
- ACCOUNT_USAGE views in the SNOWFLAKE database offer historical and cross-database metadata with 45-180 minute latency, but broader visibility. Analyze usage patterns, lineage, and governance metrics.
- Object tagging creates a semantic layer that adds business context and governance rules on top of technical metadata. Tags can represent data classifications (PII, PHI), business domains (finance, marketing), data quality indicators, or custom metadata.
Snowflake Open Catalog: The vendor-neutral open source Iceberg catalog
Permalink to “Snowflake Open Catalog: The vendor-neutral open source Iceberg catalog”The Horizon Catalog integrates with the Snowflake Open Catalog (a vendor-neutral open source catalog powered by Apache Polaris) to provide:
- A shared Iceberg catalog for externally managed tables
- Multi-engine interoperability (Snowflake, Spark, Trino, Flink, etc.)
- Vendor-neutral metadata access and governance
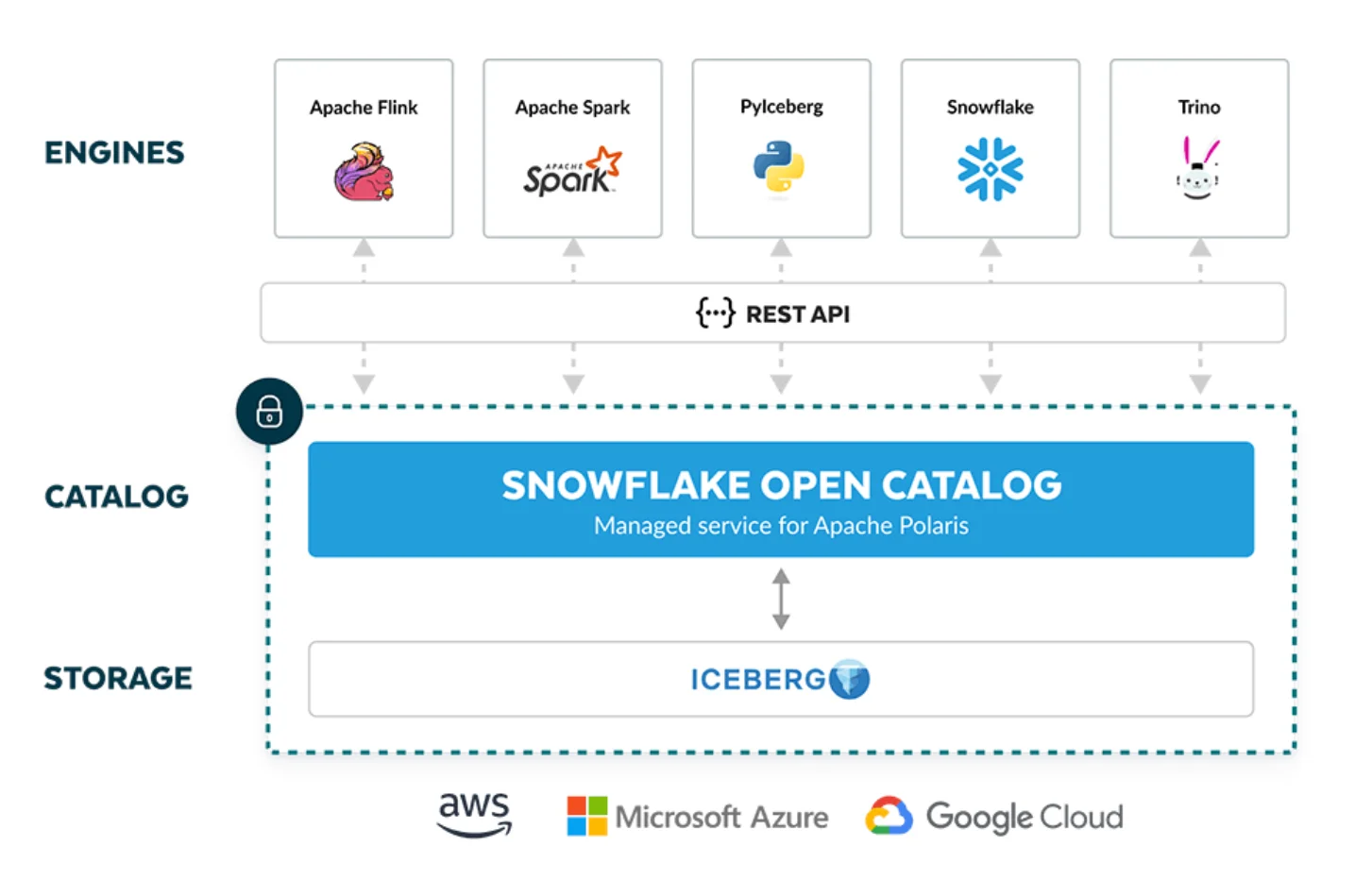
Snowflake Open Catalog for external tables. Source: Snowflake.
External catalogs like Atlan for cross-platform unification
Permalink to “External catalogs like Atlan for cross-platform unification”Most enterprises layer Snowflake metadata into a broader active metadata control and context plane like Atlan–the first data catalog to be validated as a Snowflake Ready Technology Partner.
Rather than treating the catalog as a separate documentation project, Atlan embeds data context directly in the tools data teams already use—BI platforms, notebooks, and transformation workflows.
The automation layer handles classification, documentation suggestions, and anomaly detection that would otherwise require manual effort.
When new tables appear in Snowflake, Atlan automatically discovers them, suggests tags based on column analysis, identifies relevant business owners, and surfaces related assets from other systems.
Column-level lineage extends beyond Snowflake to show complete data journeys from ingestion through transformation to consumption, enabling impact analysis across the entire data stack rather than just within the warehouse.
Organizations using this approach report a 60% reduction in time spent searching for data and higher data literacy among business stakeholders who can now discover assets without SQL expertise.
Book a demo to see how Atlan extends Snowflake’s metadata into a collaborative catalog that accelerates discovery and governance across your entire data ecosystem.
Scaling AI on Snowflake? Here’s the playbook - Watch Now
How can you set up catalog capabilities in Snowflake?
Permalink to “How can you set up catalog capabilities in Snowflake?”You can set up catalog capabilities by enabling the right features across Horizon, Open Catalog, and Snowflake’s metadata services.
The technical metadata (INFORMATION_SCHEMA) is automatically created in every database and you can use it to query metadata programmatically.
For Snowflake Horizon, you don’t need any extra setup as it’s built into Snowsight. You can use Universal Search (powered by Snowflake Cortex AI) to:
- Discover data assets (tables, columns, etc.)
- Set up tags, classifications, masking policies, and more
- Monitor data quality with data metric functions
- View lineage through ACCESS_HISTORY
- Surface externally managed Iceberg assets registered via Polaris
How does Atlan connect with Snowflake?
Permalink to “How does Atlan connect with Snowflake?”As mentioned earlier, modern enterprises build on Snowflake’s technical foundation using a unified metadata context plane like Atlan.
Atlan connects to Snowflake through standard metadata extraction, then continuously enriches technical metadata with business context, usage patterns, and cross-system relationships.
With Atlan as the data catalog for your data ecosystem (including Snowflake), you can achieve:
- A single source of truth for enterprise data and AI assets with smart search and discovery
- Automated, cross-system, column-level lineage–see complete data journeys from ingestion through transformation to consumption
- Automated metadata propagation (tags, glossary terms, descriptions) across lineage, along with bi-directional sync with Snowflake
- Business glossary that connects definitions, metrics, and assets across your data ecosystem
- Data product marketplace–data tables, dashboards, metrics, and essential business context
- Personalization based on user roles, data domains, and projects
- Real-time view of policy coverage, incidents, and breaches across your data estate
- A unified, trusted view of data health with the Data Quality Studio
- AI governance–centralized AI asset management, lineage across the AI lifecycle, custom metadata
In other words, Snowflake provides the metadata; the external catalog activates it across teams and systems.
“We are excited to offer Atlan’s modern data governance and active metadata capabilities to our customers. Atlan’s approach to data governance will help our joint customers get the most out of their data.” - Tarik Dwiek, Head of Technology Alliances at Snowflake
Real stories from real customers: How leading companies have transformed their data operations with Atlan + Snowflake
Permalink to “Real stories from real customers: How leading companies have transformed their data operations with Atlan + Snowflake”
From Siloed Queries to Unified Governance: How North Did It
"After partnering with Atlan, it took probably a couple of hours before we were integrated with Snowflake and Sigma, connecting to over 225,000 assets. Atlan started getting us immediate value through data discovery. The way I keep thinking about it was the early days of the internet. You had access to this vast amount of information, but it was really hard to find. Then, search engines made it easy to run a search and find relevant content. For us, Atlan became Google for Data. North processes over $100 billion in annual transactions across 20 subsidiaries. With 41 terabytes of data in Snowflake, their team needed unified visibility and governance. After implementing Atlan, they achieved a 700% increase in tagged Snowflake assets and project $1.4 million in annual efficiency gains."
Daniel Dowdy, Vice President of Data Analytics & Governance
North
🎧 Listen to podcast: How North Unified Its Stack with Atlan

From Manual Documentation to Automated Discovery: How Autodesk Did It
"We use a combination of a data lake and a data warehouse. Our data warehouse is Snowflake, the data lake is AWS, and of course, all the technology sits on top of the lake and warehouse to run transformations, queries, and analytics. We needed something that could help bridge the [context] gap. Atlan is the layer that brings a lot of the metadata that publishers provide to the consumers, and it's where consumers can discover and use the data they need. Autodesk scaled data collaboration across 60 teams by building a data mesh on Snowflake with Atlan. Their Analytics Data Platform now empowers domain teams to publish and govern their own data while maintaining centralized visibility and standards."
Mark Kidwell, Chief Data Architect
Autodesk
🎧 Listen to podcast: How Autodesk Unified Its Stack with Atlan
Moving forward with Snowflake data catalog
Permalink to “Moving forward with Snowflake data catalog”Snowflake provides robust foundational metadata through information schema, account usage views, and tag-based governance capabilities. Teams can start with native SQL-based discovery and tag management before adding specialized catalog platforms as complexity grows.
The key decision isn’t whether to catalog Snowflake data, but how to balance native capabilities with external tools that provide collaboration features, cross-system lineage, and automated enrichment.
Organizations that establish clear metadata extraction patterns, implement consistent tagging taxonomies, and integrate catalog platforms that enhance Snowflake’s native capabilities create environments where data discovery serves both technical and business stakeholders effectively.
Explore how Atlan builds on Snowflake’s metadata to create a collaborative catalog across your entire data stack.
FAQs about Snowflake data catalog
Permalink to “FAQs about Snowflake data catalog”1. Does Snowflake have a catalog?
Permalink to “1. Does Snowflake have a catalog?”Yes. Snowflake’s native cataloging capabilities are delivered through Snowflake Horizon. Technical metadata is captured by system metadata layers like Information Schema and Account Usage.
External tables can be cataloged using the Apache Polaris-based, vendor-neutral Open Catalog.
2. What’s the difference between Horizon Catalog & Snowflake Open Catalog?
Permalink to “2. What’s the difference between Horizon Catalog & Snowflake Open Catalog?”Snowflake Horizon Catalog is the governance and discovery layer inside Snowflake, used to manage, secure, classify, and search all Snowflake-managed data assets—including Snowflake-managed Iceberg tables.
Snowflake Open Catalog, on the other hand, is Snowflake’s managed implementation of Apache Polaris, an open, vendor-neutral catalog. It enables consistent access control and read/write interoperability for externally managed Iceberg tables across multiple compute engines, not just Snowflake.
3. How do I extract metadata from Snowflake for a catalog?
Permalink to “3. How do I extract metadata from Snowflake for a catalog?”Query the INFORMATION_SCHEMA views in each database for real-time metadata about tables, columns, and views within that database.
For cross-database visibility, use SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE views which aggregate metadata across your entire account.
Extract programmatically using SQL queries through the Snowflake connector or REST API, typically on scheduled intervals to keep external catalogs synchronized.
4. How can I create a catalog in Snowflake?
Permalink to “4. How can I create a catalog in Snowflake?”Data cataloging in Snowflake is handled through built-in schemas, metadata views, and products like Horizon Catalog and Open Catalog for Iceberg-native workloads.
5. When should I use an external catalog with Snowflake?
Permalink to “5. When should I use an external catalog with Snowflake?”Organizations add a catalog like Atlan when they need:
- Cross-system lineage beyond Snowflake
- Business glossary and data product marketplace
- AI governance (model metadata, feature stores)
- Embedded collaboration and role-based experiences
- Bi-directional tag sync and policy propagation across multiple tools
Snowflake provides metadata inside Snowflake; external catalogs unify metadata across the entire ecosystem.
6. What are the benefits of using a metadata control plane like Atlan with Snowflake?
Permalink to “6. What are the benefits of using a metadata control plane like Atlan with Snowflake?”A metadata control plane like Atlan extends Snowflake’s native cataloging by integrating metadata across tools like dbt, Looker, and Airflow. It centralizes data governance, discovery, and compliance across platforms. This is crucial for managing data in modern multi-cloud environments and ensuring AI-readiness.
7. How does Atlan integrate with Snowflake for cataloging?
Permalink to “7. How does Atlan integrate with Snowflake for cataloging?”Atlan connects to Snowflake as a metadata source, extracting technical metadata through information schema and account usage views.
It automatically discovers new tables as they’re created, enriches metadata with business context, and maintains column-level lineage that extends beyond Snowflake to show complete data journeys.
Changes in Snowflake sync continuously to Atlan rather than through batch updates, ensuring catalog entries reflect current state.
Share this article



















